Abstract
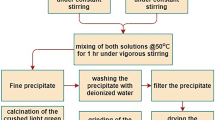
Al-mordenite and Fe-mordenite were synthesized with the tetraethylammonium as atemplate by hydrothermal method at 150°C in the Na2O–Al2O3–SiO2–H2O and Na2O–Fe2O3–SiO2–H2O system, respectively. Synthesis of several Al-mordenites substituted with Fe, Al/Fe ratio = 75/25, 50/50, 25/75, were also attempted in the Na2O–Al2O3–Fe2O3–SiO2–H2O system under the same conditions by the hydrothermal method. The continuous solid solution of Fe in Al-mordenite was successfully obtained in mordenites with various Al-Fe molar ratios. Al-mordenite crystal was tablet-like with approximately 20–30 μm in diameter and 5–10 μm in thickness. Fiber-like Fe-mordenite grew up to 20–30 μm in length and 5 μm in diameter. The morphology of Fe-substituted Al-mordenite was cubic-like with 5–10 μm in size. The size of Fe-substituted Al-mordenite decreased with the increase of Fe-content.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Mcconnelll, Am. Miner.37 (1952) 609.
V. I. Sobolev, G. I. Panov, A. S. Kharitonov, V._N. Romnnikov, A. M. Volodin and K. G. Inoue, J. Catal.158 (1996) 486.
T. Chapus, A. Tuel, Y. Ben Taarit and C. Naccache, Zeolites 14 (1994) 349.
P. S. Raghavan, S. Kannan and A. A. Belhekar, Indian J. Chem. 36A (1997) 905.
J. Kornatowski, M. Sychev, V. Goncharuk and W. H. Baur, Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 65 (1991) 581.
S. Ueda, H. Yamda, M. Koizumi and W. M. Meier, Clay Sci. 7 (1987) 49.
R. Szostak, V. Nair and T. L. Thomas, J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 183 (1987) 487.
C. T.-W. Chu and C. D. Chang, J. Phys. Chem.89 (1985) 1569.
A. S. Kharitonov, G. A. Sheveleva, G. I. Panov, V. I. Sobolev, Y. A. Pauskihtis and V. N. Romannikov, Appl. Catal. 98 (1993) 33.
P. Wu, T. Komatsu and T. Yashima, Microporous and Mesoporous Mater. 20 (1998) 139.
G. Gottardi and E. Galli, “Natural Zeolites” (Springer-Verlag, 1965) p.178.
W. M. Meier, Zeit. Krist 155 (1961) 439.
S. Ueda, T. Fukushima and M. Koizumi, J. Clay Sci. Soc. Japan 22 (1982) 18.
S. Bordiga, R. Buzzoni, F. Geobaldo, C. L. Lamberti, E. Giamello, A. Zeccina, G. Leofanti, G. Petrini, G. Tozzola and G. Vlaucl, J. Catal.158 (1996) 486.
D. Scarano, A. Zeocchina, S. Bordiga, F. Geobaldo, G. Spoto, G. Petrini, G. Leofanti, M. Padovan and G. Tozzola, J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 89 (1993) 4123.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakahira, A., Nishimura, S., Aritani, H. et al. Synthesis of Fe-substituted Al-mordenites by hydrothermal method. Journal of Materials Science 36, 1885–1889 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017521219062
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017521219062