Abstract
Purpose and background: The aim of this study was to assess the frequency of response and toxicity in adults with recurrent anaplastic astrocytoma (AA) or glioblastoma multiforme (GM) treated with concurrent continuous TMZ and TMX.
Methods: In addition to histology, eligibility included age > 18 years, Karnovsky score ≥60, normal laboratory parameters, no radiotherapy (RT) for 4 weeks, measurable disease and normal EKG. The chief exclusions were: previous TMZ, TMX or dacarbazine (DTIC); nitrosourea within 6 weeks; history of deep venous thrombosis or pulmonary emboli. All patients (pts) had received prior RT. TMZ was given at 75 mg/M2/day for 6 weeks, repeated every 10 weeks, maximum 5 cycles. Four pts received 60 mg/M2/day for 6 weeks due to extensive prior chemotherapy exposure. TMX was started at 40 mg twice daily (b.i.d.) for 1week and then was increased in three successive weeks to 60, then 80, then 100 mg b.i.d. Response was assessed before every cycle with MRI ± gadolinium (Gd).
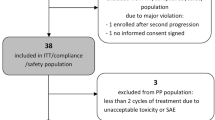
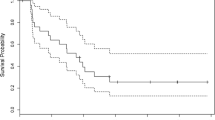
Results: Sixteen pts enrolled: GM 10, AA 6; female 6, male 10; median age 48 (21–58); prior chemotherapy 7. There was one partial response and one stable disease. Eleven pts progressed by the end of cycle 1; three pts failed due to toxicity before completing cycle 1. Median time to treatment failure was 10 weeks. The main toxicities were: transaminitis, pancytopenia, 1st division herpes zoster, deep vein thrombosis and fatigue. The study was closed due to the low response rate and frequency of toxicity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Newlands ES, Blackledge GR, Slack JA, Rustin GJ, Smith DB, Stuart NS, Quarterman CP, Hoffman R, Stevens MF, Brampton MH, Gibson AC: Phase I trial of temozolomide (CCRG 81045: M&B 39831: NSC 362856). Br J Cancer 65: 287-291, 1992
Newlands ES, O 'Reilly SM, Glaser MG, Bower M, Evans H, Brock C, Brampton MH, Colquhoun I, Lewis P, Rice-Edwards JM, Illingworth RD, Richards PG: The Charing Cross Hospital experience with temozolomide in patients with gliomas. Eur J Cancer 32A: 2236-2241, 1996
Stevens MF, Newlands ES: From triazines and triazenes to temozolomide. Eur J Cancer 29A: 1045-1047, 1993
Baer JC, Freeman AA, Newlands ES, Watson AJ, Rafferty JA, Margison GP: Depletion of O6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase correlates with potentiation of temozolomide and CCNU toxicity in human tumour cells. Br J Cancer 67: 1299-1302,1993
Lee SM, Thatcher N, Crowther D, Margison GP: Inactivation of O6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells by temozolomide. Br J Cancer 69: 452-456, 1994
Newlands ES, Stevens MFG, Wedge SR, Wheelhouse RT, Brock C: Temozolomide: a review of its discovery, chemical properties,pre-clinical development and clinical trials. Cancer Treatment Rev 23: 35-61, 1997
Mitchell RB, Dolan ME: Effect of temozolomide and dacarbazine on O6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase activity and sensitivity of human tumor cells and xenografts to 1,3-bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 32: 59-63, 1993
Brada M, Hoang-Xuan K, Rampling R, Dietrich PY, Dirix LY, Macdonald D, Heimans JJ, Zonnenberg BA, Bravo-Marques JM, Henriksson R, Stupp R, Yue N, Bruner J, Dugan M, Rao S, Zaknoen S: Multicenter phase II trial of temozolomide in patients with glioblastoma multiforme at rst relapse. Ann Oncol 12: 259-266, 2001
Cefalo G, Ruggiero A, Abate ME, Massimino M, Zucchetti P, Mascarin M, Garre ML, Sprea co F, Mastrangelo S, Clerico S, Ridola V, Mazzarella G, Di Ricco C, Donfrancesco A, Perilongo G, Lazzareschi I, Sandri S, Riccardi R: High response rate to temozolomide in heavily pretreated children and young adults with medulloblastoma. Neuro-Oncology 4(Suppl 1): S18, 2002
Gilbert MR, Friedman HS, Kuttesch JF, Prados MD, Olson JJ, Reaman GH, Zaknoen SL: A phase II study of temozolomide in patients with newly diagnosed supratentorial malignant glioma before radiation therapy. Neuro-Oncology 4: 261-267, 2002
Soffetti R, Costanza A, Ducati A, Laguzzi E, Nobile M, Ruda R: Response of recurrent/progressive ependymomas to temozolomide. Neuro-Oncology 5: 398-399, 2003
Stupp R, Dietrich PY, Ostermann Kraljevic S, Pica A, Maillard I, Maeder P, Meuli R, Janzer R, Pizzolato G, Miralbell R, Porchet F, Regli L, de Tribolet N, Mirimano RO, Leyvraz S: Promising survival for patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme treated with concomitant radiation plus temozolomide followed by adjuvant temozolomide. J Clin Oncol 20: 1375-1382, 2002
van den Bent MJ, Chinot O, Boogerd W, Bravo Marques J, Taphoorn MJ, Kros JM, van der Rijt CC, Vecht CJ, De Beule N, Baron B: Second-line chemotherapy with temozolomide in recurrent oligodendroglioma after PCV (procarbazine,lomustine and vincristine)chemotherapy: EORTC Brain Tumor Group phase II study 26972. Ann Oncol 14: 599-602, 2003
Yung WK, Albright RE, Olson J, Fredericks R, Fink K, Prados MD, Brada M, Spence A, Hohl RJ, Shapiro W, Glantz M, Greenberg H, Selker RG, Vick NA, Rampling R, Friedman H, Phillips P, Bruner J, Yue N, Osoba D, Zaknoen S, Levin VA: A phase II study of temozolomide vs.procarbazine in patients with glioblastoma multiforme at rst relapse. Br J Cancer 83: 588-593, 2000
Yung WK, Prados MD, Yaya-Tur R, Rosenfeld SS, Brada M, Friedman HS, Albright R, Olson J, Chang SM, O 'Neill AM, Friedman AH, Bruner J, Yue N, Dugan M, Zaknoen S, Levin VA: Multicenter phase II trial of temozolomide in patients with anaplastic astrocytoma or anaplastic oligoastrocytoma at rst relapse.Temodal Brain Tumor Group. J Clin Oncol 17: 2762-2771, 1999
Brock CS, Newlands ES, Wedge SR, Bower M, Evans H, Colquhoun I, Roddie M, Glaser M, Brampton MH, Rustin GJ: Phase I trial of temozolomide using an extended continuous oral schedule. Cancer Res 58: 4363-4367, 1998
Newlands ES, Rustin GJS, Evans H, Wedge SR, Brampton MH: Phase I trial of oral temozolomide administered over 6 and 7 weeks.In: Proc Ninth NCI-EORTC Symposium on New Drugs in Cancer Therapy. 1996,p 345
Khan RB, Raizer JJ, Malkin MG, Bazylewicz KA, Abrey LE: A phase II study of extended low-dose temozolomide in recurrent malignant gliomas. Neuro-Oncology 4: 39-43, 2002
Couldwell WT, Weiss MH, DeGiorgio CM, Weiner LP, Hinton DR, Ehresmann GR, Conti PS, Apuzzo ML: Clinical and radiographic response in a minority of patients with recurrent malignant gliomas treated with high-dose tamoxifen. Neurosurgery 32: 485-489, 1993
Vertosick FTJ, Selker RG, Pollack IF, Arena V: The treatment of intracranial malignant gliomas using orally administered tamoxifen therapy: preliminary results in a series of ‘failed’ patients. Neurosurgery 30: 897-902, 1992
Ahn SJ, Yoon MS, Hyuk S, Han W, Yoon YD, Han JS, Noh DY: Phospholipase C-protein kinase C mediated phospholipase D activation pathway is involved in tamoxifen induced apoptosis. J Cell Biochem 89: 520-528, 2003
Baltuch GH, Couldwell WT, Villemure J-G, Yong VW: Protein kinase C inhibitors suppress cell growth in established and low-passage glioma cell lines.A comparison between staurosporine and tamoxifen. Neurosurgery 33: 495-501, 1993
Couldwell WT, Hinton DR, He S, Chen TC, Sebat I, Weiss MH, Law RE: Protein kinase C inhibitors induce apoptosis in human malignant glioma cell lines. FEBS Lett 345: 43-46, 1994
Couldwell WT, Uhm JH, Antel JP, Yong VW: Enhanced protein kinase C activity correlates with the growth rate of malignant gliomas in vitro. Neurosurgery 29: 880-886, 1991
Horgan K, Cooke E, Hallett MB, Mansel RE: Inhibition of protein kinase C mediated signal transduction by tamoxifen.Importance for antitumour activity. Biochem Pharmacol 35: 4463-4465, 1986
Vertosick FTJ: The role of protein kinase C in the growth of human gliomas: implications for therapy. Cancer Journal 5: 328-331, 1992
Diaz AZ, Rajendran J, Spence AM, Krohn KA, Laramore GE: Early toxicity and 18F-.uoromisonidazole positron emission tomography results in a prospective phase II trial of fast neutron radiotherapy to decrease the hypoxic volume in glioblastoma multiforme followed by a photon radiotherapy boost (Abs 167). Neuro-Oncology 4: 353, 2002
Stelzer KJ, Tralins K, Mankoff DA, Silbergeld DL, Laramore GE, Spence AM: Fast neutron irradiation based onffuoro-deoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET)and MRI localization for treatment of glioblastoma multiforme (Abs 207). Neuro-Oncology 2: 296, 2000
Baltuch G, Shenouda G, Langleben A, Villemure J-G: High dose tamoxifen in the treatment of recurrent high grade glioma: a report of clinical stabilization and tumour regression. Can J Neurol Sci 20: 168-170, 1993
Chamberlain MC, Kormanik PA: Salvage chemotherapy with tamoxifen for recurrent anaplastic astrocytomas. Arch Neurol 56: 703-708, 1999
Brandes AA, Ermani M, Turazzi S, Scelzi E, Berti F, Amista P, Rotilio A, Licata C, Fiorentino MV: Procarbazine and high-dose tamoxifen as a second-line regimen in recurrent high-grade gliomas: a phase II study. J Clin Oncol 17: 645-650, 1999
Chang SM, Barker FG, Huhn SL, Nicholas MK, Page M, Rabbitt J, Prados MD: High dose oral tamoxifen and subcutaneous interferon alpha-2a for recurrent glioma. J Neuro-Oncol 37: 169-176, 1998
Caroli M, Locatelli M, Campanella R, Beretta F, Farina G, Scanni A, Arienta C: Adjuvant chemotherapy after surgery of high grade gliomas: the role of tamoxifen and temozolomide (Abs 353). Neuro-Oncology 3: 355-356, 2001
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spence, A.M., Peterson, R.A., Scharnhorst, J.D. et al. Phase II Study of Concurrent Continuous Temozolomide (TMZ) and Tamoxifen (TMX) for Recurrent Malignant Astrocytic Gliomas. J Neurooncol 70, 91–95 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:NEON.0000040837.68411.97
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:NEON.0000040837.68411.97