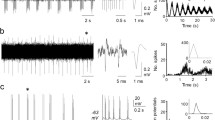
Abstract
Bilateral lesioning of the presublingual nucleus (nucleus praepositus hypoglossi) of the medulla oblongata induced significant changes in the nature of baseline spine activity in the locus coeruleus. After lesioning, the mean frequency of spike activity of locus coeruleus neurons decreased more than two-fold. The numbers of neurons with train-grouped activity and polymodal neurons increased significantly. Exclusion of the solitary tract nucleus led to an increase in the number of neurons with regular activity and some decrease in the mean discharge frequency in locus coeruleus neurons. These data support the suggestion that the presublingual nucleus plays a significant role in the transmission of afferent influences on the activity of locus coeruleus neurons.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
A. S. Amatuni, R. Sh. Sarkisyan, É. A. Korkotyan, et al., “Types of baseline spike activity in fastigial neurons of the cerebellum,” Neirofiziologiya, 23,No. 4, 441–450 (1991).
K. I. Pogodaev, Epileptology and Brain Pathochemistry [in Russian], Meditsina, Moscow (1986).
M. V. Khanbabyan, Noradrenergic Mechanisms of the Brain [in Russian], Nauka, Leningrad (1981).
D. N. Khudaverdyan, A. A. Asratyan, I. V. Varterisyan, et al., “Analysis of baseline spike activity of blue spot neurons,” Neirofiziologiya, 32,No. 4, 308–313 (2000).
F. Abad-Alegria, “Estereotaxis troncoencefalica,” Trab. Inst. Cajal Invest. Biol., 63,No. 1, 193–224 (1971).
G. Aston-Jones, M. Ennis, V. Piribone, et al., “Environmental and neural determinants of locus coeruleus discharge: functional implications,” in: Abstr. IBRO Congr., Budapest (1987), p. 105.
J. Cedarbaum and J. Aghajanian, “Activation of locus coeruleus neurons by peripheral stimuli: modulation by collateral inhibitory mechanism,” Life Sci., 13,No. 23, 1383–1394 (1978).
L. Foot, R. Freedman, and P. Oliver, “Effects of putative neurotransmitters on neuronal activity in monkey cortex,” Brain Res., 235,No. 86, 229–241 (1975).
L. Foot, “Anatomy and physiology of locus coeruleus projections to neocortex,” in: Abstr. IBRO Congr., Budapest (1987), p. 105.
S. Foot, F. Bloom, and G. Aston-Jones, “Nucleus locus coeruleus: new evidence of anatomical and physiological specificity,” Physiol. Rev., 63,No. 3, 164–171 (1983).
H. Meyer, M. Polchandhuri, et al., “Regulation of alpha (2A)-adrenoceptor expression by chronic stress in neurons of the brain stem,” Brain Res., 880,No. 1–2, 147–154 (2000).
A. Passerin, J. Cano, and B. Rabin, “Role of the locus coeruleus in shock-evoked fos expression in rat brain,” Neurosci., 101,No. 4, 1071–1080 (2000).
C. Streefland and K. Jansen, “Intramedullary projections of the solitary tract in the rat,” Chem. Senses, 24(b), 655–662 (1999).
M. Tanaka, M. Yoshida, H. Emoto, et al., “Noradrenaline systems in the hypothalamus, amygdala, and locus coeruleus are involved in the provocation of anxiety: basic studies,” Eur. J. Pharmacol., 405,No. 1–3, 397–405 (2000).
E. van Bockstaeble, J. Peoples, and P. Telegan, “Efferent projections of the nucleus of solitary tract to peri-locus coeruleus dendrites in rat brain: evidence for a monosynaptic pathway,” J. Comp. Neurol., 412,No. 3, 410–417 (1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khanbabyan, M.V., Saakyan, N.A., Sarkisyan, R.S. et al. Baseline Spike Activity of Neurons in the Locus Coeruleus of the Rat after Lesions to a Number of Medulla Oblongata Nuclei. Neurosci Behav Physiol 34, 315–319 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:NEAB.0000018738.45797.ff
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:NEAB.0000018738.45797.ff