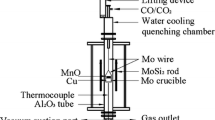
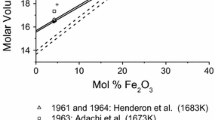
Abstract
Carbon solubility in Mn-Fe melts (xMn = 0.161 − 0.706, xFe = 0.034 − 0.633) was measured experimentally at various temperatures. By thermodynamic derivation and calculation, the relationship between activity coefficient of carbon in infinite dilute solution of manganese in Mn-C system and temperature was obtained. Using Gibbs-Duhem relationship, the experimental results of this study, and experimental data reported in references, the relationship between other thermodynamic properties in Mn-C system and temperature were obtained by thermodynamic derivation and calculation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a i :
-
Activity of component i
- a’C:
-
Calculated activity of carbon
- a’Mn:
-
Calculated activity of manganese
- e i j :
-
Interaction parameter of component j to i (standard state of wi = 0. 01)
- I:
-
Integral constant
- M j :
-
Molar mass of component j
- M l :
-
Molar mass of solvent l
- Q:
-
Effect of the second-order and above second-order terms in Wagner formula
- r:
-
Interrelation coefficient
- T:
-
Absolute temperature
- w i :
-
Mass percent of component i
- x i :
-
Molar fraction of component i
- ε ji :
-
Interaction parameter of j to i (standard state of pure i)
- ρ CC :
-
Second-order interaction parameter of C to C with standard state of graphite
- ρ C,CC :
-
Third-order interaction parameter of C to C with standard state of graphite
- γ°i:
-
Activity coefficient of component i (standard state of pure i and xi→0)
- γi:
-
Activity coefficient of component i (standard state of pure i)
- γ’C:
-
Calculated activity coefficient of carbon
- γ’Mn:
-
Calculated activity coefficient of manganese
References
Maya K, Matsuo T. Dephosphorization of High Molten Iron Treated With BaO-BaCl2-MnO Flux and Oxidation by MnO2 [J]. Tetsu-to-Hagané, 1996, 82(2): 123 (in Japanese).
Fujita M, Katayama H, Yamamoto A, et al. Dephosphorization of Fe-Mn-C Alloy With BaCO3 [J]. Tetsu-to-Hagané, 1988, 74(5): 816 (in Japanese).
Aida E, Toon M D, Sano N. Phosphorus Distribution Between Mn-Si Melts and CaO-SiO2-MnOCaF2 Slags [J]. Tetsu-to-Hagané, 1988, 74(10): 1931 (in Japanese).
Kim E J, Pak J J. Thermodynamics of Carbon in Liquid Ferro-manganese Alloys [A], ISS, eds. 2002 Steelmaking Conf Proc [C]. Warrendale, PA: ISS, 2002. 715.
Lee Y E. Thermodynamical Assessment of Liquid Mn-Fe-C System by Unified Interaction Parameter Model [J]. ISIJ International, 2003, 43(2): 144.
Katsnelson A, Sano N. Determination of Manganese and Carbon Activities of Mn-C Melts at 1 628 K [J]. ISIJ International, 1993, 33(10): 1045.
Pelton A D, Bale C W. A Modified Interaction Parameter Formalism for Non-Dilute Solutions [J]. Metall Mater Trans, 1986, 17A(7): 1211.
Bale C W, Pelton A D. The Unified Interaction Parameter Formalism: Thermodynamic Consistency and Applications [J]. Metall Mater Trans, 1990, 21A(7): 1997.
CHEN Er-bao, DONG Yuan-chi, GUO Shang-xing. Study on Thermodynamical Properties in Mn-Fe Alloy Melts [J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 1997, 33(8): 831 (in Chinese).
The Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, 19th Committee on Steelmaking. Steelmaking Data Source Book [M]. Montreux, Switzerland: Gordon and Breach Science Publishers S A, 1983.
Sigworth G K, Elliott J F. Thermodynamics of Liquid Dilute Iron Alloys [J]. Met Sci, 1974, 8(9): 298.
Chipman J. Thermoynamics of Liquid Fe-C Solutions [J]. Metall Trans, 1970, 1(8): 2163.
HUANG Xi-hu. Principle of Ironmaking and Steelmaking (Revision) [M]. Beijing, China: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1997 (in Chinese).
NI Rui-ming, MA Zhong-ting, WEI Shou-kun. Thermodynamics of Mn-Fe-C and Mn-Si-C Systems [J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 1990, 2(4): 17 (in Chinese).
Turkdogan E T. Physical Chemistry of High Temperature Technology [M]. NewYork, USA: Academic, 1980.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation Item: Item Sponsored by National Natural Science Foundation of China (50374002)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Eb., Wang, Sj. Thermodynamic Properties of Mn-C Melts. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 15, 1–6 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(08)60021-7
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(08)60021-7