Abstract
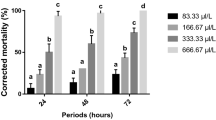
The effects of methanol extract of Peganum harmala L. seeds were evaluated against Tribolium castaneum (Herbst). Larval growth was inhibited and food intake reduced when the extract was incorporated into the diet at concentrations of 2.5,5 and 10%. All doses caused an increase in the duration of larval period and completely inhibited F0i progeny production. The main body metabolites were determined in last-instar larvae after feeding for 8 days on the diet treated with different doses. Protein and lipid contents were decreased with concentrations >2.5%. Glycogen content was reduced at a concentration of 10%. Tribolium castaneum larvae possessed two major and one minor α-amylase isoforms as determined by gel assays. Larvae fed the treated diet presented less activity of the major isoforms, while activity of the minor isoform was totally inhibited. The activity of this enzyme is not inhibited in vitro by seed extracts. Histological studies showed that P. harmala extracts caused a severe cytotoxicity on the epithelial cells of the midgut resulting in marked vacuolization of the cytoplasm and a large intercellular space. These findings suggest that seed extracts of P. harmala exert their toxic effect by severely damaging the midgut epithelial cells. This naturally occurring plant extract could be useful for control of T. castaneum.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbassi K., Mergaoui L., Kadiri A. Z., Stambouli A. and Ghaout S. (2003a) Activité biologique de l’extrait des graines de Peganum harmala sur le criquet pèlerin (Schistocerca gregaria Forskål, 1775). Journal of Orthoptera Research 12, 71–79.
Abbassi K., Mergaoui L., Kadiri A. Z., Stambouli A. and Ghaout S. (2003b) Effets des extraits de Peganum harmala (Zygophyllaceae) sur le criquet pèlerin (Schistocerca gregaria Forskål, 1775). Zoologica Baetica 13/14, 203–217.
Baker J. E. (1983) Properties of amylases from midguts of larvae of Sitophilus zeamais and Sitophilus granarium. Insect Biochemistry 13, 421–428.
Bell C. H. (1978) Limiting concentrations for fumigant efficiency in the control of insect pests, pp. 182–192. In Proceedings of the Second International Working Conference on Stored-Product Entomology, Ibadan, Nigeria.
Bellakhdar J. (1997) Médecine arabe ancienne et savoirs populaires, La pharmacopée traditionnelle. Ed. Ibis presse, Paris. 759 pp.
Benhsain N., Abbassi K., Zouiten H. and Atay-Kadiri Z. (2001) Activit insecticide de Citrullus colocynthis L. (Cucurbitaceae) et de Peganum harmala L. (Zygophyllaceae), pp. 211–217. In Proceeding du Symposium sur la Protection Intgrés des Cultures dans la Région Méditerranéenne, Rabat, Maroc.
Bradford M. M. (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry 72, 248–254.
Campos E. A. P., Xavier-Filfo J., Silva C. P. and Ary M. B. (1989) Resolution and partial characterization of proteinases and a-amylases from midguts of larvae of the bruchid beetle Callosobruchus maculatus (F). Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology B 92, 51–57.
Chen M. S., Feng G., Zen K., Richardson C. M., Valdes-Rodriguez S., Reeck G. R. and Kramer K. J. (1992) a-amylases from three species of stored grain coleopterans and their inhibition by wheat and corn proteinaceous inhibitors. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 22, 261–268.
Coats J. R., Karr L. L. and Drewes C. D. (1991) Toxicity and neurotoxic effects of monoterpenoids in insects and earthworms, pp. 305–316. In Naturally Occurring Pest Bioregulators (Edited by P. A. Hedin). ACS Symposium Series No. 449. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC.
Dagnelie P. (1973) Théories et méthodes statistiques tome 2. Presses agronomiques, Gembloux, Belgium.
Donahay E., Zalach D. and Rindner M. (1992) Comparison of the sensitivity of the development stages of three strains of the red flour beetle (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) to modified atmospheres. Journal of Economic Entomology 85, 1450–1452.
Franco O. L., Riggen D. J., Melo F. R., Bloch C., Silva C. and Grossi de Sa M. F. (2000) Activity of wheat a-amylase inhibitors towards bruchid a-amylases and structural explanation of observed specificities. European Journal of Biochemistry 267, 2166–2173.
Garcia M., Donadel O. J., Ardanaz C. E., Tonn C. E. and Sosa M. E. (2005) Toxic and repellent effects of Baccharis salicifolia essential oil on Tribolium castaneum. Pest Management Science 61, 612–618.
Hill J. M. and Schoonhoven A. V. (1981) The use of vegetable oils in controlling insect infestations in stored grains and pulses. Recent Advances in Food Science and Technology 1, 473–481.
Huang Y., Kini R. M. and Ho S. H. (1997) Toxic and antifeedant action of nutmeg oil against Tribolium castaneum (Herbst) and Sitophilus zeamais Motsch. Journal of Stored Products Research 35, 289–298.
Huang Y., Lam S. L. and Ho S. H. (2000) Bioactivities of essential oil from Elletaria cardamomum (L.) Maton. to Sitophilus zeamais Motschulsky and Tribolium castaneum (Herbst). Journal of Stored Products Research 36, 107–117.
Idrissi Hassani L. M., Ould Ahmadou M. A., Chihrane J. and Bouaichi A. (1998) Effet d’une alimentation en Peganum harmala L. (Zygophyllaceae) sur la survie et le développement ovarien du criquet pèlerin Schistocerca gregaria Forskal (Orthoptera, Acrididae). Ethnopharmacologia 23, 26–41.
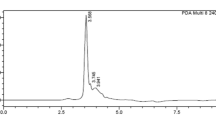
Kartal M., Altun M. L. and Kurucu S. (2003) HPLC method for the analysis of harmol, harmalol, harmine and harmaline in the seeds of Peganum harmala L. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis 31, 263–269.
Konstantopoulou L., Vassilopoulou L., Mauragani-Tsipi-dov P. and Scouras Z. G. (1992) Insecticidal effects of essential oils. A study of the effects of essential oils extracted from eleven Greek aromatic plants on Drosophila auraria. Experientia 48, 616–619.
Laemmli U. K. (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227, 680–685.
Li W. K. (1996) Extraction of alkaloids from Peganum harmala L. and study of their antihydatid chemical composition. Journal of Lanzhou Medical College 22, 16–18.
Martoja R. and Martoja M. (1967) Techniques d’histologie animale (Edited by Cie Masson). Masson & Co., Paris. 345 pp.
Mendiola-Olaya E. M., Jimenez A. V., Rodriguez S. V., Frier J. D. and Labra A. B. (2000) Digestive amylase from the larger grain borer Prostephanus truncatus Horn. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology B 126, 425–433.
Nasiruddin M. and Mordue (Luntz) A. J. (1993) The effect of azadirachtin on the midgut histology of the locusts Schistocerca gregaria and Locusta migratoria. Tissue and Cell 25, 875–884.
Ntonifor N. N., Mueller-Harvey I., Van Emden H. E and Brown R. H. (2006) Antifeedant activities of crude seed extracts of tropical African spices against Spodoptera littoralis (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). International Journal of Tropical Insect Science 26, 78–85.
Pant R. and Morris I. D. (1969) Change in active phosphorylase activity and glycogen content during larval and pupal development of Philosamia ricini. Journal of Biochemistry 66, 29–31.
Papachristos D. P. and Stamopoulos D. C. (2002) Repellent, toxic and reproduction inhibitory effects of essential oil vapours on Acanthoscelides obtectus (Say) (Coleoptera: Bruchidae). Journal of Stored Products Research 38, 117–128.
Rani P. V. and Jamil K. (1989) The effect of water hyacinth leaf extract on mortality, growth and metamorphosis of certain pests of stored products. Insect Science and Its Application 10, 327–332.
Rekha M. R., Sasikiran K. and Padmaja G. (2004) Inhibitor potential of protease and a-amylase inhibitors of sweet potato and taro on the digestive enzymes of root crop storage pests. Journal of Stored Products Research 40, 461–470.
Roe J. H. (1955) Determination of sugar in blood and spinal fluid with anthrone reagent. Journal of Biological Chemistry 212, 335–338.
Schmidt G. H., Rembold H., Adel A. I. and Breuer M. (1988) Effect of Melia azedarach fruit extract on juvenile hormone titer and protein content in the hemolymph of two species of noctuid lepidopteran larvae (Insecta: Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Phy topar asitica 26, 283–291.
Scott I. M., Jensen H., Scott J. G., Isman M. B., Arnason J. T. and Philogène B. J. R. (2003) Botanical insecticides for controlling agricultural pests: Piperamides and the Colorado potato beetle Leptinotarsa decemlineata Say (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology 54, 212–225.
Senthil Nathan S. (2006) Effects of Melia azedarach on nutritional physiology and enzyme activities of the rice leaffolder Cnaphalocrocis medinalis (Guenée) (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology 84, 98–108.
Senthil Nathan S. and Sehoon K. (2006) Effects of Melia azedarach L. extract on the teak defoliator Hyblaea puera Cramer (Lepidoptera: Hyblaeidae). Crop Protection 25, 287–291.
Shaaya E., Kostjukovski M., Eilberg J. and Sukprakarn C. (1997) Plant oils as fumigant and contact insecticides for the control of stored-product insects. Journal of Stored Products Research 33, 7–15.
Statistica Statsoft Inc. (1997) Statistica release 5.1. Tulsa, Oklahoma.
Strobl S., Maskos K., Wiegand G., Huber R., Gomis-Ruth E., and Glockshuber R. (1998) A novel strategy for inhibition of a-amylases: Yellow meal worm a-amylase in complex with Ragi bifunctional inhibitor at 2.5 A resolution. Structure 6, 911–921.
Terra W. R. and Ferreira C. (2005) Biochemistry of digestion, pp. 171–224. In Comprehensive Molecular Insect Science. Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (Edited by L. I. Gilbert, K. Iatrou and S. S. Gill). Vol. 4. Elsevier Inc., Amsterdam.
Valencia A., Bustillo A. E., Ossa G. E. and Chrispeels M. J. (2000) a-amylases of the coffee berry borer (Hypothe-nemus hampei) and their inhibition by two plant amylase inhibitors. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 30, 207–213.
Van Handel E. (1965) Micro-separation of glycogen, sugars and lipids. Analytical Biochemistry 11, 266–271.
Wang J., Zhu E., Zhou X. M., Niu C. Y and Lei C. L. (2006) Repellent and fumigant activity of essential oil from Artemisia vulgaris to Tribolium castaneum (Herbst) (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). Journal of Stored Products Research 42, 339–347.
Yang R. Z. and Tangs C. S. (1988) Plants used for pest control in China: A literature review. Economic Botany 42, 376–406.
Zettler J. L. (1991) Pesticide resistance in Tribolium castaneum and Tribolium confusum (Coleoptera: Teneb-rionidae) from flour mills in the United States. Journal of Economic Entomology 84, 763–767.
Zettler J. L. and Cuperus G. W. (1990) Pesticide resistance in Tribolium castaneum (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) and Rhyzopertha dominica (Coleoptera: Bostrichidae) in wheat. Journal of Economic Entomology 83, 1677–1681.
Ziegler J. R. (1976) Evolution of the migration response: Emigration by Tribolium and the influence of age. Evolution 30, 579–592.
Zöllner N. and Kirsch K. (1962) The quantitative determination of lipids (micromethod) by means of the sulphosphovanillin reaction common to many natural lipids (all known plasma lipids). Zeitschrift die Gesampte Expérimentale Medizin 135, 545–561.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jbilou, R., Sayah, F. Effects of Peganum harmala (Zygophyllaceae) seed extracts on the development of Tribolium castaneum (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). Int J Trop Insect Sci 27, 199–209 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742758407850971
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742758407850971