Abstract
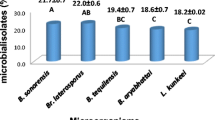
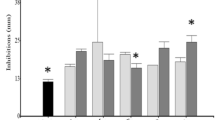
Newly isolated bacterial strains belonging to Bacillaceae (Bacillus sp.), Micrococcaceae and three unidentified strains were tested for their pathogenicity against the mite, Varroa destructor. The Bacillus sp. strain and two of the strains belonging to the Micrococcaceae family significantly decreased the time for 50% mortality of the mite population (up to 57%) and hence may be potential control agents. In in vitro bioassay whole cells, extracellular broth and cellular extract of the Bacillus sp. strain effectively killed the mites, suggesting that both endotoxins and exotoxins contributed to the killing.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aronson AI, Beckman W, Dunn P (1986) Bacillus thuringiensis and related insect pathogens. Microbiol. Rev. 50: 1–24.
Ball BV, Allen MF (1988) The prevalence of pathogens in honey bee (Apis melifera) colonies infested with the parasitic mite Varroa jacobsoni. Ann. Appl. Biol. 113: 237–244.
Bassett CL, Janisiewicz WJ (2003) Electroporation and stable maintenance of plasmid DNAs in a biocontrol strain of Pseudomonas syringae. Biotechnol. Lett. 25: 199–203.
Chang YD, Woo KS, Lee HR (1993) Taxonomy, ecology and control of honey bee mites in Korea. Korean J. Apic. 8: 35–47.
De Guzman LI, Rinderer TE, Beaman LD (1993) Survival of Varroa jacobsoni Oud. (Acari: Varroidae) away from its living host Apis melifera L. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 17: 283–290.
Glinski Z, Jarosz J (1990) Serratia marcescens artificially contaminating brood and worker honey bees, contaminates the Varroa jacobsoni mite. J. Apic. Res. 29: 107–111.
Kanga LHB, James RR, Boucias DG (2002) Hirsutella thompsonii and Metarhizium anisopliae as potential microbial control agents of Varroa destructor, a honey bee parasite. J. Invert. Pathol. 81: 175–184.
Lianou A (2003) Study of the microflora of the mite Varroa jacobsoni. BS in Agricultural Biotechnology Thesis. Athens, Greece: Agricultural University of Athens.
Liu TP, Ritter W (1988) Morphology of some microorganisms associated with the female mite Varroa jacobsoni: a survey by electron microscopy. In: Needham E, Page RE, Delfinado-Baker M, Bowman CE, eds. Africanized Honeybees and Bee Mites. Chichester, UK: Ellis Horwood, pp. 467–474.
Sammataro D, Gerson U, Needham G (2000) Parasitic mites of honey bees: life, history, implications, and impact. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 45: 519–548.
Shaw KE, Davidson G, Clark SJ, Ball BV, Pell JK, Chandler D, Sunderland KD (2002) Laboratory bioassays to assess the pathogenicity of mitosporic fungi to Varroa destructor (Acari: Mesostigmata), an ectoparasitic mite of honeybee, Apis mellifera. Biol. Control 24: 266–276.
Van Der Geest LPS, Elliot SL, Reeuwer JAJ, Beerling EAM (2000) Diseases of mites. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 24: 497–560.
Wallner K (1999) Varroacides and their residues in bee products. Apidologie 3: 235–248.
Wilkinson D, Thompson HM, Smith GC (2001) Modelling biological approaches to controlling Varroa populations. Am. Bee J. 141: 511–516.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsagou, V., Lianou, A., Lazarakis, D. et al. Newly isolated bacterial strains belonging to Bacillaceae (Bacillus sp.) and Micrococcaceae accelerate death of the honey bee mite, Varroa destructor (V. jacobsoni), in laboratory assays. Biotechnology Letters 26, 529–532 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BILE.0000019563.92959.0e
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BILE.0000019563.92959.0e