Abstract
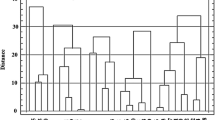
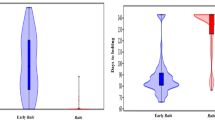
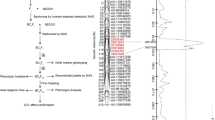
The present study was carried out to evaluate genetic divergence among eleven japonica rice cultivars and to assess the relationship between genetic distance and hybrid performance in partial non-reciprocal crosses among them. The 44 F1 hybrids along with the eleven parents were evaluated for five cold tolerance-related traits; discoloration at seedling stage, days to heading, culm length, fertility, and spikelets per panicle in a cold water screening nursery (17 °C). The eleven parents were examined for DNA polymorphism using amplified fragment length polymorphisms(AFLPs). A total of 855 polymorphic variants were generated and based on the polymorphism data, genetic distances (GDs) ranged from 0.023 to0.524. Very little heterosis was observed in hybrids for most of the traits,whereas heterosis was high for fertility. The correlation values of GDs with F1 performance were mostly non-significant except for discoloration and fertility. The correlations of GDs with mid-parent and better-parent heterosis were not significant and proved to be of no predictive value. Our results indicate that GDs based on AFLP markers are not useful for predicting heterosis for cold tolerance in japonica hybrids.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal, R.K., D.S. Brar, S. Nandi, N. Huang & G.S. Khush, 1999. Phylogenetic relationships among Oryza species revealed by AFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 98: 1320–1328.
Ahn, S.N., T.S. Kwak, K.H. Kang, Y.H. Jeon, H.C. Choi & H.P. Moon, 1998. Relationship between heterosis and genetic distance as measured by RAPDs analysis in rice. Korean J Breed 30(1): 16–23.
Burr, B., S.V. Evola, F.A. Burr & J.S. Beckman, 1983. The application of restriction fragment length polymorphisms to plant breeding. In: J.K. Setlow & A. Hollaender (Eds.), Genetic Engineering Principles and Methods, vol. 5., pp. 45–59. Plenum Press, London.
Causse, M.A., T.M. Fulton, Y.G. Cho, S.N. Ahn, J. Chunwongse, K.S. Wu, J.H. Xiao, Z.H. Yu, P.C. Ronald, S.E. Harrington, G. Second, S.R. McCouch & S.D. Tanksley, 1994. Saturated molecular map of the rice genome based on an interspecific backcross population. Genetics 138: 1251–1274.
Cerna, F.J., S.R. Cianzio, A. Rafalski, S. Tingey & D. Dyer, 1997. Relationship between seed yield heterosis and molecular marker heterozygosity in soybean. Theor Appl Genet 95: 460–467.
Chen, X., S. Temnykh, Y. Xu, Y.G. Cho & S.R. McCouch, 1997. Development of a microsatellite framework map providing genome-wide coverage in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 95: 553–567.
Cho, Y.G., S.R. McCouch, S.R. Kuiper, J. Pot, M.R. Kang, J.T.M. Groenen & M.Y. Eun, 1997. Integrated map of AFLP, SSLP, and RFLP markers using a recombinant inbred population of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 97: 370–380.
Jeong, E.G., J.D. Yea, M.K. Baek, H.P. Moon, H.C. Choi, K.M. Yoon & S.N. Ahn, 2000. Estimation of critical temperature for traits related to cold tolerance in rice. Korean J Breed 32(4): 363–368.
Koh, H.J., 1989. Breeding of Cytoplasmic Male Sterile Lines and Its Restorer Lines of Japonica Rice and Genetic Analysis of Restorer Gene. Ph.D. Thesis, Seoul National University, Korea.
Melchinger, A.E., M. Lee, K.R. Lamkey, A.R. Hallauer & W.L. Woodman, 1990. Genetic diversity for restriction fragment length polymorphisms and heterosis for two diallel sets of maize inbreds. Theor Appl Genet 80: 488–496.
Moon, H.P., M.H. Heu & C.H. Kim, 1994. Hybrid rice research in the Republic of Korea. In: S.S. Virmani (Ed.), Hybrid Rice Technology: New Developments and Future Prospects, pp. 217–226. International Rice Research Institute, Philippines.
Nei, M., 1987. Molecular Evolutionary Genetics. Columbia University Press, New York.
Panaud, O., X. Chen & S.R. McCouch, 1996. Development of microsatellite markers and chracterization of simple sequence length polymorphism (SSLP) in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Gen Genet 252: 597–607.
Rural Development Administration, 1995. Manual for Standard Evaluation Method in Agricultural Experiment and Research. Rural Development Administration, Suwon, Korea.
Rutger, J.N. & M.L. Peterson, 1979. Cold tolerance of rice in California. In: Report of a Rice Cold Tolerance Workshop. Intl Rice Res Inst, Los Banos, Philippines.
Saghai Maroof, M.A., G.P. Yang, Q. Zhang & K.A. Gravois, 1997. Correlation between marker distance and hybrid performance in U.S. southern long grain rice. Crop Sci 37: 145–150.
Satake, T. & S. Yoshida, 1977. Mechanism of sterility caused by high temperature at flowering in indica rice. JARQ 11: 127–128.
Schwartz, D. & W.J. Laughner, 1969. A molecular basis for heterosis. Science 166: 626–627.
Smith, O.S., J.S.C. Smith, S.L. Bowen, R.A. Tenborg & S.J. Wall, 1990. Similarities among a group of elite maize inbreds as measured by pedigree, F1 grain yield, heterosis and RFLPs. Theor Appl Genet 80: 833–840.
Temnykh S., G. DeClerck, A. Lukashova, L. Lipovich, S. Cantinhour & S.R. McCouch, 2001. Computational and Experimental Analysis of Microsatellites in Rice (Oryza sativa L.): Frequency, Length Variation, Transposon Associations, and Genetic Marker Potential. Genome Res 11: 1441–1452.
Temnykh, S., W.D. Park, N. Ayres, S. Cartinhour, N. Hauck, L. Lipovich, Y.G. Cho, T. Ishii & S.R. McCouch, 2000. Mapping and genome organization of microsatellite sequences in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 100: 697–712.
Vergara, B.S., 1976. Physiological and morphological adaptability of rice varieties to climate. In: Climate and Rice, pp. 67–83. Intl Rice Res Inst, Los Banos, Philippines.
Vos, P., R. Hogers, M. Bleeker, M. Rejians, T. van de Lee, M. Hornes, A. Freijters, J. Pot, J. Peleman, M. Kuiper & M. Zabeau, 1995. AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 23: 4407–4414.
Xiao, J., J. Li, L. Yuan, S.R. McCouch & S.D. Tanksley, 1996. Genetic diversity and its relationship to hybrid performance and heterosis in rice as revealed by PCR-based markers. Theor Appl Genet 92: 637–643.
Zhang, Q.F., Y.J. Gao, S.H. Yang, M.A. Saghai Maroof, S.H. Yang & J.X. Li, 1995. Molecular divergence and hybrid performance in rice. Mol Breed 1: 133–142.
Zhang, Q.F., Z.Q. Zhou, G.P. Yang, C.G. Xu, K.D. Liu & M.A. Saghai Maroof, 1996. Molecular marker heterozygosity and hybrid performance in indica and japonica rice. Theor Appl Genet 93: 1218–1224.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwon, SJ., Ahn, SN., Jeong, EG. et al. Relationship between genetic divergence and hybrid performance in japonica rice grown in a cold water-irrigated field. Euphytica 128, 389–396 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021247724233
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021247724233