Abstract
Literature is replete with studies indicating how innovation influences service quality and business performance. In addition to highlighting the research trends in the service sector under investigation, this paper explores the impact factor of innovation on service quality leading to business performance. The cross-sectional survey was the research approach used, while confirmatory factor analysis and structural equation modeling (CB-SEM) was used to analyze the data. In order to study the mediation effect of innovation on service quality and business performance among restaurants bootstrap was used to conduct mediation analysis. The study highlighted that innovation fully mediates service quality and business performance among restaurants in Ghana. Moreover, a business model that highlighted the effectiveness of innovation to service quality leading to business performance among restaurants in Ghana is being advocated. This study will encourage restaurant owners to use innovation in their daily routine to improve service to improve their company’s success.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Despite the global acceptance of innovation being the new norm for gaining a competitive advantage, restaurants in Ghana have not yet embraced that concept, and they are losing their market share and customer base [2, 3, 32]. The effective use of innovation will go a long way in influencing service quality and business performance through critical business decisions, from tactical to strategic ones. The restaurant industry is not booming in Ghana, with growth rates between 30 and 40% since 2021 [13]. But Ghana has wonderful and beautiful culture, climate, and locations that must draw tourists from the outside world (Europe, America, and Asia).
According to statistics from the Ghana Tourist Board (GTB), the tourism sector has increased in economic significance with a growth rate of 15% although it is low and needs improvement [13]. A growing number of restaurants must provide elegant, elevated, and customized service, which will improve the restaurant's reputation and competitiveness. The annual assessments on the state of restaurants by the Ghana Tourism Board [13] revealed that, despite government backing, restaurants are not doing well. According to the report above, the "hand-to-mouth" syndrome which is operated by restaurant owners using their profit to feed themselves and their families is the main cause of the poor performance and collapse of Ghanaian restaurants. Restaurant owners must restore to innovative strategies to enhance competitive advantage by introducing new ideas, skills and new knowledge.
This study considers the views of customers, owner-manager, and assistant owners. The display of the results was done with the help of the cross-sectional survey as the research approach used, while confirmatory factor analysis and structural equation modeling (CB-SEM) was used to analyze the data. The most significant contribution of this study is that without effective innovation, service quality may not occur, and without innovation, restaurants may not succeed. Therefore, effective innovation and service quality together can better influence variations in restaurant performance leading to an enhanced competitive advantage.
The current research work aims to contribute to the body of knowledge in the following areas: first, by presenting data from a developing nation, where there is little study on the topic, the paper adds to the scholarly discussion on the mediating role of innovation in the relationship between SQ and BP of restaurants. Second, the study provides scholars and practitioners with a deeper, more direct perception of the role that innovation plays in the relationship between SQ and restaurant business performance. The study further explains the outcome of how innovation influences SQ to company performance in its third section.
2 Literature review
2.1 The concept of service quality
Different concepts of service quality have been addressed by researchers, and they all concur that it involves satisfying the requirements of customers. According to Darroch [10] and Lam [23], management must evaluate a company's performance in relation to customers' expectations. Service quality, in a nutshell, relates to how well a business fulfills or exceeds a client’s expectations. Good customer service should meet the following 10 characteristics, according to Parasuraman et al. [42]: tangibles, dependability, responsiveness, competence, courtesy, credibility, security, access, communication, and client understanding. Researchers have come to the realization that service quality is believed to be a multidimensional phenomenon, thus the SERVQUAL model has been the baseline for the assessment of service quality [7, 17, 33]. Consequently, dependability, responsiveness, assurance, access, empathy, and tangibles are the six components of the SERVQUAL model that this study seeks to measure under service quality.
2.2 Dimensions of service quality
This study specifically takes into account six service quality aspects (tangibles, responsiveness, empathy, assurance, reliability, and access) that affect customer satisfaction and ultimately business performance in Ghana's restaurant sector [42]. According to Parasuraman et al. [42] and Dedeglu and Demirer [11], reliability denotes that firms offer services accurately the first time. It also shows how businesses try to keep their promises and concentrate on the results. Reliability has been named the first dimension in the SERVQUAL model. Reliability as indicated by Lam [23] refers to restaurants keeping their word in terms of the quality of services they offer.
In other concepts, assurance refers to staff who are polite, knowledgeable, and capable of inspiring confidence and trust in customers. Regardless of the educational background, age, or ethnicity of employees, Gronroos [15] asserts that providing customers with assurance requires speaking to them in their own language and paying attention to their perspectives. Nevertheless, Parasuraman et al. [42], and Lam [23] indicated that assurance refers to the staff members' attitudes, their actions, and their ability to provide the helpful, private, polite, and knowledgeable services that clients expect from restaurants. On the concept of responsiveness, Parasuraman et al. [42] and Baron and Kenny [6] indicated that being responsive to consumers centers on offering them an accurate timeline for the completion of tasks, paying them undivided attention, promoting services, and attending to their requests which restaurants are noted for. Subsequently, Darroch [10] and Lam [23], confirmed that tangibles are physical facilities, which include things like personnel, equipment, and communications supplies. Customers will evaluate a service's quality depending on how it appears to them in terms of the actual buildings, equipment, and tools required to deliver the service as well as representations of the service as confirmed by Nasution [37] and Kocoglu [21].
Parasuraman et al. [42] and Wang and Lin [48] indicated that empathy requires providing clients with care, one-on-one attention, and unique services. Expressing a sense of the client's uniqueness and specialness lies at the heart of empathy. Security, credibility, and access were reportedly used as measures of empathy in a quantitative study that indicated the essence of empathy in the service quality model. Moreover, Parasuraman et al. [42] and Berry (1985) indicated that accessibility is seen as approachability and simplicity of contact; thus, if a service is easily reachable by customers. Accessibility may have a substantial direct or indirect impact on customers leading to satisfaction as confirmed by Gronroos [15] and Schneider and White [45].
2.3 The concept of innovation
Innovation, according to the Oslo Manual, is the use of a special organizational strategy in business operations, workplace layout, or external interactions (OECD 2015). Hence, Kuhn and Marisck [22] also supported the view that innovations are the transformation of an idea or discovery into a good or service that adds value in order to meet and even exceed the demands and expectations of consumers. Similarly, to this, according to Crossan and Apaydin [9], innovation is the creation, use, and application of value-added, novelty in the business and manufacturing sectors, renewal and extension of a product, service, and market, development of new methodologies for product development, and construction of new management systems. McGrath [30] and Liao, Fei and Liu [25] measured innovation using product, process, and market innovations, whereas Mazzarol and Reboud [29] and Zack, McKeen and Singh [54] measured organizational innovations based on product, process, and administrative innovations. Unfortunately, this study only used three innovation constructs: product innovation, process innovation, and market innovation.
2.4 Innovation and business performance
Due to fierce rivalry and the unstable business climate, restaurants must constantly assess their competitive edges in relation to their rivals by implementing quick innovations. This helps to understand why innovations are becoming important to the degree of business performance. The performance, survivability, and competitiveness of companies are significantly impacted by innovations, as indicated by Hajar [53], Nonaka [39] and Huang and Li [19]. Similarly, to this, innovations give businesses a strategic orientation to gain a lasting competitive advantage, echoing the works of Mediana and Rufin [31], McGrath [30] and Lam [23]. A study by Jiménez-Jiménez and Sanz [20] indicated that quantity, kind, and firm resources invested in innovations have an impact on business performance while Ar and Baki [4] and OECD [41] also discovered that improvements in performance as measured by sales, market share, and profitability were the result of product and process changes leading to the discovery that product innovations had better performance predictive power than process innovations.
2.5 Service quality, innovation and business performance
Researchers have noted a gap in the field of innovation, particularly in the identification of the crucial variables that directly influence innovation in order to boost business performance [8]. Darroch [10] and Garcia-Morales, Lloren's-Momtesa, Verdu'-Joverb [14] suggested that as managers are functioning in a changing environment and want to improve their business performance, they should explore innovations in order to stay competitive. In this regard, academics have shown that in order to attain superior business performance, successful SQ must foster innovation. For instance, Warrier [49] and Nonaka [39] made the case that successful SQ through reliability, tangibility, empathy, responsiveness, and assurance is crucial because it supports managerial decision-making to improve business performance and raise the capacity for creativity and innovation. According to Leal-Rodrguez et al. [24], and Darroch [10] based on their study which focused on Balance Theory applied to service quality which touched on the organization, provider, and consumer triad indicated that when handled successfully will result in developing innovation and improve business performance. Nevertheless, through innovation in the tourism sector, Nawab et al. [38] and Musahara, Rukamba and Akorli [36] found that SQ has a significant indirect impact on business performance. Moreover, to support this assertion McGarth (2021) and Lam [23] also confirmed in a study that innovation has come to influence the information technology sector.
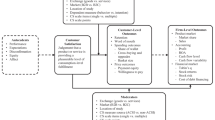
Four hypotheses indicate how innovation mediates or directly and/or indirectly influences service quality and business performance.
H1: Service quality is positively related to business performance.
H2: Service quality is certainly linked to innovations.
H3: Innovation is positively associated with business performance.
H4: Innovation mediates the relationship between Service quality and business performance.
The model below was created to serve as the study's guiding principle from the literature review previously mentioned (see Fig. 1).
3 Method
3.1 Materials and methods
The study adopted a cross-sectional survey design. The mediating effect of innovation on service quality and business performance was done during a 5-month period, from January to May 2022. Restaurants in Accra (Ghana) were selected due to Accra being the capital city and the commercial hub and home to majority of the restaurants. Taking into account the needs of the research, data was collected across 10 restaurants in Accra. The criteria for selecting the restaurant were based on the location of the restaurant, number of years in existence, and number of employees at the restaurant. Moreover, during the initial stage of the survey and prior to the questionnaire development, the research team came into contact with the owners of the restaurants that participated in the research, for two main reasons. First, to discuss the issue of innovation strategies that restaurants are using, to clarify the research objectives, and to confirm the participation of the restaurants in the research. Secondly, to help the research team narrow down the specific service quality practices that are currently implemented in the restaurant sector. The specific restaurants were ranked as 3- and 4-star. There were 478 customers for this study. The relevant sample size, according to Yamane [52] mathematical calculation, is 195 clients. However, as suggested by Miller and Smith [34] this number was increased to 250 customers due to the consideration of nonresponse bias. Nevertheless, customers were chosen using multi-stage sampling techniques while purposive sampling was used to select 10 restaurants located in Accra registered with Ghana Tourism Board, [13]. Participants (customers) were selected based on the following criteria:
-
a.
must have visited the restaurant for not less than a year;
-
b.
must have noticed new innovation strategies by the restaurant
-
c.
must have seen some level of service quality;
-
d.
willingness and availability to participate in the study.
The owner-manager and manager or assistant owner (two people) were chosen as respondents in order to eliminate one-person response bias. The owner-manager and manager or assistant owner were selected based on their experience in running the day-to-day activities of the restaurants in Ghana. However, a response rate of 97.6% was achieved due to 244 returned out of 250 questionnaires sent. The use of a face-to-face strategy is what's responsible for the high response rate. According to the sample's characteristics, most of the restaurants examined employed between 10 and 30 people, and the majority (42.8%) of employees had 6 to 10 years of working experience. It is important to note that this study deemed the minimum age of the restaurant to be chosen to be three (3) years or older because the owner/manager could determine whether or not the restaurant was performing successfully during this time.
In this study, service quality acts as the independent variable while the dependent variable is business performance, and the mediator is innovation. All of these traits were assessed using item scales developed by earlier researchers and extracted from the body of prior research and modified to suit the Ghanaian context. Specifically, a 60 items scale was adopted/adapted to measure service quality based on the review of comparable studies, from DeLone and McLean [12], Han and Baek [16], Parasuraman et al. [42], and Yang et al. [51] which centered on tangibles, dependability, responsiveness, certainty, and empathy. Again, business performance was measured using a scale adopted/adapted from Richard, Devinney, Yip, and Johnson [44]. Although business performance has been extensively examined, there isn't a complete understanding among academic researchers on the metrics that should be applied. As profits [46], sales growth [44], and market share [5] are seen to be extremely important indicators for the success of the restaurant business. According to Waweru and Ngugi [50], profits are essential for a company's sustainability and indicate how a restaurant is successful and profitable. Sales growth is considered to be the most appropriate company performance metric, according to Ahmad [1], and Maduekwe and Kamala [27]. Nevertheless, a modified six-point Likert scale was used to anchor the item scales, with 1 representing "totally disagree, without a doubt" and 6 representing "agree, without a doubt."
Subsequently, innovation was measured using the scale adopted/adapted from Wang and Ahmed [47], OECD (2015), and Mafabi et al. [28]. The scale had six points, with 1 representing “Never to less than a quarter of the time” and 6 representing “Always without fail”. The questionnaires were verified by experts and practitioners in the area. The content validity index for each variable was greater than 0.80. To encourage thoughtful, accurate responses from respondents and to lessen response bias, the items evaluating the study variables were anchored on a six-point scale.
3.2 Data analysis
Composite scores for each scale were created using quantitative data that had been gathered, checked, and cleaned. These numbers were then used for statistical analysis. In order to test the hypotheses, descriptive analyses with SPSS v19 and structural equation modeling (SEM) with AMOS software version 21TM were conducted. This allowed us to identify the kind of mediation and the extent to which innovation influences the relationship between service quality and business performance. The bootstrap technique was used to test the Preacher and Hayes-recommended mediation in particular. Due to the strong statistical power of the bootstrap method, it was also employed to determine the significance level of the mediation effect [26, 43]. Two models were thus used, Model 1 did not include the mediation effect (innovation) but Model 2 included it (innovation). The models were then compared using the Morgan and Hunt [35] approach to see which one better suited the data. Model fit indices, the proportion of projected relevant pathways, and the R2 as shown by the square multiple correlations were among the factors to be decided. The model that best suited the data was then used in further analysis to investigate the mediation effect.
Reliability was confirmed using Cronbach's alpha. Service quality, innovation, and business performance all have Cronbach's alpha values in the range of 0.83, 0.75, and 0.87, respectively. These are greater than Nunnally [40] cutoff of 0.71. Convergent validity was examined using confirmatory factor analysis. Hair, Black, Babin, and Anderson [18] found that every element in the final models for service quality, innovation, and business performance has a statistically significant and standardized factor loading of at least 0.51. In order to establish discriminant validity, Hair et al. [18] claim that correlations between constructs were assessed together with their respective construct reliabilities. The results show that the concept's reliability was greater than the correlation coefficients.
4 Results
4.1 Correlations
A zero-order correlation was carried out to ascertain the relationship between the study variables. From Table 1, the results showed that service quality and innovation have a significant and favorable relationship (r = 0.386, p 0.01), which indicates that H3 is supported. It is also evident that there was a positive and substantial association between service quality and business performance (r = 0.215, p 0.01) while there was also a relationship between innovation and business performance (r = 0.435, p 0.01). These results support the respective hypotheses H2 and H1.
4.2 Testing for mediation
An investigation of the role of innovation as a mediator between service quality and business performance was conducted. In order to evaluate the study hypothesis, two models were designed and tested to ensure the best fit was determined. The mediator variable (innovation) was not defined or added in Model 1 while for Model 2 it was included. Model 2 was chosen based on the accept/reject standards that Morgan and Hunt [35] suggested. The outcomes of the competing models are shown in Table 2. Preacher and Hayes [43] utilized a bootstrap technique to test for mediation effects of innovation between service quality and business performance after choosing a model that fits the data better. Tables 3 and 4 present the findings.
In Table 3, service quality (SQ) had a significant direct effect on business performance (BP) with = 0.075, service quality (SQ) had a significant direct effect on innovation (INNOV) with = 0.309, and innovation (INNOV) had a significant direct effect on business performance (BP) with = 0.389. Nevertheless, when innovation (INNOV) was taken into account as a mediator, the direct impact of service quality (SQ) on business performance (BP) declined from = 0.075 to = − 0.047 and became negligible, revealing a full mediation effect. This confirms the notion that innovation mediates service quality and business performance, hence H4 is approved. According to the bootstrap results (Table 4), innovation significantly mediates the relationship between service quality and business performance (z = 3.244, p 0.01; lower bounds = 0.060; upper bounds = 0.203). Hypothesis H4, according to which innovation mediates the association between service quality and business performance, is supported by the significant z-value.
5 Discussion and policy recommendations
The modern restaurant must be abreast with current trends in terms of innovation strategies that come from its clients, suppliers, internal operations, and other external sources. With the right form of innovation applied by owners of restaurants, profit margins and high market share will be achieved. In accordance with this study, service quality and business performance in Ghanaian restaurants were mediated by innovation. This proves that innovation satisfies the mediating role. Innovation is a game changer in this modern era of business. This is probably due to the fact that innovation has a direct and significant impact on how well a business performs and the reverse is true; since in the event of full mediation, the predictor variable loses its ability to affect the criterion variable without the use of a mediator. The main factor that was demonstrated in the study was that owner-managers of restaurants confirmed that when they introduced a new or improved innovative strategy to existing services, customers.
It is crucial to note that selecting an innovative approach is not an easy task and should only be undertaken after careful consideration of the plan required to increase the restaurant's clientele and market share. The chosen approach should be largely easily implementable based on the expertise and capabilities of the staff and restaurant owners. This is true whether it takes the shape of technical innovation or service base innovation. Additionally, the combination of the financial crisis and ongoing developments has greatly heightened competitiveness amongst businesses, particularly restaurants in Ghana, which must satisfy customers' requirements and aspirations. Coordination between innovative initiatives that result in effective service quality is required to accomplish this. As far as the restaurant business is concerned, employees’ insight on what is expected of them in terms of service quality leads to higher business performance, therefore high-profit margins for restaurants in Ghana. Thus, when service quality is successfully managed, it generates distinctive skills that lead to increased business performance through innovation. This study’s ramifications suggest that owner-managers of restaurants should take a keen interest in applying the dimensions of service to the creation of new goods, services, and markets in order to boost their business performance.
This can be accomplished by ensuring that employees understand the dimensions of service by employing highly trained personnel, inspiring and empowering staff members through short courses, and allowing them to participate in seminars, conferences, and exhibitions to learn new information on service and innovation. This arguably fits well with the study since Ghana's restaurant sector will suffer without innovation, and service quality will affect business performance. This study highlighted the significance of innovative techniques in enhancing customer service quality and giving restaurant operators a competitive edge. Understanding what innovation is, why it is employed, and the benefits it offers is essential for its adoption across the restaurant sector. There are not enough studies to completely grasp how innovation mediates service quality and competitive advantage, despite the fact that multiple studies examined various innovation drivers and concepts.
This study highlighted some managerial/practical implications as restaurant managers or owners of restaurants must be proactive in handling the day-to-day running of their business through innovations space. They must also apply specific innovation techniques that will be beneficial to their business. Several frameworks and models have been established to aid in the identification of the components that go into an efficient innovation strategy. As a result, it is essential to have a company model that combines both innovation initiatives and a service quality framework [48]. According to the report, the innovation strategies framework is crucial for restaurant owners since it makes it easier to incorporate new innovations brought about by technologies. Additionally, the restaurant’s culture of innovation needs to be strengthened and used to improve creative activities for greater business performance. In this regard, it would be wise for policy-makers (Ghana Tourism Board, government organizations, and stakeholders) to put into practice, which should aid them in developing and formulating sound policies and support programs on service quality to boost the business performance of restaurants in Ghana.
6 Conclusion
Businesses, especially restaurants, must meet or even beyond customer expectations if they want to remain competitive. As a result, restaurants must rely more on innovations to keep up with changing events and business trends. In conclusion, the level of service quality that will be required in the future will rise in line with rising consumer demands and expectations. Therefore, in order to stay competitive and boost their financial performance, restaurants must speed up with specific innovations to meet the current demands of customers. Future research might utilize objective measurement scales for competitive advantage to fortify the study design. Another possibility for future study would be to examine the appropriate levels of service quality which tie in with the firm's success.
Data availability
Data and materials will be provided by the corresponding author upon request.
Abbreviations
- CB-SEM:
-
Confirmatory factor analysis and structural equation modeling
- SQ:
-
Service quality
- BP:
-
Business performance
- IV:
-
Innovation
- GTB:
-
Ghana Tourist Board
References
Ahmad K. The adoption of management accounting practices in Malaysian small and medium-sized enterprises. Asian Soc Sci. 2014;10:236–49.
Alawazgre J, Hassan K, Shaukat R. Knowledge management and innovation performance in a high-tech SMEs industry. Int Small Bus J. 2014;31:454–70.
Alrubaiee L, Alzubi HM, Hanandeh R, Ali RA. Investigating the relationship between knowledge management processes and organizational performance. The mediating effect of organizational innovation. Int Rev Manag Bus Res. 2015;4:989–1009.
Ar IM, Baki B. Antecedents and performance impacts of product versus process innovation: empirical evidence from SMEs located in Turkish science and technology parks. Eur J Innov Manag. 2021;14:172–206.
Bagorogoza J, Waal AD. The role of knowledge management in creating and sustaining high performance organisations: the case of financial institutions in Uganda. World J Entrep Manag sustain Dev. 2020;6:307–24. https://doi.org/10.1108/20425961201000023.
Baron RM, Kenny DA. The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: conceptual, strategic and statistical considerations. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1986;51:1173–82. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.51.6.1173.
Callan RJ, Kyndt G. Business travelers’ perception of service quality: a prefatory study of two European city center hotels. Int J Tour Res. 2021;3(4):313–23.
Camisón C, Villar López AV. An examination of the relationship between manufacturing flexibility and firm performance: the mediating role of innovation. Int J Oper Prod Manag. 2020;30:853–78. https://doi.org/10.1108/01443571011068199.
Crossan MM, Apaydin M. A multidimensional framework of organizational innovation: a systematic review of the literature. J Manage Stud. 2020;47:1154–91. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-6486.2009.00880.x.
Darroch J. Knowledge management, innovation and firm performance. J Knowl Manag. 2015;9:101–15. https://doi.org/10.1108/13673270510602809.
Dedeoğlu BB, Demirer H. Differences in service quality perceptions of stakeholders in the hotel industry. Int J Contempt Hosp Manag. 2015;27(1):130–46.
DeLone WH, McLean ER. The DeLone and McLean model of information systems success: a ten-year update. J Manag Inf Syst. 2023;19(4):9–30. https://doi.org/10.1080/07421222.2003.11045748.
Ghana Tourism Board. Annual Report for Government of Ghana. 2021.
García-Morales VJ, Lloréns-Montesa FJ, Verdú-Joverb AJ. Influence of personal mastery on organizational performance through organizational learning and innovation in large firms and SMEs. Technovation. 2017;27:547–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.technovation.2007.02.013.
Gronroos C. Relationship approach to marketing in service contexts: the marketing and organizational behavior interface. J Bus Res. 2017;20(1):3–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-2963(90)90037-E.
Han S, Baek S. Measuring the quality of university computer labs using SERVQUAL: A longitudinal study. The Qual Management J. 2004;10(3):33–44. https://doi.org/10.1080/10686967.2003.11919071
Han S, Baek S. Antecedents and consequences of service quality in online banking: an application of the SERVQUAL instrument. Adv Consumer Res. 2014; 31, 208–214. http://www.acrwebsite.org/volumes/8887/volumes/v31/NA-31.
Hair J, Black WC, Babin BJ, Anderson RE. Multivariate data analysis. 7th ed. Upper saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education; 2020.
Huang JW, Li YH. The mediating effect of knowledge management on social interaction and innovation performance. Int J Manpow. 2019;30:285–301. https://doi.org/10.1108/01437720910956772.
Jiménez-Jiménez D, Sanz-Valle R. Innovation, organizational learning, andperformance. J Bus Res. 2021;64:408–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2010.09.010.
Kocoglu I. The relationship between organizational learning and firm performance: the mediating roles of innovation and TQM. J Glob Strat Manag. 2021;9:72–88. https://doi.org/10.20460/JGSM.2011515814.
Kuhn JS, Marisck VJ. Action learning for strategic innovation in mature organizations: key cognitive, design and contextual considerations. Act Learn Res Pract. 2020;2:27–48.
Lam WJ. Online support service quality, online learning acceptance, and student satisfaction. Internet High Educ. 2018;13:227–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2010.08.002.
Leal-Rodríguez A, Leal-Millán A, Roldán-Salgueiro JL, Ortega-Gutiérrez J. Knowledge management and the effectiveness of innovation outcomes: the role of cultural barriers. Electron J Knowl Manag. 2023;11:62–71.
Liao S, Fei W, Liu C. Relationships between knowledge inertia, organizational learning and organization innovation. Technovation. 2018;28:183–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.technovation.2007.11.005.
MacKinnon DP, Lockwood CM, Hoffman JM, West SG, Sheets V. A comparison of methods to test mediation and other intervening variable effects. Psychol Methods. 2022;7:83–104. https://doi.org/10.1037/1082-989X.7.1.83.
Maduekwe CC, Kamala P. Performance measurement by small and medium enterprises in Cape Metropolis, South Africa. Probl Perspect Manag. 2016;14:46–55. https://doi.org/10.21511/ppm.
Mafabi S, Munene J, Ntayi J. Knowledge management and organisational resilience: organisational innovation as a mediator in Uganda parastatals. J Strateg Manag. 2022;5:57–80. https://doi.org/10.1108/17554251211200455.
Mazzarol T, Reboud S. The role of complimentary actors in the development of innovation in small firms. Int J Innov Manag. 2018;12:223–53. https://doi.org/10.1142/S1363919608001960.
McGrath RG. Exploratory learning, innovative capacity, and managerial oversight. Acad Manag J. 2021;44:118–31. https://doi.org/10.2307/3069340.
Medina C, Rufín R. The mediating effect of innovation in the relationship between retailers’ strategic orientations and performance. Int J Retail Distrib Manag. 2019;37:629–55. https://doi.org/10.1108/09590550910964639.
Mensah I. Customers’ perception of food service quality, the case of Cape Coast. J Bus Enterp Dev. 2023;1(1):138–54.
Micheals G. An evaluation of an integrated perspective of perceived service quality for retail banking services in India. Int J Bank Mark. 2017;33(3):330–50.
Miller LE, Smith KL. Handling nonresponse issues. J Ext. 1983;21:45–50.
Morgan RM, Hunt SD. The commitment-trust theory of relationship marketing. J Mark. 1994;64:50–64.
Musahara H, Akorli F, Rukamba S. Capacity building interventions, entrepreneurship and performance of SMEs in Rwanda (Working Paper). Kigali: University of Rwanda, College of Business and Economics. 2014.
Nasution M. Service marketing management, a strategic perspective. West Sussex: Wiley; 2016.
Nawab S, Nazir T, Zahid MM, Fawad SM. Knowledge management, innovation and organizational performance. Int J Knowl Eng IACSIT. 2015;1:43–8. https://doi.org/10.7763/IJKE.2015.V1.7.
Nonaka I. Knowledge management: theoretical and methodological foundations. In: Smith KG, Hitt MA, editors. Great minds in management: the process of theory development. New York: Oxford University; 2017. p. 373–93.
Nunnally JC. Psychometric theory. 2nd ed. New York, NY: McGraw Hill; 1978.
OECD. Oslo manual: guidelines for collecting and interpreting innovation data, 3rd edn. Paris, 2005.
Parasuraman A, Zeithaml VA, Berry LL. A conceptual model of service quality and its implications for future research. J Mark. 1985;49(4):41–50. https://doi.org/10.2307/1251430.
Preacher KJ, Hayes AF. Contemporary approaches to assessing mediation in communication research. In: Hayes AF, Slater MD, Snyder LB, editors. The SAGE sourcebook of advanced data analysis methods for communication research. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage; 2018. p. 13–54. https://doi.org/10.4135/9781452272054.
Richard PJ, Devinney TM, Yip GS, Johnson G. Measuring organizational performance: towards methodological best practice. J Manag. 2019;35:718–804. https://doi.org/10.1177/0149206308330560.
Schneider IM, White M. Impact of organizational innovation on firm performance: evidence from Malaysian-based ICT companies. J Knowl Manag. 2014;16:617–36. https://doi.org/10.1108/13673271211246185.
Tavitiyaman P, Zhang HQ, Qu H. The effect of competitive strategies and organizational structure on hotel performance. Int J Contemp Hosp Manag. 2022;24:140–59. https://doi.org/10.1108/09596111211197845.
Wang Y, Ahmad JC. Dyadic business relationships within a business network context. J Mark. 2014;58(October):1–15.
Wang Y, Lin J. An empirical research on knowledge management orientation and organizational performance: the mediating role of organizational innovation. Afr J Bus Manage. 2023;7:604–12.
Warrier S. Knowledge management. New Dehli: VIKAS; 2019.
Waweru C, Ngugi K. Influence of financial management practices on the performance of micro and small enterprises in Kenya. Eur J Bus Manag. 2014;1:141–61.
Yang J, Houssin R, Caillaud E, Gardoni M. Macro process of knowledge management for continuous innovation. J Knowl Manag. 2014;14:573–91. https://doi.org/10.1108/13673271011059536.
Yamane T. Statistics. An introductory analysis. 2nd ed. New York, NY: Harper & Row; 1967.
Hajar I. The effect of business strategy on innovation and firm performance in small industrial sector. Int J Eng Sci (IJES). 2015;4(2):1–9.
Zack M, McKeen J, Singh S. Knowledge management and organizational performance: an exploratory analysis. J Knowl Manag. 2009;13:392–409. https://doi.org/10.1108/13673270910997088.
Acknowledgements
We want to thank the respondent for taking part of the study. we want to thank our friends for their comments and suggestions during an earlier draft of this manuscript.
Funding
The author received no funding for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Gk is the main writer of this paper. He proposed the main idea and analyzed the result. The author has read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Approval was obtained from the ethics committee of the University of Education, Winneba. The procedures used in this study adhere to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki. The questionnaire and methodology for this study was approved by the Research committee of the University of D (Ethics approval number: 54237). Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The author declares that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Kankam, G. Service quality and business performance: the mediating role of innovation. Discov Anal 1, 6 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s44257-023-00006-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s44257-023-00006-7