Abstract
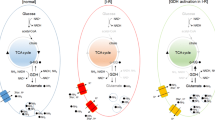
Summary: Although the precise mechanisms underlying the CNS degeneration of patients with glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase (GCDH) deficiency are still the subject of intense debate, many studies have highlighted that excitotoxicity plays a fundamental role in the neuropathology of this disease, particularly involving the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subtype of ionotropic glutamate receptors. Modulation of the glutamatergic system by these compounds involves an inhibition of glutamate uptake into synaptosomes and synaptic vesicles, and a decrease in glutamate binding. Furthermore, glutaric and 3-hydroxyglutaric acids inhibit glutamate decarboxylase, the key enzyme of GABA synthesis, and striatal GABAergic medium-spiny neurons are highly vulnerable to 3-hydroxyglutaric acid-induced neurotoxicity. In conclusion, glutaric acid and 3-hydroxyglutaric acid induce an imbalance in glutamatergic and GABAergic neurotransmission.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Anderson CM, Swanson RA (2000)Astrocyte glutamate transport:review of properties,regulation and physiological functions.Glia 32:1-14.
Bennett JP, Logan WJ, Snyder SH(1973)Amino acids as central nervous transmitters:the influence of ions,amino acid analogues,and ontogeny on transport systems for L-glutamicand L-aspartic acids and glycine into central nervous synaptosomes of the rat.J Neurochem 21:1533-1550.
Bjugstad KB, Zawada WM, Goodman SI, Free CR (2001)IGF-1 and bFGF reduce glutaric and 3-hydroxyglutaric acid toxicity in striatal cultures.J Inherit Metab Dis 24:631-647.
Calabresi P, Centonze D, Pisani A (1998)Striatal spiny neurons and cholinergic interneurons express diüerential ionotropic glutamatergic responses and vulnerability:implications for ischemia and Huntington disease.Ann Neurol 43:586-597.
de Mello CF, Kölker S, Ahlemeyer B, et al (2001)Intrastriatal administration of 3-hydroxyglutaric acid induces convulsions and striatal lesions in rats.Brain Res 916:70-75.
Frizzo ME, Schwarzbold C, Porciuncula LO, et al (2004)3-Hydroxyglutaric acid enhances glutamate uptake into astrocytes from cerebral cortex of young rats.Neurochem Int 44:345-353.
Ikonomidoú C, Bosch F, Miksa M, et al (1999)Blockade of NMDA receptors and apoptoticneurodegeneration in the developing brain.Science 283:70-74.
Kölker S, Okun JG, Ahlemeyer B, et al (2002a)Chronic treatment with glutaric acid induces partial tolerance to excitotoxicity in neuronal cultures from chick embryo telencephalons. J Neurosci Res 685:424-431.
Kölker S, Köhr G, Ahlemeyer B, et al (2002b)Ca 2 + and Na + dependence of 3-hydroxy-glutarate-induced excitotoxicity in rimary neuronal cultures fromchick embryo telence halons. Pediatr Res 52:199-206.
Kölker S, Koeller DM, Sauer S, et al (2004)Excitotoxicity and bioenergetics in glutaryl-CoAdehydrogenase de ficiency.J Inherit Metab Dis 27:805-812.
Leibel RL, Shih VE, Goodman SI, et al (1980)Glutaric acidemia:a metabolic disorder causingprogressive choreoathetosis.Neurology 30:1163-1168.
Lima TTF, Begnini J, Bastiani J, et al (1998)Pharmacological evidence for GABAergic and glutamatergic involvement in the convulsant and behavioral eüects of glutaric acid.Brain Res 802:55-60.
Porciúncula LO, Dal-Pizzol A Jr, Coitinho AS, Emanuelli T, Souza DO, Wajner M (2000) Inhibition of synaptosomal [3 H ]glutamate uptake and [3 H ]glutamate binding to plasma membranes from brain of young rats by glutaric acid in vitro. JNeurolSi 173:93-96.
Porciúncula LO, Emanuelli T, Tavares RG, et al (2004)Glutaric acid stimulates glutamate binding and astrocyte uptake and inhibits vesicular glutamate uptake in forebrain from young rats.Neurochem Int 45:1075-1086.
Rosa RB, Schwarzbold C, Dalcin KB, et al (2004)Evidence that 3-hydroxyglutaric acid interacts with NMDA receptors in synaptic membranes from cerebral cortex of young rats. Neurochem Int 45:1087-1094.
Stokke O, Goodman SI, Moe PG (1976)Inhibition of brain glutamate decarboxylase by glutarate,glutaconate and β-hydroxyglutarate:explanation of the symptoms in glutaric aciduria?Clin Chim Acta 66:411-415.
Ullrich K, Flott-Rahmel B, Schluff P, et al (1999)Glutaric aciduria type I:pathomechanisms of neurodegeneration.J Inherit Metab Dis 22:392-403.
Whetsell WO, Schwarcz R (1983)The organotypic tissue culture model of corticostriatal system used for examining amino acid neurotoxicity and its antagonism:studies on kainic acid, quinolinic acid and ()-2-amino-7-phosphonoheptanoic acid.J Neural TransmSuppl 19:53.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wajner, M., KÖlker, S., Souza, D.O. et al. Modulation of glutamatergic and GABAergic neurotransmission in glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency. J Inherit Metab Dis 27, 825–828 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BOLI.0000045765.37043.fb
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BOLI.0000045765.37043.fb