Abstract
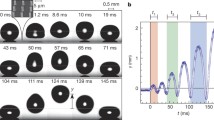
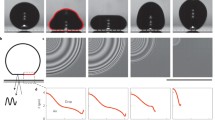
We have carried out an experimental study of liquid drop impact on superhydrophobic substrates covered by a carpet of chemically coated nano-wires. The micro-structure of the surface is similar to some biological ones (Lotus leaf for example). In this situation the contact angle can then be considered as equal to 180 degrees, with no hysteresis. Due to its initial inertia, the drop experiences a flattening phase after it hits the surface, taking the shape of a pancake. Once it reaches its maximal lateral extension, the drop begins to retract and bounces back. We have extracted the lateral extension of the drop, and we propose a model that explains the trend. We find a limit initial velocity beyond which the drop protrudes into the nano-wire carpet. We discuss the relevance of practical issues in terms of self-cleaning surfaces or spray-cooling.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yarin A L. Drop impact dynamics: Splashing, spreading, receding, bouncing …. Annual Review Fluid Mechanics, 2006, 38, 159–192.
Deegan R D, Brunet P, Eggers J. Complexities in splashing. Nonlinearity, 2008, 21, C1–C11.
Thoroddsen S T, Sakakibara J. Evolution of the fingering pattern of an impacting drop. Physics of Fluids, 1998, 10, 1359–1374.
Chen R H, Chiu S L, Lin T H. Resident time of a compound drop impinging on a hot surface. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2007, 27, 2079–2085.
Chen R H, Chiu S L, Lin T H. On the collision behaviors of a diesel drop impinging on a hot surface. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2007, 32, 587–595.
Brunet P, Lapierre F, Thomy V, Coffinier Y, Boukherroub R. Extreme resistance of super-hydrophobic surfaces to impalement: Reversible electrowetting related to the impacting/bouncing drop test. Langmuir, 2008, 24, 11203–11208.
Lau K K S, Bico J, Teo K B K, Chhowalla M, Amaratunga G A J, Milne W I, McKinley G H, Gleason K K. Superhydrophobic carbon nanotube forests. Nano Letters, 2003, 3, 1701–1705.
Bartolo D, Bouamrirene F, Verneuil E, Buguin A, Silberzan P, Moulinet S. Bouncing or sticky droplets: Impalement transitions on superhydrophobic micropatterned surfaces. Europhysics Letters, 2006, 74, 299–305.
Reyssat M, Pepin A, Marty F, Chen Y, Quere D. Bouncing transitions on microtextured materials. Europhysics Letters, 2006, 74, 306–312.
Bonn D, Eggers J, Indekeu J, Meunier J, Rolley E. Wetting and spreading. Review of Modern Physics, 2009, in press.
Clanet C, Beguin C, Richard D, Quere D. Maximal deformation of an impacting drop. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2004, 517, 199–208.
Biance A L, Chevy F, Clanet C, Lagubeau G, Quere D. On the elasticity of an inertial liquid shock. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2006, 554, 47–66.
Bartolo D, Josserand C, Bonn D. Retraction dynamics of aqueous drops upon impact on non-wetting surfaces. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2006, 545, 329–338.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Merlen, A., Brunet, P. Impact of Drops on Non-wetting Biomimetic Surfaces. J Bionic Eng 6, 330–334 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1672-6529(08)60141-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1672-6529(08)60141-9