Abstract
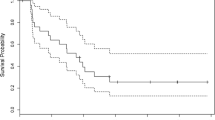
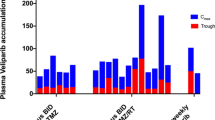
Standard treatment for GBM is radiation (RT) and temozolomide (TMZ). Arsenic trioxide (ATO) is synergistic with RT based on several mechanisms of action previously identified, however not tested herein. The MTD of ATO, RT and TMZ was determined in a Phase I trial. We now present the combined Phase I/II data. Patients with newly diagnosed malignant gliomas were eligible for treatment. Patients were treated with RT (60 GY), TMZ (75 mg/m2 daily × 42 days) and ATO 0.20 mg/kg daily in week 1 then twice a week ×5 weeks, after completing RT they were treated with TMZ 5/28 for up to 12 months. MRIs were performed every 8 weeks. A total of 42 patients were enrolled in both the Phase I and II trials for this study treatment. Of the 42 enrolled patients (24 M and 18 W) the median age was 54 (24–80) and median KPS 90 (60–100). 28 patients had a GBM and 14 had anaplastic glioma (AG). All patients completed RT/TMZ/ATO and went on to maintenance TMZ. Median number of post RT cycles of TMZ was 4 (0–12). Median PFS was 7 m for GBM and 75 m for AG and median OS was 17 m for GBM and NR for AG. Best response was CR in 2, SD in 28, PR in 5 and PD in 7. There were no unexpected adverse events. Grade 3 toxicities likely attributable to ATO included prolonged Qtc (n = 1), elevated liver enzymes (n = 2 for ALT/n = 1 for AST) and elevated bilirubin (n = 1). Adding ATO to RT and TMZ is feasible with no increased side effects. The addition of arsenic did not improve overall survival in the GBM patients as compared to historic data. MGMT status was analyzed in 20 of the 42 patients where tissue was available for retrieval and MGMT testing.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stupp R et al (2009) Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol 10(5):459–466
Wick W (2015) Long-term analysis of the NOA-04 randomized phase III trial of sequential radiochemotherapy of anaplastic glioma with PCV or temozolomide. ASCO Conference
Dolecek TA et al (2012) CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2005–2009. Neuro Onco 14(Suppl 5):v1–v49
Gilbert MR, Sulman EP, Mehta MP (2014) Bevacizumab for newly diagnosed glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 370(21):2048–2049
Kizilbash SH et al (2014) The impact of concurrent temozolomide with adjuvant radiation and IDH mutation status among patients with anaplastic astrocytoma. J Neurooncol 120(1):85–93
Miller WH Jr., et al (2002) Mechanisms of action of arsenic trioxide. Cancer Res 62(14):3893–3903
Yedjou C et al (2010) Basic mechanisms of arsenic trioxide (ATO)-induced apoptosis in human leukemia (HL-60) cells. J Hematol Oncol 3:28
Ning S, Knox SJ (2006) Optimization of combination therapy of arsenic trioxide and fractionated radiotherapy for malignant glioma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 65(2):493–498
Ning S, Knox SJ (2004) Increased cure rate of glioblastoma using concurrent therapy with radiotherapy and arsenic trioxide. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 60(1):197–203
Zhen Y et al (2010) Arsenic trioxide-mediated Notch pathway inhibition depletes the cancer stem-like cell population in gliomas. Cancer Lett 292(1):64–72
Nasr R (2010) Eradication of acute promyelocytic leukemia-initiating cells by PML/RARA-targeting. Int J Hematol 91(5):742–747
Zhou W et al (2015) Arsenic trioxide disrupts glioma stem cells via promoting PML degradation to inhibit tumor growth. Oncotarget 6(35):37300–37315
Fatoo A et al (2011) Understanding the role of tumor stem cells in glioblastoma multiforme: a review article. J Neurooncol 103(3):397–408
Lim SK et al (2011) Glioblastoma multiforme: a perspective on recent findings in human cancer and mouse models. BMB Rep 44(3):158–164
Grimm SA et al (2012) Phase I study of arsenic trioxide and temozolomide in combination with radiation therapy in patients with malignant gliomas. J Neurooncol 110(2):237–243
Macdonald DR et al (1990) Response criteria for phase II studies of supratentorial malignant glioma. J Clin Oncol 8(7):1277–1280
Nayak L et al (2015) Radiotherapy and temozolomide for anaplastic astrocytic gliomas. J Neurooncol 123(1):129–134
Iwanami A et al (2013) PML mediates glioblastoma resistance to mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)-targeted therapies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(11):4339–4344
Iwanami A et al (2013) Arsenic reverses glioblastoma resistance to mTOR-targeted therapies. Cell Cycle 12(10):1473–1474
Funding
This study was funded by an industry grant from Cephalon.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors listed have no related conflicts of interest to disclose.
Research involving human participants
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumthekar, P., Grimm, S., Chandler, J. et al. A phase II trial of arsenic trioxide and temozolomide in combination with radiation therapy for patients with malignant gliomas. J Neurooncol 133, 589–594 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-017-2469-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-017-2469-x