Abstract
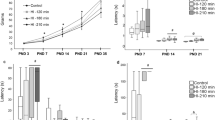
Neonatal Hypoxia-Ischemia (HI) triggers a cascade of biochemical events that result in neuronal injury, but the mechanisms underlying these processes are not completely understood, and information regarding the effect of HI on the synthesis of brain glycoconjugates is lacking. The present work evaluates the effects of neonatal HI on hippocampal ganglioside synthesis. Seven-day-old rat pups were exposed to HI for 2.5 h according to the modified Levine model and samples from hyppocampus were obtained at 30 min as well as at 1, 2 and 4 days later. The activity for synthesis of gangliosides was evaluated by determining the incorporation of N-acetyl [3H]neuraminc acid ([3H]NeuAc) into the endogenous gangliosides of Golgi membranes and by determining the activity of Sial-T2 (GD3 synthase) and GalNAc-T (GM2 synthase), the two enzymes acting on sialyllactosylceramide (GM3) at the branching point of synthesis of a- and b-ganglioside pathway. Northern blot experiments were also conducted to determine transcription levels of the mRNAs specific for these transferases. Neonatal HI caused a relative increase of in vitro [3H]NeuAc incorporation into endogenous lactosylceramide, which was most noticeable at 30 min and 1 day post-event and disappeared by day 2 and 4. The transient accumulation of [3H]GM3 correlated with decreases in the activities of GD3- and GM2 synthase measured at 30 min and at 1 day after the HI insult. No significant variations in the expression of the genes for these enzymes were observed. Results suggest that transient accumulation of GM3 may be due to post-translational events negatively modulating both GD3- and GM2 synthase activities.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Raichle, M. E. 1983. The pathophysiology of brain ischemia. Ann. Neurol. 13:2–10.
Schmidt-Kastner, R. and Freund, T. F. 1991. Selective vulnerability of the hippocampus in brain ischemia. Neuroscience 40:599–636.
Vannucci, R. C. 1993. Mechanisms of perinatal hypoxicischemic brain damage. Seminars in Perinatology 17:330–337.
Zeller, C. B. and Marchase, R. B. 1992. Gangliosides as modulators of cell function. Am. J. Physiol. 2C62 (Cell Physiol. 31):C1341–C1355.
Qi, Y. and Xue, Q. 1991. Ganglioside levels in hypoxic brains from neonatal and premature infants. Mol. Chem. Neuropathol. 14:87–97.
Tan, W. K. M., Williams, C. E., Mallard, C. E., and Gluckman, P. D. 1994. Monosialoganglioside GM1 treatment after a hypoxic-ischemic episode reduces the vulnerability of the fetal sheep brain to subsequent injuries. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 170:663–670.
Levine, S. 1960. Anoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in rats. Am. J. Pathol. 36:1–17.
Rice, J. E. III, Vannucci, R. C., and Brierley, J. B. 1981. The influence of immatutity on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the rat. Ann. Neurol. 9:131–141.
Bômont, L., Bilger, A., Boyet, S., Vert, P., and Nehlig, A. 1992. Acute hypoxia induces specific changes in local cerebral glucose utilization at different potsnatal ages in the rat. Dev. Brain Res. 66:33–45.
MaxzÚd, M. K., Daniotti, J. L., and Maccioni, H. J. F. 1995. Functional Coupling of glycosyl transfer steps for synthesis of gangliosides in Golgi membranes from Neural Retinal Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 270:20207–20214.
Nores, G. A., Mizutamari, R. K., and Kremer, D. M. 1994. Chromatographic tank designed to obtain highly reproducible high-performance thin-layer chromatograms of gangliosides and neutral glycosphingolipids. J. Chromatogr. A. 686:155–157.
Daniotti, J. L., Landa, C. A., and Maccioni, H. J. F. 1994. Regulation of ganglioside composition and synthesis is different in developing chick retinal pigment epithelium and neural retina. J. Neurochem. 62:1131–1136.
Chomczynski, P. and Sacchi, N. 1987. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenolchoroform extraction. Anal. Biochem. 162:156–159.
Daniotti, J. L., Rosales Fritz, V., Kunda, P., Nishi, T., and Maccioni, H. J. F. 1997. Clonning, chacterization and developmental expression of α2,8 sialyltransferase (GD3 synthase, ST8) gene in chick brain and retina. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 15:767–776.
Maccioni, H. J. F., Daniotti, J. L., and Martina, J. L. 1999. Organization of gangliosides synthesis in the Golgi apparatus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1437:101–118.
Panzetta, P., Maccioni, H. J., and Caputto, R. 1980. Synthesis of retinal gangliosides during chick embryonic development. J. Neurochem. 35:100–108.
Yu, R. K., Macala, L. J., Taki, T., Weinfield, H. M., and Yu, F. S. 1988. Developmental changes in ganglioside composition and synthesis in embryonic rat brain. J. Neurochem. 150:1825–1829.
Watanabe, Y., Nara, K., Takahashi, H., Nagai, Y., and Sanai, Y. 1996. The molecular cloning and expression of α2,8-Sialyltransferase (GD3 Synthase) in a rat brain. J. Biochem. 120:1020–1027.
Hidari, K. I.-P. J., Ichikawa, S., Furukawa, K., Yamasaki, M., and Hirabayashi, Y. 1994. β1-4-N-acetyl-galactosaminyltransferase can synthesize both asialo-glycosphingolipid GM2 and glycosphingolipid GM2 in vitro and in vivo: Isolation and characterization of β1-4-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase cDNA clone from rat ascistes hepatoma cell line AH7974F. Biochem. J. 303:967–965.
Moretto, M. B., Mattos-Dutra, A., Arteni, N., Meirelles, R., Freitas, M., Netto, C. A., and Pessoa-Pureur, R. 1999. Effects of neonatal cerebral hypoxia-ischemia on the in vitro phosphorylation of synapsin 1 in rat synaptosomes. Neurochem. Res., 24:1265–1271.
Gu, X., Preuß, U., Gu, T., and Yu, R. K. 1995. Regulation of sialyl-transferase activities by phosphorylation and dephosphorilation. J. Neurochem. 64:2295–2302.
Scheideler, M. and Dawson, G. 1986. Direct demonstration of activation of UDP-N-Acetylgalactosamine: [GM3] N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase by cyclic AMP. J. Neurochem. 46:1639–1643.
Martina, J. A., Daniotti, J. L., and Maccioni, H. J. F. 1998. Influence of N-glycosylation and N-glycan trimming on the activity and intracellular traffic of GD3 synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 273:3725–3731.
Martina, J. A., Daniotti, J. L., and Maccioni, H. J. F. 2000. GM1 synthase depends on N-glycosylation for enzyme activity and trafficking to the Golgi complex. Neurochem. Res. 25:725–731.
Petito, C. K. and Lapinski, R. L. 1986. Postischemic alterations in ultrastructural cytochemistry of neuronal Golgi apparatus. Lab. Invest. 55:696–702.
Giraudo, C. G., Daniotti, J. L., and Maccioni, H. J. F. 2001. Physical and functional association of glycolipid N-acetylgalactosaminyl and galactosyl transferases in the Golgi Complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98:1625–1630.
Rafols, J. A., Daya, A. M., O'Neil, B. J., Krause, G. S., Neumar, R. W., and White, B. C. 1995. Global brain ischemia and reperfusion: Golgi apparatus ultrastructure in neurons selectively vulnerable to death. Acta Neuropathol. (Berl) 90:17–30.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trindade, V.M.T., Daniotti, J.L., Raimondi, L. et al. Effects of Neonatal Hypoxia/Ischemia on Ganglioside Expression in the Rat Hippocampus. Neurochem Res 26, 591–597 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010974917308
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010974917308