Abstract
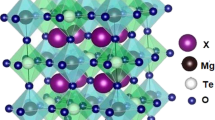
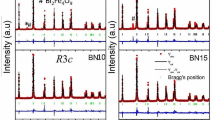
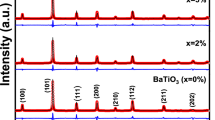
The scientific research findings emphasize the need to replace lead-based ferroelectric ceramics with environmentally friendly alternatives, driving heightened research interest in materials rivaling the performance of lead zirconate titanate (PZT). Among potential substitutes, bismuth layered structure ferroelectrics (BLSF), or Aurivillius compounds, have gained prominence. Our focus is on synthesizing Y-doped strontium bismuth niobate (SrBi2−xYxNb2O9), a BLSF material. Employing the solid-state treatment method, the structural, electrical, and dielectric properties of undoped and doped ceramics were scrutinized. Characterization involved X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Dielectric properties were systematically evaluated across frequencies and temperatures. XRD revealed the formation of the pure phase structure SrBi2Nb2O9 at 1100 °C, with no secondary phases. FTIR exhibited characteristic bands at approximately 619 cm−1 and 810 cm−1. SEM displayed thin plate-like grains and crystallites (sizes < 1 nm and 24 nm, respectively). The SrBi2−xYxNb2O9 ceramic demonstrated low dielectric loss values. Yttrium substitution for bismuth notably shifted the ferroelectric–paraelectric transition temperature from 460 to 435 °C, influencing dielectric constant behavior at higher frequencies. Structural and property changes were attributed to physicochemical phenomena, elucidated by considering density and lattice parameters.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The manuscript has no associated data.
References
G. Yueqiu, C. Hongyi, X. Shuhong, L. Xujun, J. Electron. Mater. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-017-5947-1
B.R. Kumar, N.V. Prasad, G. Prasad, G.S. Kumar, Trans. Indian Ceram. Soc. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/0371750X.2019.1610068
R.F. Abreu, S.O. Saturno, J.P.C. do Nascimento, E.O. Sancho, J.E.V. de Morais, J.C. Sales, D.X. Gouveia, H.D. de Andrade, I.S. Queiroz Jr., A.S.B. Sombra, J. Electromagn. Waves Appl. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/09205071.2020.1787231
M. Uehara, R. Mizutani, S. Yasuoka, T. Shimizu, H. Yamada, M. Akiyama, H. Funakubo, Appl. Phys. Express (2022). https://doi.org/10.35848/1882-0786/ac8048
M. Afqir, A. Tachafine, D. Fasquelle, M. Elaatmani, J.C. Carru, A. Zegzouti, M. Daoud, A. Oufakir, Appl. Ceram. (2019). https://doi.org/10.2298/PAC1903281A
Y. Shi, Y. Pu, J. Li, R. Shi, W. Wang, Q. Zhang, L. Guo, Ceram. Int. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.01.129
Z. Hu, V. Koval, H. Zhang, K. Chen, Y. Yue, D. Zhang, H. Yan, J. Adv. Ceram. (2023). https://doi.org/10.26599/JAC.2023.9220754
V.A. Isupov, Inorg. Mater. (2007). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0020168507090129
R.F. Abreu, S.O. Saturno, E.O. Sancho, X.D. Gouveia, A.S.B. Sombra, J. Electron. Mater. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-018-06859-z
S.W. Hwang, T.H. Noh, I.S. Cho, Catalysts (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9050393
R. Verma, A. Chauhan, K.M. Batoo, R. Kumar, M. Hadhi, E.H. Raslan, Effect of calcination temperature on structural and morphological properties of bismuth ferrite nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 47(3), 3680–3691 (2021)
J. Hou, Z. Dai, C. Liu, S. Yasui, Y. Cong, S. Gu, Enhanced photoelectric properties for BiZn0. 5Zr0. 5O3 modified KNN-based lead-free ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 960, 170639 (2023)
Y.I. Yurasov, M.I. Tolstunov, A.V. Nazarenko, A.A. Pavelko, A.V. Yudin, I.A. Verbenko, L.A. Reznitchenko, Dielectric and piezoelectric properties of modified lead-free NaNbO3–KNbO3/PVDF composite ceramics. J. Adv. Dielectr. 11(05), 2160015 (2021)
H. Zhang, T. Wei, Q. Zhang, W. Ma, P. Fan, D. Salamon, S.T. Zhang, B. Nan, H. Tan, Z, G, Ye. J. Mater. Chem. C (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/D0TC04381H
A. Imane, Z. Abdelouahad, N. Elbinna, E. Mohamed, D. Mohamed, J. Ceram. Process. Res. 24(2), 222–229 (2023)
B.R. Kannan, B.H. Venkataraman, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2255-x
T. Wei, B. Jia, L. Shen, C. Zhao, L. Wu, B. Zhang, X. Tao, S. Wu, Y. Liang, J. Eur. Ceram. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2020.04.014
V. Shrivastava, A.K. Jha, R.G. Mendiratta, Solid State Commun. (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssc.2004.10.006
J.N. Kiran, M. Sreenivasulu, K.S. Rao, K.S. Rao, S. Nagamani, T. Nagamalleswari, Today: Proc. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.10.119
Z.Ž Lazarević, Č Jovalekić, M. Gilić, V. Ivanovski, A. Umićević, D. Sekulić, N.Ž Romčević, Sci. Sinter. (2017). https://doi.org/10.2298/SOS1703277L
R. Sahebi, M.R. Roknabadi, M. Behdani, Optik (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.164204
R. Sahebi, M.R. Roknabadi, M. Behdani, Mater. Res. Express. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab6c17
K. Yadav, Mater. Today: Proc. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.01.467
R. Ramaraghavulu, S. Buddhudu, Ferroelectr (2014). https://doi.org/10.1080/00150193.2014.874924
S.K. Patri, R.N.P. Choudhary, Appl. Phys. A (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-008-4796-4
C. Keeney, S. Groh, S. Kulkarni, M.E. Roy, R.W. Pemble, R.W. Whatmore, J. Appl. Phys. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4734983
S. Supriya, Micron (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micron.2022.103344
J.N. Kiran, J.A. Kiran, S. Nagamani, Mater. Today: Proc. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2023.05.230
P. Pandey, S.K. Makineni, A. Samanta, A. Sharma, S.M.B. DasNithin, C. Srivastava, A.K. Singh, D. Raabe, B. Gault, K. Chattopadhyay, Acta Mater. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2018.09.049
B.H. Venkataraman, K.B.R. Varma, Solid State Ion. (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2003.12.020
A. Dwivedi, K.N. Singh, M. Hait, P.K. Bajpai, J. Eng. Sci. (2022). https://doi.org/10.30919/es8d760
A. Grünebohm, M. Marathe, R. Khachaturyan, R. Schiedung, D.C. Lupascu, V.V. Shvartsman, J. Phys. Condens. Matter 34(7), 073002 (2021)
A.V. Pavlenko, D.V. Stryukov, M.V. Vladimirov, A.E. Ganzha, S.A. Udovenko, A. Joseph, N.V. Ter-Oganessian (2021). arXiv:2112.04579
P. Chaudhary, S. Dabas, M. Kumar, A. Kumar, O.P. Thakur, Bull. Mater. Sci. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-020-02216-1
A. Khokhar, P.K. Goyal, O.P. Thakur, A.K. Shukla, K. Sreenivas, Mater. Chem. Phys. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2014.11.074
M. Afqir, A. Tachafine, D. Fasquelle, M. Elaatmani, J.C. Carru, A. Zegzouti, M. Daoud, Dielectric properties of SrBi1. 8RE0. 2Nb2O9 (RE= Yb, Tm, Tb, Gd, Er, Sm and Ce) ceramics. Solid State Sci. 73, 51–56 (2017)
R.F. Abreu, S.O. Saturno, J.P.C. do Nascimento, E.O. Sancho, J.E.V. De Morais, J.C. Sales, A.S.B. Sombra, Dielectric characterisation and numerical investigation of SrBi2Nb2O9–Bi2O3 composites for applications in microwave range. J. Electromagn. Waves Appl. 34(12), 1705–1718 (2020)
T.P. Wendari, S. Arief, N. Mufti, V. Suendo, A. Prasetyo, J. Baas, G.R. Blake, Ceram. Int. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2014.11.074
L. Zhang, Y. Nie, C. Hu, J. Qu, Appl. Catal. B Environ. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.06.015
E. Shi, Y. Gao, B.P. Finkenauer, A.H. Coffey, L. Dou, Chem. Soc. Rev. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CS00886D
Y. Yan, L. Jin, L. Feng, G. Cao, Mater. Sci. Eng. B (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2006.02.060
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: IA, MD, and AZ; Methodology: IA, MA, MD, and AZ; Data curation and writing of the original draft: IA; Validation and writing, reviewing, and editing of the manuscript: IA, MD, AZ, MA.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Anasser, I., Daoud, M., Zegzouti, A. et al. Synthesis, characterization, and dielectric properties of Y-doped strontium bismuth niobate (SrBi2−xYxNb2O9) ceramics: a lead-free ferroelectric alternative with enhanced performance. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43207-024-00389-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43207-024-00389-7