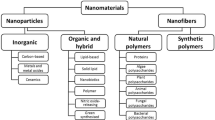
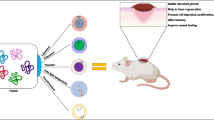
Abstract
Wound regeneration is a typical physiological mechanism consisting of a series of molecular and cellular processes that take place after the commencement of a tissue lesion to reestablish a barrier between the body and the external surroundings. Chronic non-healing wounds, on the other hand, require additional therapeutic qualities which could be obtained by using exosomes (Exo) and nanoparticles (NPs) to stimulate rapid and superior healing results. Many scientists have worked to understand the mechanisms of wound healing, and there are several reviews on the subject. To the best of our understanding, nevertheless, there has been little study on the utilization of Exo and NPs in wound healing. Our research aims to bridge that knowledge gap. This study first reviews previous studies on wounds and standard wound management methods. To close the gap in current research, we extensively discuss the state-of-the-art in engineered BioM-based wound healing approaches, including engineered exosome BioM-based procedures and nanoparticle-based BioMs for wound healing. Furthermore, current applications of BioM-based wound healing techniques are described. This study then closes by reviewing existing knowledge and discussing the multiple applications of synthesized BioM NPs for infectious wound healing.
Graphical Abstract

















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- antBA:
-
Antibacterial activity
- ADMSCs:
-
Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells
- ADSCs:
-
Adipose-derived stem cells
- Ag NPs:
-
Silver nanoparticles
- Biomimetics:
-
BioMs
- BMSCs:
-
Bone marrow-derived MSCs
- CBC:
-
Caryocar brasiliense Cambess
- CNT-PDA:
-
Carbon nanotubes- dopamine
- CO NPs:
-
Cerium oxide nanoparticles
- EVs:
-
Extracellular vesicles
- Exo:
-
Exosome
- FT-IR:
-
Fourier transforms infrared
- G-MSC:
-
Gingival- mesenchymal stem cells
- GelMA:
-
Gelatin methacryloyl
- GFs:
-
Growth factors
- GT-PDA:
-
Gelati-dopamine
- hADSCs:
-
Human adipose-derived stem cells
- hucMSCs:
-
Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells
- LPS pre-MSCs:
-
LPS-preconditioned mesenchymal stromal cells
- MSC-Exosomes:
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exos
- MPO:
-
Mentha pulegium essential oil
- N-SuC NPs:
-
N-succinyl chitosan
- NanoTech:
-
Nanotechnology
- NMeds:
-
Nanomedicines
- NMats:
-
Nanomaterials
- NPs:
-
Nanoparticles
- NSLCs:
-
Nanostructured lipid carriers
- Me NPs:
-
Metal nanoparticles
- PECE:
-
Poly (ethylene glycol)-poly(ε-caprolactone)-poly (ethylene glycol)
- PHPV:
-
Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate)
- rPDA:
-
Reduced polydopamine
- SA:
-
Sodium alginate
- SeNPs:
-
Selenium Nanoparticles
- SLi NPs:
-
Solid Lipid NPs
- SMSCs:
-
Synovium mesenchymal stem cells
- XRD:
-
X-ray diffraction
- ZnO NP:
-
Zinc oxide nanoparticles
- ZnO/SA:
-
Zinc oxide/sodium alginate
- ZnO/Mgt-NCs:
-
Zn O/Magnetite-based nanocomposites
References
J.A.D. Whitney, Overview: acute and chronic wounds. Nurs. Clin. N. Am. 40, 191–205 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CNUR.2004.09.002
M. Rodrigues, N. Kosaric, C.A. Bonham, G.C. Gurtner, Wound healing: a cellular perspective. Physiol. Rev. 99, 665–706 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1152/PHYSREV.00067.2017
X. Zhan, Z. Wen, X. Chen, Q. Lei, Y. Chen, L. Zhou, G. Zheng, F. Kong, J. Guo, Y. Duan, Y. Lai, P. Yin, C.J. Brinker, H. Chen, W. Zhu, Polyphenol-mediated biomimetic mineralization of sacrificial metal-organic framework nanoparticles for wound healing. Cell. Rep. Phys. Sci. 3, 101103 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.XCRP.2022.101103
ECB12: 12th European Congess on Biotechnology, J Biotechnol. 118 (2005) 1–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JBIOTEC.2005.06.005.
F. Nudelman, N.A.J.M. Sommerdijk, Biomineralization as an inspiration for materials chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51, 6582–6596 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/ANIE.201106715
G. Mangone, R.L. Dopko, J.M. Zelenski, Deciphering landscape preferences: investigating the roles of familiarity and biome types. Landsc. Urban Plan. 214, 104189 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2021.104189
V. Tallapaneni, D. Pamu, T.N. Shilpa, V.V. Satyanarayana Reddy Karri, S.K. Mohankumar, Emerging role of inorganic and metal nanoparticles for the delivery of combination of drugs in wound healing and tissue regeneration. Nanocarriers Deliv. Combin. Drugs. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-820779-6.00012-8
M. Ullah, A. Wahab, D. Khan, S. Saeed, S.U. Khan, N. Ullah, T.A. Saleh, Modified gold and polymeric gold nanostructures: toxicology and biomedical applications. Colloids Interface Sci. Commun. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colcom.2021.100412
B.H.J. Gowda, S. Mohanto, A. Singh, A. Bhunia, M.A. Abdelgawad, S. Ghosh, M.J. Ansari, S. Pramanik, Nanoparticle-based therapeutic approaches for wound healing: a review of the state-of-the-art. Mater. Today Chem. 27, 101319 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MTCHEM.2022.101319
X. Zheng, X. Zhang, J. Zhao, W. Oyom, H. Long, R. Yang, L. Pu, Y. Bi, D. Prusky, Meyerozyma guilliermondii promoted the deposition of GSH type lignin by activating the biosynthesis and polymerization of monolignols at the wounds of potato tubers. Food. Chem. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.135688
G. Cheng, B. Li, Nanoparticle-based photodynamic therapy: new trends in wound healing applications. Mater. Today Adv. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtadv.2019.100049
M. Fang, H. Zhang, Y. Wang, H. Zhang, D. Zhang, P. Xu, Biomimetic selenium nanosystems for infectious wound healing. Eng. Regener. 4, 152–160 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engreg.2023.01.004
A. Joorabloo, T. Liu, Engineering exosome-based biomimetic nanovehicles for wound healing. J. Control Release 356, 463–480 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.03.013
K. Rilla, A.M. Mustonen, U.T. Arasu, K. Härkönen, J. Matilainen, P. Nieminen, Extracellular vesicles are integral and functional components of the extracellular matrix. Matrix Biol. 75–76, 201–219 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matbio.2017.10.003
L. Filipović, M. Kojadinović, M. Popović, Exosomes and exosome-mimetics as targeted drug carriers: where we stand and what the future holds? J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2021.103057
D. Ferreira, J.N. Moreira, L.R. Rodrigues, New advances in exosome-based targeted drug delivery systems, Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 172 (2022). Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2022.103628.
S. Fu, Y. Wang, X. Xia, J.C. Zheng, Exosome engineering: current progress in cargo loading and targeted delivery. NanoImpact (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.impact.2020.100261
M. Xiong, Q. Zhang, W. Hu, C. Zhao, W. Lv, Y. Yi, Y. Wang, H. Tang, M. Wu, Y. Wu, The novel mechanisms and applications of exosomes in dermatology and cutaneous medical aesthetics. Pharmacol. Res. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105490
J. Aslam, S. Zehra, M. Mobin, M.A. Quraishi, C. Verma, R. Aslam, Metal/metal oxide-carbohydrate polymers framework for industrial and biological applications: current advancements and future directions. Carbohydr. Polym. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2023.120936
E. Zhang, P. Phan, Z. Zhao, Cellular nanovesicles for therapeutic immunomodulation: a perspective on engineering strategies and new advances. Acta Pharm. Sin. B (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2022.08.020
E. Desideri, F. Ciccarone, M.R. Ciriolo, D. Fratantonio, Extracellular vesicles in endothelial cells: from mediators of cell-to-cell communication to cargo delivery tools. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 172, 508–520 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.06.030
B.H.J. Gowda, S. Mohanto, A. Singh, A. Bhunia, M.A. Abdelgawad, S. Ghosh, M.J. Ansari, S. Pramanik, Nanoparticle-based therapeutic approaches for wound healing: a review of the state-of-the-art. Mater. Today Chem. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtchem.2022.101319
M.H. Norahan, S.C. Pedroza-González, M.G. Sánchez-Salazar, M.M. Álvarez, G. Trujillo de Santiago, Structural and biological engineering of 3D hydrogels for wound healing. Bioact. Mater. 24, 197–235 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.11.019
A. Awasthi, S. Vishwas, M. Gulati, L. Corrie, J. Kaur, R. Khursheed, A. Alam, F.F.A. Alkhayl, F.R. Khan, S. Nagarethinam, R. Kumar, K.R. Arya, B. Kumar, D.K. Chellappan, G. Gupta, K. Dua, S.K. Singh, Expanding arsenal against diabetic wounds using nanomedicines and nanomaterials: success so far and bottlenecks. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2022.103534
S. Roy, I. Hasan, B. Guo, Recent advances in nanoparticle-mediated antibacterial applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2023.215075
J. Zhou, D. Yao, Z. Qian, S. Hou, L. Li, A.T.A. Jenkins, Y. Fan, Bacteria-responsive intelligent wound dressing: simultaneous in situ detection and inhibition of bacterial infection for accelerated wound healing. Biomaterials 161, 11–23 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.01.024
M.S. Hassani, M. Salehi, A. Ehterami, S. Mahami, F.S. Bitaraf, M. Rahmati, Evaluation of collagen type I and III, TGF-β1, and VEGF gene expression in rat skin wound healing treated by Alginate/Chitosan hydrogel containing Crocetin. Biochem. Eng. J. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2023.108895
L. Zhang, W. Tan, M. Zhang, Z. Ma, T. Zhao, Y. Zhang, Preparation and characterization of Panax notoginseng saponins loaded hyaluronic acid/carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogel for type o diabetic wound healing. Mater. Today Commun. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.105284
P. Sharma, S. Neogi, Performance-based design and manufacturing of filament wound Type-4 cylinders for compressed gas storage. Compos Struct. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2023.116710
R.G. Frykberg, J. Banks, Challenges in the treatment of chronic wounds. Adv. Wound Care (New Rochelle). 4, 560–582 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1089/WOUND.2015.0635
N. Harris, S. Fulchand, J. Nazaroff, S. Li, J.Y. Tang, 1517 Natural history of spontaneous wound healing in recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa wound types using a mobile photography application. J. Investig. Dermatol. 143, S260 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JID.2023.03.1534
J.T. Patterson, J.A. Becerra, M. Brown, I. Roohani, C. Zalavras, J.N. Carey, Antibiotic bead pouch versus negative pressure wound therapy at initial management of AO/OTA 42 type IIIB open tibia fracture may reduce fracture related infection: a retrospective analysis of 113 patients. Injury 54, 744–750 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2022.12.018
A.K. Kar, A. Singh, D. Singh, N. Shraogi, R. Verma, J. Saji, P. Jagdale, D. Ghosh, S. Patnaik, Biopolymeric composite hydrogel loaded with silver NPs and epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) effectively manages ROS for rapid wound healing in type II diabetic wounds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 218, 506–518 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.06.196
J.S. Low, K.K. Mak, S. Zhang, M.R. Pichika, P. Marappan, K. Mohandas, M.K. Balijepalli, In vitro methods used for discovering plant derived products as wound healing agents—an update on the cell types and rationale. Fitoterapia (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2021.105026
P. Li, B. Li, C. Wang, X. Zhao, Y. Zheng, S. Wu, J. Shen, Y. Zhang, X. Liu, In situ fabrication of co-coordinated TCPP-Cur donor-acceptor-type covalent organic framework-like photocatalytic hydrogel for rapid therapy of bacteria-infected wounds. Composite B (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2023.110506
D. Woodley, Y. Hou, X. Tang, C. Tan, K. Zhang, L. Bainvoll, W. Li, M. Chen, Topical type VII collagen increased elastic fiber formation, accelerated wound closure and reduced scarring of diabetic pigskin wounds. J. Investig. Dermatol. 143, 260 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JID.2023.03.1536
M.F. Hossain, Wound care: a material solution. Encyclopedia Renew. Sustain. Mater. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-803581-8.10997-X
R. Dong, B. Guo, Smart wound dressings for wound healing. Nano Today 41, 101290 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2021.101290
S. Talebian, M. Mehrali, N. Taebnia, C.P. Pennisi, F.B. Kadumudi, J. Foroughi, M. Hasany, M. Nikkhah, M. Akbari, G. Orive, A. Dolatshahi-Pirouz, Self-healing hydrogels: the next paradigm shift in tissue engineering? Adv. Sci. 6, 1801664 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.201801664
A.J. Clasky, J.D. Watchorn, P.Z. Chen, F.X. Gu, From prevention to diagnosis and treatment: biomedical applications of metal nanoparticle-hydrogel composites. Acta Biomater. 122, 1–25 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2020.12.030
N. Fallah, M. Rasouli, M.R. Amini, The current and advanced therapeutic modalities for wound healing management. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 20, 1883–1899 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-021-00868-2
L. Zhang, M. Liu, Y. Zhang, R. Pei, Recent progress of highly adhesive hydrogels as wound dressings. Biomacromolecules 21, 3966–3983 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.0c01069
S. Pourshahrestani, E. Zeimaran, N.A. Kadri, N. Mutlu, A.R. Boccaccini, Polymeric hydrogel systems as emerging biomaterial platforms to enable hemostasis and wound healing. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 9, 2000905 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.202000905
Z. Kopecki, Development of next-generation antimicrobial hydrogel dressing to combat burn wound infection. Biosci. Rep. (2021). 10.1042/BSR20203404.
C. Pang, A. Ibrahim, N.W. Bulstrode, P. Ferretti, An overview of the therapeutic potential of regenerative medicine in cutaneous wound healing. Int. Wound J. 14, 450–459 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1111/iwj.12735
A. Sood, M.S. Granick, N.L. Tomaselli, Wound dressings and comparative effectiveness data. Adv. Wound Care (New Rochelle). 3, 511–529 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1089/wound.2012.0401
D.L. Steed, the D.U. Study Group *, Clinical evaluation of recombinant human platelet—derived growth factor for the treatment of lower extremity diabetic ulcers. J. Vasc. Surg. 21, 71–81 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0741-5214(95)70245-8.
A. Przekora, A concise review on tissue engineered artificial skin grafts for chronic wound treatment: can we reconstruct functional skin tissue in vitro? Cells 9, 1622 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9071622
M.A. Mofazzal Jahromi, P. Sahandi Zangabad, S.M. Moosavi Basri, K. Sahandi Zangabad, A. Ghamarypour, A.R. Aref, M. Karimi, M.R. Hamblin, Nanomedicine and advanced technologies for burns: preventing infection and facilitating wound healing. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 123, 33–64 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2017.08.001
Q. Li, K. Liu, T. Jiang, S. Ren, Y. Kang, W. Li, H. Yao, X. Yang, H. Dai, Z. Chen, Injectable and self-healing chitosan-based hydrogel with MOF-loaded α-lipoic acid promotes diabetic wound healing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 131, 112519 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2021.112519
R. White, C. McIntosh, A review of the literature on topical therapies for diabetic foot ulcers. Part 2: advanced treatments. J. Wound Care 18, 335–341 (2009). https://doi.org/10.12968/jowc.2009.18.8.43633
R. Serra, A. Rizzuto, A. Rossi, P. Perri, A. Barbetta, K. Abdalla, S. Caroleo, C. Longo, B. Amantea, G. Sammarco, S. de Franciscis, Skin grafting for the treatment of chronic leg ulcers—a systematic review in evidence-based medicine. Int. Wound J. 14, 149–157 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1111/iwj.12575
D.K. Ozhathil, M.W. Tay, S.E. Wolf, L.K. Branski, A narrative review of the history of skin grafting in burn care. Medicina (B Aires). 57, 380 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57040380
C. Dai, S. Shih, A. Khachemoune, Skin substitutes for acute and chronic wound healing: an updated review. J. Dermatol. Treat. 31, 639–648 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/09546634.2018.1530443
E. Eriksson, P.Y. Liu, G.S. Schultz, M.M. Martins-Green, R. Tanaka, D. Weir, L.J. Gould, D.G. Armstrong, G.W. Gibbons, R. Wolcott, O.O. Olutoye, R.S. Kirsner, G.C. Gurtner, Chronic wounds: treatment consensus. Wound Repair Regen. 30, 156–171 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1111/wrr.12994
S. Homaeigohar, A.R. Boccaccini, Antibacterial biohybrid nanofibers for wound dressings. Acta Biomater. 107, 25–49 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2020.02.022
M.M. Mihai, M.B. Dima, B. Dima, A.M. Holban, Nanomaterials for wound healing and infection control. Materials 12, 2176 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12132176
N. Aminu, I. Bello, N.M. Umar, N. Tanko, A. Aminu, M.M. Audu, The influence of nanoparticulate drug delivery systems in drug therapy. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 60, 101961 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2020.101961
J. Boateng, O. Catanzano, Silver and Silver Nanoparticle‐Based Antimicrobial Dressings, in: Therapeutic Dressings and Wound Healing Applications, Wiley, 2020: pp. 157–184. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119433316.ch8.
Stem Cells and Regenerative Medicine, Goodman’s Medical Cell Biology. (2021) 361–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-817927-7.00013-2.
Z. Xu, M. Dong, S. Yin, J. Dong, M. Zhang, R. Tian, W. Min, L. Zeng, H. Qiao, J. Chen, Why traditional herbal medicine promotes wound healing: research from immune response, wound microbiome to controlled delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2023.114764
A. Joorabloo, T. Liu, Recent advances in nanomedicines for regulation of macrophages in wound healing. J. Nanobiotechnol. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/S12951-022-01616-1
X. Li, X. Xie, W. Lian, R. Shi, S. Han, H. Zhang, L. Lu, M. Li, Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells overexpressing Nrf2 accelerate cutaneous wound healing by promoting vascularization in a diabetic foot ulcer rat model. Exp. Mol. Med. 50, 1–14 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-018-0058-5
S. Amini-Nik, Y. Yousuf, M.G. Jeschke, Scar management in burn injuries using drug delivery and molecular signaling: current treatments and future directions. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 123, 135–154 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2017.07.017
L. Xie, X. Long, M. Mo, J. Jiang, Q. Zhang, M. Long, M. Li, Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes alleviate skin fibrosis in systemic sclerosis by inhibiting the IL-33/ST2 axis via the delivery of microRNA-214. Mol. Immunol. 157, 146–157 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MOLIMM.2023.03.017
W. Pan, H. Chen, A. Wang, F. Wang, X. Zhang, Challenges and strategies: scalable and efficient production of mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes for cell-free therapy. Life Sci. 319, 121524 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.LFS.2023.121524
J. Li, X. Sun, J. Dai, J. Yang, L. Li, Z. Zhang, J. Guo, S. Bai, Y. Zheng, X. Shi, Biomimetic multifunctional hybrid sponge via enzymatic cross-linking to accelerate infected burn wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 225, 90–102 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.12.024
P.M. Wong, L. Yang, L. Yang, H. Wu, W. Li, X. Ma, I. Katayama, H. Zhang, New insight into the role of exosomes in vitiligo. Autoimmun. Rev. 19, 102664 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.AUTREV.2020.102664
J.S. Heo, S. Kim, C.E. Yang, Y. Choi, S.Y. Song, H.O. Kim, Human adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: a key player in wound healing, tissue eng. Regen. Med. 18, 537–548 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/S13770-020-00316-X/FIGURES/6
B. Sridharan, H.G. Lim, Exosomes and ultrasound: The future of theranostic applications. Mater. Today Bio 19, 100556 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MTBIO.2023.100556
A.I. Toma, J.M. Fuller, N.J. Willett, S.L. Goudy, Oral wound healing models and emerging regenerative therapies. Transl. Res. 236, 17–34 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TRSL.2021.06.003
C.K. Sen, Human wound and its burden: updated 2020 compendium of estimates. Adv. Wound Care (New Rochelle). 10, 281–292 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1089/WOUND.2021.0026
T. Ma, B. Fu, X. Yang, Y. Xiao, M. Pan, Adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote cell proliferation, migration, and inhibit cell apoptosis via Wnt/β-catenin signaling in cutaneous wound healing. J. Cell Biochem. 120, 10847–10854 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/JCB.28376
X. Zhou, B.A. Brown, A.P. Siegel, M.S. El Masry, X. Zeng, W. Song, A. Das, P. Khandelwal, A. Clark, K. Singh, P.R. Guda, M. Gorain, L. Timsina, Y. Xuan, S.C. Jacobson, M.V. Novotny, S. Roy, M. Agarwal, R.J. Lee, C.K. Sen, D.E. Clemmer, S. Ghatak, Exosome-mediated crosstalk between keratinocytes and macrophages in cutaneous wound healing. ACS Nano 14, 12732–12748 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.0c03064
I.K. Herrmann, M.J.A. Wood, G. Fuhrmann, Extracellular vesicles as a next-generation drug delivery platform. Nat. Nanotechnol. 16, 748–759 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-021-00931-2
E. Issaka, J.N.O. Amu-Darko, M. Adams, S. Yakubu, E. Gyimah, N. Ali, J. Cui, M. Bilal, Zinc imidazolate metal-organic frameworks-8-encapsulated enzymes/nanoenzymes for biocatalytic and biomedical applications. Catal. Lett. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-022-04140-x
E. Issaka, S. Yakubu, H. Sulemana, A. Kerkula, O. Nyame-do Aniagyei, Current status of the direct detection of MPs in environments and implications for toxicology effects. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceja.2023.100449
E. Issaka, M.A. Wariboko, N.A.N. Johnson, O.N. Aniagyei, Advanced visual sensing techniques for on-site detection of pesticide residue in water environments. Heliyon (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13986
R. Misra, S. Acharya, N. Sushmitha, Nanobiosensor-based diagnostic tools in viral infections: special emphasis on Covid-19. Rev. Med. Virol. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/rmv.2267
Z. Tu, M. Chen, M. Wang, Z. Shao, X. Jiang, K. Wang, Z. Yao, S. Yang, X. Zhang, W. Gao, C. Lin, B. Lei, C. Mao, Engineering bioactive M2 macrophage-polarized anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antibacterial scaffolds for rapid angiogenesis and diabetic wound repair. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31, 2100924 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202100924
Z. Xu, B. Liang, J. Tian, J. Wu, Anti-inflammation biomaterial platforms for chronic wound healing. Biomater. Sci. 9, 4388–4409 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/D1BM00637A
Y. Yuan, D. Fan, S. Shen, X. Ma, An M2 macrophage-polarized anti-inflammatory hydrogel combined with mild heat stimulation for regulating chronic inflammation and impaired angiogenesis of diabetic wounds. Chem. Eng. J. 433, 133859 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.133859
S. Sharifi, M.J. Hajipour, L. Gould, M. Mahmoudi, Nanomedicine in healing chronic wounds: opportunities and challenges. Mol. Pharm. 18, 550–575 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.0c00346
Y. Xi, J. Ge, M. Wang, M. Chen, W. Niu, W. Cheng, Y. Xue, C. Lin, B. Lei, Bioactive Anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antioxidative silicon-based nanofibrous dressing enables cutaneous tumor photothermo-chemo therapy and infection-induced wound healing. ACS Nano 14, 2904–2916 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.9b07173
W. Li, J. Cao, Y. Du, H. Ye, W. Shan, X. Chen, H. Wu, G. Krishna Murakonda, X. Xu, Ampelopsis grossedentata leaf extract induced gold nanoparticles as wound healing dressing for abdominal wound dehiscence in nursing care. J. Clust. Sci. 33, 1139–1147 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-021-02040-5
N.T.T. Thao, H.M.S.M. Wijerathna, R.S. Kumar, D. Choi, S.H.S. Dananjaya, A.P. Attanayake, Preparation and characterization of succinyl chitosan and succinyl chitosan nanoparticle film: in vitro and in vivo evaluation of wound healing activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 193, 1823–1834 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJBIOMAC.2021.11.015
C. Carbone, C. Caddeo, M.A. Grimaudo, D.E. Manno, A. Serra, T. Musumeci, Ferulic acid-NLC with Lavandula essential oil: a possible strategy for wound-healing? Nanomaterials 10, 898 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10050898
R. Augustine, A.A. Zahid, A. Hasan, Y.B. Dalvi, J. Jacob, Cerium oxide nanoparticle-loaded gelatin methacryloyl hydrogel wound-healing patch with free radical scavenging activity. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 7, 279–290 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.0c01138
S.B. Balakrishnan, M. Alam, N. Ahmad, M. Govindasamy, S. Kuppu, S. Thambusamy, Electrospinning nanofibrous graft preparation and wound healing studies using ZnO nanoparticles and glucosamine loaded with poly(methyl methacrylate)/polyethylene glycol. New J. Chem. 45, 7987–7998 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NJ05409G
T. Wang, J. Wang, R. Wang, P. Yuan, Z. Fan, S. Yang, Preparation and properties of ZnO/sodium alginate bi-layered hydrogel films as novel wound dressings. New J. Chem. 43, 8684–8693 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/C9NJ00402E
S. Rathinavel, K. Priyadharshini, D. Panda, A review on carbon nanotube: an overview of synthesis, properties, functionalization, characterization, and the application. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 268, 115095 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MSEB.2021.115095
B. Murugesan, N. Pandiyan, K. Kasinathan, A. Rajaiah, M. Arumuga, P. Subramanian, J. Sonamuthu, S. Samayanan, V.R. Arumugam, K. Marimuthu, C. Yurong, S. Mahalingam, Fabrication of heteroatom doped NFP-MWCNT and NFB-MWCNT nanocomposite from imidazolium ionic liquid functionalized MWCNT for antibiofilm and wound healing in Wistar rats: synthesis, characterization, in-vitro and in-vivo studies. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 111, 110791 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MSEC.2020.110791
O. Forero-Doria, E. Polo, A. Marican, L. Guzmán, B. Venegas, S. Vijayakumar, S. Wehinger, M. Guerrero, J. Gallego, E.F. Durán-Lara, Supramolecular hydrogels based on cellulose for sustained release of therapeutic substances with antimicrobial and wound healing properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 242, 116383 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2020.116383
E. Hafez, S.M. Shaban, M.H. Kim, A.Y. Elbalaawy, D. gi Pyun, D.H. Kim, Fabrication of activated carbon fiber functionalized core–shell silver nanoparticles based in situ and low-cost technology for wound dressings with an enhanced antimicrobial activity and cell viability. J. Mol. Liq. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2022.119561
E. Naseri, A. Ahmadi, A review on wound dressings: antimicrobial agents, biomaterials, fabrication techniques, and stimuli-responsive drug release. Eur. Polym. J. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2022.111293
L. Li, D. Chen, J. Chen, C. Yang, Y. Zeng, T. Jin, Y. Zhang, X. Sun, H. Mao, Z. Mu, X. Shen, Z. Ruan, X. Cai, Gelatin and catechol-modified quaternary chitosan confer cotton dressings with rapid hemostasis and high-efficiency antimicrobial capacities to manage severe bleeding wounds. Mater. Des. 229, 111927 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATDES.2023.111927
T.K. Kumawat, V. Kumawat, V. Sharma, A. Pandit, B. Sharma, S. Nag, N. Kumari, M. Biyani, Overview and summary of antimicrobial wound dressings and its biomedical applications. Antimicrob. Dress. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-95074-9.00004-X
J.A. Ross, N. Allan, M. Olson, C. Schatz, P.N. Nation, J.P. Gawaziuk, J. Sethi, S. Liu, S. Logsetty, Comparison of the efficacy of silver-based antimicrobial burn dressings in a porcine model of burn wounds. Burns 46, 1632–1640 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.burns.2020.04.004
R.S. Khan, A.H. Rather, T.U. Wani, S. ullah Rather, A. Abdal-hay, F.A. Sheikh, A comparative review on silk fibroin nanofibers encasing the silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agents for wound healing applications. Mater. Today Commun. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.103914
X. Chen, H. Li, X. Qiao, T. Jiang, X. Fu, Y. He, X. Zhao, Agarose oligosaccharide-silver nanoparticle-antimicrobial peptide-composite for wound dressing. Carbohydr. Polym. 269, 118258 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2021.118258
V. Edwards-Jones, In vitro studies of a silver surgical site dressing, PrimasealTM post-op silver dressing, and its activity against common wound pathogens. Int. J. Surg. Open 36, 100410 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJSO.2021.100410
K. Shanmugapriya, H.W. Kang, Engineering pharmaceutical nanocarriers for photodynamic therapy on wound healing: review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.110110
V. Vijayakumar, S.K. Samal, S. Mohanty, S.K. Nayak, Recent advancements in biopolymer and metal nanoparticle-based materials in diabetic wound healing management. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 122, 137–148 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.10.120
S. Wilk, A. Przekora, P. Kazimierczak, D. Medina-Cruz, L. Martínez, C. O’Connell, L.B. Truong, K. Reczyńska-Kolman, H. Barabadi, J.L. Cholula-Diaz, E. Pamuła, Y. Huttel, J.M. García-Martín, T.J. Webster, A. Benko, Nanocomposite scaffolds and coatings for wound healing and infection control. Antimicrob. Activity Nanoparticles (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-821637-8.00007-9
L. Zheng, B. Gu, S. Li, B. Luo, Y. Wen, M. Chen, X. Li, Z. Zha, H.T. Zhang, X. Wang, An antibacterial hemostatic AuNPs@corn stalk/chitin composite sponge with shape recovery for promoting wound healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 296, 119924 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2022.119924
A.A. Menazea, M.K. Ahmed, Wound healing activity of Chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol embedded by gold nanoparticles prepared by nanosecond laser ablation. J. Mol. Struct. 1217, 128401 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MOLSTRUC.2020.128401
A.L. Wani, G.G. Hammad Ahmad Shadab, M. Afzal, Lead and zinc interactions—an influence of zinc over lead related toxic manifestations. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2020.126702
S. Awasthi, R. Chauhan, S. Srivastava, The importance of beneficial and essential trace and ultratrace elements in plant nutrition, growth, and stress tolerance. Plant Nutr. Food Secur. Era Clim. Chang. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-822916-3.00001-9
V. Dhiman, N. Kondal, ZnO Nanoadsorbents: a potent material for removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater. Colloids Interface Sci. Commun. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colcom.2021.100380
R.G. Saratale, I. Karuppusamy, G.D. Saratale, A. Pugazhendhi, G. Kumar, Y. Park, G.S. Ghodake, R.N. Bharagava, J.R. Banu, H.S. Shin, A comprehensive review on green nanomaterials using biological systems: recent perception and their future applications. Colloids Surf. B 170, 20–35 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.05.045
L. Ye, X. He, E. Obeng, D. Wang, D. Zheng, T. Shen, J. Shen, R. Hu, H. Deng, The CuO and AgO co-modified ZnO nanocomposites for promoting wound healing in Staphylococcus aureus infection. Mater. Today Bio. 18, 100552 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MTBIO.2023.100552
Z.B. Akkuş-Dağdeviren, A. Fürst, J. David Friedl, M. Tribus, A. Bernkop-Schnürch, Nanoarchitectonics of layer-by-layer (LbL) coated nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) for enzyme-triggered charge reversal. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 629, 541–553 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2022.08.190
P. Graván, A. Aguilera-Garrido, J.A. Marchal, S.A. Navarro-Marchal, F. Galisteo-González, Lipid-core nanoparticles: classification, preparation methods, routes of administration and recent advances in cancer treatment. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2023.102871
C. Tapeinos, M. Battaglini, G. Ciofani, Advances in the design of solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers for targeting brain diseases. J. Control Release 264, 306–332 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.08.033
S. Aziz Hazari, H. Kaur, R. Karwasra, M.A.S. Abourehab, A. Ali Khan, P. Kesharwani, An overview of topical lipid-based and polymer-based nanocarriers for treatment of psoriasis. Int. J. Pharm. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2023.122938
H. Nsairat, D. Khater, F. Odeh, F. Al-Adaileh, S. Al-Taher, A.M. Jaber, W. Alshaer, A. Al Bawa, M.S. Mubarak, Lipid nanostructures for targeting brain cancer. Heliyon (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07994
W. Zha, J. Wang, Z. Guo, Y. Zhang, Y. Wang, S. Dong, C. Liu, H. Xing, X. Li, Efficient delivery of VEGF-A mRNA for promoting diabetic wound healing via ionizable lipid nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 632, 122565 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJPHARM.2022.122565
B. Carletto, A.Y. Koga, A. Novatski, R.M. Mainardes, L.C. Lipinski, P.V. Farago, Ursolic acid-loaded lipid-core nanocapsules reduce damage caused by estrogen deficiency in wound healing. Colloids Surf. B 203, 720 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COLSURFB.2021.111720
V. Pils, L. Terlecki-Zaniewicz, M. Schosserer, J. Grillari, I. Lämmermann, The role of lipid-based signalling in wound healing and senescence. Mech. Ageing Dev. 198, 111527 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MAD.2021.111527
H.S. Kim, X. Sun, J.-H. Lee, H.-W. Kim, X. Fu, K.W. Leong, Advanced drug delivery systems and artificial skin grafts for skin wound healing. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 146, 209–239 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2018.12.014
S. Saghazadeh, C. Rinoldi, M. Schot, S.S. Kashaf, F. Sharifi, E. Jalilian, K. Nuutila, G. Giatsidis, P. Mostafalu, H. Derakhshandeh, K. Yue, W. Swieszkowski, A. Memic, A. Tamayol, A. Khademhosseini, Drug delivery systems and materials for wound healing applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 127, 138–166 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2018.04.008
Y. Liang, M. Li, Y. Yang, L. Qiao, H. Xu, B. Guo, pH/glucose dual responsive metformin release hydrogel dressings with adhesion and self-healing via dual-dynamic bonding for athletic diabetic foot wound healing. ACS Nano 16, 3194–3207 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c11040
F. Yan, F. Cheng, C. Guo, G. Liang, S. Zhang, S. Fang, Z. Zhang, Curcumin-regulated constructing of defective zinc-based polymer-metal-organic framework as long-acting antibacterial platform for efficient wound healing. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 641, 59–69 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2023.03.050
Y. Lu, P. Shan, W. Lu, X. Yin, H. Liu, X. Lian, J. Jin, Y. Qi, Z. Li, Z. Li, ROS-responsive and self-amplifying polymeric prodrug for accelerating infected wound healing. Chem. Eng. J. 463, 2311 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.142311
J. Huang, S. Wang, X. Wang, J. Zhu, Z. Wang, X. Zhang, K. Cai, J. Zhang, Combination wound healing using polymer entangled porous nanoadhesive hybrids with robust ROS scavenging and angiogenesis properties. Acta Biomater. 152, 171–185 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2022.08.069
Y. Zhang, Y. Pan, Y. Liu, X. Li, L. Tang, M. Duan, J. Li, G. Zhang, Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells stimulate regenerative wound healing via transforming growth factor-β receptor inhibition. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 12, 434 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-021-02517-0
D.H. Hoang, T.D. Nguyen, H.-P. Nguyen, X.-H. Nguyen, P.T.X. Do, V.D. Dang, P.T.M. Dam, H.T.H. Bui, M.Q. Trinh, D.M. Vu, N.T.M. Hoang, L.N. Thanh, U.T.T. Than, Differential wound healing capacity of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes originated from bone marrow, adipose tissue and umbilical cord under serum- and xeno-free condition. Front. Mol. Biosci. (2020). https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2020.00119
H. Haidari, R. Bright, X.L. Strudwick, S. Garg, K. Vasilev, A.J. Cowin, Z. Kopecki, Multifunctional ultrasmall AgNP hydrogel accelerates healing of S. aureus infected wounds. Acta Biomater. 128, 420–434 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ACTBIO.2021.04.007
L. Jaiswal, S. Shankar, J.W. Rhim, D.H. Hahm, Lignin-mediated green synthesis of AgNPs in carrageenan matrix for wound dressing applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 159, 859–869 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJBIOMAC.2020.05.145
Y. Zou, R. Xie, E. Hu, P. Qian, B. Lu, G. Lan, F. Lu, Protein-reduced gold nanoparticles mixed with gentamicin sulfate and loaded into konjac/gelatin sponge heal wounds and kill drug-resistant bacteria. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 148, 921–931 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.01.190
L. Sturm, M. Flood, A. Montoya, L. Mody, M. Cassone, Updates on infection control in alternative health care settings. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 35, 803–825 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idc.2021.04.013
F.U. Khan, S. Shah, G. Abbas, H.U. Khan, T. Ahmad, W. Ullah, A. Khan, F. UllahKhan, T.H. Mallhi, Y.H. Khan, Y. Fang, Antibiotics safety case studies: hospitals. Clin. Case Stud. Med. Saf. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-98802-5.00003-0
M. Bassetti, M. Baguneid, E. Bouza, M. Dryden, D. Nathwani, M. Wilcox, European perspective and update on the management of complicated skin and soft tissue infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus after more than 10 years of experience with linezolid. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 20, 3–18 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1111/1469-0691.12463
S.A. Alsakhawy, H.H. Baghdadi, M.A. El-Shenawy, S.A. Sabra, L.S. El-Hosseiny, Encapsulation of thymus vulgaris essential oil in caseinate/gelatin nanocomposite hydrogel: in vitro antibacterial activity and in vivo wound healing potential. Int. J. Pharm. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.122280
A.G. Tabriz, D. Douroumis, Recent advances in 3D printing for wound healing: a systematic review. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2022.103564
F. Mushtaq, Z.A. Raza, S.R. Batool, M. Zahid, O.C. Onder, A. Rafique, M.A. Nazeer, Preparation, properties, and applications of gelatin-based hydrogels (GHs) in the environmental, technological, and biomedical sectors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 218, 601–633 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.07.168
N.J. Buote, Updates in wound management and dressings, veterinary clinics of North America—small animal. Practice 52, 289–315 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cvsm.2021.12.001
S.A. Shah, M. Sohail, S.A. Khan, M. Kousar, Improved drug delivery and accelerated diabetic wound healing by chondroitin sulfate grafted alginate-based thermoreversible hydrogels. Mater. Sci. Eng. C (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2021.112169
M. Gruppuso, G. Turco, E. Marsich, D. Porrelli, Polymeric wound dressings, an insight into polysaccharide-based electrospun membranes. Appl. Mater. Today (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmt.2021.101148
S. Hasan, M.A. Hasan, M.U. Hassan, M. Amin, T. Javed, L. Fatima, Biopolymers in diabetic wound care management: a potential substitute to traditional dressings. Eur. Polym. J. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2023.111979
B.I. Oladapo, S.A. Zahedi, S.O. Ismail, D.B. Olawade, Recent advances in biopolymeric composite materials: future sustainability of bone-implant. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 150, 505 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2021.111505
N.G. Fischer, C. Aparicio, Junctional epithelium and hemidesmosomes: tape and rivets for solving the “percutaneous device dilemma” in dental and other permanent implants. Bioact Mater. 18, 178–198 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.03.019
Y. Li, Y. Xiao, C. Liu, The horizon of materiobiology: a perspective on material-guided cell behaviors and tissue engineering. Chem. Rev. 117, 4376–4421 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00654
N. Khosravi, R.S. Da Costa, J.E. Davies, New insights into spatio-temporal dynamics of mesenchymal progenitor cell ingress during peri-implant wound healing: Provided by intravital imaging. Biomaterials 273, 120837 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2021.120837
S.A. Shah, M. Sohail, M. Karperien, C. Johnbosco, A. Mahmood, M. Kousar, Chitosan and carboxymethyl cellulose-based 3D multifunctional bioactive hydrogels loaded with nano-curcumin for synergistic diabetic wound repair. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 227, 1203–1220 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.11.307
S.A. Shah, M. Sohail, S.A. Khan, M. Kousar, Improved drug delivery and accelerated diabetic wound healing by chondroitin sulfate grafted alginate-based thermoreversible hydrogels. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 126, 112169 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MSEC.2021.112169
A. da F. Ferreira, P. da S. Cunha, V.M. Carregal, P. de C. da Silva, M.C. de Miranda, M. Kunrath-Lima, M.I.A. de Melo, C.C.F. Faraco, J.L. Barbosa, F. Frezard, V. Resende, M.A. Rodrigues, A.M. de Goes, D.A. Gomes, Extracellular Vesicles from Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells Accelerate Migration and Activate AKT Pathway in Human Keratinocytes and Fibroblasts Independently of miR-205 Activity, Stem Cells Int. 2017, 1–14 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9841035.
J. Ding, X. Wang, B. Chen, J. Zhang, J. Xu, Exosomes derived from human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells stimulated by deferoxamine accelerate cutaneous wound healing by promoting angiogenesis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 1–12 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/9742765
D.R. Cooper, C. Wang, R. Patel, A. Trujillo, N.A. Patel, J. Prather, L.J. Gould, M.H. Wu, Human adipose-derived stem cell conditioned media and exosomes containing MALAT1 promote human dermal fibroblast migration and ischemic wound healing. Adv. Wound Care (New Rochelle). 7, 299–308 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1089/wound.2017.0775
G. Pelizzo, M.A. Avanzini, A. Icaro Cornaglia, A. De Silvestri, M. Mantelli, P. Travaglino, S. Croce, P. Romano, L. Avolio, G. Iacob, M. Dominici, V. Calcaterra, Extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal cells: perspective treatment for cutaneous wound healing in pediatrics. Regen. Med. 13, 385–394 (2018). https://doi.org/10.2217/rme-2018-0001
D. Ismail, A. Aboulkhair, Histological evaluation of the emerging role of adipose stem cells-derived exosomes in cutaneous wound healing in Albino rats, Egyptian. J. Histol. 41, 459–472 (2018). https://doi.org/10.21608/ejh.2018.4507.1015
B. Zhang, X. Wu, X. Zhang, Y. Sun, Y. Yan, H. Shi, Y. Zhu, L. Wu, Z. Pan, W. Zhu, H. Qian, W. Xu, Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell exosomes enhance angiogenesis through the Wnt4/β-catenin pathway. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 4, 513–522 (2015). https://doi.org/10.5966/sctm.2014-0267
L. Hu, J. Wang, X. Zhou, Z. Xiong, J. Zhao, R. Yu, F. Huang, H. Zhang, L. Chen, Exosomes derived from human adipose mensenchymal stem cells accelerates cutaneous wound healing via optimizing the characteristics of fibroblasts. Sci. Rep. 6, 32993 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep32993
Q. Shi, Z. Qian, D. Liu, J. Sun, X. Wang, H. Liu, J. Xu, X. Guo, GMSC-derived exosomes combined with a chitosan/silk hydrogel sponge accelerates wound healing in a diabetic rat skin defect model. Front. Physiol. (2017). https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2017.00904
S.-C. Tao, S.-C. Guo, M. Li, Q.-F. Ke, Y.-P. Guo, C.-Q. Zhang, Chitosan wound dressings incorporating exosomes derived from microRNA-126-overexpressing synovium mesenchymal stem cells provide sustained release of exosomes and heal full-thickness skin defects in a diabetic rat model. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 6, 736–747 (2017). https://doi.org/10.5966/sctm.2016-0275
L. Wang, L. Hu, X. Zhou, Z. Xiong, C. Zhang, H.M.A. Shehada, B. Hu, J. Song, L. Chen, Exosomes secreted by human adipose mesenchymal stem cells promote scarless cutaneous repair by regulating extracellular matrix remodelling. Sci. Rep. 7, 13321 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-12919-x
R. Dalirfardouei, K. Jamialahmadi, A.H. Jafarian, E. Mahdipour, Promising effects of exosomes isolated from menstrual blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell on wound-healing process in diabetic mouse model. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 13, 555–568 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/term.2799
D. Ti, H. Hao, C. Tong, J. Liu, L. Dong, J. Zheng, Y. Zhao, H. Liu, X. Fu, W. Han, LPS-preconditioned mesenchymal stromal cells modify macrophage polarization for resolution of chronic inflammation via exosome-shuttled let-7b. J. Transl. Med. 13, 308 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-015-0642-6
C. Li, Y. An, Y. Sun, F. Yang, Q. Xu, Z. Wang, Adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote wound healing through the WNT/β-catenin signaling pathway in dermal fibroblasts. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 18, 2059–2073 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12015-022-10378-0
A. Shabbir, A. Cox, L. Rodriguez-Menocal, M. Salgado, E. Van Badiavas, Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes induce proliferation and migration of normal and chronic wound fibroblasts, and enhance angiogenesis in vitro. Stem Cells Dev. 24, 1635–1647 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1089/scd.2014.0316
Y.J. Kim, S. mi Yoo, H.H. Park, H.J. Lim, Y.L. Kim, S. Lee, K.W. Seo, K.S. Kang, Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells stimulates rejuvenation of human skin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 493, 1102–1108 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BBRC.2017.09.056
Y. Liang, X. Zhao, T. Hu, Y. Han, B. Guo, Mussel-inspired, antibacterial, conductive, antioxidant, injectable composite hydrogel wound dressing to promote the regeneration of infected skin. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 556, 514–528 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCIS.2019.08.083
P. Ehsani, M.R. Farahpour, M. Mohammadi, S. Mahmazi, S. Jafarirad, Green fabrication of ZnO/magnetite-based nanocomposite - using Salvia officinalis extract with antibacterial properties enhanced infected full-thickness wound. Colloids Surf. A 628, 127362 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.127362
R. Augustine, A. Hasan, N.K. Patan, Y.B. Dalvi, R. Varghese, A. Antony, R.N. Unni, N. Sandhyarani, A.-E. Al Moustafa, Cerium oxide nanoparticle incorporated electrospun poly(3-hydroxybutyrate- co-3-hydroxyvalerate) membranes for diabetic wound healing applications. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 6, 58–70 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.8b01352
V.T. Arantes, A.A.G. Faraco, F.B. Ferreira, C.A. Oliveira, E. Martins-Santos, P. Cassini-Vieira, L.S. Barcelos, L.A.M. Ferreira, G.A.C. Goulart, Retinoic acid-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles surrounded by chitosan film support diabetic wound healing in in vivo study. Colloids Surf. B 188, 110749 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.110749
K. Khezri, M.R. Farahpour, S. Mounesi Rad, Efficacy of Mentha pulegium essential oil encapsulated into nanostructured lipid carriers as an in vitro antibacterial and infected wound healing agent. Colloids Surf. A 589, 124414 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.124414
J. Pires, S.T. Cargnin, S.A. Costa, V.D.G. Sinhorin, A.S. Damazo, A.P. Sinhorin, de R.C. Bicudo, L. Cavalheiro, de D.M.S. Valladão, A.R. Pohlmann, S.S. Guterres, S.R. Ferrarini, Healing of dermal wounds property of Caryocar brasiliense oil loaded polymeric lipid-core nanocapsules: formulation and in vivo evaluation. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 150 (2020) 5356. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2020.105356.
M. Liu, W. Chen, X. Zhang, P. Su, F. Yue, S. Zeng, S. Du, Improved surface adhesion and wound healing effect of madecassoside liposomes modified by temperature-responsive PEG-PCL-PEG copolymers. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 151, 105373 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2020.105373
M. Tiboni, S. Coppari, L. Casettari, M. Guescini, M. Colomba, D. Fraternale, A. Gorassini, G. Verardo, S. Ramakrishna, L. Guidi, B. Di Giacomo, M. Mari, R. Molinaro, M.C. Albertini, Prunus spinosa extract loaded in biomimetic nanoparticles evokes in vitro anti-inflammatory and wound healing activities. Nanomaterials 11, 36 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11010036
L.N. Kasiewicz, K.A. Whitehead, Lipid nanoparticles silence tumour necrosis factor α to improve wound healing in diabetic mice. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 4, 75–82 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/btm2.10123
V. Laghezza Masci, A. Taddei, T. Courant, O. Tezgel, F. Navarro, F. Giorgi, D. Mariolle, A. Fausto, I. Texier, Characterization of collagen/lipid nanoparticle-curcumin cryostructurates for wound healing applications. Macromol. Biosci. 19, 1800446 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/mabi.201800446
Y. Fu, J. Zhang, Y. Wang, J. Li, J. Bao, X. Xu, C. Zhang, Y. Li, H. Wu, Z. Gu, Reduced polydopamine nanoparticles incorporated oxidized dextran/chitosan hybrid hydrogels with enhanced antioxidative and antibacterial properties for accelerated wound healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 257, 117598 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117598
Acknowledgements
The listed author(s) are thankful to their representative universities for providing the literature services.
Funding
The authors declare that they have no known competing, financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EI: conceptualization, investigation, data curation, resources, validation, formal analysis, writing—original draft, writing-review and editing, supervision, resources.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Issaka, E. State-of-the-Art of Synthesized Exosomes and NPs-Based Biomimetic Nanoparticles for Wound Rehabilitation: A Review. Biomedical Materials & Devices 2, 241–274 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s44174-023-00112-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s44174-023-00112-w