Abstract
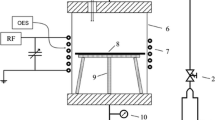
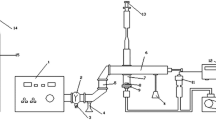
Fluorinated thin layers were created on chemithermomechanical pulp (CTMP) sisal paper surfaces with fluorotrimethylsilane (FTMS) radio frequency-plasma conditions. It was found that the FTMS-discharge environments caused implantation of fluorine and –Si(CH3) x groups into the surface layers of the paper substrates. Attenuated Total Reflectance-Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy and Electron Spectroscopy for Chemical Analysis, as well as Atomic Force Microscopy and Scanning Electron Microscopy analyses revealed a smooth surface for the FTMS plasma-treated paper, apparently covered completely with a cross-linked polymerized network. Although the plasma reaction takes place with the cellulose, hemicelluloses and lignin, it appears that the chemical linkage is mainly to the lignin component on the CTMP paper surface by means of mainly C–O–Si–F, with some C–Si–F structures. The CTMP fibers apparently have a high lignin surface concentration. The water absorption for the plasma-treated CTMP paper was reduced from greater than 300 to 17 g of water/m2 and the contact angle increased from less than 15° to greater than 120° the strength properties were only slightly reduced and the brightness was essentially unaffected with the FTMS plasma treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bellamy L.J.1975. The Infrared Spectra of Complex Molecules, 3rd edn. Chapman & Hall, London.
Chen-Yang Y.W., Liao J.D., Kau J.Y., Huang J., Chang W.T. and Chen C.W.2000. Surface modifications of expanded poly(tetrafluoroethylene) sheets assisted by CO2 antenna coupling microwave plasma. Macromolecules33: 5638–5643.
Denes F. and Young R.A.1998. Surface modification of polysaccharides under cold plasma conditions. In: Dumitriu S. (ed.), Polysaccharides, Marcel Dekker Inc., New York, pp. 1087–1135.
Denes A.R. and Young R.A.1999. Reduction of weathering degradation of wood through plasma-polymer coating. Holzforschung53 (6): 632–640.
Denes F., Sarmadi A.M., Hop C.E.C.A. and Young R.A.1994. Plasma polymerization of methyl metacrylate. J. Appl. Polym. Sci.54: 55–75.
Denes F., Hua Z.Q., Barrios E., Evans J. and Young R.A.1995. Influence of RF-cold plasma treatment on the surface properties of paper. J. Mol. Struct.–Pure Appl. Chem.A32 (8&9): 1405–1443.
Denes A.R., Tshabalata M.A., Rowell R., Denes F. and Young R.A.1999. Hexamethyldisiloxane-plasma coating of wood surfaces for creating water repellent characteristics. Holzforschung53 (3): 318–326.
Fonseca J.L.C., Tasker S., Apperley D.C. and Badyal J.P.S.1996. Plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition of organosilicon materials: a comparison of hexamethyldisilane and tetramethylsilane precursors. Macromolecules29: 1705–1710.
France R.M. and Short R.D.1998. Plasma treatment of polymers: the effects of energy transfer from an argon plasma on the surface chemistry of polystyrene, and polypropylene. A high-energy resolution of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study. Langmuir14: 4827–4835.
Hua Z.Q., Sitaru R., Denes F. and Young R.A.1997. Mechanisms of oxygen-and argon-RF-plasma induced surface chemistry of cellulose. Plasmas and Polymers2 (3): 199–224.
ISCCSCT (Infrared Spectroscopy Committee of Chicago Society for Coating Technology) 1980. An Infrared Spectroscopy Atlas for the Coatings Industry (VandeBerg J.T. et al., eds). Federation of Societies for Coating Technology, Philadelphia, PA.
Mackie N.M., Castner D.G. and Fisher E.R.1998. Characterization of pulsed-plasma-polymerized aromatic films. Langmuir14: 1227–1235.
Ramírez A.L.2001. Encolado alcalino en función de la actividad iónica del medio. Master Thesis (in Spanish), University of Guadalajara, Guadalajara, México.
Ramos J., Flores G., Dávalos F., Navarro F., Becerra B., Denes F. and Young R.A.2001. Surface bleaching of ctmp paper using hydrogen peroxide and sodium perborate assisted by cold plasma. International Mechanical Pulping Conference Proceedings, Helsinki, Finland, Vol. I, pp. 11–18.
Sabharwal H.S., Denes F., Nielsen L. and Young R.A.1993. Formation of free-radicals on lignocellulosic fibers by argon plasma treatment. J. Agric. Food Chem.41: 2202–2207.
Sahin H.T., Monolache S., Young R.A. and Denes F.2002. Surface fluorination of paper in CF4-RF plasma environments. Cellulose9: 171–181.
Sapieha S., Verreault M., Klemberg-Sapieha J.E., Sacher E. and Wertheimer M.R.1990. X-ray photoelectron study of the plasma fluorination of lignocellulose. Appl. Surface Sci.44: 165–169.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Navarro, F., Dávalos, F., Denes, F. et al. Highly hydrophobic sisal chemithermomechanical pulp (CTMP) paper by fluorotrimethylsilane plasma treatment. Cellulose 10, 411–424 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1027381810022
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1027381810022