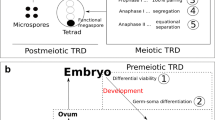
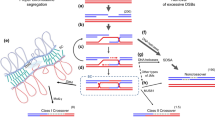
Abstract
Mendel’s laws state that each of the two alleles would segregate during gamete formation and show the same transmission ratio in the next generation. However, an unexpected biased allele transmission was first detected in Drosophila a century ago, and was subsequently observed in other animals, plants, and microorganisms. Such segregation distortion (SD) shows substantial effects in population structure and fitness of the progenies, which would ultimately lead to reproductive isolation and speciation. Here, we trace the early investigations on the violation of Mendelian genetic principle, which appears as a wide-existence phenomenon rather than a case of exception. The occurence of SD in the whole genome was observed in a number of plant species at the single- and multi-locus level. Biased transmission ratio might occur at meiosis stage due to asymmetric movement of the chromosome; transmission ratio advantage is also caused by interaction and battle between the alleles from respective genomes at the genetic and molecular level. The origin of a SD system is likely to be determined by coevolution of the killer and protector via recurrent breakdown or rebalance loop. These updated understandings also promote genetic improvement of hybrid crops.


(This figure is modified from Dawe et al. 2018)
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akera T, Chmátal L, Trimm E, Yang K, Aonbangkhen C, Chenoweth DM, Janke C, Schultz RM, Lampson MA (2017) Spindle asymmetry drives non-mendelian chromosome segregation. Science 358:668–672
Alheit KV, Reif JC, Maurer HP, Hahn V, Weissmann EA, Miedaner T, Würschum T (2011) Detection of segregation distortion loci in triticale (× Triticosecale Wittmack) based on a high-density DArT marker consensus genetic linkage map. BMC Genom 12:380
Bauer H, Willert J, Koschorz B, Herrmann BG (2005) The t complex-encoded GTPase-activating protein Tagap1 acts as a transmission ratio distorter in mice. Nat Genet 37:969–973
Bauer H, Veron N, Willert J, Herrmann BG (2007) The t-complex-encoded guanine nucleotide exchange factor Fgd2 reveals that two opposing signaling pathways promote transmission ratio distortion in the mouse. Genes Dev 21:143–147
Bauer H, Schindler S, Charron Y, Willert J, Kusecek B, Herrmann BG (2012) The nucleoside diphosphate kinase gene Nme3 acts as quantitative trait locus promoting non-Mendelian inheritance. PLoS Genet 8:e1002567
Beeman RW, Friesen KS, Denell RE (1992) Maternal-effect selfish genes in flour beetles. Science 256:89–92
Bélanger S, Clermont I, Esteves P, Belzile F (2016) Extent and overlap of segregation distortion regions in 12 barley crosses determined via a Pool-GBS approach. Theor Appl Genet 129:1393–1404
Ben-David E, Burga A, Kruglyak L (2017) A maternal-effect selfish genetic element in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 356:1051–1055
Bodénès C, Chancerel E, Ehrenmann F, Kremer A, Plomion C (2016) High-density linkage mapping and distribution of segregation distortion regions in the oak genome. DNA Res 23:115–124
Braden AW (1958) Influence of time of mating on the segregation ratio of alleles at the T locus in the house mouse. Nature 181:786–787
Bravo Núñez MA, Lange JJ, Zanders SE (2018) A suppressor of a wtf poison-antidote meiotic driver acts via mimicry of the driver's antidote. PLoS Genet 14:e1007836
Brennan AC, Hiscock SJ, Abbott RJ (2014) Interspecific crossing and genetic mapping reveal intrinsic genomic incompatibility between two Senecio species that form a hybrid zone on Mount Etna, Sicily. Heredity (Edinb) 113:195–204
Burt A, Trivers R (2006) Genes in conflict: the biology of selfish genetic elements. The Belknap Press of Harvard University Press, London
Charron Y, Willert J, Lipkowitz B, Kusecek B, Herrmann BG, Bauer H (2019) Two isoforms of the RAC-specific guanine nucleotide exchange factor TIAM2 act oppositely on transmission ratio distortion by the mouse t-haplotype. PLoS Genet 15:e1007964
Chen JJ, Ding JH, Ouyang YD, Du HY, Yang JY, Cheng K, Zhao J, Qiu SQ, Zhang XL, Yao JL, Liu KD, Wang L, Xu CG, Li XH, Xue YB, Xia M, Ji Q, Lu JF, Xu ML, Zhang QF (2008) A triallelic system of S5 is a major regulator of the reproductive barrier and compatibility of indica-japonica hybrids in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:11436–11441
Corbett-Detig RB, Zhou J, Clark AG, Hartl DL, Ayroles JF (2013) Genetic incompatibilities are widespread within species. Nature 504:135–137
Dawe RK, Lowry EG, Gent JI, Stitzer MC, Swentowsky KW, Higgins DM, Ross-Ibarra J, Wallace JG, Kanizay LB, Alabady M, Qiu WH, Tseng KF, Wang N, Gao Z, Birchler JA, Harkess AE, Hodges AL, Hiatt EN (2018) A kinesin-14 motor activates neocentromeres to promote meiotic drive in maize. Cell 173:839–850
Du HY, Ouyang YD, Zhang CJ, Zhang QF (2011) Complex evolution of S5, a major reproductive barrier regulator, in the cultivated rice Oryza sativa and its wild relatives. New Phytol 191:275–287
Dunn LC (1939) The inheritance of taillessness (anury) in the house mouse. III. taillessness in the balanced lethal line 19. Genetics 24:728–731
Dunn LC, Bennett D (1968) A new case of transmission ratio distortion in the house mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 61:570–573
Gershenson S (1928) A new sex-ratio abnormality in Drosophila obscura. Genetics 13:488–507
Giesbers AKJ, den Boer E, Ulen J, van Kaauwen MPW, Visser RGF, Niks RE, Jeuken MJW (2019) Patterns of transmission ratio distortion in interspecific lettuce hybrids reveal a sex-independent gametophytic barrier. Genetics 211:263–276
Hammer MF, Schimenti J, Silver LM (1989) Evolution of mouse chromosome 17 and the origin of inversions associated with t haplotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:3261–3265
Harushima Y, Nakagahra M, Yano M, Sasaki T, Kurata N (2001) A genome-wide survey of reproductive barriers in an intraspecific hybrid. Genetics 159:883–892
Harushima Y, Nakagahra M, Yano M, Sasaki T, Kurata N (2002) Diverse variation of reproductive barriers in three intraspecific rice crosses. Genetics 160:313–322
Herrmann BG, Koschorz B, Wertz K, McLaughlin KJ, Kispert A (1999) A protein kinase encoded by the t complex responder gene causes non-mendelian inheritance. Nature 402:141–146
Hickey WA, Craig GB Jr (1966) Genetic distortion of sex ratio in a mosquito, Aedes aegypti. Genetics 53:1177–1196
Koide Y, Shinya Y, Ikenaga M, Sawamura N, Matsubara K, Onishi K, Kanazawa A, Sano Y (2012) Complex genetic nature of sex-independent transmission ratio distortion in Asian rice species: the involvement of unlinked modifiers and sex-specific mechanisms. Heredity (Edinb) 108:242–247
Koide Y, Ogino A, Yoshikawa T, Kitashima Y, Saito N, Kanaoka Y, Onishi K, Yoshitake Y, Tsukiyama T, Saito H, Teraishi M, Yamagata Y, Uemura A, Takagi H, Hayashi Y, Abe T, Fukuta Y, Okumoto Y, Kanazawa A (2018) Lineage-specific gene acquisition or loss is involved in interspecific hybrid sterility in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115:E1955–E1962
Kubo T, Yoshimura A, Kurata N (2016) Pollen killer gene S35 function requires interaction with an activator that maps close to S24, another pollen killer gene in rice. G3 (Bethesda) 6:1459–1468
Kusano A, Staber C, Ganetzky B (2001) Nuclear mislocalization of enzymatically active RanGAP causes segregation distortion in Drosophila. Dev Cell 1:351–361
Kusano A, Staber C, Ganetzky B (2002) Segregation distortion induced by wild-type RanGAP in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:6866–6870
Kusano A, Staber C, Chan HY, Ganetzky B (2003) Closing the (Ran)GAP on segregation distortion in Drosophila. BioEssays 25:108–115
Larracuente AM, Presgraves DC (2012) The selfish segregation distorter gene complex of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 192:33–53
Li XH, Wang XJ, Wei YL, Brummer EC (2011) Prevalence of segregation distortion in diploid alfalfa and its implications for genetics and breeding applications. Theor Appl Genet 123:667–679
Li GW, Li XT, Wang Y, Mi JM, Xing F, Zhang DH, Dong QY, Li XH, Xiao JH, Zhang QF, Ouyang YD (2017) Three representative inter and intra-subspecific crosses reveal the genetic architecture of reproductive isolation in rice. Plant J 92:349–362
Li GW, Jin JY, Zhou Y, Bai XF, Mao DH, Tan C, Wang GW, Ouyang YD (2019) Genome-wide dissection of segregation distortion using multiple inter-subspecific crosses in rice. Sci China Life Sci 62:507–516
Loegering WQ, Sears ER (1963) Distorted inheritance of stem-rust resistance of timstein wheat caused by a pollen-killing gene. Can J Genet Cytol 5:65–72
Long YM, Zhao LF, Niu BX, Su J, Wu H, Chen YL, Zhang QY, Guo JX, Zhuang CX, Mei MT, Xia JX, Wang L, Wu HB, Liu YG (2008) Hybrid male sterility in rice controlled by interaction between divergent alleles of two adjacent genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:18871–18876
Lyon MF, Zenthon J, Evans EP, Burtenshaw MD, Willison KR (1988) Extent of the mouse t complex and its inversions shown by in situ hybridization. Immunogenetics 27:375–382
Merrill C, Bayraktaroglu L, Kusano A, Ganetzky B (1999) Truncated RanGAP encoded by the Segregation Distorter locus of Drosophila. Science 283:1742–1745
Mi JM, Lei Y, Kim SR, Prahalada GD, Ouyang YD, Mou TM (2019) An effective strategy for fertility improvement of indica-japonica hybrid rice by pyramiding S5-n, f5-n, and pf12-j. Mol Breeding 39:138
Mi JM, Li GW, Xu CH, Yang JY, Yu HH, Wang GW, Li XH, Xiao JH, Song HZ, Zhang QF, Ouyang YD (2020) Artificial selection in domestication and breeding prevents speciation in rice. Mol Plant 13:650–657
Ouyang YD (2019) Understanding and breaking down the reproductive barrier between Asian and African cultivated rice: a new start for hybrid rice breeding. Sci China Life Sci 62:1114–1116
Ouyang YD, Zhang QF (2013) Understanding reproductive isolation based on the rice model. Annu Rev Plant Biol 64:111–135
Ouyang YD, Zhang QF (2018) The molecular and evolutionary basis of reproductive isolation in plants. J Genet Genom 45:613–620
Ouyang YD, Liu YG, Zhang QF (2010) Hybrid sterility in plant: stories from rice. Curr Opin Plant Biol 13:186–192
Ouyang YD, Li GW, Mi JM, Xu CH, Du HY, Zhang CJ, Xie WB, Li XH, Xiao JH, Song HZ, Zhang QF (2016) Origination and establishment of a trigenic reproductive isolation system in rice. Mol Plant 9:1542–1545
Raju NB (1979) Cytogenetic behavior of spore killer genes in neurospora. Genetics 93:607–623
Reflinur, Kim B, Jang SM, Chu SH, Bordiya Y, Akter MB, Lee J, Chin JH, Koh HJ (2014) Analysis of segregation distortion and its relationship to hybrid barriers in rice. Rice 7:3
Ren RS, Ray R, Li PF, Xu JH, Zhang M, Liu G, Yao XF, Kilian A, Yang XP (2015) Construction of a high-density DArTseq SNP-based genetic map and identification of genomic regions with segregation distortion in a genetic population derived from a cross between feral and cultivated-type watermelon. Mol Genet Genom 290:1457–1470
Rhoades MM (1942) Preferential segregation in maize. Genetics 27:0395–0407
Rick CM (1966) Abortion of male and female gametes in the tomato determined by allelic interaction. Genetics 53:85–96
Rick CM (1971) The tomato ge locus: linkage relations and geographic distribution of alleles. Genetics 67:75–85
Rooades MM, Vilkomerson H (1942) On the anaphase movement of chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 28:433–436
Sandler L, Novitski E (1957) Meiotic drive as an evolutionary force. Am Nat 91:105–110
Seidel HS, Rockman MV, Kruglyak L (2008) Widespread genetic incompatibility in C. elegans maintained by balancing selection. Science 319:589–594
Seymour DK, Chae E, Arioz BI, Koenig D, Weigel D (2019) Transmission ratio distortion is frequent in Arabidopsis thaliana controlled crosses. Heredity 122:294–304
Shen RX, Wang L, Liu XP, Wu J, Jin WW, Zhao XC, Xie XR, Zhu QL, Tang HW, Li Q, Chen LT, Liu YG (2017) Genomic structural variation-mediated allelic suppression causes hybrid male sterility in rice. Nat Commun 8:1310
Sibov ST, De Souza Jr CL, Garcia AAF, Silva AR, Garcia AF, Mangolin CA, De Souza AP (2003) Molecular mapping in tropical maize (Zea mays L.) using microsatellite markers. 1 Quantitative trait loci (QTL) for grain yield, plant heigth, ear height and grain moisture. Hereditas 139(2):107–115
Sturtevant AH, Dobzhansky T (1936) Geographical distribution and cytology of “sex ratio” in Drosophila pseudoobscura and related species. Genetics 21:473–490
Turner BC, Perkins DD (1979) Spore killer, a chromosomal factor in neurospora that kills meiotic products not containing it. Genetics 93:587–606
Xie YY, Niu BX, Long YM, Li GS, Tang JT, Zhang YL, Ren D, Liu YG, Chen LT (2017a) Suppression or knockout of SaF/SaM overcomes the Sa-mediated hybrid male sterility in rice. J Integr Plant Biol 59:669–679
Xie YY, Xu P, Huang JL, Ma SJ, Xie XR, Tao DY, Chen LT, Liu YG (2017b) Interspecific hybrid sterility in rice is mediated by OgTPR1 at the S1 locus encoding a peptidase-like protein. Mol Plant 10:1137–1140
Xie YY, Tang JT, Xie XR, Li XJ, Huang JL, Fei Y, Han JL, Chen SF, Tang HW, Zhao XC, Tao DY, Xu P, Liu YG, Chen LT (2019) An asymmetric allelic interaction drives allele transmission bias in interspecific rice hybrids. Nat Commun 10:2501
Yamamoto E, Takashi T, Morinaka Y, Lin S, Wu J, Matsumoto T, Kitano H, Matsuoka M, Ashikari M (2010) Gain of deleterious function causes an autoimmune response and Bateson–Dobzhansky–Muller incompatibility in rice. Mol Genet Genom 283:305–315
Yang JY, Zhao XB, Cheng K, Du HY, Ouyang YD, Chen JJ, Qiu SQ, Huang JY, Jiang YH, Jiang LW, Ding JH, Wang J, Xu CG, Li XH, Zhang QF (2012) A killer-protector system regulates both hybrid sterility and segregation distortion in rice. Science 337:1336–1340
Yu HG, Hiatt EN, Chan A, Sweeney M, Dawe RK (1997) Neocentromere-mediated chromosome movement in maize. J Cell Biol 139:831–840
Yu XW, Zhao ZG, Zheng XM, Zhou JW, Kong WY, Wang PR, Bai WT, Zheng H, Zhang H, Li J, Liu JF, Wang QM, Zhang L, Liu K, Yu Y, Guo XP, Wang JL, Lin QB, Wu FQ, Ren YL, Zhu SS, Zhang X, Cheng ZJ, Lei CL, Liu SJ, Liu X, Tian YL, Jiang L, Ge S, Wu CY, Tao DY, Wang HY, Wan JM (2018) A selfish genetic element confers non-Mendelian inheritance in rice. Science 360:1130–1132
Zhang D, Easterling KA, Pitra NJ, Coles MC, Buckler ES, Bass HW, Matthews PD (2017) Non-Mendelian single-nucleotide polymorphism inheritance and atypical meiotic configurations are prevalent in hop. Plant Genome. https://doi.org/10.3835/plantgenome2017.04.0032
Zhou W, Tang Z, Hou J, Hu N, Yin T (2015) Genetic map construction and detection of genetic loci underlying segregation distortion in an intraspecific cross of Populus deltoides. PLoS One 10:e0126077
Zhu YF, Yu YM, Cheng K, Ouyang YD, Wang J, Gong L, Zhang QH, Li XH, Xiao JH, Zhang QF (2017) Processes underlying a reproductive barrier in indica-japonica rice hybrids revealed by transcriptome analysis. Plant Physiol 174:1683–1696
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31991223), the Hubei Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (2019CFA061), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2662020SKPY005), and the National Program for Support of Top-notch Young Professionals.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interests to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, F., Ouyang, Y. Recurrent breakdown and rebalance of segregation distortion in the genomes: battle for the transmission advantage. aBIOTECH 1, 246–254 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42994-020-00023-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42994-020-00023-0