Abstract
ChatGPT is one example of an artificial intelligence (AI) tool that is gaining attention in the field of language education due to its potential as a digital language learning assistant. ChatGPT allows for customized interactions and real-time feedback to improve language learning. Yet, there is a study void on English as a Foreign Language (EFL) teachers and students’ use of ChatGPT in language learning. To fill this void, this a cross-sectional survey study investigates the perceptions and preferences of the 80 EFL teachers and the 46 EFL students in East Java, Indonesia. The study’s primary objective is to gain insight into how they perceive about using ChatGPT to improve their language learning. The results revealed possible benefits, such as better language competency and individualized learning experiences, as well as problems, such as language accuracy and technological dependence. The study also highlights the importance of pedagogical support, curricular alignment, user-friendly interfaces, and compelling interactive activities for successful integration. In light of these results, this study suggests ways in which teachers might better include ChatGPT as a digital language learning assistant. This study contributes to the body of knowledge of ChatGPT’s function in EFL instruction and will guide the improvement of other digital tools for language learning.
Graphical Abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
The use of AI tools as digital language learning aids has gained a lot of attention in the field of language education in recent years. These resources have the potential to transform language instruction for practice, immediate feedback, and expert guidance [12]. ChatGPT, a language model developed by OpenAI, is one such AI tool that has received interest because it can generate text responses that are very similar to those of human beings [14, 23]. ChatGPT distinguishes itself from other chatbots and virtual assistants by acknowledging and challenging user assumptions and automatically answers questions using thousands of web resources [10]. Conversational engagements with users are enabled through ChatGPT by the application of deep learning algorithms and large-scale language models [3, 9]. As researchers delve deeper into the possibilities and preferences of ChatGPT, they guide future pedagogical practices and add to the growing body of knowledge about how to best use AI in language learning [16, 22]. As a result, the introduction of AI-powered technologies such as ChatGPT into the field of language education paves the way for innovative approaches to teaching foreign languages by providing students with individualized guidance and engaging activities.
There are a number of obstacles that make it difficult to learn EFL. As Kefalaki et al. [13] points out, traditional approaches to language learning frequently rely on standardized curriculum and teaching methods that lack personalization and have difficulty catering to students’ varying requirements. However, teachers in traditional classrooms sometimes lack the time and materials to adapt instruction to each student’s needs [18]. Students may feel left behind or unengaged with this one-size-fits-all approach, hindering language development [11]. One of the most important parts of learning a new language is getting constructive criticism on how one is doing [24]. When teaching EFL, it might be difficult for teachers to give each student customized feedback due to class sizes [7]. Therefore, students may not receive timely feedback on their language mistakes, reducing their opportunities to correct and enhance their proficiency. Without timely feedback, language learners may experience frustration, lose motivation, and struggle to make progress [22]. The need for novel approaches that can deliver individualized support and design interesting scenarios for language acquisition is therefore all the more pressing in light of these difficulties.
The usefulness of ChatGPT as a digital language learning assistant becomes apparent in this context [3]. Because of its features, ChatGPT can provide EFL students with one-on-one help that is unavailable from more conventional methods. By simulating real conversation and providing immediate feedback, ChatGPT creates a one-of-a-kind opportunity for individualized language study. Unlike more conventional approaches, ChatGPT can be modified to meet the needs of individual students by giving them individualized feedback and additional opportunity for practice [15, 17]. By analyzing student input with deep learning algorithms and large-scale language models, ChatGPT can help students improve their language skills by focusing on areas where they need the most help. Further, ChatGPT's conversational capabilities can make for a lively and interesting classroom setting [18, 21]. ChatGPT allows for students to practice their language abilities in a natural setting by having real conversations with one another [10, 19]. By engaging in meaningful conversation, students are able to practice what they have learned, increase their fluency, and boost their self-esteem.
As a digital language learning assistant, ChatGPT offers a viable alternative to improve the efficacy and efficiency of EFL instruction by tackling the difficulties of individualization and timely feedback [25]. It has the potential to revolutionize the way in which language is taught and learned by offering customized support, real-time feedback, and interesting dialogue [2]. On the other hand, traditional methods of teaching EFL might have problems catering to students’ unique needs and failing to give them timely, meaningful feedback on their progress. The advent of ChatGPT as a digital language learning aid provides an innovative approach to overcoming these obstacles [19]. By allowing users to tailor their language lessons and receive immediate feedback, ChatGPT improves the quality of EFL teaching and fosters more interesting and productive language learning [3, 14]. Because to ChatGPT’s potential, teachers may meet the needs of their students of all backgrounds in a more effective and interesting way while fostering their language acquisition [26].
Recent studies have examined how AI technologies, such as ChatGPT, can help language acquisition. The incorporation of ChatGPT into environments designated for language learning has demonstrated promise in terms of boosting a variety of facets related to the acquisition of languages [8]. ChatGPT has shown promise in a number of ways, one of which being the speed with which it can deliver feedback [9, 14]. In traditional language learning, teachers personally check and modify students' work after a given period. ChatGPT analyses students’ responses in real time, allowing them to discover and rectify errors [8]. This immediate feedback mechanism promotes a continuous learning cycle, allowing students to more effectively correct their errors and reinforce their language skills [3, 6]. In addition to providing instant feedback and interactive conversations, ChatGPT has been found to assist students with language practice [4, 8]. The language model can generate prompts, exercises, and sample dialogues tailored to the individual needs of learners [1, 5, 6, 12]. This personalized practice enables students to focus on specific language areas they need to improve, offering targeted reinforcement and facilitating their language development.
Studies using ChatGPT as a language learning assistance show promising results. ChatGPT’s helpful and interactive responses can help students practice their language abilities without judgement or humiliation [4, 6, 8, 10, 14, 20]. This pleasant learning experience boosts learners’ self-confidence, encourages active involvement, and keeps them studying languages. While these results illustrate the potential advantages of including ChatGPT as a language learning assistant, more thorough study into the opinions and experiences of both EFL teachers and students is still necessary. Understanding these viewpoints will reveal ChatGPT’s strengths, weaknesses, and applications in real-world language acquisition. This current research might inform pedagogical practices and bridge the gap between the exciting potential of AI technology and their actual deployment in EFL classrooms. The existing previous studies have demonstrated the potential of ChatGPT in language learning contexts, demonstrating its capacity to provide immediate feedback, engage students in interactive conversations, and facilitate language practice. These data imply that ChatGPT can improve EFL learners’ competency, confidence, and motivation. However, more research is needed to determine how EFL teachers and students perceive ChatGPT as a digital language learning assistant. Insights gained from this current study can provide EFL teachers and students better incorporate AI tools, such ChatGPT, into their EFL classrooms.
Despite the promising results shown in studies regarding ChatGPT’s role as a language learning assistant, there are several considerations and limitations that merit attention. One significant concern is the potential for ChatGPT’s responses to lack nuanced understanding and contextual awareness, which could lead to inaccuracies or misinterpretations of users’ input. Additionally, overreliance on ChatGPT might hinder the development of critical language skills such as creativity and independent problem-solving, as students and teachers may overly depend on the model’s predefined responses. Moreover, the absence of emotional intelligence in ChatGPT may limit its ability to provide empathetic and personalized support, crucial in language learning environments with complex emotional and cultural nuances. Furthermore, there is a risk of overemphasizing correctness over effective communication, potentially leading learners to prioritize conforming to predefined language norms rather than expressing themselves authentically. Therefore, while ChatGPT shows promise in enhancing language learning experiences, careful consideration of these limitations is essential for its integration into EFL classrooms.
This study aims to address current gaps in the literature by investigating the perceptions of EFL teachers and students in East Java, Indonesia regarding the potential of ChatGPT as a digital language learning assistant. By delving into their viewpoints, this study seeks not only to provide detailed insights into the feasibility, benefits, challenges, and limitations associated with the integration of ChatGPT into EFL classrooms within the local educational context but also to contribute to the broader knowledge base on AI in education. Through this exploration, the study aims to uncover unique insights and practices that may have broader implications for language education globally. By understanding how ChatGPT is perceived and utilized in a specific educational context, this research can offer valuable lessons and strategies that can be adapted and applied in diverse educational settings worldwide. Moreover, by critically examining the impact of ChatGPT on language learning experiences, this study intends to contribute to the ongoing discourse on the role of AI technologies in shaping the future of education. The findings of this investigation are expected not only to inform the development of localized pedagogical practices in East Java but also to stimulate further research and innovation in the broader field of AI-enhanced language learning.
2 Method
2.1 Research design
This study employed a cross-sectional survey design to investigate the perceptions and experiences of EFL teachers and students in East Java, Indonesia regarding the integration of ChatGPT as a language learning assistant. A survey approach was chosen due to its efficiency in collecting data from a large number of participants within a short period. The cross-sectional survey design allowed for the collection of data at a specific point in time, providing a snapshot of participants’ views and experiences. This design facilitated a comprehensive exploration of various aspects, such as the usefulness of ChatGPT, satisfaction with feedback mechanisms, and attitudes towards AI technologies in language learning.
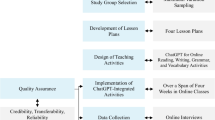
By utilizing the survey design, the researcher aimed to gain insights into the current state of perceptions and experiences related to ChatGPT. The data collected from a diverse group of EFL teachers and students allowed for a broad representation of perspectives. It is important to note that the cross-sectional survey design has limitations. It does not establish causal relationships or track changes over time. Additionally, self-report measures used in surveys may introduce response bias. However, efforts were made to ensure confidentiality and anonymity, and clear instructions were provided to encourage honest responses. In summary, the cross-sectional survey design was chosen for its efficiency in gathering data from EFL teachers and students in East Java, Indonesia. It provided a snapshot of their perceptions and experiences regarding the integration of ChatGPT as a language learning assistant. While the design has limitations, it served as an effective methodological approach for exploring the current state of perceptions and experiences related to ChatGPT in language education (Fig. 1).
2.2 Participants
The participants in this study consisted of 80 EFL teachers and 46 EFL students from various educational institutions in East Java, Indonesia. Convenience sampling was employed to select participants based on their accessibility and willingness to participate. Participants were approached through communication with school administrators and through announcements in educational institutions, ensuring a diverse representation. Inclusion criteria involved being an active EFL teacher or student, while exclusion criteria considered individuals not currently engaged in EFL education. The difference in participant numbers between EFL teachers and students reflects the varied distribution of educators and learners in the sampled institutions. While the study acknowledges the potential biases and limited generalizability associated with convenience sampling, efforts were made to mitigate these concerns. Participants were recruited from different schools and universities to enhance the diversity of the sample, aiming for a more comprehensive representation of perspectives within the EFL education context in East Java. This approach allows for a nuanced understanding of the impact of ChatGPT on both teaching and learning aspects in EFL classrooms. Efforts were also made to include participants with varying levels of teaching experience and language proficiency, further enriching the dataset. Including both EFL teachers and students in the study is crucial for obtaining a comprehensive understanding of the integration of ChatGPT as a language learning assistant. EFL teachers provide valuable insights into the pedagogical implications and challenges, while EFL students’ experiences shed light on their engagement, satisfaction, and perceived benefits of using ChatGPT as a language learning tool. This dual perspective offers a more holistic and nuanced exploration of perceptions and experiences related to ChatGPT in the context of EFL education in East Java, Indonesia.
2.3 Survey instrument
The survey instrument used in this study underwent a rigorous development process to ensure its validity and reliability. Expert judgments were sought from two Ph.D. scholars with expertise in technology-enhanced language learning. These experts played a critical role in refining the questionnaire, which aimed to assess the perceptions and experiences of EFL teachers and students regarding ChatGPT as a language learning assistant. Both experts are actively engaged in research and hold doctoral degrees in their respective fields, specializing in technologies and language education. They provided valuable feedback on the initial draft of the survey, focusing on the clarity, relevance, and alignment of the 14 closed-ended questions tailored for both EFL teachers and students. Specifically, they offered insights on the appropriateness of language, comprehensibility of questions, and relevance of content to ensure the survey effectively captured the participants’ perspectives on the potential benefits, challenges, and strategies associated with integrating ChatGPT into language education. In addition, demographic information was collected, including gender, age, educational background, and frequency of technology use in language learning/teaching. Similarly, EFL students were provided with a questionnaire comprising 14 items to gauge their perceptions of the potential benefits, challenges, and strategies related to using ChatGPT as a digital language learning assistant. The questionnaire also included a section to gather demographic information, including gender, age, educational background, and frequency of technology use in language learning. The instrument used in this research was statistically examined using SPSS version 26 and demonstrated high reliability, as evidenced by a rather high Cronbach/s alpha coefficient (α = 0.842). Moreover, the composite reliability value exceeded 0.70, further affirming the validity and reliability of the instrument in assessing the encounters both EFL teachers’ and EFL students’ perceptions in this study.
2.4 Data collection procedure
The data collection procedure involved distributing the survey questionnaire to the participants over the course of 1 week. The questionnaire was administered electronically, utilizing online survey platforms to ensure efficiency and convenience for participants. Clear instructions and guidelines were provided to ensure consistency in completing the questionnaire. Efforts were made to maximize participation and ensure the representativeness of the sample. Participants were encouraged to complete the questionnaire within the given timeframe, and reminders were sent to enhance the response rate.
2.5 Data analysis
Once the data collection period concluded, the collected data were analyzed quantitatively using statistical software. Descriptive statistics, such as means, frequencies, and percentages, were computed to summarize the responses for each item in the questionnaire. This quantitative analysis provided an overview of participants’ perspectives on the potential benefits, challenges, and strategies related to ChatGPT as a language learning assistant. In addition to analyzing the responses to closed-ended questions, demographic information collected from participants, including gender, age, educational background, and frequency of technology use in language learning/teaching, was also examined. This analysis allowed for insights into the characteristics of the participants and potential variations in responses based on these demographic factors. Table 1 presents the demographic information of this current study.
The demographic characteristics of the participants in this study, including EFL teachers and EFL students, provide valuable insights into the profile of the respondents.
Regarding the gender distribution, among the EFL teachers, 47 (58.75%) were male, while 33 (41.25%) were female. This indicates a slightly higher representation of male teachers in the sample. Similarly, among the EFL students, 32 (69.57%) were male, and 14 (30.43%) were female.
In terms of age, the EFL teachers in the study exhibit a varied distribution. The majority of teachers (36, or 45%) fell within the 35–44 age range, indicating a considerable number of middle-aged teachers. Additionally, there were 10 teachers (12.5%) in the 25–34 age range, 24 teachers (30%) in the 45–54 age range, and 8 teachers (10%) who were 55 years old or above. It is worth noting that no teachers in the sample were in the 18–24 age range.
Regarding educational background, a diverse range of qualifications was observed among the EFL teachers. The largest group consisted of teachers with a Bachelor's degree (37, or 46.25%), followed by those with a Master’s degree (38, or 47.5%). There were also a smaller number of teachers with a Doctorate/Ph.D. (5, or 6.25%) and no teachers with a high school diploma.
The frequency of technology use in language learning/teaching among the EFL teachers varied. The majority of teachers (52, or 65%) reported using technology frequently in their language teaching practices, while a smaller number reported using it occasionally (14, or 17.5%). Only a few teachers indicated that they rarely (2, or 2.5%) or always (2, or 2.5%) utilized technology in language learning/teaching.
These demographic characteristics provide a comprehensive understanding of the participants’ background and experiences, which can further inform the analysis and interpretation of the findings in relation to the integration of ChatGPT as a digital language learning assistant.
2.6 Ethical considerations
Throughout the research process, I prioritized ethical considerations, recognizing the importance of safeguarding the rights and well-being of participants. To mitigate potential participant bias or pressure to participate, I took deliberate steps to ensure informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. This involved a transparent and comprehensive explanation of the research objectives, procedures, confidentiality measures, anonymity assurances, and their unequivocal right to withdraw without facing any penalty. Special attention was paid to fostering an environment that encouraged voluntary and unbiased participation. The research adhered strictly to ethical guidelines for studies involving human subjects, emphasizing the protection of the participants’ rights throughout the entire process. The study, employing a cross-sectional survey design and utilizing a questionnaire specifically developed for this research, remained committed to upholding ethical principles in its pursuit of valuable insights into the impact of ChatGPT on language learning in EFL classrooms. This study was approved unconditionally by the Ethics Committee of Universitas Negeri Malang (KEP UM).
3 Findings
3.1 EFL teachers’ perceptions of the potential of ChatGPT as a digital language learning assistant
The results of this study provide important insight into how EFL teachers perceive ChatGPT’s potential as a digital language learning assistant. This section analyzes questionnaire responses to reveal what EFL teachers perceive ChatGPT can do and how it can improve their language learning. The following paragraphs present a summary of the key findings, highlighting teachers’ perspectives on the potential benefits, challenges, and strategies related to using ChatGPT as a digital language learning assistant. Table 2 present the results of the questionnaire from EFL teachers.
The findings of the study provide a deep understanding of EFL teachers’ perceptions of ChatGPT as a digital language learning assistant. The statistical analysis of the data reveals important insights into the potential benefits, challenges, and strategies associated with integrating ChatGPT in EFL classrooms.
In terms of the potential benefits, the results indicate that a majority of EFL teachers (63.7%) perceive that utilizing ChatGPT can benefit EFL students in terms of language acquisition and proficiency. This finding is supported by a mean score of 4.08, suggesting a generally positive perception among the participants. The relatively low standard deviation of 0.839 indicates a degree of agreement among the teachers regarding the potential effectiveness of ChatGPT in enhancing language learning outcomes. This statistical evidence supports the argument that ChatGPT can be a valuable tool for improving students’ language skills.
Furthermore, the findings suggest that ChatGPT has the potential to enhance EFL students’ engagement and motivation in language learning activities. A significant proportion of EFL teachers (56.3%) hold this perception, as indicated by a mean score of 4.13 and a relatively low standard deviation of 0.862. This statistical evidence supports the notion that ChatGPT can serve as a tool to promote active student participation and increase their motivation to engage in language learning tasks. Increased engagement and motivation are key factors in facilitating effective language acquisition and skill development.
Additionally, the results indicate that EFL teachers believe ChatGPT can facilitate students’ access to authentic language resources and knowledge. A substantial proportion of teachers (36.2%) express this perception, with a mean score of 3.69 and a standard deviation of 1.038. This statistical evidence suggests that integrating ChatGPT can provide EFL students with opportunities to explore authentic language materials, which can contribute to their overall language proficiency and cultural understanding.
While the findings highlight the potential benefits of ChatGPT, they also shed light on the challenges and limitations associated with its use. For instance, a significant number of EFL teachers (37.5%) acknowledge that EFL students may face challenges when using ChatGPT as a language learning assistant. This finding is supported by a mean score of 3.19 and a relatively high standard deviation of 1.202. The wide range of responses suggests a variability in teachers' perceptions regarding the challenges students might encounter. This statistical evidence emphasizes the importance of addressing these challenges, such as technical difficulties or limitations in generating accurate language output, to ensure a successful integration of ChatGPT in EFL classrooms.
Moreover, the findings indicate that EFL teachers may have concerns about the accuracy and reliability of language generated by ChatGPT for EFL students’ learning purposes. This perception is expressed by a significant proportion of teachers (32.5%), as supported by a mean score of 3.05 and a standard deviation of 1.113. The statistical evidence suggests a need to address these concerns and ensure that the language generated by ChatGPT aligns with students’ learning goals and objectives.
Additionally, the findings reveal potential challenges and obstacles in integrating ChatGPT into EFL curricula, as acknowledged by a considerable number of teachers (40%). This perception is supported by a mean score of 3.37 and a standard deviation of 1.048. The statistical evidence underscores the importance of careful planning and implementation strategies to overcome these challenges and effectively integrate ChatGPT into EFL instructional practices.
Furthermore, the results indicate that EFL teachers may require additional training and skills to effectively incorporate ChatGPT into their teaching practices. This perception is expressed by a significant proportion of teachers (55%), as evidenced by a mean score of 3.49 and a standard deviation of 0.914. The statistical evidence highlights the need for professional development opportunities and support for teachers to enhance their confidence and competence in using ChatGPT as a language learning tool.
In conclusion, the comprehensive analysis of the findings reveals the multifaceted perceptions of EFL teachers regarding ChatGPT as a digital language learning assistant. While the results highlight the potential benefits of using ChatGPT in terms of language acquisition, engagement, and access to authentic resources, they also draw attention to the challenges and concerns that need to be addressed for successful integration. The statistical evidence provides a rigorous foundation for understanding the complexities surrounding the use of ChatGPT in EFL classrooms and supports the argument for careful planning, training, and ongoing support to maximize the benefits and minimize the limitations associated with its implementation.
3.2 EFL students’ perceptions of the potential of ChatGPT as a digital language learning assistant
The following section presents the findings of the study, focusing on EFL students’ perceptions of ChatGPT as a digital language learning assistant. Through a comprehensive analysis of the collected data, this section explores the students’ perspectives on the potential benefits, challenges, and overall effectiveness of integrating ChatGPT into their language learning experiences. Table 3 presents the results of the questionnaire from the EFL students’ perceptions.
Based on the findings, it is evident that EFL students perceive ChatGPT as a potentially beneficial tool for their language acquisition and proficiency in English. The majority of students (63%) expressed a strong agreement (SA) with the statement, highlighting the positive impact of utilizing ChatGPT. This perception is further supported by the absence of any respondents who disagreed or strongly disagreed with the statement (0%). The narrow standard deviation (Std. Dev. = 0.620) indicates a high level of consensus among the students.
Similarly, the findings reveal that ChatGPT has the potential to enhance students’ engagement and motivation in language learning activities. A substantial percentage of students (63%) strongly agreed (SA) with this statement, indicating their belief in the positive influence of ChatGPT on their motivation levels. The absence of any respondents who disagreed or strongly disagreed demonstrates a consensus among the students regarding the motivational benefits of using ChatGPT. The small standard deviation (Std. Dev. = 0.620) suggests a high level of agreement among the students.
Furthermore, students perceived the use of ChatGPT for personalized feedback and individualized instruction as helpful in their EFL learning. A significant proportion of students (39.1%) expressed a strong agreement (SA) with this statement, emphasizing the potential of ChatGPT to cater to their individual learning needs. Additionally, a notable percentage of students (50%) agreed (A) with the statement, further supporting the belief in the usefulness of ChatGPT for personalized feedback. The moderate standard deviation (Std. Dev. = 0.713) indicates some variation in the responses but still reflects a general agreement among the students.
Regarding access to authentic language resources and knowledge, the findings indicate that students perceive ChatGPT as a facilitator. Nearly half of the students (47.8%) agreed (A) that ChatGPT can enhance their access to authentic language resources. A smaller percentage of students (26.1%) strongly agreed (SA) with this statement. The absence of any respondents who disagreed (D) or strongly disagreed (SD) suggests a general consensus among the students regarding the facilitative role of ChatGPT in accessing authentic language resources. The moderate standard deviation (Std. Dev. = 0.855) indicates some variability in the responses.
However, despite the perceived benefits, the findings also highlight potential challenges and limitations associated with the use of ChatGPT. A notable percentage of students (26.1%) expressed concerns or limitations when using ChatGPT as a language learning assistant. Some students (17.4%) agreed (A) that they may face challenges or limitations, while a smaller percentage (8.7%) strongly agreed (SA). This indicates the recognition of potential difficulties that students may encounter when utilizing ChatGPT. The higher standard deviation (Std. Dev. = 1.278) suggests some diversity in the students’ responses, reflecting varying degrees of concern and limitations.
In terms of accuracy and reliability, some students (26.1%) expressed concerns regarding the language generated by ChatGPT for their learning purposes. While a considerable percentage (28.3%) agreed (A) with this statement, an almost equal proportion of students (26.1%) strongly agreed (SA). This indicates a certain level of skepticism among the students regarding the accuracy and reliability of the language produced by ChatGPT. The standard deviation (Std. Dev. = 1.107) suggests some variability in the students’ perceptions.
The findings also shed light on potential challenges or obstacles that may arise in using ChatGPT for EFL learning. A significant proportion of students (43.5%) agreed (A) that potential challenges or obstacles can arise, while a smaller percentage (10.9%) strongly agreed (SA). This implies that students recognize the existence of potential hurdles when integrating ChatGPT into their language learning journey. However, a noteworthy percentage of students (37%) remained neutral (N) on this statement. The moderate standard deviation (Std. Dev. = 0.810) indicates some variation in the students’ perceptions.
It is evident from the findings that students acknowledge the need for additional support and guidance to effectively utilize ChatGPT as a language learning assistant. A considerable proportion of students (34.8%) expressed a strong agreement (SA) with this statement, indicating their recognition of the importance of support. Additionally, a notable percentage of students (32.6%) agreed (A) with the statement, further emphasizing the need for assistance. The standard deviation (Std. Dev. = 1.087) suggests some diversity in the students’ responses, reflecting varying degrees of perceived support requirements.
Moreover, the findings indicate that ChatGPT may not be suitable for all students’ learning styles and preferences. A significant percentage of students (32.6%) agreed (A) with this statement, while a smaller proportion (21.7%) strongly agreed (SA). This suggests that students acknowledge the potential mismatch between ChatGPT and their individual learning styles and preferences. The standard deviation (Std. Dev. = 1.026) indicates some variability in the students’ perceptions.
The findings also highlight the importance of proper training and support in effectively utilizing ChatGPT as a language learning assistant. The majority of students (60.9%) agreed (A) with this statement, while a notable percentage (26.1%) strongly agreed (SA). This indicates the students’ recognition of the role of training and support in optimizing their use of ChatGPT. The small standard deviation (Std. Dev. = 0.674) suggests a high level of agreement among the students.
Furthermore, the findings emphasize the significance of clear guidelines and expectations for using ChatGPT in enhancing its effectiveness in students’ language learning. The majority of students (67.4%) agreed (A) with this statement, while a considerable proportion (28.3%) strongly agreed (SA). This demonstrates the students’ belief in the positive impact of well-defined guidelines. The small standard deviation (Std. Dev. = 0.524) suggests a high level of consensus among the students.
Lastly, the findings indicate that engaging in collaborative learning activities involving ChatGPT can promote peer interaction and language practice. A substantial percentage of students (45.7%) agreed (A) with this statement, while an equal proportion (45.7%) strongly agreed (SA). This suggests that students recognize the potential of ChatGPT in facilitating peer interaction and language practice. The standard deviation (Std. Dev. = 0.706) indicates some variability in the students’ perceptions but still reflects a general agreement.
In conclusion, the findings provide valuable insights into EFL students’ perceptions of ChatGPT as a digital language learning assistant. While students perceive numerous potential benefits, such as language acquisition, engagement, and access to resources, they also acknowledge challenges and limitations, including concerns about accuracy and reliability. The findings emphasize the importance of support, training, clear guidelines, and collaborative activities to optimize the use of ChatGPT. These insights contribute to a comprehensive understanding of the students’ perspectives and inform future instructional practices in digital language learning.
4 Discussion
The findings of this study offer crucial insights into the perspectives of both EFL teachers and students regarding the potential of ChatGPT as a digital language learning assistant. The investigation aimed to uncover a comprehensive understanding of the views held by participants in relation to the integration of ChatGPT in EFL courses. The results illuminate a range of opinions, revealing both favorable and unfavorable perceptions. While some respondents acknowledged the benefits of ChatGPT, such as immediate feedback and interactive language practice, concerns were raised by both teachers and students. Specifically, challenges were identified in terms of the model's occasional lack of contextual understanding, potential inaccuracies in responses, and limitations in providing personalized and empathetic feedback.
The majority of students studying EFL who participated in this research believed that ChatGPT may be an effective instrument for English language learning and improvement. These findings are consistent with those found in recent research [12] that demonstrated the beneficial impact that AI technologies have on language learning. The students enjoyed the opportunity to practice their language skills without fear of being judged or embarrassed [6, 10]. ChatGPT's capacity to give rapid feedback and engage students in engaging dialogues was well received by the students [18]. This uplifting educational experience does more than just bolster the learners’ self-confidence; it also stimulates active involvement and a sense of motivation [14]. According to Lund and Wang [16] and Su and Yang [22], the findings provide credence to the hypothesis that ChatGPT has the potential to increase students' involvement and motivation in activities related to language acquisition.
Moreover, the students also expressed a strong belief that ChatGPT serves as a valuable tool for providing tailored feedback and individualized instruction, catering to their specific educational needs. They highlighted ChatGPT's ability to assess their responses in real-time and deliver focused reinforcement, which aligns with previous research emphasizing AI tools’ potential in offering personalized support [6]. This individualized approach allows students to concentrate on specific language skills they perceive as needing improvement, thereby facilitating their overall language proficiency [5, 8, 11, 24]. EFL teachers echoed these sentiments, emphasizing ChatGPT’s potential to provide targeted feedback that addresses students’ individual learning gaps. They observed that such personalized practice enables students to focus on specific aspects of language where they require additional support, thereby enhancing their language acquisition process. This perspective is supported by recent studies advocating for AI tools’ role in delivering customized learning experiences tailored to students’ unique needs and learning styles. However, it is important to acknowledge certain students’ concerns regarding the accuracy and reliability of language generated by ChatGPT. These concerns align with earlier research highlighting ongoing challenges in AI’s ability to consistently produce accurate language output [9, 14]. Such feedback underscores the need for continual improvements in AI technologies to ensure they meet the rigorous standards expected in language learning environments. While students and teachers recognize ChatGPT’s potential for delivering personalized instruction and targeted feedback, ongoing developments are crucial to address concerns related to language accuracy and reliability. These insights contribute to a nuanced understanding of ChatGPT’s role in language education, highlighting both its strengths and areas for further improvement in AI-assisted learning environments.
The findings also show that ChatGPT may be able to improve students’ access to real-world language resources, which is an essential component of language learning. The students viewed ChatGPT's ability to automatically answer queries by utilizing thousands of online resources as a useful tool for facilitating learning. This is consistent with findings from earlier research that highlighted the potential of AI systems to provide access to authentic language resources [19]. According to Hassani and Silva [10], the presence of real language materials in a classroom can enhance students' language learning experiences and introduce them to a wide range of linguistic situations. However, it is essential to address the difficulties and roadblocks that students can have when utilizing ChatGPT, as was noted by a sizeable fraction of the students who participated in this study. These obstacles may include the requirement for additional help and direction in addition to technical difficulties [1, 21, 25]. Other limits of AI-generated language may also be a factor.
The findings from both EFL teachers and students shed light on the indispensable role of receiving tailored instruction and support to effectively utilize ChatGPT as a language learning assistant. The students expressed a strong preference for guidance and assistance from their teachers in maximizing the benefits of ChatGPT. They emphasized the value of teachers providing structured training sessions and ongoing assistance to help them navigate the complexities of using ChatGPT for language learning tasks. This sentiment resonates with earlier research emphasizing the crucial role of teacher support in facilitating the integration of AI tools in educational contexts [4, 14, 17]. Similarly, EFL teachers highlighted the importance of providing clear rules and expectations to students regarding the use of ChatGPT. They emphasized the need for establishing guidelines that outline appropriate usage, expectations for interaction with the tool, and strategies for incorporating ChatGPT into language learning activities. This aligns with previous studies stressing the significance of well-defined protocols in AI-assisted language learning environments [13, 18, 21]. Teachers emphasized that clear guidelines not only help students navigate ChatGPT effectively but also ensure its integration aligns with instructional objectives and promotes meaningful language learning outcomes. These nuanced insights underscore the pivotal role of both pedagogical support from teachers and structured guidelines in optimizing the educational benefits of ChatGPT for language learning.
The findings also indicate that collaborative learning activities employing ChatGPT may be able to increase peer interaction as well as language practice. The students noted that ChatGPT’s capacity to encourage peer contact through conversational interactions was one of the platform’s many strengths. This outcome is consistent with findings from earlier studies [10, 19, 20] that have highlighted the potential of AI technologies in boosting peer collaboration and communication. Students can improve their fluency and their language skills through the use of collaborative learning activities [8]. These activities can provide students with opportunity to practice their language skills in a natural context. On the other hand, it is essential to address the issues that have been brought up by students who believe that ChatGPT may not be appropriate for all ways of learning and preferences. According to Ariyaratne et al. [2], this finding points to the necessity of additional research into the flexibility and customisation elements of ChatGPT in order to better accommodate various learning styles.
As a result, the outcomes of this research offer insightful perspectives on how EFL teachers and students view ChatGPT’s capabilities as a digital language learning assistant. The study provides evidence that ChatGPT may have positive effects on language learning, student engagement, access to resources, personalized feedback, and individualized training. However, the study also underlines the obstacles and limitations associated with ChatGPT. These challenges and limitations include concerns regarding accuracy and reliability, the requirement for additional help and guidance, and the mismatch with individual learning styles and preferences. These findings not only add to the current body of information concerning the role of AI in language instruction, but they also have the potential to serve as a roadmap for the development of effective pedagogical approaches for the incorporation of ChatGPT into EFL classes. In order to overcome the constraints that have been observed and to investigate the adaptability and customization characteristics of ChatGPT in greater depth, additional study is required.
5 Conclusion
This study’s findings offer crucial insights into how both the EFL teachers and students perceive the utility of ChatGPT as a digital language learning assistant. The results indicate that ChatGPT holds the potential to not only enhance students’ interest in learning English but also to bolster their motivation and facilitate access to more authentic materials, as reported by the students. Furthermore, both students and teachers recognize the value of the tailored feedback and individualized training provided by ChatGPT in facilitating EFL acquisition, empowering students with increased opportunities for independent study and practice. Yet, the study also brings to light certain concerns voiced by both the EFL teachers and students regarding the use of ChatGPT. The students worry about the correctness and reliability of the language generated by the model, which may pose barriers to its effective utilization as a language learning assistant. Additionally, both students and teachers emphasize the importance of comprehensive training and clear instructions for utilizing ChatGPT, underscoring the need for additional support and guidance. These findings hold significant implications for the integration of ChatGPT and other AI technologies in language learning contexts. While this study showcases the promising aspects of ChatGPT, it also underscores the importance of addressing concerns and constraints to fully realize its potential. Incorporating ChatGPT into EFL classrooms should be informed by the outcomes of this research and attentive to the perspectives of both students and teachers. It is essential to acknowledge the limitations of this study. The small sample size may limit the generalizability of the results to the broader population of EFL teachers and students. Additionally, while the study captures insights from both students and teachers, future research endeavors should aim to further explore their perspectives and investigate pedagogical strategies and instructional practices that can optimize ChatGPT’s role in language acquisition.
Data Availability
The data and materials supporting the findings of this study are available upon request. Researchers interested in accessing the data can contact Joko Slamet at joko.slamet.2202219@students.um.ac.id to obtain the necessary information and make arrangements for data access.
Abbreviations
- AI:
-
Artificial intelligence
- EFL:
-
English as a Foreign Language
- SD:
-
Strongly disagree
- D:
-
Disagree
- N:
-
Neutral
- A:
-
Agree
- SA:
-
Strongly agree
- Std. Dev.:
-
Standard deviation
References
Ali JKM, Shamsan MAA, Hezam TA, Mohammed AA. Impact of ChatGPT on learning motivation: teachers and students’ voices. J Engl Stud Arabia Felix. 2023;2(1):41–9.
Ariyaratne S, Iyengar KP, Nischal N, et al. A comparison of ChatGPT-generated articles with human-written articles. Skeletal Radiol. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-023-04340-5.
Biswas SS. Role of chat GPT in public health. Ann Biomed Eng. 2023;51(5):868–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-023-03172-7.
Cai Q, Lin Y, Yu Z. Factors influencing learner attitudes towards ChatGPT-assisted language learning in higher education. Int J Hum Comput Interact. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1080/10447318.2023.2261725.
Chan CKY, Hu W. Students’ voices on generative AI: perceptions, benefits, and challenges in higher education. Int J Educ Technol High Educ. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-023-00411-8.
Chen H, Yuan K, Huang Y, Guo L, Wang Y, Chen J. Feedback is all you need: from ChatGPT to autonomous driving. Science China Inf Sci. 2023;66(6): 166201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-023-3740-x.
Chiu TKF, Moorhouse BL, Chai CS, Ismailov M. Teacher support and student motivation to learn with artificial intelligence (AI) based chatbot. Interact Learn Environ. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2023.2172044.
Duha MSU. ChatGPT in education: an opportunity or a challenge for the future? TechTrends. 2023;67(3):402–3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11528-023-00844-y.
Haman M, Školník M. Behind the ChatGPT hype: are its suggestions contributing to addiction? Ann Biomed Eng. 2023;51(6):1128–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-023-03201-5.
Hassani H, Silva ES. The role of ChatGPT in data science: how AI-assisted conversational interfaces are revolutionizing the field. Big Data and Cogn Comput. 2023;7(2):62. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc7020062.
Hendriani S, Naimah N, Yunita W, Yulnetri Y, Putra HE. EFL Learners’ preference of grammar learning model amid Covid-19 pandemic: a mixed-methods study. Int J Instr. 2023;16(2):853–70. https://doi.org/10.29333/iji.2023.16245a.
Kasneci E, Sessler K, Küchemann S, Bannert M, Dementieva D, Fischer F, Gasser U, Groh G, Günnemann S, Hüllermeier E, Krusche S, Kutyniok G, Michaeli T, Nerdel C, Pfeffer J, Poquet O, Sailer M, Schmidt A, Seidel T, Kasneci G. ChatGPT for good? On opportunities and challenges of large language models for education. Learn Individ Differ. 2023;103: 102274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2023.102274.
Kefalaki M, Diamantidaki F, Rudolph J. Editorial 5(SI1): technology and education: innovation or hindrance? J Appl Learn Teach. 2022. https://doi.org/10.37074/jalt.2022.5.s1.1.
Kim S-G. Using ChatGPT for language editing in scientific articles. Maxillofac Plastic Reconstruct Surg. 2023;45(1):13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40902-023-00381-x.
Liebrenz M, Schleifer R, Buadze A, Bhugra D, Smith A. Generating scholarly content with ChatGPT: ethical challenges for medical publishing. Lancet Digit Health. 2023;5(3):e105–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2589-7500(23)00019-5.
Lund BD, Wang T. Chatting about ChatGPT: how may AI and GPT impact academia and libraries? Library Hi Tech News. 2023;40(3):26–9. https://doi.org/10.1108/LHTN-01-2023-0009.
Qureshi R, Shaughnessy D, Gill KAR, Robinson KA, Li T, Agai E. Are ChatGPT and large language models “the answer” to bringing us closer to systematic review automation? Syst Rev. 2023;12(1):72. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-023-02243-z.
Rudolph J, Tan S, Tan S. ChatGPT: Bullshit spewer or the end of traditional assessments in higher education? J Appl Learn Teach. 2023. https://doi.org/10.37074/jalt.2023.6.1.9.
Seetharaman R. Revolutionizing medical education: can ChatGPT boost subjective learning and expression? J Med Syst. 2023;47(1):61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-023-01957-w.
Shaikh S, Yayilgan SY, Klimova B, Pikhart M. Assessing the usability of ChatGPT for formal English language learning. Eur J Investig Health Psychol Educ. 2023;13(9):1937–60.
Shen Y, Heacock L, Elias J, Hentel KD, Reig B, Shih G, Moy L. ChatGPT and other large language models are double-edged swords. Radiology. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.230163.
Su (苏嘉红) J, Yang (杨伟鹏) W. Unlocking the power of ChatGPT: a framework for applying generative AI in education. ECNU Rev Educ. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1177/20965311231168423
Tang G. Academic journals cannot simply require authors to declare that they used ChatGPT. Irish J Med Sci. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-023-03374-x.
Tran OTT, Pham VPH. The effects of online peer feedback on students’ writing skills during corona virus pandemic. Int J Instr. 2023;16(1):881–96. https://doi.org/10.29333/iji.2023.16149a.
Zheng H, Zhan H. ChatGPT in scientific writing: a cautionary tale. Am J Med. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.02.011.
Zhou J, Ke P, Qiu X, Huang M, Zhang J. ChatGPT: potential, prospects, and limitations. Front Inf Technolo Electron Eng. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1631/FITEE.2300089.
Acknowledgements
I would like to express my sincere appreciation to all the participants for their valuable contributions to this study. Their time, insights, and willingness to share their perspectives have greatly enriched our understanding of the potential of ChatGPT as a digital language learning assistant. I extend my heartfelt appreciation to the anonymous reviewers for their valuable and constructive comments. Your collaboration and assistance have been instrumental in the successful completion of this study.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant or financial support from external sources. However, I have obtained support through the 100% APC Discount and Waiver Service from Springer Nature (NDIYNJMYMJK5).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The author, Joko Slamet, played a significant role in the study. He conceptualized the research design, collected and analyzed the data, and drafted the manuscript. His contributions also included the interpretation of the findings and critical revisions of the manuscript for intellectual content. He has reviewed and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This study was approved unconditionally by the Ethics Committee of Universitas Negeri Malang (KEP UM).
Informed consent
In adherence to rigorous ethical standards, explicit informed consent was obtained from every individual participant who was thoughtfully included in the study.
Competing interests
No financial or non-financial competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Slamet, J. Potential of ChatGPT as a digital language learning assistant: EFL teachers’ and students’ perceptions. Discov Artif Intell 4, 46 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s44163-024-00143-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s44163-024-00143-2