Abstract
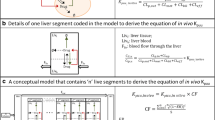
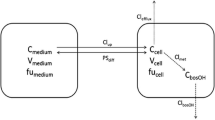
Purpose. The objective of the present study was to develop hepatic clearance models which incorporate a unidirectional carrier-mediated uptake and bidirectional diffusional transport processes for drug transport in the sinusoidal membrane of hepatocytes as well as nonlinear intrinsic elimination.
Methods. Two models were derived which view the liver as two separate compartments, i.e., sinusoid and hepatocyte. Model I assumes the instantaneous complete mixing of drugs within each compartment (similar to that of the 'well-stirred' model), while model II assumes that the drug concentrations in both compartments decrease progressively in the direction of the hepatic blood flow path (similar to that of the 'parallel-tube' model). Computer simulations were performed using a range of steady-state infusion rates for a substrate, while varying theV max (capacity) and K m (Michaelis-Menten constant) for the carrier-mediated uptake process, the diffusional clearance, the V max and K m for the intrinsic elimination process, blood flow and protein binding.
Results. Simulations in which V max and K m for the sinusoidal membrane transporter and the diffusional clearance were varied, demonstrated that these membrane transport processes could affect the clearance of drugs to a significant extent in both models. The estimates for clearance of substrates with the same pharmacokinetic parameters are always lower in model I than in model II, although the quantitative differences in parameter estimates between models varied, depending on the steady state infusion rates.
Conclusions. These more general hepatic clearance models will be most useful for describing the hepatic clearance of hydrophilic compounds, such as organic anions or cations, which exhibit facilitated uptake and limited membrane diffusion in hepatocytes.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
S. Iida, T. Mizuma, N. Sakuma, M. Hayashi, and S. Awazu. Drug Metab. Disp. 17:341–344 (1989).
H. M. Solomon and L. S. Schanker. Biochem. Pharmacol. 12:621–626 (1963).
W. P. Geng, A. J. Schwab, C. A. Goresky, and K. S. Pang. Hepatology 22:1188–1207, 1995.
M. Yamazaki, S. Akiyama, R. Nishigaki, and Y. Sugiyama. Pharm. Res. 13:1559–1564, 1996.
R. P. J. Oude Elferink, D. K. F. Meijer, F. Kuipers, P. L. M. Jansen, A. K. Groen, and G. M. M. Groothuis. Biochim. Biophy. Acta 1241:215–268 (1995).
M. Vore. In F. C. Kauffman (ed), Conjugation-Deconjugation Reactions in Drug Metabolism and Toxicity, Springer-Verlag, New York, 1994, pp. 311–338.
L. Bass, S. Keiding, K. Winkler, and N. Tygstrup. J. Theor. Biol. 61:393–409 (1976).
M. Yokota, T. Iga, Y. Sugiyama, A. Suyama, S. Awazu, and M. Hanano. J. Pharm. Dyn. 4:287–293, (1981).
B. A. Saville, M. R. Gray, and Y. K. Tam. Drug Metab. Rev. 24:49–88 (1992).
R. Kroker, M. S. Anwer, and D. Hegner. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Exp. Pathol. Pharmakol. 303:287–293 (1978).
I. A. M. deLannoy and K. S. Pang. Drug. Metab. Dispos. 14:513–520 (1986).
S. Miyauchi, Y. Sugiyama, Y. Sawada, K. Morita, T. Iga, and N. Hanano. J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 15:25–38 (1987).
S. Miyauchi, Y. Sugiyama, T. Iga, and M. Hanano. J. Pharm. Sci. 77:688–692 (1988).
E. L. Forker and B. A. Luxon. Am. J. Physiol. 244:G573–G577 (1983).
M. S. Roberts and M. Rowland. J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 14:227–260 (1986).
X. Deroubaix, T. Coche, E. Depiereux, and E. Feytmans. Am. J. Physiol. 260:G189–G196 (1991).
C. V. Greenway and F. J. Burczynski. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 65:1193–1199 (1987).
W. P. Geng, K. Poon, and K. S. Pang. J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 23:347–378 (1995).
R. B. Hornbeck. Numerical Methods, Quantum Publishers, Inc., New York, 1975, pp. 185–226.
X. Deroubaix, T. Coche, Depiereux, and E. Feytmans. Am. J. Physiol. 257:G210–G220 (1989).
S. Miyauchi, Y. Sawada, T. Iga, M. Hanano, and Y. Sugiyama. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 16:1019–1024, 1993.
M. E. Morris and Y. Li. Pharm. Res. 8:S-322, 1991.
S. Miyauchi, Y. Sugiyama, T. Iga, and M. Hanano. J. Pharm. Sci. 77:688–692, 1988.
N. Muranushi, S. Miyauchi, H. Suzuki, Y. Sugiyama, M. Hanano, H. Kinoshita, T. Oguma, and H. Yamada. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 14:279–290 (1993).
L. Gariepy, D. Fenyves, I. Kassissia, and J.-P. Villenueve. Hepatology 18:823–831 (1993).
R. Hori, K. Okumura, M. Yasuhara, and H. Katayama. Biochem. Pharmacol. 34:2679–2683 (1985).
J. C. Fernandez-Checa, M. Ookhtens, and N. Kaplowitz. J. Biol. Chem. 268(15):10836–10841 (1993).
Y. Kwon and M. E. Morris. Pharm. Res. 12:1109–1114 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwon, Y., Morris, M.E. Membrane Transport in Hepatic Clearance of Drugs I: Extended Hepatic Clearance Models Incorporating Concentration-Dependent Transport and Elimination Processes. Pharm Res 14, 774–779 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012106623696
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012106623696