Abstract
Years of intensive research has brought us extensive knowledge on the genetic and molecular factors involved in Alzheimer's disease (AD). In addition to the mutations in the three main causative genes of familial AD (FAD) including presenilins and amyloid precursor protein genes, studies have identified several genes as the most plausible genes for the onset and progression of FAD, such as triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2, sortilin-related receptor 1, and adenosine triphosphate-binding cassette transporter subfamily A member 7. The apolipoprotein E ε4 allele is reported to be the strongest genetic risk factor for sporadic AD (SAD), and it also plays an important role in FAD. Here, we reviewed recent developments in genetic and molecular studies that contributed to the understanding of the genetic phenotypes of FAD and compared them with SAD. We further reviewed the advancements in AD gene therapy and discussed the future perspectives based on the genetic phenotypes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease that is biologically defined by the presence of β-amyloid-containing plaques and tau-containing neurofibrillary tangles (NFT). After years of intensive research, we have gained extensive knowledge of the genetic factors and their mechanisms in AD. Genetically, AD can be categorized as sporadic AD (SAD) and familial AD (FAD) based on family history (Jia et al. 2020b). FAD accounts for 15–25% of total AD and has presented a useful model in studying the pathogenesis and trajectory of the disorder's progress (Goldman et al. 2011).
AD is affected by multiple genes, which can be further divided into pathogenic genes and risk genes. Known AD pathogenic genes include presenilin 1 (PSEN1), presenilin 2 (PSEN2), and amyloid precursor protein (APP). These types of genes mainly cause early onset AD (EOAD), accounting for about 1% of all AD patients (Goate et al. 1991; Levy-Lahad et al. 1995; Sherrington et al. 1995). Apolipoprotein E (APOE) ε4 is a widely confirmed risk gene for SAD, usually late-onset AD (LOAD), accounting for about 50% of this type of patients (Strittmatter et al. 1993; Coon et al. 2007). In SAD, an APOE ε4 allele can increase the risk of AD by about three times, while two APOE ε4 alleles can increase the risk of AD by approximately 12 times (Liu et al. 2013; Jia et al. 2020c). Interestingly, recent large cohort studies also found that the genetic risk effect of APOE ε4 are higher in FAD with unknown mutation than in SAD (Jia et al. 2020c).
In addition to the three major pathogenic genes and APOE ε4, genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have revealed a large number of AD susceptibility loci, while whole genome sequencing (WGS) and whole exome sequencing (WES) studies have identified many AD-associated rare variants. These variants are enriched in triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM2), sortilin-related receptor 1 (SORL1), adenosine triphosphate-binding cassette transporter subfamily A member 7 (ABCA7), complement receptor 1 (CR1), cluster of differentiation 33 (CD33), clusterin (CLU), bridging integrator 1 (BIN1), and death-associated protein kinase 1 (DAPK1) (Li et al. 2006, 2021; Rogaeva et al. 2007; Beecham et al. 2009; Carrasquillo et al. 2009; Bellenguez et al. 2022; Jack 2022). Many of them have been verified in FAD population. For example, the rare variant TREM2 G145T was present in several members of a family with probable AD-type dementia without the three known pathogenic variants (Karsak et al. 2020). Some rare SORL1 variants are reported in FAD pedigrees (Gomez-Tortosa et al. 2018). In 77.3% of ABCA7 carriers' families, there were AD patients (Bossaerts et al. 2021).
Here, we reviewed recent advances in genetic studies that have contributed to the understanding of AD pathogenesis. We summarized the genetic and molecular mechanisms involved such as the amyloid cascade hypothesis, tau-dependent pathology, synaptic dysfunction, neuro-inflammation and oxidative stress, and lipid metabolism. We further compared the pathogenesis between FAD and SAD and reviewed preclinical and clinical studies of AD gene therapy. Such integration is not only helpful for understanding the commonality and heterogeneity in pathogenesis, but also conducive to clinical diagnosis and classification, development of gene-targeted therapies, and design of clinical trials based on different genetic phenotypes.
Pathogenic Genes for FAD
There are several large genetic cohort studies of FAD in the world (Fig. 1). FAD research is mainly concentrated in the United States of America (Bateman et al. 2012; Chhatwal et al. 2022), United Kingdom (Oxtoby et al. 2018; Weston et al. 2018), Colombia (Ramirez Aguilar et al. 2019; Quiroz et al. 2020), France (Rovelet-Lecrux et al. 2012; Zarea et al. 2016), and China (Jia et al. 2005, 2020b; Quan et al. 2020), and gradually forming multi-center collaboration. The most representative FAD study is the Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer Network (DIAN) study in the United States of America, which found many AD genetic and diagnostic biomarkers (Bateman et al. 2012; Chhatwal et al. 2022). The largest FAD cohort study is the Chinese familial Alzheimer's Network (CFAN), aiming to recruit 40,000 subjects in FAD (clinicaltrials.gov registration ID: NCT03657732). From genetic cohort studies, three main causative genes of FAD including PSEN1, PSEN2, and APP, and many associated variants were reported. For example, PSEN1 E280A (glutamic acid-to-alanine mutation at codon 280) variant was reported from Colombia kindred (Lopera et al. 1997), which further initiated the Colombia PSEN1 E280A cohort of autosomal dominant Alzheimer's disease (ADAD). PSEN1 V97L mutation was reported from Chinese families (Jia et al. 2005), which further initiated the CFAN cohort.

Reproduced from the map of the world, which was downloaded from the website (http://bzdt.ch.mnr.gov.cn/index.html), with drawing review No.: GS(2020)4401, and supervised by Ministry of Natural Resources of China
Major FAD cohort studies in the world. FAD research is mainly concentrated in the United States of America, United Kingdom, Colombia, France, and China, gradually forming a situation of international multicenter cooperation. DIAN: Dominantly inherited Alzheimer network; CFAN: Chinese familial Alzheimer's network; GMAJ: Genetics of Mendelian forms of young onset AD; ADAD: Autosomal-dominant AD.
APP
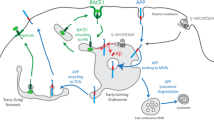
APP is a transmembrane protein widely expressed in the central nervous system and peripheral tissues. Proteolytic cleavage of APP generates the Aβ peptide, which aggregates into plaques, is one of the major hallmarks of AD (Tackenberg et al. 2020). Amyloid-β protein precursor (AβPP) can be cleaved by proteases in canonical and non-canonical pathways. In the canonical pathway, AβPP is cut by α-secretase, producing a soluble APPα peptide and α-C-terminal fragment which can be further cleaved by γ-secretase, generating APP intracellular domain (AICD) and a non-pathogenic three kDa product (Guo et al. 2021). In non-canonical pathway, AβPP is cut by β-secretase, producing a soluble APPβ peptide and β-C-terminal fragment which can be further cleaved by γ-secretase, generating Aβ48 or Aβ49 and AICD. Aβ48 or Aβ49 continued to produce Aβ45, Aβ42, Aβ38 or Aβ46, Aβ43, and Aβ40, respectively, under the action of γ-secretase (Andrew et al. 2016). The anomalous processing of APP leads to the production of Aβ40 and Aβ42 monomers, which further oligomerize and aggregate into senile plaques in AD (Zou et al. 2007; Tiwari et al. 2019). APP V717I was the first gene mutation found to be linked with inherited AD, which could influence the stability of Aβ deposition, alter translational regulation at the mRNA level of this protein, or increase long Aβ secretion to foster amyloid deposition (Goate et al. 1991; Almqvist et al. 1993; Suzuki et al. 1994). Subsequent studies have identified more APP mutations, all of which contribute to FAD. Interestingly, most of these mutations found in APP are located in exons 16 and 17 on chromosome 21, near the α-secretase cleavage site, in the central part of the Aβ peptide or near the γ-secretase site of the attack, giving rise to an increase or alteration in Aβ production (Aβ 1–42 fragment) (Theuns et al. 2006; Tian et al. 2010; Piaceri et al. 2013), or alteration of Aβ42:40 ratio (Tian et al. 2010). The Australian APP L723P mutation causes local unfolding of the C-terminal turn of the APP transmembrane domain helix, and increases its accessibility to water required for cleavage of the protein backbone by γ-secretase in the ε-site, resulting in accumulation of the pathogenic forms of Aβ (Bocharov et al. 2019). The Swedish APP K670N/M671L mutation in exon 16 occurs at the amino terminal of Aβ is proximal to the β-secretase cleavage site, and it increases the production of total Aβ through dramatically enhancing β-secretase cleavage of APP17 (Mullan et al. 1992; Vassar et al. 1999). Osaka mutation (APP E693Δ) is the deletion of codon 693 of APP gene, resulting in mutant Aβ lacking the 22nd glutamate, which accelerates Aβ oligomerization without forming amyloid fibrils and disrupts synaptic function to cause cognitive impairment in humans (Tomiyama et al. 2020).
Aβ can promote tau pathology, and its toxicity is also tau-dependent (Gotz et al. 2008). Aβ alone does not cause neurodegeneration but induces toxicity through the phosphorylation of wild-type tau in an N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor-dependent pathway (Tackenberg et al. 2009). APP is involved in several neuroplasticity-signaling pathways, such as NMDA-protein kinase A (PKA)-cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element binding protein (CREB)-brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), reelin, wingless, and notch (Forero et al. 2006). Hippocampal accumulation of mutant APP and Aβ is responsible for abnormal mitochondrial dynamics and defective biogenesis, reduced microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2), autophagy, mitophagy, synaptic proteins and dendritic spines, and changes in mitochondrial structure and function, leading to neuronal dysfunction and impaired hippocampal-based learning and memory (Manczak et al. 2018; Reddy et al. 2018). In a novel APP knock-in mouse model (APP Swedish, Arctic and Austrian), fibrillar Aβ in microglia is associated with lipid dyshomeostasis, which is consistent with lysosomal dysfunction and foam cell phenotypes as well as profound immuno-metabolic perturbations (Xia et al. 2022). A rat model with three APP mutations and humanized Aβ sequence knocked into the rat's APP gene exhibited pathologies and disease progression resembling those in human patients. Specifically, Aβ plaques were deposited in relevant brain regions, and other mechanisms were found, including microglia activation and gliosis, progressive synaptic degeneration, tau pathology, neuronal apoptosis and necroptosis, brain atrophy, and AD-relevant cognitive deficits (Pang et al. 2022).
PSEN1
PSEN1 serves as a catalytic subunit of γ-secretase complex, which mediates the proteolytic liberation of Aβ from AβPP. PSEN1 is also involved in non-proteolytic functions such as protein trafficking, regulation of ion channel, cholesterol metabolism, and homeostatic synaptic scaling (Li et al. 2000; Pratt et al. 2011; Cho et al. 2019). PSEN1 mutation leads to the production of longer amyloidogenic Aβ peptides and increased Aβ42:40 ratio (Selkoe 2001; Fernandez et al. 2014), causing the most aggressive form of inherited AD. PSEN1 mutation carriers with an earlier age of onset and considerable phenotypic variability show mutation-specific effects and a trend towards a reduced abundance of newborn neurons, supporting a premature aging phenotype and altered neurogenesis (Arber et al. 2021). PSEN1 mutants potentiate cell cycle arrest and apoptosis, and the degree to which the different mutants inhibit cell cycle progression correlates with the age of onset (Janicki et al. 2000). PSEN1 S169del mutation altered APP processing and Aβ generation, and promoted senile plaque formation as well as learning and memory deficits in mice (Zhang et al. 2020a). PSEN1 V97L mutation induced self-replication of Aβ oligomers (AβO) in astrocytes and triggered neuronal injury in mice (Wang et al. 2019).
Other pathogenic mechanisms are also reported in PSEN1 mutation models. In the PSEN1 ΔE9 cells, the elevated cellular cholesterol level contributes to the altered APP processing by increasing APP localized in lipid rafts (Cho et al. 2019). In primary fibroblasts from patients bearing PSEN1 mutations, Aβ42 oligomers are recruited to lipid rafts, resulting in lipid peroxidation, calcium dyshomeostasis and membrane permeabilization, and amyloid toxicity (Evangelisti et al. 2013). Primary hippocampal neurons from PSEN1 transgenic mice exhibit increased production of Aβ peptide 42/43 and vulnerability to excitotoxicity in a gene dosage-dependent manner. Neurons expressing mutant PSEN1 exhibit enhanced calcium responses to glutamate increased oxyradical production and mitochondrial dysfunction (Guo et al. 1999). PSEN1 mutations also increase oxidative stress and perturb calcium signaling in lymphocytes in ways that alter their production of inflammatory cytokines that are critical for proper immune responses (Mattson 2002; Schuessel et al. 2006). Inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα), interleukin (IL)-1α, IL-1β, IL-1 receptor antagonist, and IL-6, are significantly greater in the hippocampus and cerebral cortex of PSEN1 mutant mice as compared to wild-type mice (Lee et al. 2002).
PSEN2
PSEN2 forms the catalytic core of the γ-secretase complex, a function shared with its homolog PSEN1, which is ultimately responsible for Aβ formation (Pizzo et al. 2020). Besides its enzymatic activity, PSEN2 is a multifunctional protein, which is specifically involved in the modulation of several cellular processes, such as proinflammatory response, mitochondrial function, ubiquilin, and autophagy (Pizzo et al. 2020). AD-causing mutations shift Aβ length by destabilizing γ-secretase-Aβ interactions, which is fundamental to the disease (Szaruga et al. 2017, 2021).
PSEN2 mutations either increase Aβ production or alter the Aβ42/40 ratio that contributes to the development of AD (Loy et al. 2014; Pang et al. 2021). PSEN2 N141I mutation produces an AD phenotype with a wide range of onset ages overlapping both EOAD and LOAD, often associated with seizures, rapidly progressive dementia, neurologic and behavioral symptoms, high penetrance and typical AD neuropathology (Jayadev et al. 2010; Muchnik et al. 2015). PSEN2 participates in maintaining the basal and cytokine-induced expression of the innate immunity regulating microRNA, and its dysfunction or deficiency could result in disrupted innate immune homeostasis and unchecked proinflammatory activation (Jayadev et al. 2013; Fung et al. 2020). AD-linked PSEN2 mutants alter multiple Ca2+ pathways and the functional consequences of this Ca2+ dysregulation in AD pathogenesis (Greotti et al. 2019; Galla et al. 2020). They decrease the Ca2+ content of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), modulate Ca2+ shuttling between the ER and mitochondria, and reinforce ER-mitochondria tethering (Zampese et al. 2011; Rossini et al. 2021). PSEN2 knock-out neurons show a marked reduction in ER-mitochondria apposition and a slight alteration in mitochondrial respiration (Rossi et al. 2021). PSEN2 mutation also actions on autophagy, depending on its ability to partially deplete ER Ca2+ content and reduce cytosolic Ca2+ response upon inositol trisphosphate-linked cell stimulations (Fedeli et al. 2019). Overexpression of PSEN2 N141I mutation causes cell starvation and cell death, and ubiquilin expression protects cells against starvation by modulating biogenesis and endoproteolysis of PSEN2 proteins (Rothenberg et al. 2010). PSEN2 mutation is also involved in the abnormalities of lipid profile, where the levels of cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein and triglyceride are increased, but the level of high-density lipoprotein is decreased (Nguyen et al. 2006).
APOE ε4 and Other Risk Genes in FAD
Over 130 AD-associated susceptibility loci have been identified by GWAS, while WGS and WES studies have identified AD-associated rare variants. Except for APOE, these variants are enriched in TREM2, SORL1, ABCA7, CR1, CD33, CLU, BIN1, and more genes, but with smaller effect size, lower population prevalence, or both compared with APOE ε4 (Li et al. 2021; Bellenguez et al. 2022; Jack 2022). Studies have identified several genes as the most plausible genes for FAD, including TREM2, SORL1, and ABCA7 (Campion et al. 2019; Scheltens et al. 2021).
APOE
APOE is a lipoprotein that is expressed in the brain, liver, and myeloid cells, and it is involved in cholesterol and lipid transportation, neuronal growth, and immune-regulation. Three different alleles of APOE encode three isoforms, including APOE ε2, APOE ε3, and APOE ε4 (Poirier et al. 1993). Although the three isoforms differ by only two amino acids, the structure and function of APOE isoforms are significantly altered (Neuner et al. 2020). The APOE ε4 allele is the strongest genetic risk factor for AD. One copy of the ε4 allele increases the risk of AD by two to six times, and the presence of two copies increases the risk by 7.2 to 21.8 times (Genin et al. 2011; Jia et al. 2020c; Qin et al. 2021). It is widely accepted that carrying the APOE ε4 allele reduces the age of onset by about 12 years (Corder et al. 1993; Belloy et al. 2019). Since its identification, APOE ε4 allele has been regarded as a risk factor for SAD instead of FAD, because it is neither necessary nor sufficient to cause AD (Cacace et al. 2016), and its inheritance does not follow an autosomal dominant pattern such as APP, PSEN1, and PSEN2 mutations (van Duijn et al. 1994; Frisoni et al. 2022). However, studies indicate that APOE ε4 also plays an important role in FAD. Actually, APOE ε4 was first identified and shown to be associated with the increased risk of AD in late-onset FAD, and then association studies in cohorts identified it as a major genetic risk factor for late-onset SAD (Pericak-Vance et al. 1991; Corder et al. 1993; Strittmatter et al. 1993). Subsequently, a study demonstrated a significant association between APOE ε4 and EOAD which is modified by a family history of dementia. Among patients, the APOE ε4 allele frequency was 1.6 times higher in those with positive family history than in those without (van Duijn et al. 1994). In spite of this, they think the APOE ε4 allele cannot fully explain familial aggregation of EOAD as among APOE ε4 carriers as well as non-carriers the risk of EOAD increased significantly for those with a positive family history of dementia (van Duijn et al. 1994).
However, a recent study in a cohort of 404 Chinese pedigrees with FAD showed different results. They found that among patients without PSENs/APP mutations, 44.31% carried one APOE ε4 allele, while 14.85% carried two APOE ε4 alleles (Jia et al. 2020b). These percentages were much higher than those in SAD patients. Furthermore, patients with two ε4 alleles are more likely to develop FAD than those with a single ε4 allele and other subtypes of AD, indicating that increased APOE ε4 gene dosage may promote the development of FAD (Jia et al. 2020c). This phenomenon called the APOE ε4 diploid enhancement of familial aggregation has been reported in other studies, suggesting that APOE ε4 plays an important role in familial aggregation (Martinez et al. 1998; Huang et al. 2004). These results urge a reappraisal of the impact of APOE ε4 in FAD. In addition, some studies in FAD suggest that APOE ε4 influences the age at which AD occurs, where onset age decreases in presence of the ε4 allele (Velez et al. 2016; Reyes-Dumeyer et al. 2022). Another study showed that at the age of 85, the lifetime risk of AD without reference to APOE genotype was 11% to 14% for male and female, respectively, while the risk ranged from 51% to 60% for APOE ε4/ε4 carriers, and from 23% to 30% for APOE ε3/ε4 carriers, which is consistent with semi-dominant inheritance of a moderately penetrant gene (Genin et al. 2011).
APOE ε4 negatively impacts a plethora of biological processes associated with AD in human patients. Namely, APOE ε4 accelerates neurodegeneration and cognitive deficits; increases Aβ deposition by promoting its production and fibrillization and impairing degradation/clearance pathways; increases the accumulation of tau pathology by increasing its phosphorylation and fibrillization, and accelerating its spread; amplifies gliosis and inflammation by exacerbating neuroinflammatory response, impairing astrocytes ability to maintain synapses, increasing neurons phagocytosis and decreasing toxic proteins removal; disrupts network activity and functional connectivity within or between brain regions; and reduces central nervous system glucose metabolism (Koutsodendris et al. 2022). Other pathogenic mechanisms include lipid metabolism, neuronal signaling, mitochondrial function, and blood–brain barrier (Long et al. 2019; Serrano-Pozo et al. 2021; Jackson et al. 2022; Koutsodendris et al. 2022; Martens et al. 2022). It is possible that APOE ε4-induced detrimental effects could work independently or in concert with one another. Of note, the precise mechanism by which APOE ε4 increases AD risk remains inconclusive, so further investigation of the APOE gene is critical for developing therapeutics (Koutsodendris et al. 2022).
TREM2
TREM2 is a single-pass transmembrane receptor of the immunoglobulin superfamily that was initially identified in monocyte-derived dendritic cells and mouse macrophages (Ulland et al. 2018). TREM2 is a receptor for Aβ that mediates microglial function, including proliferation, survival, clustering, and phagocytosis (Ulland et al. 2017; Zhao et al. 2018). It is essential for microglia-mediated synaptic refinement during the early stages of brain development (Filipello et al. 2018). TREM2 promotes the optimal microglial function required to attenuate AD progression, enabling microglial progression to a fully mature disease-associated microglia profile and ultimately sustaining the microglial response to Aβ plaque-induced pathology (Ulland et al. 2018).
The minor allele frequency of R47H in the TREM2 gene was much lower while the effect size was as high as APOE ε4 (Guerreiro et al. 2013; Jonsson et al. 2013). The association of R47H with elevated LOAD risk was successfully replicated in European-American, Spanish, French-Caucasian, North American-Caucasian and African-American populations, but failed in Han Chinese population (Carmona et al. 2018). In TREM2 R47H carriers, the role of TREM2 receptor in the microglial clearance of aggregation-prone proteins is compromised (Korvatska et al. 2015). TREM2 R47H mutation AD also demonstrates upregulation of interferon type I response and pro-inflammatory cytokines accompanied by induction of natural killer group 2 member D (NKG2D) stress ligands (Korvatska et al. 2020). It induces and exacerbates tau-mediated spatial memory deficits in female mice (Sayed et al. 2021). Furthermore, transcriptomic changes from these mice had substantial overlaps with TREM2 R47H microglia in human AD brains, including robust increases in proinflammatory cytokines, activation of AKT signaling, and elevation of a subset of disease-associated microglia signatures (Sayed et al. 2021). In a family with probable AD-type dementia without the three known pathogenic variants, another rare variant TREM2 G145T was present in severely affected, putatively affected, and unaffected members, suggesting incomplete penetrance and variable age of onset. This variant led to intrinsically disordered region shortening and structural changes of TREM2, resulting in an impairment of cellular responses upon receptor activation (Karsak et al. 2020). The absence of TREM2 resulted in repetitive behavior and altered sociability in mice, impaired synapse elimination, enhanced excitatory neurotransmission, and reduced long-range functional connectivity (Filipello et al. 2018). Deleting TREM2 exacerbated tau accumulation and spreading, and promoted brain atrophy only if Aβ pathology is present, indicating that TREM2 may slow AD progression and reduce tau-driven neurodegeneration by restricting the degree to which Aβ facilitates the spreading of pathogenic tau (Lee et al. 2021).
SORL1
The SORL1 gene is a regulator of endosomal traffic and recycling in human neurons. SORL1 encodes sorting-related receptor with A-type repeats (SORLA), a key protein involved in APP processing and the secretion of Aβ peptide (Campion et al. 2019). Some rare SORL1 variants are reported in FAD pedigrees, supporting the putative autosomal dominant inheritance and cause of EOAD (Gomez-Tortosa et al. 2018). These variants include SORL1 T588I change, T2134 alteration, Trp848Ter, Gly1871Val, Glu270Lys, Gly852Ala, Arg1702Met, Asn1809Ser, Asp2065Val, Ala2173Thr, a splice-site variant (chromosome position 121,466,486 G > A), Arg1303Cys, c.3050-2A > G, c.5195G > C, V1482fs (Pottier et al. 2012; Thonberg et al. 2017). Depletion of SORL1 significantly impacts the endosomal recycling pathway in neurons for APP and glutamate receptor subunit α-Amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (GLUA1) at the level of the recycling endosome and trafficking to the cell surface, conversely, increased SORL1 expression enhances endosomal recycling for APP and GLUA1 (Mishra et al. 2022b). Truncating mutation of SORL1 results in mitochondrial dysfunction and enlarged endosomes in human neurons due to SORL1 haploinsufficiency, while complete loss of SORL1 leads to additional defects in lysosome function and autophagy (Barthelson et al. 2020; Hung et al. 2021). A study of cortices and hippocampus of SORL1-deficient mice showed increased synapsin 1 and 2, however, the specific role of SORL1 in synaptic function in FAD remains unclear (Hartl et al. 2016; Perdigao et al. 2020). There are also LOAD cases with rare SORL1 variants, such as SORL1 A528T, T947M, and A674S. Functionally, the variants impair SORL1 protein function and weaken its interaction with full-length APP, altering levels of Aβ and interfering with APP trafficking (Cuccaro et al. 2016; Louwersheimer et al. 2017).
ABCA7
There were AD patients in 77.3% of the families of ABCA7 carriers, suggesting a positive family history of the disease (Bossaerts et al. 2021). In a Belgian AD cohort, 22 affected members carried an ABCA7 E709fs. All carriers except one presented with memory complaints (Van den Bossche et al. 2016). Two rare ABCA7 variants (rs143718918 and rs538591288) were identified in two independent German AD families, respectively. The rs143718918 variant causes a missense mutation, and the rs538591288 deletion causes a frameshift mutation of ABCA7 (May et al. 2018). ABCA7 heterozygous variant c.3706C > T p.(Avg 1236Cys) was found in seven affected members in a Saudi family, which is likely pathogenic because of the presenting complex neurological disease due to decreased clearance of Aβ and α-synuclein (Algahtani et al. 2020). Missense variants in ABCA7 (P143S and A1507T) were significantly associated with FAD when compared with the East Asian controls in the ExAC database (Zhang et al. 2020b). ABCA7 rs376824416 3’-UTR splice was identified in four siblings of one family in a non-Hispanic White and African-American cohort, which was nominally associated with LOAD (Kunkle et al. 2017). A missense mutation in ABCA7 G1820S co-segregated with AD in one pedigree, which induced protein mislocalization and resulted in a lack of functional protein at the plasma membrane (Bossaerts et al. 2022).
ABCA7 belongs to the “A” subfamily of the adenosine triphosphate-binding cassette transporters. ABCA7 deficiency results in accelerated Aβ production, likely by facilitating endocytosis and/or processing of APP (Aikawa et al. 2018). While ABCA7 has been shown to mediate phagocytic activity in macrophages, it is also involved in the microglial Aβ clearance pathway (Abe-Dohmae et al. 2021). ABCA7 loss of function may contribute to AD pathogenesis by altering proper microglial responses to acute inflammatory challenges during the development of amyloid pathology (Aikawa et al. 2019). ABCA7 also regulates brain fatty acid metabolism during lipopolysaccharide-induced acute inflammation (Aikawa et al. 2021). ABCA7-deficient mice's brain had significantly lower levels of several sphingomyelin (SM) species with long-chain fatty acids, and anomalies in synaptic plasticity in the synapse of the lateral entorhinal cortex, that were rescued by extracellular SM supplementation (Iqbal et al. 2022).
Table 1 summarized the mechanisms of the major pathogenic and risk genes for AD.
Other Risk Genes
The confirmed genetic risk variants from SAD showed enrichment in FAD as well, but the risk scores were not statistically significant probably due to the small sample size (Reyes-Dumeyer et al. 2022). Some rare protein-damaging variants in TREM2, SORL1 and ABCA7 do have moderate-to-high effect, and cause FAD in an autosomal dominant nature, as described above, but most of them were present as singletons (Campion et al. 2019; Scheltens et al. 2021). There is disagreement about whether these loci reached genome-wide significance in association with AD, due to the differences in the criteria and number of subjects included, different analysis methods and research strategies (Campion et al. 2019; Scheltens et al. 2021; Reyes-Dumeyer et al. 2022). Functional annotation of these risk loci indicates that, next to Aβ metabolism, the modulation of the immune response, cholesterol, lipid dysfunction, endocytosis, and vascular factors play a role in the development of AD (Di Marco et al. 2015; Van Cauwenberghe et al. 2016; Naj et al. 2017; Bennett et al. 2018; Verheijen et al. 2018). The exact functional consequences of additional missense variants as well as corresponding levels of AD risk remain to be determined.
Mechanisms of FAD vs. SAD
In general, FAD and SAD share common mechanisms, such as toxicity of Aβ and hyperphosphorylation of tau, oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and autophagy dysfunction (Wang et al. 2014; Manoharan et al. 2016; Kodamullil et al. 2017; Li et al. 2017; Moloudizargari et al. 2017; Sawikr et al. 2017; Tönnies et al. 2017; Wu et al. 2017; Chen 2018; Kaur et al. 2019; Lu et al. 2019; Paroni et al. 2019). The most common mechanism is about Aβ. SAD and FAD both exhibit abundant deposition of Aβ peptides within brain cells, the extracellular space of the brain parenchyma, and the walls of the cerebral vasculature (Roher et al. 2016). Interestingly, AβPP levels in both PSEN-FAD and SAD remained within the limits of normal confidence established by non-demented, age-matched individuals (Roher et al. 2013). A study revealed that perturbations of intraneuronal signaling pathways comprise a common mechanistic denominator in both FAD and SAD, and such alterations lead to increases in AβO formation and phosphorylation of tau (Van Dooren et al. 2014). In addition, biomarker changes for FAD, in many but not all cases, appear to be similar to those for SAD (Lista et al. 2015).
Although sharing some common mechanisms, there are also differences between FAD and SAD. The familial form is due to mutations in pathogenic genes, while many genetic and environmental factors as well as unknown factors may contribute to determining the SAD form (Frisoni et al. 2022). FAD patients usually have an earlier age of onset and longer course than SAD patients (Armstrong 2014). FAD has more severe Aβ load and tau pathology, an earlier and quicker development of NFT, faster neuronal demise, and a diverse spectrum of distinctive neuropathological findings in the gray matter, including unusual 'cotton wool' amyloid plaques, Lewy bodies, Pick bodies, and ectopic neurons as well as white matter changes with atypical clusters of amyloid plaques and a variable degree of microhemorrhages (Gomez-Isla et al. 1999; Maarouf et al. 2008; Frisoni et al. 2022). Other co-morbidities like cerebrovascular disease, argyrophilic grain disease and hippocampal sclerosis were present in SAD but not in FAD (Cairns et al. 2015). In FAD, Aβ deposits are linked to increased synthesis or overproduction of Aβ peptides, while in SAD, Aβ accumulation may be the result of chronic AβPP/Aβ overproduction and limited degradation/clearance (Meraz-Rios et al. 2014; Roher et al. 2016). GWAS in SAD population showed that most of the risk genes affected the production and clearance of Aβ (Bertram et al. 2007). Increased Aβ42/43 production does not occur in most SAD cases (Ray et al. 1998). A study revealed that Notch1, Erb-B4, neurexin, neurofilament-L, neurofilament-M, α-tubulin, β-tubulin, dynein, and tau were substantially decreased in PSEN-FAD relative to SAD, while glial fibrillary acidic protein and neuroligin were increased (Roher et al. 2013). Equating SAD and PSEN-FAD only on the bases of their amyloid and NFT deposits hampered a better understanding of their pathogenesis and pathophysiology (Roher et al. 2016). Another study found that type I filaments were mostly in the brains of individuals with SAD, and type II filaments were found in individuals with FAD and other conditions (Yang et al. 2022). In FAD, the lifetime risk of dementia is very high, nearly 100% (Bateman et al. 2011), while in SAD, the percentage is lower, about 22%–95% in APOE ε4-related AD and 7%–35% in APOE ε4-unrelated AD (Genin et al. 2011; Reiman et al. 2020). More differentiating mechanisms should be studied in the future.
AD Gene Therapy
Based on different genetic phenotypes of AD, vast avenues for gene therapy interventions are opened, aiming to tackle the disease at its source, mostly a faulty DNA/gene/protein, to repair it and allow the cells to fix the problem. Gene therapy involves inserting new genetic material into living cells using viruses. A deep understanding of the neuropathology of AD has also led to the development of numerous viral-mediated gene-transfer approaches (Khan et al. 2020; Mendell et al. 2021).
Preclinical Studies of AD Gene Therapy
In rodent lesion models for AD, human neural stem cells (NSC) were used in place of fibroblasts to deliver nerve growth factor (NGF), which improved cognitive function (Wu et al. 2008; Lee et al. 2012). NSC's BDNF basal production and genetically modified NSC also showed efficacy in AD transgenic mouse models (Blurton-Jones et al. 2009; Wu et al. 2016). Fibroblast growth factor2 (FGF2) gene delivery via adeno-associated viruses serotype 2/1 hybrid (AAV2/1) could enhance neurogenesis and hippocampal Aβ clearance in AD mouse model, putting forward its usage as an alternative in AD therapy (Kiyota et al. 2011). Modified NSC-producing neprilysin led to improvement in synaptic density, and alleviated AD pathology in transgenic mice (Blurton-Jones et al. 2014). Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) transplantation and miRNA-937 overexpression in MSC also showed efficacy on cognitive capabilities in AD mouse models (Tanna et al. 2014; Liu et al. 2015; Naaldijk et al. 2017; Parambi et al. 2022). In a recent preclinical study, by deleting a gene called Bax in FAD mice, the survival rate of stem cells was increased, leading to more neurons mature in hippocampus, such targeted augmentation of neurogenesis restored new neurons number in the engram, the dendritic spine density and the transcription signature ultimately led to the rescue of memory (Mishra et al. 2022a).
In addition, one preclinical study showed that peripheral administration of antisense oligonucleotides (ASO) targeting AβPP reversed AβPP and low-density lipoprotein-related protein-1 (LRP-1) overexpression in the aged SAMP8 mouse of AD (Erickson et al. 2012). Treatment of AD mice with a single dose of ASO that increases exon 19 splicing corrected APOE receptor 2 splicing for up to six months and improved synaptic function and learning and memory (Hinrich et al. 2016). Using an ASO to reduce APOE expression in the brains of APP/PSEN1-21 mice prior to plaque deposition strongly affected the initiation of Aβ pathology, while lowering APOE after Aβ seeding modulated plaque size and toxicity (Huynh et al. 2017). In another study, delivering the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1 alpha (PGC1-α) gene using a modified virus to mice brain cells reduced the development of AD, and the treated mice showed better memory, no loss of brain cells in the hippocampus and had very few amyloid plaques after four months of injection (Katsouri et al. 2016).
Clinical Trials of AD Gene Therapy
Some approaches have entered clinical trials. One approach is the delivery of NGF, which is hypothesized to promote the survival of cholinergic neurons (Fischer et al. 1987). Intracerebral delivery of NGF using recombinant AAV to the basal forebrain of patients with mild to moderate AD showed safety and well tolerance (Rafii et al. 2014). However, efficacy endpoints were not met in the subsequent phase 2 study (Rafii et al. 2018). Another study subjected 10 patients with early AD with NGF gene ex vivo or in vivo, and the researchers found a positive response of neurons showing cell hypertrophy, axonal sprouting, and activation of functional markers, and the sprouting induced by NGF persisted for 10 years after gene transfer and appeared safe (Tuszynski et al. 2015). Thus, the study needs confirmation of precise gene targeting. In a recent breakthrough, scientists found a genetic snipping technique which can be used to turn APOE4, the gene that is responsible to cause Aβ proteins in the brain, into APOE3 (Khan et al. 2020). Taken together, gene editing and transferrin and penetratin-tagged liposomal nanoparticles might be the answer to solve gene format and dosage issue (Dos Santos Rodrigues et al. 2019; Williams et al. 2020).
In addition to the above clinical studies of gene therapy, there are more evidence showing that AD variants are used for therapy. For example, since PSEN1 E280A variant was reported from Colombia, it has been further translated into a phase 2 clinical trial (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT01998841), examining the effectiveness and safety of the drug crenezumab in presymptomatic participants carrying this variant in autosomal-dominant AD (ADAD) population (Tariot et al. 2018). Lecanemab, E2801, Gantenerumab and Solanezumab are used in phase 2/3 clinical trials in individuals with mutations causing dominantly inherited AD from the DIAN population (NCT01760005, NCT05269394, NCT05552157). LX1001, a serotype rh.10 AAV gene transfer vector expressing the cDNA coding for human APOE2 is used in a phase 1/2 clinical trial in individuals with APOE4 homozygote AD (NCT03634007).
Future Perspective of AD Gene Therapy
Gene therapy is the recent addition as therapeutic agents for AD, however, they are yet to be clinically approved. Because different genetic subtypes of AD show different symptoms or disease courses, whether there is overlap and conversion between different subtypes requires further research. For example, the synaptic loss is more obvious in EOAD, which can affect acetylcholine, norepinephrine γ-aminobutyric acid and humoral protein levels (Bigio et al. 2002). Therefore, the clinical trials of gene therapy for EOAD should intervene earlier than the usual prototype disease, and considering the polygenic nature of most AD cases, the combined treatment of multiple neurotransmitters as well as multiple genes may be more effective in improving symptoms than the single-target cholinergic drugs. Attention should be paid to genetic phenotypes when conducting clinical trials of AD gene therapy, which can enable researchers to design experiments more accurately, select appropriate subjects, and obtain reliable efficacy and safety results.
In addition to genetic phenotypes, AD gene therapy should also consider gene-environment interactions, since various environmental factors contribute to the complex etiology of AD. Studies in both animal models and humans have shown that environmental AD risk factors, such as diet, lifestyle, alcohol, smoking and pollutants, can induce epigenetic modifications of key AD-related genes and pathways namely oxidative stress (Migliore et al. 2022). Furthermore, among the environmental risk factors, many are preventable, such as depression, social isolation, low educational levels, hearing impairment, physical inactivity, smoking, obesity, hypertension, diabetes, alcohol abuse, and air pollution (Jia et al. 2020a; Livingston et al. 2020). As a result, the environmental risk factors should also be taken into account when conducting gene therapy clinical trials, especially for LOAD patients and patients from different environmental settings. For example, selecting patients with similar environmental factors, or setting environmental factors as covariates when conducting multi-center gene therapy clinical trials.
Conclusions
Several genes contributed to the genetic pathogenesis and high risk of FAD. Different pathogenic genes showed various phenotypes and underling molecular mechanisms, some of which are shared with SAD, while some are unique to specific mutations. Future gene therapy for AD should pay more attention to the genetic phenotypes and adopt more precise and individualized treatment strategies in designing clinical trials.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- AAV2/1:
-
Adeno-associated viruses serotype 2/1 hybrid
- ABCA7:
-
Adenosine triphosphate-binding cassette transporter subfamily A member 7
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- ADAD:
-
Autosomal-dominant Alzheimer’s disease
- AICD:
-
APP intracellular domain
- APOE:
-
Apolipoprotein E
- APP:
-
Amyloid precursor protein
- ASO:
-
Antisense oligonucleotides
- AβO:
-
Aβ oligomers
- AβPP:
-
Amyloid-β protein precursor
- BDNF:
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor
- BIN1:
-
Bridging integrator 1
- CD33:
-
Cluster of differentiation 33
- CFAN:
-
Chinese familial Alzheimer’s network
- CLU:
-
Clusterin
- CR1:
-
Complement receptor 1
- CREB:
-
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element binding protein
- DAPK1:
-
Death-associated protein kinase 1
- DIAN:
-
Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer network
- EOAD:
-
Early onset AD
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- FAD:
-
Familial AD
- FGF2:
-
Fibroblast growth factor 2
- GLUA1:
-
Glutamate receptor subunit α-Amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid
- GWAS:
-
Genome-wide association studies
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- LOAD:
-
Late-onset AD
- LRP-1:
-
Low-density lipoprotein-related protein-1
- MAP2:
-
Microtubule-associated protein 2
- MSC:
-
Mesenchymal stem cells
- NFT:
-
Neurofibrillary tangles
- NGF:
-
Nerve growth factor
- NKG2D:
-
Natural killer group 2 member D
- NMDA:
-
N-methyl-d-aspartate
- NSC:
-
Neural stem cells
- PGC1-α:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1 alpha
- PKA:
-
Protein kinase
- PSEN1:
-
Presenilin 1
- PSEN2:
-
Presenilin 2
- SAD:
-
Sporadic AD
- SM:
-
Sphingomyelin
- SORL1:
-
Sortilin-related receptor 1
- SORLA:
-
Sorting-related receptor with A-type repeats
- TNFα:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
- TREM2:
-
Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2
- WES:
-
Whole exome sequencing
- WGS:
-
Whole genome sequencing
References
Abe-Dohmae S, Yokoyama S (2021) ABCA7 links sterol metabolism to the host defense system: molecular background for potential management measure of Alzheimer’s disease. Gene 768:145316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2020.145316
Aikawa T, Holm ML, Kanekiyo T (2018) ABCA7 and pathogenic pathways of Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Sci 8:27. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci8020027
Aikawa T, Ren Y, Yamazaki Y et al (2019) ABCA7 haplodeficiency disturbs microglial immune responses in the mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 116:23790–23796. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1908529116
Aikawa T, Ren Y, Holm ML et al (2021) ABCA7 Regulates brain fatty acid metabolism during LPS-induced acute inflammation. Front Neurosci 15:647974. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2021.647974
Algahtani H, Shirah B, Alshareef A et al (2020) A novel variant c.3706C > T p. (Avg 1236Cys) in the ABCA7 gene in a Saudi patient with susceptibility to Alzheimer’s disease 9. Intractable Rare Dis Res 9:151–155. https://doi.org/10.5582/irdr.2020.03033
Almqvist E, Lake S, Axelman K et al (1993) Screening of amyloid precursor protein gene mutation (APP 717 Val–>Ile) in Swedish families with Alzheimer’s disease. J Neural Transm Park Dis Dement Sect 6:151–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02261009
Andrew RJ, Kellett KA, Thinakaran G et al (2016) A greek tragedy: the growing complexity of Alzheimer amyloid precursor protein proteolysis. J Biol Chem 291:19235–19244. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.R116.746032
Arber C, Lovejoy C, Harris L et al (2021) Familial Alzheimer’s disease mutations in PSEN1 lead to premature human stem cell neurogenesis. Cell Rep 34:108615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108615
Armstrong RA (2014) Factors determining disease duration in Alzheimer’s disease: a postmortem study of 103 cases using the Kaplan–Meier estimator and cox regression. Biomed Res Int 2014:623487. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/623487
Barthelson K, Pederson SM, Newman M et al (2020) Brain transcriptome analysis reveals subtle effects on mitochondrial function and iron homeostasis of mutations in the SORL1 gene implicated in early onset familial Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Brain 13:142. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13041-020-00681-7
Bateman RJ, Aisen PS, De Strooper B et al (2011) Autosomal-dominant Alzheimer’s disease: a review and proposal for the prevention of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res Ther 3:1. https://doi.org/10.1186/alzrt59
Bateman RJ, Xiong C, Benzinger TL et al (2012) Clinical and biomarker changes in dominantly inherited Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med 367:795–804. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1202753
Beecham GW, Martin ER, Li YJ et al (2009) Genome-wide association study implicates a chromosome 12 risk locus for late-onset Alzheimer disease. Am J Hum Genet 84:35–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2008.12.008
Bellenguez C, Kucukali F, Jansen IE et al (2022) New insights into the genetic etiology of Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias. Nat Genet 54:412–436. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-022-01024-z
Belloy ME, Napolioni V, Greicius MD (2019) A Quarter century of APOE and Alzheimer’s disease: progress to date and the path forward. Neuron 101:820–838. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2019.01.056
Bennett RE, Robbins AB, Hu M et al (2018) Tau induces blood vessel abnormalities and angiogenesis-related gene expression in P301L transgenic mice and human Alzheimer’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115:E1289–E1298. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1710329115
Bertram L, McQueen MB, Mullin K et al (2007) Systematic meta-analyses of Alzheimer disease genetic association studies: the AlzGene database. Nat Genet 39:17–23. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1934
Bigio EH, Hynan LS, Sontag E et al (2002) Synapse loss is greater in presenile than senile onset Alzheimer disease: implications for the cognitive reserve hypothesis. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 28:218–227. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2990.2002.00385.x
Blurton-Jones M, Kitazawa M, Martinez-Coria H et al (2009) Neural stem cells improve cognition via BDNF in a transgenic model of Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:13594–13599. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0901402106
Blurton-Jones M, Spencer B, Michael S et al (2014) Neural stem cells genetically-modified to express neprilysin reduce pathology in Alzheimer transgenic models. Stem Cell Res Ther 5:46. https://doi.org/10.1186/scrt440
Bocharov EV, Nadezhdin KD, Urban AS et al (2019) Familial L723P mutation can shift the distribution between the alternative APP transmembrane domain cleavage cascades by local unfolding of the epsilon-cleavage site suggesting a straightforward mechanism of Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis. ACS Chem Biol 14:1573–1582. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.9b00309
Bossaerts L, Hens E, Hanseeuw B et al (2021) Premature termination codon mutations in ABCA7 contribute to Alzheimer’s disease risk in Belgian patients. Neurobiol Aging 106:307.e1–e7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2021.04.023
Bossaerts L, Hendrickx Van de Craen E, Cacace R et al (2022) Rare missense mutations in ABCA7 might increase Alzheimer’s disease risk by plasma membrane exclusion. Acta Neuropathol Commun 10:43. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-022-01346-3
Cacace R, Sleegers K, Van Broeckhoven C (2016) Molecular genetics of early-onset Alzheimer’s disease revisited. Alzheimers Dement 12:733–748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2016.01.012
Cairns NJ, Perrin RJ, Franklin EE et al (2015) Neuropathologic assessment of participants in two multi-center longitudinal observational studies: the Alzheimer disease neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) and the dominantly Inherited Alzheimer network (DIAN). Neuropathology 35:390–400. https://doi.org/10.1111/neup.12205
Campion D, Charbonnier C, Nicolas G (2019) SORL1 genetic variants and Alzheimer disease risk: a literature review and meta-analysis of sequencing data. Acta Neuropathol 138:173–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-019-01991-4
Carmona S, Zahs K, Wu E et al (2018) The role of TREM2 in Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. Lancet Neurol 17:721–730. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30232-1
Carrasquillo MM, Zou F, Pankratz VS et al (2009) Genetic variation in PCDH11X is associated with susceptibility to late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Genet 41:192–198. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.305
Chen YG (2018) Research progress in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Chin Med J (Engl) 131:1618–1624. https://doi.org/10.4103/0366-6999.235112
Chhatwal JP, Schultz SA, McDade E et al (2022) Variant-dependent heterogeneity in amyloid beta burden in autosomal dominant Alzheimer’s disease: cross-sectional and longitudinal analyses of an observational study. Lancet Neurol 21:140–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(21)00375-6
Cho YY, Kwon OH, Park MK et al (2019) Elevated cellular cholesterol in Familial Alzheimer’s presenilin 1 mutation is associated with lipid raft localization of beta-amyloid precursor protein. PLoS ONE 14:e0210535. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0210535
Coon KD, Myers AJ, Craig DW et al (2007) A high-density whole-genome association study reveals that APOE is the major susceptibility gene for sporadic late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. J Clin Psychiatry 68:613–618. https://doi.org/10.4088/jcp.v68n0419
Corder EH, Saunders AM, Strittmatter WJ et al (1993) Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease in late onset families. Science 261:921–923. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.8346443
Cuccaro ML, Carney RM, Zhang Y et al (2016) SORL1 mutations in early- and late-onset Alzheimer disease. Neurol Genet 2:e116. https://doi.org/10.1212/NXG.0000000000000116
Di Marco LY, Venneri A, Farkas E et al (2015) Vascular dysfunction in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease–A review of endothelium-mediated mechanisms and ensuing vicious circles. Neurobiol Dis 82:593–606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2015.08.014
Dos Santos RB, Kanekiyo T, Singh J (2019) ApoE-2 brain-targeted gene therapy through transferrin and penetratin tagged liposomal nanoparticles. Pharm Res 36:161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-019-2691-7
Erickson MA, Niehoff ML, Farr SA et al (2012) Peripheral administration of antisense oligonucleotides targeting the amyloid-beta protein precursor reverses AbetaPP and LRP-1 overexpression in the aged SAMP8 mouse brain. J Alzheimers Dis 28:951–960. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-2011-111517
Evangelisti E, Wright D, Zampagni M et al (2013) Lipid rafts mediate amyloid-induced calcium dyshomeostasis and oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Alzheimer Res 10:143–153. https://doi.org/10.2174/1567205011310020004
Fedeli C, Filadi R, Rossi A et al (2019) PSEN2 (presenilin 2) mutants linked to familial Alzheimer disease impair autophagy by altering Ca(2+) homeostasis. Autophagy 15:2044–2062. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2019.1596489
Fernandez MA, Klutkowski JA, Freret T et al (2014) Alzheimer presenilin-1 mutations dramatically reduce trimming of long amyloid beta-peptides (Abeta) by gamma-secretase to increase 42-to-40-residue Abeta. J Biol Chem 289:31043–31052. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.581165
Filipello F, Morini R, Corradini I et al (2018) The Microglial innate immune receptor TREM2 is required for synapse elimination and normal brain connectivity. Immunity 48:979–991. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2018.04.016
Fischer W, Wictorin K, Bjorklund A et al (1987) Amelioration of cholinergic neuron atrophy and spatial memory impairment in aged rats by nerve growth factor. Nature 329:65–68. https://doi.org/10.1038/329065a0
Forero DA, Casadesus G, Perry G et al (2006) Synaptic dysfunction and oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease: emerging mechanisms. J Cell Mol Med 10:796–805. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1582-4934.2006.tb00439.x
Frisoni GB, Altomare D, Thal DR et al (2022) The probabilistic model of Alzheimer disease: the amyloid hypothesis revised. Nat Rev Neurosci 23:53–66. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41583-021-00533-w
Fung S, Smith CL, Prater KE et al (2020) Early-onset familial Alzheimer disease variant PSEN2 N141I heterozygosity is associated with altered microglia phenotype. J Alzheimers Dis 77:675–688. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-200492
Galla L, Redolfi N, Pozzan T et al (2020) Intracellular calcium dysregulation by the Alzheimer’s disease-linked protein presenilin 2. Int J Mol Sci 21:770. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030770
Genin E, Hannequin D, Wallon D et al (2011) APOE and Alzheimer disease: a major gene with semi-dominant inheritance. Mol Psychiatry 16:903–907. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2011.52
Goate A, Chartier-Harlin MC, Mullan M et al (1991) Segregation of a missense mutation in the amyloid precursor protein gene with familial Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 349:704–706. https://doi.org/10.1038/349704a0
Goldman JS, Hahn SE, Catania JW et al (2011) Genetic counseling and testing for Alzheimer disease: joint practice guidelines of the American college of medical genetics and the national society of genetic counselors. Genet Med 13:597–605. https://doi.org/10.1097/GIM.0b013e31821d69b8
Gomez-Isla T, Growdon WB, McNamara MJ et al (1999) The impact of different presenilin 1 andpresenilin 2 mutations on amyloid deposition, neurofibrillary changes and neuronal loss in the familial Alzheimer’s disease brain: evidence for other phenotype-modifying factors. Brain 122(Pt 9):1709–1719. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/122.9.1709
Gomez-Tortosa E, Ruggiero M, Sainz MJ et al (2018) SORL1 variants in familial Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 61:1275–1281. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-170590
Gotz J, Ittner LM, Schonrock N et al (2008) An update on the toxicity of Abeta in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 4:1033–1042. https://doi.org/10.2147/ndt.s3016
Greotti E, Capitanio P, Wong A et al (2019) Familial Alzheimer’s disease-linked presenilin mutants and intracellular Ca(2+) handling: A single-organelle, FRET-based analysis. Cell Calcium 79:44–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceca.2019.02.005
Guerreiro R, Wojtas A, Bras J et al (2013) TREM2 variants in Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med 368:117–127. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1211851
Guo Q, Sebastian L, Sopher BL et al (1999) Neurotrophic factors [activity-dependent neurotrophic factor (ADNF) and basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF)] interrupt excitotoxic neurodegenerative cascades promoted by a PS1 mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:4125–4130. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.96.7.4125
Guo Y, Wang Q, Chen S et al (2021) Functions of amyloid precursor protein in metabolic diseases. Metabolism 115:154454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154454
Hartl D, Nebrich G, Klein O et al (2016) SORLA regulates calpain-dependent degradation of synapsin. Alzheimers Dement 12:952–963. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2016.02.008
Hinrich AJ, Jodelka FM, Chang JL et al (2016) Therapeutic correction of ApoER2 splicing in Alzheimer’s disease mice using antisense oligonucleotides. EMBO Mol Med 8:328–345. https://doi.org/10.15252/emmm.201505846
Huang W, Qiu C, von Strauss E et al (2004) APOE genotype, family history of dementia, and Alzheimer disease risk: a 6-year follow-up study. Arch Neurol 61:1930–1934. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.61.12.1930
Hung C, Tuck E, Stubbs V et al (2021) SORL1 deficiency in human excitatory neurons causes APP-dependent defects in the endolysosome-autophagy network. Cell Rep 35:109259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109259
Huynh TV, Liao F, Francis CM et al (2017) Age-dependent effects of apoe reduction using antisense oligonucleotides in a model of beta-amyloidosis. Neuron 96:1013–1023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2017.11.014
Iqbal J, Suarez MD, Yadav PK et al (2022) ATP-binding cassette protein ABCA7 deficiency impairs sphingomyelin synthesis, cognitive discrimination, and synaptic plasticity in the entorhinal cortex. J Biol Chem 298:102411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102411
Jack CR Jr (2022) Advances in Alzheimer’s disease research over the past two decades. Lancet Neurol 21:866–869. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(22)00298-8
Jackson RJ, Meltzer JC, Nguyen H et al (2022) APOE4 derived from astrocytes leads to blood-brain barrier impairment. Brain 145:3582–3593. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awab478
Janicki SM, Stabler SM, Monteiro MJ (2000) Familial Alzheimer’s disease presenilin-1 mutants potentiate cell cycle arrest. Neurobiol Aging 21:829–836. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0197-4580(00)00222-0
Jayadev S, Leverenz JB, Steinbart E et al (2010) Alzheimer’s disease phenotypes and genotypes associated with mutations in presenilin 2. Brain 133:1143–1154. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awq033
Jayadev S, Case A, Alajajian B et al (2013) Presenilin 2 influences miR146 level and activity in microglia. J Neurochem 127:592–599. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.12400
Jia J, Xu E, Shao Y et al (2005) One novel presenilin-1 gene mutation in a Chinese pedigree of familial Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 7:119–124. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-2005-7204
Jia L, Du Y, Chu L et al (2020a) Prevalence, risk factors, and management of dementia and mild cognitive impairment in adults aged 60 years or older in China: a cross-sectional study. Lancet Public Health 5:e661–e671. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2468-2667(20)30185-7
Jia L, Fu Y, Shen L et al (2020b) PSEN1, PSEN2, and APP mutations in 404 Chinese pedigrees with familial Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 16:178–191. https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.12005
Jia L, Xu H, Chen S et al (2020c) The APOE epsilon4 exerts differential effects on familial and other subtypes of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 16:1613–1623. https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.12153
Jonsson T, Stefansson H, Steinberg S et al (2013) Variant of TREM2 associated with the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med 368:107–116. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1211103
Karsak M, Glebov K, Scheffold M et al (2020) A rare heterozygous TREM2 coding variant identified in familial clustering of dementia affects an intrinsically disordered protein region and function of TREM2. Hum Mutat 41:169–181. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.23904
Katsouri L, Lim YM, Blondrath K et al (2016) PPARgamma-coactivator-1alpha gene transfer reduces neuronal loss and amyloid-beta generation by reducing beta-secretase in an Alzheimer’s disease model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113:12292–12297. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1606171113
Kaur D, Sharma V, Deshmukh R (2019) Activation of microglia and astrocytes: a roadway to neuroinflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. Inflammopharmacology 27:663–677. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-019-00580-x
Khan S, Barve KH, Kumar MS (2020) Recent Advancements in pathogenesis, diagnostics and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Neuropharmacol 18:1106–1125. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X18666200528142429
Kiyota T, Ingraham KL, Jacobsen MT et al (2011) FGF2 gene transfer restores hippocampal functions in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease and has therapeutic implications for neurocognitive disorders. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:E1339–1348. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1102349108
Kodamullil AT, Iyappan A, Karki R et al (2017) Of mice and men: comparative analysis of neuro-inflammatory mechanisms in human and mouse using cause-and-effect models. J Alzheimers Dis 59:1045–1055. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-170255
Korvatska O, Leverenz JB, Jayadev S et al (2015) R47H variant of TREM2 associated with Alzheimer Disease in a large late-onset family: clinical, genetic, and neuropathological study. JAMA Neurol 72:920–927. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.0979
Korvatska O, Kiianitsa K, Ratushny A et al (2020) Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid Cell 2 R47H exacerbates immune response in Alzheimer’s disease Brain. Front Immunol 11:559342. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.559342
Koutsodendris N, Nelson MR, Rao A et al (2022) Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer’s disease: findings, hypotheses, and potential mechanisms. Annu Rev Pathol 17:73–99. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-030421-112756
Kunkle BW, Carney RM, Kohli MA et al (2017) Targeted sequencing of ABCA7 identifies splicing, stop-gain and intronic risk variants for Alzheimer disease. Neurosci Lett 649:124–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2017.04.014
Lee J, Chan SL, Mattson MP (2002) Adverse effect of a presenilin-1 mutation in microglia results in enhanced nitric oxide and inflammatory cytokine responses to immune challenge in the brain. Neuromolecular Med 2:29–45. https://doi.org/10.1385/NMM:2:1:29
Lee HJ, Lim IJ, Park SW et al (2012) Human neural stem cells genetically modified to express human nerve growth factor (NGF) gene restore cognition in the mouse with ibotenic acid-induced cognitive dysfunction. Cell Transplant 21:2487–2496. https://doi.org/10.3727/096368912X638964
Lee SH, Meilandt WJ, Xie L et al (2021) Trem2 restrains the enhancement of tau accumulation and neurodegeneration by beta-amyloid pathology. Neuron 109:1283–1301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2021.02.010
Levy-Lahad E, Wasco W, Poorkaj P et al (1995) Candidate gene for the chromosome 1 familial Alzheimer’s disease locus. Science 269:973–977. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.7638622
Li YM, Xu M, Lai MT et al (2000) Photoactivated gamma-secretase inhibitors directed to the active site covalently label presenilin 1. Nature 405:689–694. https://doi.org/10.1038/35015085
Li Y, Grupe A, Rowland C et al (2006) DAPK1 variants are associated with Alzheimer’s disease and allele-specific expression. Hum Mol Genet 15:2560–2568. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddl178
Li Q, Liu Y, Sun M (2017) Autophagy and Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Mol Neurobiol 37:377–388. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-016-0386-8
Li Y, Laws SM, Miles LA et al (2021) Genomics of Alzheimer’s disease implicates the innate and adaptive immune systems. Cell Mol Life Sci 78:7397–7426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-021-03986-5
Lista S, O’Bryant SE, Blennow K et al (2015) Biomarkers in sporadic and familial Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 47:291–317. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-143006
Liu Y, Wang DA (2015) Viral vector-mediated transgenic cell therapy in regenerative medicine: safety of the process. Expert Opin Biol Ther 15:559–567. https://doi.org/10.1517/14712598.2015.995086
Liu CC, Liu CC, Kanekiyo T et al (2013) Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer disease: risk, mechanisms and therapy. Nat Rev Neurol 9:106–118. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2012.263
Livingston G, Huntley J, Sommerlad A et al (2020) Dementia prevention, intervention, and care: 2020 report of the lancet commission. Lancet 396:413–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30367-6
Long JM, Holtzman DM (2019) Alzheimer disease: an update on pathobiology and treatment strategies. Cell 179:312–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2019.09.001
Lopera F, Ardilla A, Martinez A et al (1997) Clinical features of early-onset Alzheimer disease in a large kindred with an E280A presenilin-1 mutation. JAMA 277:793–799
Louwersheimer E, Cohn-Hokke PE, Pijnenburg YA et al (2017) Rare genetic variant in sorl1 may increase penetrance of Alzheimer’s disease in a family with several generations of APOE-varepsilon4 homozygosity. J Alzheimers Dis 56:63–74. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-160091
Loy CT, Schofield PR, Turner AM et al (2014) Genetics of dementia. Lancet 383:828–840. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60630-3
Lu J, Cao Q, Wang C et al (2019) Structure-based peptide inhibitor design of amyloid-β aggregation. Front Mol Neurosci 12:54. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2019.00054
Maarouf CL, Daugs ID, Spina S et al (2008) Histopathological and molecular heterogeneity among individuals with dementia associated with Presenilin mutations. Mol Neurodegener 3:20. https://doi.org/10.1186/1750-1326-3-20
Manczak M, Kandimalla R, Yin X et al (2018) Hippocampal mutant APP and amyloid beta-induced cognitive decline, dendritic spine loss, defective autophagy, mitophagy and mitochondrial abnormalities in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 27:1332–1342. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddy042
Manoharan S, Guillemin GJ, Abiramasundari RS et al (2016) The role of reactive oxygen species in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease, parkinson’s disease, and huntington’s disease: a mini review. Oxid Med Cell Long 2016:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/8590578
Martens YA, Zhao N, Liu CC et al (2022) ApoE Cascade Hypothesis in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias. Neuron 110:1304–1317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2022.03.004
Martinez M, Campion D, Brice A et al (1998) Apolipoprotein E epsilon4 allele and familial aggregation of Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 55:810–816. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.55.6.810
Mattson MP (2002) Oxidative stress, perturbed calcium homeostasis, and immune dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurovirol 8:539–550. https://doi.org/10.1080/13550280290100978
May P, Pichler S, Hartl D et al (2018) Rare ABCA7 variants in 2 German families with Alzheimer disease. Neurol Genet 4:e224. https://doi.org/10.1212/NXG.0000000000000224
Mendell JR, Al-Zaidy SA, Rodino-Klapac LR et al (2021) Current clinical applications of in vivo gene therapy with AAVs. Mol Ther 29:464–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.12.007
Meraz-Rios MA, Franco-Bocanegra D, Toral Rios D et al (2014) Early onset alzheimer’s disease and oxidative stress. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2014:375968. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/375968
Migliore L, Coppede F (2022) Gene-environment interactions in Alzheimer disease: the emerging role of epigenetics. Nat Rev Neurol 18:643–660. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41582-022-00714-w
Mishra R, Phan T, Kumar P et al (2022a) Augmenting neurogenesis rescues memory impairments in Alzheimer’s disease by restoring the memory-storing neurons. J Exp Med 219:e20220391. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20220391
Mishra S, Knupp A, Szabo MP et al (2022b) The Alzheimer’s gene SORL1 is a regulator of endosomal traffic and recycling in human neurons. Cell Mol Life Sci 79:162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-022-04182-9
Moloudizargari M, Asghari MH, Ghobadi E et al (2017) Autophagy, its mechanisms and regulation: Implications in neurodegenerative diseases. Ageing Res Rev 40:64–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2017.09.005
Muchnik C, Olivar N, Dalmasso MC et al (2015) Identification of PSEN2 mutation p.N141I in Argentine pedigrees with early-onset familial Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 36:2674–2677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.06.011
Mullan M, Crawford F, Axelman K et al (1992) A pathogenic mutation for probable Alzheimer’s disease in the APP gene at the N-terminus of beta-amyloid. Nat Genet 1:345–347. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0892-345
Naaldijk Y, Jager C, Fabian C et al (2017) Effect of systemic transplantation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells on neuropathology markers in APP/PS1 Alzheimer mice. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 43:299–314. https://doi.org/10.1111/nan.12319
Naj AC, Schellenberg GD, Alzheimer’s Disease Genetics C (2017) Genomic variants, genes, and pathways of Alzheimer’s disease: An overview. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 174:5–26. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.b.32499
Neuner SM, Tcw J, Goate AM (2020) Genetic architecture of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 143:104976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2020.104976
Nguyen HN, Son DJ, Lee JW et al (2006) Mutant presenilin 2 causes abnormality in the brain lipid profile in the development of Alzheimer’s disease. Arch Pharm Res 29:884–889. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02973910
Oxtoby NP, Young AL, Cash DM et al (2018) Data-driven models of dominantly-inherited Alzheimer’s disease progression. Brain 141:1529–1544. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awy050
Pang Y, Li T, Wang Q et al (2021) A Rare Variation in the 3’ untranslated region of the presenilin 2 gene is linked to Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurobiol 58:4337–4347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-021-02429-3
Pang K, Jiang R, Zhang W et al (2022) An App knock-in rat model for Alzheimer’s disease exhibiting Abeta and tau pathologies, neuronal death and cognitive impairments. Cell Res 32:157–175. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-021-00582-x
Parambi DGT, Alharbi KS, Kumar R et al (2022) Gene therapy approach with an emphasis on growth factors: theoretical and clinical outcomes in neurodegenerative diseases. Mol Neurobiol 59:191–233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-021-02555-y
Paroni G, Bisceglia P, Seripa D (2019) Understanding the amyloid hypothesis in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 68:493–510. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-180802
Perdigao C, Barata MA, Araujo MN et al (2020) Intracellular trafficking mechanisms of synaptic dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Cell Neurosci 14:72. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2020.00072
Pericak-Vance MA, Bebout JL, Gaskell PC Jr et al (1991) Linkage studies in familial Alzheimer disease: evidence for chromosome 19 linkage. Am J Hum Genet 48:1034–1050
Piaceri I, Nacmias B, Sorbi S (2013) Genetics of familial and sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Front Biosci (elite Ed) 5:167–177. https://doi.org/10.2741/e605
Pizzo P, Basso E, Filadi R et al (2020) Presenilin-2 and calcium handling: molecules, organelles, cells and brain networks. Cells 9:2166. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9102166
Poirier J, Davignon J, Bouthillier D et al (1993) Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 342:697–699. https://doi.org/10.1016/0140-6736(93)91705-q
Pottier C, Hannequin D, Coutant S et al (2012) High frequency of potentially pathogenic SORL1 mutations in autosomal dominant early-onset Alzheimer disease. Mol Psychiatry 17:875–879. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2012.15
Pratt KG, Zimmerman EC, Cook DG et al (2011) Presenilin 1 regulates homeostatic synaptic scaling through Akt signaling. Nat Neurosci 14:1112–1114. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2893
Qin W, Li W, Wang Q et al (2021) Race-related association between APOE Genotype and Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Alzheimers Dis 83:897–906. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-210549
Quan M, Zhao T, Tang Y et al (2020) Effects of gene mutation and disease progression on representative neural circuits in familial Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res Ther 12:14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13195-019-0572-2
Quiroz YT, Zetterberg H, Reiman EM et al (2020) Plasma neurofilament light chain in the presenilin 1 E280A autosomal dominant Alzheimer’s disease kindred: a cross-sectional and longitudinal cohort study. Lancet Neurol 19:513–521. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30137-X
Rafii MS, Baumann TL, Bakay RA et al (2014) A phase1 study of stereotactic gene delivery of AAV2-NGF for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 10:571–581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2013.09.004
Rafii MS, Tuszynski MH, Thomas RG et al (2018) Adeno-associated viral vector (Serotype 2)-nerve growth factor for patients with Alzheimer disease: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Neurol 75:834–841. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2018.0233
Ramirez Aguilar L, Acosta-Uribe J, Giraldo MM et al (2019) Genetic origin of a large family with a novel PSEN1 mutation (Ile416Thr). Alzheimers Dement 15:709–719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2018.12.010
Ray WJ, Ashall F, Goate AM (1998) Molecular pathogenesis of sporadic and familial forms of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Med Today 4:151–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1357-4310(98)01229-5
Reddy PH, Yin X, Manczak M et al (2018) Mutant APP and amyloid beta-induced defective autophagy, mitophagy, mitochondrial structural and functional changes and synaptic damage in hippocampal neurons from Alzheimer’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 27:2502–2516. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddy154
Reiman EM, Arboleda-Velasquez JF, Quiroz YT et al (2020) Exceptionally low likelihood of Alzheimer’s dementia in APOE2 homozygotes from a 5000-person neuropathological study. Nat Commun 11:667. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-14279-8
Reyes-Dumeyer D, Faber K, Vardarajan B et al (2022) The national institute on aging late-onset Alzheimer’s disease family based study: a resource for genetic discovery. Alzheimers Dement 18:1889–1897. https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.12514
Rogaeva E, Meng Y, Lee JH et al (2007) The neuronal sortilin-related receptor SORL1 is genetically associated with Alzheimer disease. Nat Genet 39:168–177. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1943
Roher AE, Maarouf CL, Malek-Ahmadi M et al (2013) Subjects harboring presenilin familial Alzheimer’s disease mutations exhibit diverse white matter biochemistry alterations. Am J Neurodegener Dis 2:187–207
Roher AE, Maarouf CL, Kokjohn TA (2016) Familial presenilin mutations and sporadic Alzheimer’s disease pathology: is the assumption of biochemical equivalence justified? J Alzheimers Dis 50:645–658. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-150757
Rossi A, Galla L, Gomiero C et al (2021) Calcium signaling and mitochondrial function in presenilin 2 knock-out mice: looking for any loss-of-function phenotype related to Alzheimer’s disease. Cells 10:204. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020204
Rossini M, Garcia-Casas P, Filadi R et al (2021) Loosening ER-mitochondria coupling by the expression of the presenilin 2 loop domain. Cells 10:1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10081968
Rothenberg C, Srinivasan D, Mah L et al (2010) Ubiquilin functions in autophagy and is degraded by chaperone-mediated autophagy. Hum Mol Genet 19:3219–3232. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddq231
Rovelet-Lecrux A, Legallic S, Wallon D et al (2012) A genome-wide study reveals rare CNVs exclusive to extreme phenotypes of Alzheimer disease. Eur J Hum Genet 20:613–617. https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2011.225
Sawikr Y, Yarla NS, Peluso I et al (2017) Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease: the preventive and therapeutic potential of polyphenolic nutraceuticals. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol 108:33–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.apcsb.2017.02.001
Sayed FA, Kodama L, Fan L et al (2021) AD-linked R47H-TREM2 mutation induces disease-enhancing microglial states via AKT hyperactivation. Sci Transl Med 13:eabe3947. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.abe3947
Scheltens P, De Strooper B, Kivipelto M et al (2021) Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 397:1577–1590. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32205-4
Schuessel K, Frey C, Jourdan C et al (2006) Aging sensitizes toward ROS formation and lipid peroxidation in PS1M146L transgenic mice. Free Radic Biol Med 40:850–862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2005.10.041
Selkoe DJ (2001) Alzheimer’s disease: genes, proteins, and therapy. Physiol Rev 81:741–766. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.2001.81.2.741
Serrano-Pozo A, Das S, Hyman BT (2021) APOE and Alzheimer’s disease: advances in genetics, pathophysiology, and therapeutic approaches. Lancet Neurol 20:68–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30412-9
Sherrington R, Rogaev EI, Liang Y et al (1995) Cloning of a gene bearing missense mutations in early-onset familial Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 375:754–760. https://doi.org/10.1038/375754a0
Strittmatter WJ, Saunders AM, Schmechel D et al (1993) Apolipoprotein E: high-avidity binding to beta-amyloid and increased frequency of type 4 allele in late-onset familial Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90:1977–1981. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.90.5.1977
Suzuki N, Cheung TT, Cai XD et al (1994) An increased percentage of long amyloid beta protein secreted by familial amyloid beta protein precursor (beta APP717) mutants. Science 264:1336–1340. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.8191290
Szaruga M, Munteanu B, Lismont S et al (2017) Alzheimer’s-causing mutations shift abeta length by destabilizing gamma-secretase-abetan interactions. Cell 170:443–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.07.004
Szaruga M, Munteanu B, Lismont S et al (2021) Alzheimer’s-causing mutations shift abeta length by destabilizing gamma-secretase-abetan interactions. Cell 184:2257–2258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2021.03.058
Tackenberg C, Brandt R (2009) Divergent pathways mediate spine alterations and cell death induced by amyloid-beta, wild-type tau, and R406W tau. J Neurosci 29:14439–14450. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3590-09.2009
Tackenberg C, Kulic L, Nitsch RM (2020) Familial Alzheimer’s disease mutations at position 22 of the amyloid beta-peptide sequence differentially affect synaptic loss, tau phosphorylation and neuronal cell death in an ex vivo system. PLoS ONE 15:e0239584. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0239584
Tanna T, Sachan V (2014) Mesenchymal stem cells: potential in treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther 9:513–521. https://doi.org/10.2174/1574888x09666140923101110
Tariot PN, Lopera F, Langbaum JB et al (2018) The Alzheimer's Prevention Initiative Autosomal-Dominant Alzheimer's Disease Trial: A study of crenezumab versus placebo in preclinical PSEN1 E280A mutation carriers to evaluate efficacy and safety in the treatment of autosomal-dominant Alzheimer's disease, including a placebo-treated noncarrier cohort. Alzheimers Dement (N Y) 4:150–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trci.2018.02.002
Theuns J, Marjaux E, Vandenbulcke M et al (2006) Alzheimer dementia caused by a novel mutation located in the APP C-terminal intracytosolic fragment. Hum Mutat 27:888–896. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.20402
Thonberg H, Chiang HH, Lilius L et al (2017) Identification and description of three families with familial Alzheimer disease that segregate variants in the SORL1 gene. Acta Neuropathol Commun 5:43. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-017-0441-9
Tian Y, Bassit B, Chau D et al (2010) An APP inhibitory domain containing the Flemish mutation residue modulates gamma-secretase activity for Abeta production. Nat Struct Mol Biol 17:151–158. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1743
Tiwari S, Atluri V, Kaushik A et al (2019) Alzheimer’s disease: pathogenesis, diagnostics, and therapeutics. Int J Nanomedicine 14:5541–5554. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S200490
Tomiyama T, Shimada H (2020) APP Osaka mutation in familial Alzheimer’s disease-its discovery, phenotypes, and mechanism of recessive inheritance. Int J Mol Sci 21:1413. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21041413
Tönnies E, Trushina E (2017) Oxidative stress, synaptic dysfunction, and Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 57:1105–1121. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-161088
Tuszynski MH, Yang JH, Barba D et al (2015) Nerve growth factor gene therapy: activation of neuronal responses in Alzheimer disease. JAMA Neurol 72:1139–1147. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.1807
Ulland TK, Colonna M (2018) TREM2 - a key player in microglial biology and Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurol 14:667–675. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41582-018-0072-1
Ulland TK, Song WM, Huang SC et al (2017) TREM2 maintains microglial metabolic fitness in Alzheimer’s disease. Cell 170:649–663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.07.023
Van Cauwenberghe C, Van Broeckhoven C, Sleegers K (2016) The genetic landscape of Alzheimer disease: clinical implications and perspectives. Genet Med 18:421–430. https://doi.org/10.1038/gim.2015.117
Van Dooren T, Princen K, De Witte K et al (2014) Derailed intraneuronal signalling drives pathogenesis in sporadic and familial Alzheimer’s disease. Biomed Res Int 2014:167024. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/167024
Van den Bossche T, Sleegers K, Cuyvers E et al (2016) Phenotypic characteristics of Alzheimer patients carrying an ABCA7 mutation. Neurology 86:2126–2133. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000002628
van Duijn CM, de Knijff P, Cruts M et al (1994) Apolipoprotein E4 allele in a population-based study of early-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Genet 7:74–78. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0594-74
Vassar R, Bennett BD, Babu-Khan S et al (1999) Beta-secretase cleavage of Alzheimer’s amyloid precursor protein by the transmembrane aspartic protease BACE. Science 286:735–741. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.286.5440.735
Velez JI, Lopera F, Sepulveda-Falla D et al (2016) APOE*E2 allele delays age of onset in PSEN1 E280A Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Psychiatry 21:916–924. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2015.177
Verheijen J, Sleegers K (2018) Understanding Alzheimer disease at the interface between genetics and transcriptomics. Trends Genet 34:434–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2018.02.007
Wang X, Wang W, Li L et al (2014) Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1842:1240–1247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.10.015
Wang W, Hou TT, Jia LF et al (2019) Toxic amyloid-beta oligomers induced self-replication in astrocytes triggering neuronal injury. EBioMedicine 42:174–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.03.049
Weston PSJ, Nicholas JM, Henley SMD et al (2018) Accelerated long-term forgetting in presymptomatic autosomal dominant Alzheimer’s disease: a cross-sectional study. Lancet Neurol 17:123–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(17)30434-9
Williams T, Borchelt DR, Chakrabarty P (2020) Therapeutic approaches targeting apolipoprotein E function in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurodegener 15:8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-020-0358-9
Wu S, Sasaki A, Yoshimoto R et al (2008) Neural stem cells improve learning and memory in rats with Alzheimer’s disease. Pathobiology 75:186–194. https://doi.org/10.1159/000124979
Wu CC, Lien CC, Hou WH et al (2016) Gain of BDNF function in engrafted neural stem cells promotes the therapeutic potential for Alzheimer’s disease. Sci Rep 6:27358. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep27358
Wu XL, Pina-Crespo J, Zhang YW et al (2017) Tau-mediated neurodegeneration and potential implications in diagnosis and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Chin Med J (Engl) 130:2978–2990. https://doi.org/10.4103/0366-6999.220313
Xia D, Lianoglou S, Sandmann T et al (2022) Novel App knock-in mouse model shows key features of amyloid pathology and reveals profound metabolic dysregulation of microglia. Mol Neurodegener 17:41. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-022-00547-7
Yang Y, Arseni D, Zhang W et al (2022) Cryo-EM structures of amyloid-beta 42 filaments from human brains. Science 375:167–172. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abm7285
Zampese E, Fasolato C, Kipanyula MJ et al (2011) Presenilin 2 modulates endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-mitochondria interactions and Ca2+ cross-talk. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:2777–2782. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1100735108
Zarea A, Charbonnier C, Rovelet-Lecrux A et al (2016) Seizures in dominantly inherited Alzheimer disease. Neurology 87:912–919. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000003048
Zhang S, Cai F, Wu Y et al (2020a) A presenilin-1 mutation causes Alzheimer disease without affecting Notch signaling. Mol Psychiatry 25:603–613. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-018-0101-x
Zhang W, Jiao B, Xiao T et al (2020b) Association of rare variants in neurodegenerative genes with familial Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 7:1985–1995. https://doi.org/10.1002/acn3.51197
Zhao Y, Wu X, Li X et al (2018) TREM2 Is a receptor for beta-amyloid that mediates microglial function. Neuron 97:1023–1031. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2018.01.031
Zou L, Wang Z, Shen L et al (2007) Receptor tyrosine kinases positively regulate BACE activity and Amyloid-beta production through enhancing BACE internalization. Cell Res 17:389–401. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2007.5
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Mengmeng Guo, for his literature search for the preclinical studies of gene therapy section.
Funding
This work was supported by the Key Project of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U20A20354); Beijing Brain Initiative from Beijing Municipal Science & Technology Commission (Z201100005520016, Z201100005520017); National major R&D projects of China-Scientific technological innovation 2030 (2021ZD0201802); the National Key Scientific Instrument and Equipment Development Project (31627803); the Key Project of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81530036); Youth Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (82101503); Beijing Postdoctoral Research Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JJ and MQ conceived the idea and framework of the manuscript. MQ, SC, QW and SW wrote different sections of the manuscript. MQ and SC created the figure. SC, QW and MQ created the table. Everyone participated in the discussion, revision, and approval of the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The author declares no competing financial interests.
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
All authors approved to publish the paper.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Quan, M., Cao, S., Wang, Q. et al. Genetic Phenotypes of Alzheimer’s Disease: Mechanisms and Potential Therapy. Phenomics 3, 333–349 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-023-00098-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-023-00098-x