Abstract
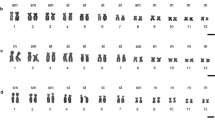
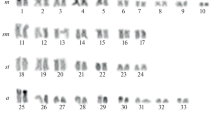
Cytogenetic and molecular data on Alytes muletensis (Amphibia: Discoglossidae) are compared with other representatives of archaeobatrachian frogs: Bombina variegata pachypus, Pelobates cultripes, Pelodytes punctatus, Xenopus laevis, and Discoglossus. A. muletensis has the karyotype typical for the genus Alytes, 38 elements with either one or two arms, some of which can be considered as ‘microchromosomes’. The NORs are located on the telomeres of the tenth chromosome pair which agrees with the state in A. obstetricians but differs from A. cisternasii reflecting phylogenetic affinities. C-banding and staining with DAPI and chromomycin A3 revealed important blocks of telomeric CMA-positive heterochromatin on the smaller chromosomes of Alytes, similar to the state found in Discoglossus. Phylogenetic analysis of 750 bp of fragments of the mitochondrial 16S and 12S rRNA genes corroborated that Discoglossus and Alytes are sister taxa which together probably form the sister group of the Bombinatorinae. Centromeric heterochromatin in Alytes may be responsible for the retention of a plesiomorphic asymmetric karyotype which independently has evolved into a symmetric karyotype through centric fusions in Bombina and Discoglossus. The HindIII satellite DNA family was present in all archaeobatrachians studied but absent in hyloid and ranoid neobatrachians.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arntzen JW, García-Paris M (1995) Morphological and allozyme studies of midwife toads (genus Alytes), including the description of two new taxa from Spain. Bijdr Dierk 65: 5–34.
Capriglione T, Cardone A, Odierna G, Olmo E (1994) Further data on the occurrence and evolution of satellite DNA families in the lacertid genome. Chromosome Res 2: 327–330.
Charlesworth B, Sniegowski P, Stephan W (1994) The evolutionary dynamics of repetitive DNA in eukaryotes. Nature 371: 215–220.
Duellman WE, Trueb L (1986) Biology of Amphibians. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Feller AE, Hedges SB (1998) Molecular evidence for the early history of living amphibians. Mol Phyl Evol 9: 509–516.
Ford LS, Cannatella DC (1993) Themajor clades of frogs. Herp Monogr 7: 94–117.
Garagna S, Broccoli D, Redi CA, Searle JB, Cooke HJ, Capanna E (1995) Robertsonian metacentrics of the mouse lose telomeric sequences but retain some minor satellite DNA in the pericentromeric area. Chromosoma 103: 685–692.
Glaw F, Köhler J, Hofrichter R, Dubois A (1998) Systematik der Amphibien. Liste der rezenten Familien, Gattungen und Arten. In: Hofrichter R, ed. Amphibien. Augsburg: Naturbuch Verlag, pp 252–258.
Green DM (1988) Cytogenetics of the endemic New Zealand frog, Leiopelma hochstetteri: extraordinary supernumerary chromosome variation and a unique sex-chromosome system. Chromosoma 97: 55–70.
Hay HJM, Ruvinsky I, Hedges SB, Maxson LR (1995) Phylogenetic relationships of amphibian families inferred from DNA sequences of mitochondrial 12S and 16S ribosomal RNA genes. Mol Biol Evol 12: 928–937.
Herrero P (1984) Estudios citogenéticos en Baleaphryne muletensis. In: Hemmer H, Alcover JA, eds. Història Biològica del Ferreret. Mallorca: Moll, pp 223–230.
Howell WM, Black DA (1980) Controlled silver staining of nucleolus organizer regions with a protective colloidal developer: 1–step method. Experientia 36 1014–1015.
King M (1990) Amphibia. Animal Cytogenetics Vol. 4. Bornträger: Stuttgart.
Lanza B, Cei M, Crespo E (1976) Further immunological evi-dence for the validity of the family Bombinidae (Amphibia, Salentia). Monit Zool Ital NS 10: 311–314.
Luke S, Verma RS, Conte RA, Mathews T (1992) Molecular characterization of the secondary constriction region (qh) of human chromosome 9 with pericentric inversion. J Cell Sci 103: 919–923.
Maxson L, Szymura JM (1984) Relationships among discoglossid frogs: an albumin perspective. Amphibia-Reptilia 5: 245–252.
Mayol J, Alcover JA (1981) Survival of Baleaphryne (Amphibia: Anura: Discoglossidae) on Mallorca. Amphibia-Reptilia 3/4: 343–345.
Mayr B. Schweizer D, Capanna E, eds. Cytotaxonomy and Vertebrate Evolution. London: Acaemic Press, pp 233–348.
Morescalchi A, Olmo E, Stingo V (1977) Trends of karyological evolution in pelobatoid frogs. Experientia 33: 1577–1578.
Nardi I, Batistoni R, Marracci S, Lanza B (1999) Repetitive DNA components of the large Hydromantes genome: phylogenetic and molecular aspects. Herpetologica 55: 131–139.
Odierna G, Aprea G, Capriglione T, Parisi P, Arribas O, Morescalchi MA (1999) Chromosomal and molecular analysis of some repeated families in Discoglossus Otth, 1837 (Anura, Discoglossidae): taxonomic and phylogenetic implications. Ital J Zool 66: 273–283.
Olmo E, Morescalchi A, Stingo V, Odierna G (1982) Genome characteristics and the systematics of the Discoglossidae (Amphibia Salentia). Monit Zool Ital NS 16: 283–299.
Sanchiz B (1998) Encyclopedia of Paleoherpetology. Part 4. Salientia. München: Verlag Dr. Friedrich Pfeil.
Sanchiz FB, Adrover R (1977) Anfibios fósiles del Pleistoceno de Mallorca. Doñana Acta Vertebrata 4: 5–25.
Schmid M (1978) Chromosome banding in Amphibia. I. Constitutive heterochromatin and nucleolar organizer regions in Bufo and Hyla. Chromosoma 66: 83–103.
Schmid M, Vitelli L, Batistoni R (1987) Chromosome banding in Amphibia. XI. Constitutive hetrochromatin, nucleolus organizer, 18+28S and 5S ribosomal RNA genes in Ascaphidae, Pipidae, Discoglossidae and Pelobatidae. Chromosoma 95: 139–145.
Schweizer D (1976) Simultaneous staining of R-bands and specific heterochromatic regions (DA-DAPI bands) in human chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet 27: 190–193.
Sumner AT (1972) A simple technique for demonstrating centromeric heterochromatin. Expl Cell Res 75: 304–306.
Swofford DL (1998) PAUP *.Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony ( * and other methods), Version 4. Sunderland: Sinauer.
Vences M, Kosuch J, Lötters S et al. (2000) Phylogeny and classification of poison frogs (Amphibia: Dendrobatidae), based on mitochondrial 16S and 12S ribosomal RNA gene sequences. Mol Phyl Evol. 15: 34–40.
Vitelli L, Batistoni R, Andronico F, Nardi I, Barsacchi-Pilone G (1982) Chromosomal localization of 18S.28S and 5S ribosomal RNA genes in evolutionary diverse anuran amphibians. Chromosoma 84: 475–491.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Odierna, G., Andreone, F., Aprea, G. et al. Cytological and molecular analysis in the rare discoglossid species, Alytes muletensis (Sanchiz & Adrover 1977) and its bearing on archaeobatrachian phylogeny. Chromosome Res 8, 435–442 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009266904940
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009266904940