Abstract
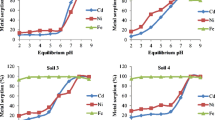
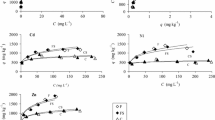
Disposal of sewage sludge creates the potential for heavy metal accumulation in theenvironment. This study assessed nine soils currently used as Dedicated Land Disposal units(DLDs) for treatment and disposal of municipal sewage sludge in the vicinity of Sacramento,California. Adsorption characteristics of these soils for Cd, Cu, Ni, Zn, Pb, and Cr were studiedby simultaneously mixing these elements in the range of 0-50 µmol L-1 with sludgesupernatant and reacting with the soil using a soil:supernatant ratio of 1:30, pH = 4.5 or 6.5, andconstant ionic strength (0.01 M Na-acetate). The concentration of metals in the supernatant wasdetermined after a 24 hr equilibration period. Adsorption isotherms showed that metal sorptionwas linearly related to its concentration in the supernatant solution. The distribution coefficientKd (Kd = concentration on solid phase/concentration in solution phase) was computed as theslope of the sorption isotherm. The distribution coefficients were significantly correlated to soilorganic matter content for Ni, Cu, Cd, and Pb at pH 4.5 and for Ni, Cu, Zn, and Cd at pH 6.5.There was also a correlation between Kd and soil specific surface area but no relationship to othersoil properties such as CEC, clay content, and noncrystalline Fe and Al materials. Therefore, soilorganic carbon and surface area appear to be the most important soil properties influencing metaladsorption through formation of organo-metal complexes. The Kd values for all elements werehigher at pH 6.5 than at 4.5. Selectivity between metals resulted in the following metal affinitiesbased on their Kd values: Pb>Cu>Zn>Ni>Cd≈Cr at pH 4.5 andPb>Cu≈Zn>Cd>Ni>Cr at pH 6.5.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison, J. D., Brown, D. S. and Novo-Gradac, K. J.: 1991, MINTEQA2PRODEFA2, A Geochemical Assessment Model for Environmental Systems: Version 3. 11. U. S. EPA. Athens, Georgia.
Behel, D. Jr, Darrell, D. W., Nelson, E. and Sommers, L. E.: 1983, J. Environ.Qual. 12, 181.
Boyd, S. A., Sommers, L. E. and Nelson, D. W.: 1981, Soil Sci.Soc.Am.J. 45, 1241.
Carte r. D. L., Mortland, M. M. and Kemper, W. D.: 1982, 'Specific surfaces’, in A. Klute (ed.) Methods of Soil Analysis.Part I-Physical and Mineralogical Methods, 2nd ed. Soil Science Society of America, Madison, Wisconsin, pp. 413423.
Chairidchai, P. and Ritchie, G. S. P.: 1990, Soil Sci.Soc.Am.J. 54, 1242.
Chang, A. C., Page, A. L., Warneke, J. E., Resketo, M. R. and Jones, T. E.: 1983, J.Environ.Qual. 12, 391.
Cline, G. R. and O'Connor, G. A.: 1984, Soil Sci. 138, 248.
Dahlgren, R. A. and Marrett, D. J.: 1991, Soil Sci.Soc.Am.J. 55, 1382.
Eary, L. E. and Rai, D.: 1991, Soil Sci.Soc.Am.J. 55, 676.
Elrashidi, M. A. and O'Connor. G. A.: 1982, Soil Sci.Soc.A m.J. 46, 1153.
Elliott, H. A. and Denneny, C. M.: 1982, J.Environ.Qual. 11, 658.
Garcia-Miragaya, J.: 1984, Soil Sci. 138, 147.
Gee, G. W. and Bauder, J. W.: 1986, 'Particle-Size Analysis’, in A. Klute (ed.), Methods of Soil Analysis.Part I-Physical and Mineralogical Methods, 2nd ed. Soil Science Society of America, Madison, Wisconsin, pp. 38341 1.
Harter, R. D.: 1992, Soil Sci.Soc.Am.J. 56, 444.
Holmgren, G. G. S.: 1967, Soil Sci.Soc.Am.Proc. 31, 210.
Inskeep, W. P. and Baham, J.: 1983, Soil Sci.Soc.Am.J. 47, 1109.
James, B. R. and Bartlett, R. J.: 1983a, J.Environ.Qual. 12, 173.
James, B. R. and Bartlett, R. J.: 1983b, J.Environ.Qual. 12, 177.
Kuo, S. and Baker, A. S.: 1980, Soil Sci.Soc.Am.J. 44, 969.
Kurdi, F. and Doner, H. E.: 1983, Soil Sci.Soc.Am.J. 47, 873.
McKeague, J. A. (ed.): 1976, Manual on Sampling and Methods of Analysis, Soil Res. Inst., Agriculture Canada, Ottawa.
Nelson, R. E.: 1982, 'Carbonate and Gypsum’, in A. L. Page (ed.), Methods of Soil Analysis.Part 2-Chemical and Microbiological Properties, 2nd ed. Soil Science Society of America, Madison, Wisconsin, pp. 181–197.
Page, A. L. and Chang, A. C.: 1981, 'Trace Metals in Soils and Plants Receiving Municipal Wastewater Irrigation’, in F. M. D'Itri (ed.), Municipal Wastewater in Agriculture, Academic Press; New York, pp. 351–372.
Petruzzelli, G., Guidi, G. and Lubrano, L.: 1985, Commun.Soil Sci.Plant Anal. 16, 971.
Sadiq, M.: 1981, Commun.Soil Sci.Plant Anal. 12, 619.
Santillan-Medrano, J. and Jurinak, J. J.: 1975, Soil Sci.Soc.Am.Proc. 39, 851.
Soil Survey Staff: 1984, Procedures for Collecting Soil Samples and Methods of Analysis for Soil Survey. Soil Survey Investigations, Rep. No. 1. USDA-SCS Agric. Handb. 436. U. S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC.
Sommers, L. E.: 1977, J.Environ.Qual. 6, 225.
Sposito, G., Lund, L. J. and Chang, A. C.: 1982, Soil Sci.Soc.A m.J. 46, 260.
Sposito, G., Holtzclaw, K. M. and LeVesque-Madore, C. S.: 1979, Soil Sci.Soc.Am.J. 43, 1148.
Sposito, G., Holtzclaw, K. M. and LeVesque-Madore, C. S.: 1981, Soil Sci.Soc.Am.J. 45, 465.
Sposito, G. and Mattigod, S. V.: 1979, GEOCHEM: A Computer Program for the Calculation of Chemical Equilibria in Soil Solutions and Other Natural Water Systems. Dep. Soil and Environ. Sci., University of California, Riverside.
Susetyo, W., Dobbs, J. C., Carreira, L. A., Azarraga, L. V. and Grimm, D. M.: 1990, Anal.Chem. 62, 1215.
Whittig, L. D. and Allardice, W. R.: 1986, 'X-Ray Diffraction Techniques’, in A. Klute (ed.), Methods of Soil Analysis.Part [-Physical and Mineralogical Methods, 2nd ed. Soil Science Society of America, Madison, Wisconsin, pp. 331–362.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, S., Walker, W.J., Dahlgren, R.A. et al. Simultaneous Sorption of Cd, Cu, Ni, Zn, Pb, and Cr on Soils Treated with Sewage Sludge Supernatant. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 93, 331–345 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022169531878
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022169531878