Abstract
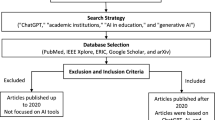
Artificial intelligence (AI) technologies have the potential to completely transform how we teach and learn in higher education. ChatGPT, a language model developed by OpenAI, is one such tool that can deliver individualized recommendations to students, increase collaboration and communication, and improve student learning results. However, there are some obstacles to overcome, such as ethical concerns and implementation issues. This study reviews related work on the use of artificial intelligence in education, with a focus on ChatGPT and its possible applications in higher education. It also examines the benefits and drawbacks of adopting ChatGPT in higher education, as well as implementation advice. Finally, the report discusses future directions for ChatGPT research in higher education. According to the findings of this paper, ChatGPT represents a significant opportunity for higher education institutions to improve the quality and accessibility of education; however, its implementation must be approached with caution and a clear understanding of the opportunities and challenges involved.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Atlas, S. (2023). ChatGPT for higher education and professional development: A guide to conversational AI. Chicago 3.
Celik, I. (2023). Towards Intelligent-TPACK: An empirical study on teachers’ professional knowledge to ethically integrate artificial intelligence (AI)-based tools into education. Computers in Human Behavior, 138, 107468.
Dogan, M. E., Dogan, T. G., & Bozkurt, A. (2023). The use of artificial intelligence (AI) in online learning and distance education processes: A systematic review of empirical studies. Applied Sciences, 13(5), 3056.
Halaweh, M. (2023). ChatGPT in education: Strategies for responsible implementation. Contemporary Educational Technology, 15, 2.
Haleem, A., Javaid, M., & Singh, R. P. (2022). An era of ChatGPT as a significant futuristic support tool: A study on features, abilities, and challenges. BenchCouncil transactions on benchmarks, standards and evaluations, 2(4)
Kashyap, R., & ChatGPT OpenAI. (2023). A first chat with ChatGPT: the first step in the road-map for AI (Artificial Intelligence). Available at SSRN.
Mhlanga, D. (2023). Open AI in education, the responsible and ethical use of ChatGPT towards lifelong learning. Education, the Responsible and Ethical Use of ChatGPT Towards Lifelong Learning (February 11, 2023).
Qin, C. (2023). Is chatgpt a general-purpose natural language processing task solver?. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.06476.
Sallam, M. (2023). ChatGPT utility in health care education, research, and practice: Systematic review on the promising perspectives and valid concerns. Healthcare, 11(6). MDPI.
Sullivan, M., Kelly, A., & McLaughlan, P. (2023). ChatGPT in higher education: Considerations for academic integrity and student learning. Journal of Applied Learning and Teaching, 6(1).
Surameery, N. M. S., & Shafiq, M. Y. (2023). Use chat gpt to solve programming bugs. International Journal of Information Technology & Computer Engineering (IJITC) ISSN: 2455–5290, 3(01), 17–22.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The only one main and corresponding author conducted all aspects of the research presented in this paper and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This study was exempt from ethics approval because it did not involve human or animal subjects. The data used in this study were publicly available and did not require informed consent from participants.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors confirm that there are no known conflicts of interest associated with this publication.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rawas, S. ChatGPT: Empowering lifelong learning in the digital age of higher education. Educ Inf Technol 29, 6895–6908 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-023-12114-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-023-12114-8