Abstract
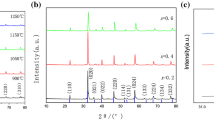
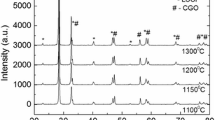
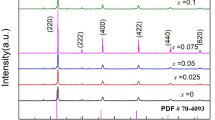
Herein, we report a facilely synthesized Sm0.5Sr0.5CoO3 (SSC) nano-catalyst as a cathode material for the solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC). The SSC nano-catalyst was synthesized by a sol–gel process using citric acid and metal nitrates and calcination was performed at a relatively low temperature of 1250 ℃. The crystallinity and morphology of the catalyst were observed by the X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscope. The average particle size of the SSC powder was 100 nm after calcination at 1250 °C. The resulting SSC material was employed as a cathode for the SOFC. The SOFC cell with highly active SSC showed a peak power density of 900 mWcm−2 at 700 °C. The single cell with an SSC cathode showed excellent stability under the accelerated operating conditions of 0.5A/cm2 and 650 °C for 1250 min. The cell performance was enhanced during the initial hours of the long-term operation which is attributed to the cathode activation process and improved cathode/buffer layer interface contact. This work features a cost-effective, scalable, and reproducible method for the production of highly robust SSC cathode material for the SOFC under relatively low calcination temperatures.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.C. Singhal, Solid oxide fuel cells for stationary, mobile, and military applications. Solid State Ion. 152–153, 405–410 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-2738(02)00349-1
M.Z. Khan, M.T. Mehran, R.-H. Song, J.-W. Lee, S.-B. Lee, T.-H. Lim, A simplified approach to predict performance degradation of a solid oxide fuel cell anode. J. Power Sources. 391, 94–105 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2018.04.080
S. Kim, D. Woo Joh, D.-Y. Lee, J. Lee, H. Sung Kim, M. Zubair Khan, J. Eun Hong, S.-B. Lee, S. Joo Park, R.-H. Song, M. Taqi Mehran, C. Kyun Rhee, T.-H. Lim, Microstructure tailoring of solid oxide electrolysis cell air electrode to boost performance and long-term durability. Chem. Eng. J. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.128318
M.Z. Khan, A. Iltaf, H.A. Ishfaq, F.N. Khan, W.H. Tanveer, R.-H. Song, M.T. Mehran, M. Saleem, A. Hussain, Z. Masaud, Flat-tubular solid oxide fuel cells and stacks: a review. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 9, 745–770 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/21870764.2021.1920135
M.Z. Khan, R.-H. Song, S.-B. Lee, T.-H. Lim, Lifetime prediction of anode-supported solid oxide fuel cell on the basis of individual components degradation. ECS Trans. 91, 621–627 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1149/09101.0621ecst
H. Yokokawa, N. Sakai, T. Horita, K. Yamaji, M.E. Brito, H. Kishimoto, Thermodynamic and kinetic considerations on degradations in solid oxide fuel cell cathodes. J. Alloys Compd. 452, 41–47 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2006.12.150
E.D. Wachsman, K.T. Lee, Lowering the temperature of solid. Science 334(2011), 935–939 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1204090
M.T. Mehran, T. Kim, M.Z. Khan, S. Lee, T. Lim, R. Song, Highly durable nano-oxide dispersed ferritic stainless steel interconnects for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cells. J. Power Sources. 439, 227109 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2019.227109
J.H. Park, H.-N. Im, K.T. Lee, Understanding redox cycling behavior of Ni–YSZ anodes at 500 °C in solid oxide fuel cells by electrochemical impedance analysis. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 58, 606–613 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43207-021-00136-2
A. Hussain, R.-H. Song, D.W. Joh, J.-E. Hong, S.-B. Lee, T.-H. Lim, Development of high-performance anode-supported planar SOFC with large area by 4-layer co-firing process. ECS Trans. 103, 73–81 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1149/10301.0073ecst
T.-H. Kim, M.Z. Khan, R.-H. Song, S.-B. Lee, T.-H. Lim, J.-E. Hong, Development of oxide dispersed ferritic steel as a solid oxide fuel cell interconnect. ECS Trans. 91, 2307–2312 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1149/09101.2307ecst
H.A. Ishfaq, M.Z. Khan, M.T. Mehran, R. Raza, W.H. Tanveer, S. Bibi, A. Hussain, H.A. Muhammad, R.-H. Song, Boosting performance of the solid oxide fuel cell by facile nano-tailoring of La0.6Sr0.4CoO3-δ cathode. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.11.109
M.Z. Khan, R.-H. Song, M.T. Mehran, S.-B. Lee, T.-H. Lim, Controlling cation migration and inter-diffusion across cathode/interlayer/electrolyte interfaces of solid oxide fuel cells: a review. Ceram. Int. 47, 5839–5869 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.11.002
J. Seo, H.-W. Kim, J.H. Yu, H.J. Park, Electrochemical properties of Ba0.5Sr0.5Co0.8Fe0.2O3 and BaZr0.65Ce0.20Y0.15O3 composite cathodes on Y-doped barium–cerium–zirconium oxide solid electrolyte. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 59, 217–223 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43207-021-00169-7
Y. Li, W. Zhang, Y. Zheng, J. Chen, B. Yu, Y. Chen, M. Liu, Controlling cation segregation in perovskite-based electrodes for high electro-catalytic activity and durability. Chem. Soc. Rev. 46, 6345–6378 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CS00120G
Z. Masaud, M. Zubair Khan, A. Hussain, H. Ahmad Ishfaq, R.-H. Song, S.-B. Lee, D.W. Joh, T.-H. Lim, Recent activities of solid oxide fuel cell research in the 3D printing processes. Trans. Korean Hydrogen New Energy Soc. 32, 11–40 (2021). https://doi.org/10.7316/KHNES.2021.32.1.11
M.Z. Khan, R.-H. Song, S.-B. Lee, J.-W. Lee, T.-H. Lim, S.-J. Park, Effect of GDC interlayer on the degradation of solid oxide fuel cell cathode during accelerated current load cycling. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 39, 20799–20805 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2014.07.022
Z. Duan, M. Yang, A. Yan, Z. Hou, Y. Dong, Y. Chong, M. Cheng, W. Yang, Ba0.5Sr0.5Co0.8Fe0.2O3−δ as a cathode for IT-SOFCs with a GDC interlayer. J. Power Sources. 160, 57–64 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2006.01.092
D. Kim, I. Jeong, K.J. Kim, K.T. Bae, D. Kim, J. Koo, H. Yu, K.T. Lee, A brief review of heterostructure electrolytes for high-performance solid oxide fuel cells at reduced temperatures. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 59, 131–152 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43207-021-00175-9
S. Jo, B. Sharma, D.-H. Park, J. Myung, Materials and nano-structural processes for use in solid oxide fuel cells: a review. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 57, 135–151 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43207-020-00022-3
S.F. Mohammad, S. Ahmad, H.A. Rahman, A. Muchtar, Effect of SSC loading and calcination temperature on the phase and microstructure formation of SSC-SDCC cathode. Int. J. Integr. Eng. 11, 161–168 (2019). https://doi.org/10.30880/ijie.2019.11.07.021
R. Liu, D. Xu, S. Li, Z. Lü, Y. Xue, D. Wang, W. Su, Solid-state synthesis and properties of SmCoO3. Front. Chem. China 1, 398–401 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11458-006-0065-2
R. Pelosato, G. Cordaro, D. Stucchi, C. Cristiani, G. Dotelli, Cobalt based layered perovskites as cathode material for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cells: a brief review. J. Power Sources. 298, 46–67 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.08.034
S.J. Skinner, Recent advances in Perovskite-type materials for solid oxide fuel cell cathodes. Int. J. Inorg. Mater. 3, 113–121 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1466-6049(01)00004-6
Y. Cao, M.J. Gadre, A.T. Ngo, S.B. Adler, D.D. Morgan, Factors controlling surface oxygen exchange in oxides. Nat. Commun. 10, 1346 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-08674-4
M.T. Mehran, M.Z. Khan, S.-B. Lee, T.-H. Lim, S. Park, R.-H. Song, Improving sulfur tolerance of Ni-YSZ anodes of solid oxide fuel cells by optimization of microstructure and operating conditions. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 43, 11202–11213 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.04.200
J.M. Vohs, R.J. Gorte, High-performance SOFC cathodes prepared by infiltration. Adv. Mater. 21, 943–956 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200802428
D. Ding, X. Li, S.Y. Lai, K. Gerdes, M. Liu, Enhancing SOFC cathode performance by surface modification through infiltration. Energy Environ Sci. 7, 552 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ee42926a
Z. Jiang, C. Xia, F. Chen, Nano-structured composite cathodes for intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cells via an infiltration/impregnation technique. Electrochim Acta. 55, 3595–3605 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2010.02.019
T.E. Burye, J.D. Nicholas, Improving La0.6Sr0.4Co0.8Fe0.2O3−δ infiltrated solid oxide fuel cell cathode performance through precursor solution desiccation. J Power Sources. 276, 54–61 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.11.082
T.E. Burye, J.D. Nicholas, Precursor solution additives improve desiccated La0.6Sr0.4Co08Fe0.2O3–x infiltrated solid oxide fuel cell cathode performance. J Power Sources. 301, 287–298 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.10.012
Y.-H. Song, S.U. Rehman, H.-S. Kim, H.-S. Song, R.-H. Song, T.-H. Lim, J.-E. Hong, S.-J. Park, J.-Y. Huh, S.-B. Lee, Facile surface modification of LSCF/GDC cathodes by epitaxial deposition of Sm0.5 Sr0.5 CoO 3 via ultrasonic spray infiltration. J. Mater. Chem. A Mater. 8, 3967–3977 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/C9TA11704K
W. Wang, M.D. Gross, J.M. Vohs, R.J. Gorte, The stability of LSF-YSZ electrodes prepared by infiltration. J. Electrochem. Soc. 154, B439 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2709510
S. Ke, Y. Wang, Z. Pan, Effects of precipitant and surfactant on co-precipitation synthesis of Nd2Si2O7 ceramic pigment. Dyes Pigm. 118, 145–151 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2015.03.016
C.R. Michel, E. Delgado, G. Santillán, A.H. Martínez, A. Chávez-Chávez, An alternative gas sensor material: synthesis and electrical characterization of SmCoO3. Mater. Res. Bull. 42, 84–93 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2006.05.008
H.Y. Tu, Y. Takeda, N. Imanishi, O. Yamamoto, Ln1−Sr CoO3(Ln = Sm, Dy) for the electrode of solid oxide fuel cells. Solid State Ion. 100, 283–288 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-2738(97)00360-3
M. Thommes, K. Kaneko, Av. Neimark, J.P. Olivier, F. Rodriguez-Reinoso, J. Rouquerol, K.S.W. Sing, Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chemi. 87, 1051–1069 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1515/pac-2014-1117
V. Mariyappan, M. Keerthi, S.-M. Chen, G. Boopathy, Facile synthesis of α -Sm2S3/MoS 2 bimetallic sulfide as a high-performance electrochemical sensor for the detection of antineoplastic drug 5-fluorouracil in a biological samples. J Electrochem Soc. 167, 117506 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1149/1945-7111/aba1a5
F.-H. Chen, J.-L. Her, S. Mondal, M.-N. Hung, T.-M. Pan, Impact of Ti doping in Sm2 O3 dielectric on electrical characteristics of a-InGaZnO thin-film transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 193515 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4807014
P.A.W. van der Heide, Systematic x-ray photoelectron spectroscopic study of La1?xSrx-based perovskite-type oxides. Surf. Interface Anal. 33, 414–425 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1002/sia.1227
D. Kim, J.W. Park, B.-H. Yun, J.H. Park, K.T. Lee, Correlation of time-dependent oxygen surface exchange kinetics with surface chemistry of La0.6 Sr0.4 Co0.2 Fe08 O 3−δ catalysts. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 11, 31786–31792 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b06569
A. Nenning, A.K. Opitz, C. Rameshan, R. Rameshan, R. Blume, M. Hävecker, A. Knop-Gericke, G. Rupprechter, B. Klötzer, J. Fleig, Ambient pressure XPS study of mixed conducting perovskite-type SOFC cathode and anode materials under well-defined electrochemical polarization. J. Phys. Chem. C. 120, 1461–1471 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b08596
X. Ge, Z. Li, L. Yin, Metal-organic frameworks derived porous core/shellCoP@C polyhedrons anchored on 3D reduced graphene oxide networks as anode for sodium-ion battery. Nano Energy 32, 117–124 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2016.11.055
M.Z. Khan, M.T. Mehran, R.-H. Song, J.-W. Lee, S.-B. Lee, T.-H. Lim, S.-J. Park, Effect of GDC interlayer thickness on durability of solid oxide fuel cell cathode. Ceram. Int. 42, 6978–6984 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.01.085
M.Z. Khan, M.T. Mehran, R.H. Song, S.B. Lee, T.H. Lim, Effects of applied current density and thermal cycling on the degradation of a solid oxide fuel cell cathode. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 43, 12346–12357 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.04.175
M.Z. Khan, R.H. Song, A. Hussain, S.B. Lee, T.H. Lim, J.E. Hong, Effect of applied current density on the degradation behavior of anode-supported flat-tubular solid oxide fuel cells. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 40, 1407–1417 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2019.11.017
C. Xia, Sm0.5Sr0.5CoO3 cathodes for low-temperature SOFCs. Solid State Ion. 149, 11–19 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-2738(02)00131-5
J. Chen, X. Yang, D. Wan, B. Li, L. Lei, T. Tian, B. Chi, F. Chen, Novel structured Sm0.5Sr0.5CoO3-δ cathode for intermediate and low temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Electrochim Acta. 341, 136031 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2020.136031
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the technical resources and lab facilities from the Pak-Austria Fachhochschule: Institute of Applied Sciences and Technology, Haripur, Pakistan, and Sungkyunkwan University, Suwon, South Korea. The authors are thankful to Dr. Rizwan Raza and Muhammad Measam Ali for their support and valuable suggestions in this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmed, S., Kazmi, W.W., Hussain, A. et al. Facile and low-temperature synthesis approach to fabricate Sm0.5Sr0.5CoO3−δ cathode material for solid oxide fuel cell. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 60, 272–282 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43207-022-00261-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43207-022-00261-6