Abstract
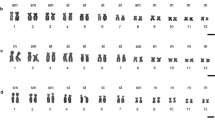
The karyotypes of 14 species of Anura from 9 genera of the suborders Amphicoela, Aglossa, Opisthocoela and Anomocoela were analysed with various banding techniques and conventional cytogenetic methods. The 18S + 28S and 5S ribosomal RNA genes were localized by means of in situ hybridization. No Q-, R- and G-banding patterns in the euchromatic segments of the metaphase chromosomes could be demonstrated in any of the species; this does not seem to be caused by a higher degree of spiralization of the amphibian chromosomes, but by the special DNA organization in these organisms. In most karyotypes, constitutive heterochromatin is present at centromeres, telomeres and nucleolus organizer regions (NORs), but rarely in interstitial positions. The heterochromatic regions are either quinacrine positive and mithramycin negative or vice versa. All species examined possess only one homologous pair of NORs; these display the brightest mithramycin fluorescence in the karyotypes. Many specimens exhibited unequal labelling of the two NORs both after silver and mithramycin staining as well as after in situ hybridization with 3H-18S + 28S rRNA. In four species, between one and six chromosome pairs with homologous 5S rRNA sites could be identified. The 5S rRNA genes and the 18S + 28S rRNA genes are closely linked in two species. In the male meiosis of the Amphicoela and Opisthocoela, there are intersitial, subterminal and terminal chiasmata in the bivalents, whereas only terminal chiasmata are observed in the bivalents of the Aglossa and Anomocoela. No heteromorphic sex-specific chromosomes could be demonstrated in any of the species. The differential staining techniques revealed that the chromosomal structure in these four suborders is largely the same as in the highly evolved anuran suborders Procoela and Diplasiocoela.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bachmann K (1972) Genome size in mammals. Chromosoma 37:85–93
Bailly S (1976) Localisation et signification des zones Q observées sur les chromosomes mitotiques de l'amphibien Pleurodeles waltlii Michah. après coloration par la moutarde de quinacrine. Chromosoma 54:61–68
Barr HJ, Esper H (1963) Nucleolar size in cells of Xenopus laevis in relation to nucleolar competition. Exp Cell Res 31:211–214
Barsacchi-Pilone G, Nardi I, Batistoni R, Andronico F, Beccari E (1974) Chromosome location of the genes for 28S, 18S and 5S ribosomal RNA in Triturus marmoratus (Amphibia Urodela). Chromosoma 49:135–153
Barsacchi-Pilone G, Nardi I, Andronico F, Batistoni R, Durante M (1977) Chromosomal location of the ribosomal RNA genes in Triturus vulgaris meridionalis (Amphibia, Urodela). I. Localization of the DNA sequences complementary to 5S rRNA on mitotic and lampbrush chromosomes. Chromosoma 63:127–134
Bernardi G, Olofsson B, Filipski J, Zerial M, Salinas J, Cuny G, Meunier-Rotival M, Rodier M (1985) The mosaic genome of warm-blooded vertebrates. Science 228:953–958
Birnstiel ML, Wallace H, Sirlin JL, Fischberg M (1966) Localization of the ribosomal DNA complements in the nucleolus organizer region of Xenopus laevis. In: Vincent WS, Miller OL (eds) International symposium on the nucleolus. Its structure and function. NCI monograph 23, National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, pp 431–448
Birstein VJ (1982) Structural characteristics of genome organization in amphibians: differential staining of chromosomes and DNA structure. J Mol Evol 18:73–91
Comings DE (1975) Mechanisms of chromosome banding. VIII. Hoechst 33 258-DNA interactions. Chromosoma 52:229–243
De Lucchini S, Vitelli L, Batistoni R (1981) Bandeggio cromosomico in alcune specie di anfibi anuri. I. “C-banding”. Atti Soc Tosc Sci Nat Mem, Serie B, 88:93–101
Elsdale TR, Fischberg M, Smith SA (1958) A mutation that reduces nucleolar number in Xenopus laevis. Exp Cell Res 14:642–643
Estes R (1970) New fossil pelobatid frogs and a review of the genus Eopelobates. Bull Mus Comp Zool 139:337–340
Estes R, Reig OA (1973) The early fossil record of frogs. A review of the evidence. In: Vial JL (ed) Evolutionary biology of the anurans. Univ Missouri Press, Columbia, Missouri, pp 11–63
Hecht MK (1963) A reevaluation of the history of the frogs. II. Syst Zool 12:20–35
Hennen S, Mizuno S, Macgregor HC (1975) In situ hybridization of ribosomal DNA labeled with 125iodine to metaphase and lampbrush chromosomes from newts. Chromosoma 50:349–369
Holmquist G (1987) DNA sequences in G-bands and R-bands. In: Adolph KW (ed) Chromosome and chromatin structure. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, in press
Kahn J (1962) The nucleolar organizer in the mitotic chromosome complement in Xenopus laevis. Q J Microsc Sci 103:407–409
Kezer J, Macgregor HC (1973) The nucleolar organizer of Plethodon cinereus cinereus (Green). II. The lampbrush nucleolar organizer. Chromosoma 42:427–444
Kuro-o M, Ikebe C, Kohno S (1986) Cytogenetic studies of Hynobiidae (Urodela). IV. DNA replication bands (R-banding) in the genus Hynobius and the banding karyotype of Hynobius nigrescens Stejneger. Cytogenet Cell Genet 43:14–18
Lubs H, Hostetter T, Ewing L (1972) Paris Conference: Standardization in human cytogenetics. Birth defects. Original article series, vol 8, no 7. The National Foundation, New York
Macgregor HC, Kezer J (1973) The nucleolar organizer of Plethodon cinereus cinereus (Green). I. Location of the nucleolar organizer by in situ nucleic acid hybridization. Chromosoma 42:415–426
Macgregor HC, Mizuno S (1976) In situ hybridization of nicktranslated 3H-ribosomal DNA to chromosomes from salamanders. Chromosoma 54:15–25
Macgregor HC, Vlad M, Barnett L (1977) An investigation of some problems concerning nucleolus organizers in salamanders. Chromosoma 59:283–299
Mayol J, Alcover JA (1981) Survival of Baleaphryne Sanchiz and Adrover, 1979 (Amphibia: Anura: Discoglossidae) on Mallorca. Amphibia-Reptilia 3/4:343–345
Mayol J, Alcover JA, Alomar G, Pomar G, Jurado J, Jaume D (1980) Supervivència de Baleaphryne (Amphibia: Anura: Discoglossidae) a les muntanyes de Mallorca. Nota preliminar. Butll Inst Cat Hist Nat 45 (Sec Zool, 3):115–119
Miller L, Brown DD (1969) Variation in the activity of nucleolar organizers and their ribosomal gene content. Chromosoma 28:430–444
Miller L, Knowland J (1970) Reduction of ribosomal RNA synthesis and ribosomal RNA genes in a mutant of Xenopus laevis which organizes only a partial nucleolus. II. The number of ribosomal RNA genes in animals of different nucleolar types. J Mol Biol 53:329–338
Morescalchi A (1973) Amphibia. In: Chiarelli AB, Capanna E (eds) Cytotaxonomy and vertebrate evolution. Academic Press, London New York, pp 233–348
Morescalchi A (1980) Evolution and karyology of the amphibians. Boll Zool 47 (Suppl):113–126
Nardi I, Barsacchi-Pilone G, Batistoni R, Andronico F (1977) Chromosome location of the ribosomal RNA genes in Triturus vulgaris meridionalis (Amphibia, Urodela). II. Intraspecific variability in number and position of the chromosome loci for 18S + 28S ribosomal RNA. Chromosoma 64:67–84
Nardi I, De Lucchini S, Barsacchi-Pilone G, Andronico F (1978) Chromosome location of the ribosomal RNA genes in Triturus vulgaris meridionalis (Amphibia, Urodela). IV. Comparison between in situ hybridization with 3H 18S + 28S rRNA and ASSAT staining. Chromosoma 70:91–99
Olmo E, Morescalchi A (1978) Genome and cell sizes in frogs: a comparison with salamanders. Experientia 34:44–46
Olmo E, Morescalchi A, Stingo V, Odierna G (1982) Genome characteristics and the systematics of the Discoglossidae (Amphibia, Salientia). Monit Zool Ital 16:283–299
Olofsson B, Bernardi G (1983) Organization of nucleotide sequences in the chicken genome. Eur J Biochem 130:241–245
Pardue ML (1973) Localization of repeated DNA sequences in Xenopus chromosomes. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 38:475–482
Pardue ML, Gall JG (1975) Nucleic acid hybridization to the DNA of cytological preparations. Methods Cell Biol 10:1–16
Pardue ML, Brown DD, Birnstiel ML (1973) Location of the genes for 5S ribosomal RNA in Xenopus laevis. Chromosoma 42:191–203
Ragghianti M, Bucci Innocenti S, Mancino G (1973) Bandeggiatura indotta da “C-, G-e Q-staining methods” e pattern di replicazione dei cromosomi di Triturus. Rend Accad Naz Lincei 55:764–770
Sanchíz FB, Adrover R (1979) Anfibios fósiles del Pleistoceno de Mallorca. Doñana, Acta Vertebrata 4:5–25
Schempp W, Schmid M (1981) Chromosome banding in Amphibia. VI. BrdU-replication patterns in Anura and demonstration of XX/XY sex chromosomes in Rana esculenta. Chromosoma 83:697–710
Schmid M (1978a) Chromosome banding in Amphibia. I. Constitutive heterochromatin and nucleolus organizer regions in Bufo and Hyla. Chromosoma 66:361–388
Schmid M (1978b) Chromosome banding in Amphibia. II. Constitutive heterochromatin and nucleolus organizer regions in Ranidae, Microhylidae and Rhacophoridae. Chromosoma 68:131–148
Schmid M (1980a) Chromosome evolution in Amphibia. In: Müller H (ed) Cytogenetics of vertebrates. Birkhäuser, Basel Boston Stuttgart, pp 4–27
Schmid M (1980b) Chromosome banding in Amphibia. IV. Differentiation of GC-and AT-rich chromosome regions in Anura. Chromosoma 77:83–103
Schmid M (1980c) Chromosome banding in Amphibia. V. Highly differentiated ZW/ZZ sex chromosomes and exceptional genome size in Pyxicephalus adspersus (Anura, Ranidae). Chromosoma 80:69–96
Schmid M (1982) Chromosome banding in Amphibia. VII. Analysis of the structure and variability of NORs in Anura. Chromosoma 87:327–344
Schmid M, Olert J, Klett C (1979) Chromosome banding in Amphibia. III. Sex chromosomes in Triturus. Chromosoma 71:29–55
Schmid M, Löser C, Schmidtke J, Engel W (1982) Evolutionary conservation of a common pattern of activity of nucleolus organizers during spermatogenesis in vertebrates. Chromosoma 86:149–179
Schnedl W, Breitenbach M, Mikelsaar A-V, Stranzinger G (1977) Mithramycin and DIPI: a pair of fluorochromes specific for GC-and AT-rich DNA respectively. Hum Genet 36:299–305
Schweizer D (1976) Reverse fluorescent chromosome banding with chromomycin and DAPI. Chromosoma 58:307–324
Sekiya K, Nakagawa H (1983) Cytogenetics of Xenopus laevis. I. G-banding pattern of Xenopus laevis chromosomes. Experientia 39:786–787
Sims SH, Macgregor HC, Pellat PS, Horner HA (1984) Chromosome 1 in crested and marbled newts (Triturus). An extraordinary case of heteromorphism and independent chromosome evolution. Chromosoma 89:169–185
Sinclair JH, Brown DD (1971) Retention of common nucleotide sequences in the ribosomal deoxyribonucleic acid of eukaryotes and some of their physical characteristics. Biochemistry 10:2761–2769
Stern R (1972) Satellite DNAs of Xenopus mulleri. Carnegie Inst Wash Yearb 71:22
Stock AD, Mengden GA (1975) Chromosome banding pattern conservatism in birds and nonhomology of chromosome banding patterns between birds, turtles, snakes and amphibians. Chromosoma 50:69–77
Szabo P, Lee MR, Elder FB, Prensky W (1978) Localization of 5S RNA and rRNA genes in the Norway rat. Chromosoma 65:161–172
Thiery JP, Macaya G, Bernardi G (1976) An analysis of eukaryotic genomes by density gradient centrifugation. J Mol Biol 108:219–235
Tymowska J, Fischberg M (1982) A comparison of the karyotype, constitutive heterochromatin, and nucleolar organizer regions of the new tetraploid species Xenopus epitropicalis Fischberg and Picard with those of Xenopus tropicalis Gray (Anura, Pipidae), Cytogenet Cell Genet 34:149–157
Vitelli L, Batistoni R, Andronico F, Nardi I, Barsacchi-Pilone G (1982) Chromosomal localization of 18S + 28S and 5S ribosomal RNA genes in evolutionary diverse anuran amphibians. Chromosoma 84:475–491
Ward DC, Reich E, Goldberg IH (1965) Base specifity in the interaction of polynucleotides with antibiotic drugs. Science 149:1259–1263
Weisblum B (1973) Fluorescent probes of chromosomal DNA structure: three classes of acridines. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 38:441–449
Wolf K, Quimby MC (1964) Amphibian cell culture: permanent cell line from the bullfrog (Rana catesbeiana). Science 114:1578–1580
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmid, M., Vitelli, L. & Batistoni, R. Chromosome banding in Amphibia. Chromosoma 95, 271–284 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00294784
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00294784