Abstract
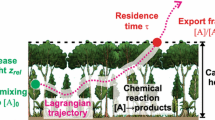
A stochastic trajectory model was used to estimate scalar fluxfootprints in neutral stabilityfor canopies of varying leaf area distributions andleaf area indices. An analytical second-order closure model wasused to predict mean wind speed, second moments and the dissipationrate of turbulent kinetic energy within a forest canopy.The influence of source vertical profile on the flux footprint wasexamined. The fetch is longer for surface sourcesthan for sources at higher levels in the canopy. In order tomeasure all the flux components, and thus the total flux, with adesired accuracy, sources were located at the forest floor in thefootprint function estimation. The footprint functions werecalculated for five observation levels above the canopy top. Itwas found that at low observation heights both canopy density andcanopy structure affect the fetch. The higher abovethe canopy top the flux is measured, the more pronounced is the effectof the canopy structure. The forest fetch for flux measurements isstrongly dependent on the required accuracy: The 90% flux fetchis greater by a factor of two or more compared to the 75% fetch. Theupwind distance contributing 75% of flux is as large as 45 timesthe difference between canopy height and the observation heightabove the canopy top, being even larger for low observationlevels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albini, F.: 1981, 'A Phenomenological Model forWind Speed and Shear Stress Profiles in Vegetation Cover Layers', J. Appl. Meteorol. 20, 1325–1335.
Aubinet, M., Grelle, A., Ibrom, A. Rannik, Ñ., Moncrieff, J., Foken, T., Kowalski, A., Martin, P., Berbigier, P., Bernhofer, C., Clement, R., Elbers, J., Granier, A., Grünwald, T., Morgenstern, K., Pilegaard, K., Rebmann, C., Snijders, W., Valentini, R., and Vesala, T.: 2000, 'Estimates of the Annual Net Carbon and Water Exchange of European Forests: The EUROFLUX Methodology', Adv. Ecol. Res. 30, 113–175.
Baldocchi, D.: 1992, 'A Lagrangian Random-Walk Model for Simulating Water Vapor, CO2 and Sensible Heat Flux Densities and Scalar Profiles over and within a Soybean Canopy', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 61, 113–144.
Baldocchi, D.: 1997, 'Flux Footprints within and over Forest Canopies', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 85, 273–292.
Baldocchi, D. and Meyers, T.: 1998, 'On Using Eco-Physiological, Micrometeorological and Biogeochemical Theory to Evaluate Carbon Dioxide, Water Vapor and Trace Gas Fluxes over Vegetation: A Perspective', Agric. For. Meteorol. 90, 1–26.
Ball, J., Woodrow, I., and Berry, J.: 1988, 'A Model Predicting Stomatal Conductance and its Contribution to the Control of Photosynthesis under Different Environmental Conditions', in J. Biggens (ed.), Progress in Photosynthetic Research, Martinus Nijhoff, Dordrecht, pp. 221–224.
Campbell, G.: 1985, Soil Physics with BASIC, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 150 pp. (with diskette).
Cellier, P. and Brunet, Y.: 1992, 'Flux-Gradient Relationships above Tall Plant Canopies', Agric. For. Meteorol. 58, 93–117.
Cescatti, A.: 1998, 'Effects of Needle Clumping in Shoots and Crowns on the Radiative Regime of a Norway Spruce Canopy', Ann. Sci. Forest. 55, 89–102.
Chen, J.: 1996, 'Optically-Based Methods for Measuring Seasonal Variation of Leaf Area Index in Boreal Conifer Stands', Agric. For. Meteorol. 80, 135–163.
Chen, J., Black, T., and Adams, R.: 1991, 'Evaluation of Hemispherical Photography for Determining Plant Area Index and Geometry of a Forest Stand', Agric. For. Meteorol. 56, 129–143.
Falge, E., Graber,W., Siegwolf, R., and Tenhunen, J.: 1996, 'A Model of the Gas Exchange Response of Picea Abies to Habitat Conditions', Trees 10, 277–287.
Farquhar, G. and von Caemmerer, S.: 1982, 'Modelling of Photosynthetic Response to Environmental Conditions', in O. Lange, P. Nobel, C. Osmond, and H. Ziegler (eds.), Physiological Plant Ecology II, Vol. 12 B, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp. 549–587.
Finn, D., Lamb, B., Leclerc, M., and Horst, T.: 1996, 'Experimental Evaluation of Analytical and Lagrangian Surface-Layer Footprint Models', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 80, 283–308.
Flesch, T. and Wilson, J.: 1992, 'A Two-Dimensional Trajectory-Simulation Model for Non-Gaussian, Inhomogeneous Turbulence within Plant Canopies', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 61.
Foken, T. and Wichura, B.: 1996, 'Tools for Quality Assessment of Surface-Based Flux Measurements', Agric. For. Meteorol. 78, 83–105.
Goulden, M., Daube, B., Fan, S.-M., Sutton, D., Bazzaz, A., Munger, J., and Wofsy, S.: 1997, 'Physiological Responses of a Black Spruce Forest to Weather', J. Geophys. Res. 102, 28987–8996.
Horst, T. and Weil, J.: 1992, 'Footprint Estimation for Scalar Flux Measurements in the Atmospheric Surface Layer', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 59, 279–296.
Horst, T. and Weil, J.: 1994, 'How Far Is Far Enough?: The Fetch Requirements for Micrometeorological Measurement of Surface Fluxes', J. Atmos. Oceanic Tech. 11, 1018–1025.
Kurbanmuradov, O., Rannik, Ñ., Sabelfeld, K., and Vesala, T.: 1999, 'Direct and Adjoint Monte Carlo for the Footprint Problem', Monte Carlo Meth. Appl. 5, 85–111.
Kurbanmuradov, O., Rannik, Ñ., Sabelfeld, K., and Vesala, T.: 2001, 'Evaluation of Mean Concentration and Fluxes in Turbulent Flows by Lagrangian Stochastic Models', Math. Comp. Simul. 54, 459–476.
Lindroth, A., Grelle, A., and Moren, A.-S.: 1998, 'Long-Term Measurments of Boreal Forest Carbon Balance Reveal Large Temperature Sensitivity', Global Change Biol. 4, 443–450.
Malhi, Y., Baldocchi, D., and Jarvis, P.: 1999, 'The Carbon Balance of Tropical, Temperate and Boreal Forests', Plant Cell Environ. 22, 715–740.
Markkanen, T., Rannik, Ñ., Keronen, P., Suni, T., and Vesala, T.: 2001, 'Eddy Covariance Fluxes over a Boreal Scots Pine Forest', Boreal Environ. Res. 6, 65–78.
Massman, W.: 1997, 'An Analytical One-Dimensional Model of Momentum Transfer by Vegetation of Arbitrary Structure', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 83, 407–421.
Massman, W. and Weil, J.: 1999, 'An Analytical One-Dimensional Second-Order Closure Model of Turbulece Statistics and the Lagrangian Time Scale within and above Plant Canopies of Arbitrary Structure', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 91, 81–107.
Meyers, T. and Paw U, K.: 1986, 'Testing a Higher Order Closure Model for Modeling Airflow within and above Plant Canopies', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 37, 297–311.
Nilson, T.: 1971, 'A Theoretical Analysis of the Frequency of Gaps in Plant Stands', Agric. Meteorol. 8, 25–38.
Rannik, Ñ., Aubinet, M., Kurbanmuradov, O., Sabelfeld, K., Markkanen, T., and Vesala, T.: 2000, 'Footprint Analysis for the Measurements over a Heterogeneous Forest', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 97, 137–166.
Raupach, M.: 1989, 'A Practical Lagrangian Method for Relating Scalar Concentrations to Source Distributions in Vegetation Canopies', Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 115, 609–632.
Reynolds, A.: 1998, 'On the Formulation of Lagrangian Stochastic Models of Scalar Dispersion within Plant Canopies', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 88, 77–86.
Running, S.: 1998, 'A Blueprint for Improved Global Change Monitoring of the Terrestrial Biosphere', Earth Observer 10, 8–12.
Schmid, H.: 1994, 'Source Areas for Scalar and Scalar Fluxes', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 67, 293–318.
Schuepp, H., Leclerc, M., MacPherson, J., and Desjardins, R.: 1990, 'Footprint Prediction of Scalar Fluxes fromAnalytical Solutions of the Diffusion Equation', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 50, 355–373.
Thomson, D.: 1987, 'Criteria for the Selection of Stochastic Models of Particle Trajectories in Turbulent Flows', J. Fluid Mech. 180, 529–556.
Valentini, R., Matteucci, G., Dolman, A., Schulze, E., Rebmann, C., Moors, E., Granier, A., Gross, P., Jensen, N., Pilegaard, K., Lindroth, A., Grelle, A., Bernhofer, C., Grünwald, T., Aubinet, M., Ceulemans, R., Kowalski, A., Vesala, T., Rannik, Ñ., Berbigier, B., Lousteau, D., Guðmundsson, J., Thorgeirsson, H., Ibrom, A., Morgenstern, K., Clement, R., Moncrieff, J., Montagnani, L., Minerbi, S., and Jarvis, P.: 2000, 'Respiration as the Main Determinant of Carbon Balance in European Forests', Nature 404, 861–865.
Wang, Y., Jarvis, P., and Benson, M.: 1990, 'Two-Dimensional Needle-Area Density Distribution within the Crowns of Pinus Radiata', For. Ecol. Manage. 32, 217–237.
Wofsy, S., Goulden, M., Munger, J., Fan, S., Bakwin, P., Daube, B., Bassow, S., and Bazzaz, F.: 1993, 'Net Exchange of CO2 in a Midlatitude Forest', Science 260, 1314–1317.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Markkanen, T., Rannik, Ü., Marcolla, B. et al. Footprints and Fetches for Fluxes over Forest Canopies with Varying Structure and Density. Boundary-Layer Meteorology 106, 437–459 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021261606719
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021261606719