Abstract
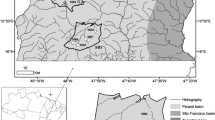
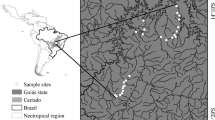
The comprehension of the ecological structure and the functioning of natural and/or impacted lotic ecosystems is the purpose of most studies concerning rivers and streams. This study aimed to investigate the main factors influencing the zooplankton community organization in nine impacted tropical streams of three different sub-basins of the Cinzas River basin, Paraná state, Brazil. We tested the hypothesis that macro-factors such as productivity, current velocity, habitat structure, and stream order and stretches (headwater, middle and mouth), are the main factors structuring the zooplankton community in tropical streams. Zooplankton was represented by 101 taxa, mainly testate amoebae, followed by rotifers, cladocerans and copepods. Results showed that the greatest differences in physical and chemical characteristics and those related to zooplankton community structure were observed among the three sub-basins studied. However, we found that these differences were not related to the environmental heterogeneity, but were rather influenced mainly by spatial factors related to stochasticity in the structuring of planktonic communities. Thus, our results suggest that connectivity between environments within the same sub-basin, associated with random processes driven by dispersal, may determine the existence or not of spatial patterns, among stream order or stretches, and temporal patterns, between seasons, in the community attributes here analyzed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alves, G. M., Velho, L. F. M., Costa, D. M., & Lansac-Tôha, F. A. (2012). Size structure of testate amoebae (Arcellinida and Euglyphida) in different habitats from a lake in the upper Paraná River floodplain. The European Journal of Protistology, 48, 169–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejop.2011.10.004
APHA. (2017). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (23rd ed.). American Public Health Association.
Arrieira, R. L., Alves, G. M., Schwind, L. T. F., & Lansac-Tôha, F. A. (2015). Local factors affecting the testate amoebae community (Protozoa: Arcellinida; Euglyphida) in a neotropical floodplain. Journal of Limnology, 74(3), 444–452. https://doi.org/10.4081/jlimnol.2015.1078
Bicudo, C. E. M., & Bicudo, D. (2006). Amostragem em Limnologia. Editora Rima: São Carlos.
Bie, T., Meester, L., Brendonck, K., Martens, B., Goddeeris, D., Ercken, H., Hampel, L., Denys, L., Vanhecke, K., Van Der Gucht, J., Van Wichelen, W., & Vyverman, S. D. (2012). Body size and dispersal mode as key traits determining metacommunity structure of aquatic organisms. Ecology Letters, 15, 740–747. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2012.01794.x
Blatterer, H. (2002). Some conditions for the distribution and abundance of ciliates (Protozoa) in running waters — Do we really find every species everywhere? Internationale Vereinigung Für Theoretische Und Angewandte Limnologie: Verhandlungen, 28, 1046–1049. https://doi.org/10.1080/03680770.2001.11901877
Bovo-Scomparin, V. M., Train, S., & Rodrigues, L. C. (2013). Influence of reservoirs on phytoplankton dispersion and functional traits: A case study in the Upper Paraná River, Brazil. Hydrobiologia, 702, 115–127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-012-1313-8
Czerniawski, R., & Domagala, J. (2010). Similarities in zooplankton community between River Drawa and its two tributaries (Polish part of River Odra). Hydrobiologia, 638, 137–149. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-009-0036-y
Czerniawski, R., & Pilecka-Rapacz, M. (2011). Summer zooplankton in small rivers in relation to selected conditions. Central European Journal of Biology, 6, 659–674. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11535-011-0024-x
Czerniawski, R. (2013). Zooplankton community changes between forest and meadow sections in small headwater streams, NW Poland. Biologia, 68, 448–458. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-013-0170-x
Czerniawski, R., & Domagała, J. (2014). Small dams profoundly alter the spatial and temporal composition of zooplankton communities in running waters. International Review of Hydrobiology, 99(4), 300–311. https://doi.org/10.1002/iroh.201301674
Czerniawski, R., & Kowalska-Góralska, M. (2018). Spatial changes in zooplankton communities in a strong human-mediated river ecosystem. PeerJ. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.5087
Dejenie, T., Declerck, A. S., Asmelash, T., Risch, S., Mergeay, J., De Bie, T., & Meester, L. (2012). Cladoceran community composition in tropical semi-arid highland reservoirs in Tigray (Northern Ethiopia): A metacommunity perspective applied to young reservoirs. Limnologica, 42, 137–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.limno.2011.09.008
Diniz, L. P., Petsch, D. K., & Bonecker, C. C. (2021). Zooplankton β diversity dynamics and metacommunitystructure depend on spatial and temporal scales in a Neotropical floodplain. Freshwater Biology, 66, 1328–1342. https://doi.org/10.1111/fwb.13719
Dodson, S. I., & Frey, D. G. (2001). Cladocera and other Branchiopoda. In: Thorp, J. H., Covich, A. P. (Eds.) Ecology and classificartion of North American Freshwater Invertebrates. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 850–914. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-012690647-9/50022-3
Ejsmont-Karabin, J., & Kruk, M. (1998). Effects of contrasting land use on free-natation rotifer Communities of stream in Masurian Lake District, Poland. In: Wurdak, E., Wallace, R., Segers, H. (Eds.) Rotifera VIII: A comparative approach. Developments in hydrobiology (Vol. 134). Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-4782-8_31
Elmi, D., Webster, D. R., & Fields, D. M. (2021). Response of the copepod Acartia tonsa to the hydrodynamic cues of small-scale, dissipative eddies in turbulence. Journal of Experimental Biology. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.237297
Elmoor-Loureiro, L. M. A. (1997). Manual de Identificação de Cladóceros Límnicos do Brasil. Universal.
Ferreira, F. C., Souza, U. P., & Petrere, J. R. M. (2010). Zonação longitudinal da ictiofauna em ambientes lóticos. Boletim Da Sociedade Brasileira De Limnologia, 38, 1–17.
Fulone, L. J., Vieira, L. C. G., Velho, L. F. M., & Lima, A. F. (2008). Influence of depth and rainfall on testate amoebae (Protozoa-Rhizopoda) compositions from two streams in northwestern São Paulo state. Acta Limnologica Brasiliensia, 20(1), 29–34.
Golec-Fialek, C., Lansac-Tôha, F. M., & Bonecker, C. C. (2021). Response of the zooplankton community to extreme hydrological variations in a temporary lake in a neotropical floodplain system. Limnologica, 86, 125834. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.limno.2020.125834
Gomes, A. C. A. M., Gomes, L. F., Roitman, I., Pereira, H. R., Junior, A. F. C., da Costa, E. M. M., Silva, M. L. C., Jacobson, T. K. B. J., Ribeiro, R. J. C., Miranda Filho, R. J., Avila, M. L., & Vieira, L. C. G. (2020). Forest cover influences zooplanktonic communities in Amazonian streams. Aquatic Ecology, 54, 1067–1078. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10452-020-09794-6
Gomes, L. F., Barbosa, J. C., Barbosa, H., Vieira, M. C., & Vieira, L. C. G. (2020). Environmental and spatial influences on stream zooplankton communities of the Brazilian Cerrado. Community Ecology, 21(1), 25–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42974-020-00008-5
Gutierrez, M. F., Simões, N. R., Frau, D., Saigo, M., & Licursi, M. (2020). Responses of stream zooplankton diversity metrics to eutrophication and temporal environmental variability in agricultural catchments. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 192, 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08766-5
Heino, J., Melo, A. S., & Bini, L. M. (2015a). Recomceptualising the beta adversity-environmental heterogeneity relationship in running water systems. Freshwater Biology, 60, 223–235. https://doi.org/10.1111/fwb.12502
Heino, J., Melo, A. S., Bini, L. M., Altermatt, F., Al-Shami, S. A., Angeler, D. G., et al. (2015b). A comparative analysis reveals weak relationships between ecological factors and beta diversity of stream insect metacommunities at two spatial levels. Ecology and Evolution, 5, 1235–1248. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.1439
Hubbell, S. P. (2011). A teoria neutra unificada da biodiversidade e biogeografia (MPB-32). Princeton University Press. https://doi.org/10.1515/9781400837526
Illies, J., & Botosaneanu, L. (1963). Problèmes et méthodes de la classification et de la zonation écologique des eaux courantes, considerées surtout du point de vue faunistique: Avec 18 figures dans le texte et en supplément. Internationale Vereinigung Für Theoretische Und Angewandte Limnologie: Verhandlungen, 12, 1–57. https://doi.org/10.1080/05384680.1963.11903811
Jati, S., Bortolini, J. C., Moresco, G. A., Paula, A. C. M. D., Rodrigues, L. C., Iatskiu, P., Pineda, A., Zanco, B. F., Silva, M. V., & Souza, Y. R. (2017). Phytoplankton community in the last undammed stretch of the Paraná River: Considerations on the distance from the dam. Acta Limnologica Brasiliensia. https://doi.org/10.1590/S2179-975X4017
Kwok, K. W., Leung, K. M., Lui, G. S., Chu, V. K., Lam, P. K., Morritt, D., Maltby, L., Brock, T. C. M., Van den Brink, P. J., Warne, M. S. J., & Crane, M. (2007). Comparison of tropical and temperate freshwater animal species’ acute sensitivities to chemicals: implications for deriving safe extrapolation factors. Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management: an International Journal, 3(1), 49–67. https://doi.org/10.1002/ieam.5630030105
Koste, W. (1978). Rotatoria: Die Rädertiere Mitteleuropas. Ein Bestimmungswerk berg. Von Max Voigt. Überordnung Monogononta. Volume I-II. Gebrüder Borntraaeger, Berlin
Krudglova, A. N. (2008). Planktonic fauna of small salmon rivers in the Kola Peninsula. Inland Water Biology, 1, 8–13. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995082908030024
Lair, N. (2005). Abiotic against biotic factors: lessons drawn from rotifers in the Middle Loire, a meandering river monitored from 1995 to 2002, during low flow periods. Hydrobiology, 546, 457–472. https://doi.org/10.1007/1-4020-4408-9_48
Lair, N. (2006). A review of regulation mechanisms of metazoan plankton in riverine ecosystems: Aquatic habitat versus biota. River Research and Applications, 22, 567–593. https://doi.org/10.1002/rra.923
Lampert, W., & Sommer, U. (2007). Limnoecology: The ecology of lakes and streams. Oxford University Press.
Lansac-Tôha, F. A., Bonecker, C. C., Velho, L. F. M., Simões, N. R., Dias, J. D., Alves, G. M., & Takahashi, E. M. (2009). Biodiversity of zooplankton communities in the Upper Paraná River floodplain: Interanual variation from long-term studies. Brazilian Journal of Biology, 69, 539–549. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1519-69842009000300009
Lansac-Tôha, F. A., Velho, L. F. M., Costa, D. M., Simões, N. R., & Alves, G. M. (2014). Structure of the testate amoeba community in different habitats in a neotropical floodplain. Brazilian Journal of Biology, 74, 181–190. https://doi.org/10.1590/1519-6984.24912
Lansac-Tôha, F. A., Velho, L. F. M., & Bonecker, C. C. (2004). Composition, species richness and abundance of the zooplankton community. In S. M. Thomaz, A. A. Agostinho, & N. S. Hahn (Eds.), The Upper Paraná River and its floodplain: Physical aspects, ecology and conservation (pp. 145–190). Backhuys Publishers.
Lansac-Tôha, F. M., Heino, J., Quirino, B. A., Moresco, G. A., Zapata, O. E. P., Meira, B. R., Rodrigues, L. C., Jati, S., Lansac-Tôha, F. A., & Velho, L. F. M. (2019). Differently dispersing organism groups show contrasting beta diversity patterns in a dammed subtropical river basin. Science of the Total Environment, 691, 1271–1281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.236
Padovesi-Fonseca, C., Souza Rezende, R., Da Costa, D. F., & Martins-Silva, M. J. (2021). Spatial scales drive zooplankton diversity in savanna Cerrado streams. Community Ecololgy, 1, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42974-021-00052-9
Paggi, J. C. (1995). Crustacea Cladocera. In: Lopretto EC, Tell G (Eds.). Ecosistemas de aguas continentales. Metodologías para su estúdio (pp. 909–951). Sur, La Plata.
Perbiche-Neves, G., Serafim-Júnior, M., Portinho, J. L., Shimabukuro, E. M., Ghidini, A. G., & Brito, L. (2012). Effect of atypical rainfall on lotic zooplankton: Comparing downstream of a reservoir and tributaries with free stretches. Tropical Ecology, 53, 149–162.
Picapedra, P. H. S., Fernandes, C., & Lansac-Tôha, F. A. (2017). Zooplankton community in the Upper Parnaíba River (Northeastern, Brazil). Brazilian Journal of Biology, 77, 402–412. https://doi.org/10.1590/1519-6984.20215
Picapedra, P. H. S., Fernandes, C., & Baumgartner, G. (2019). Structure and ecological aspects of zooplankton (Testate amoebae, Rotifera, Cladocera and Copepoda) in highland streams in southern Brazil. Acta Limnologica Brasiliensia. https://doi.org/10.1590/S2179-975X2917
Portinho, J. L., Perbiche-Neves, G., & Nogueira, M. G. (2016). Zooplankton community and tributary effects in free-flowing section downstream a large tropical reservoir. International Review of Hydrobiology, 101, 48–56. https://doi.org/10.1002/iroh.201501798
Pryor, S. C., Barthelmie, R. J., & Kjellström, E. (2005). Potential climate change impact on wind energy resources in northern Europe: Analyses using a regional climate model. Climate Dynamics, 25, 815–835. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-005-0072-x
Reid, J. W. (1985). Chave de identificação e lista de referências bibliográficas para as espécies continentais sulamericanas de vida livre da ordem Cyclopoida (Crustacea, Copepoda) (pp. 95–107). São Paulo, Instituto de Biociências da Universidade de São Paulo. https://doi.org/10.11606/issn.2526-3358.bolzoo.1985.122293
Rocha, B. D. S., Souza, C. A. D., Machado, K. B., Vieira, L. C. G., & Nabout, J. C. (2020). The relative influence of the environment, land use, and space on the functional and taxonomic structures of phytoplankton and zooplankton metacommunities in tropical reservoirs. Freshwater Science, 39, 321–333. https://doi.org/10.1086/708949
Sampaio, E. V., Rocha, O., Matsumura-Tundisi, T., & Tundisi, J. G. (2002). Composition and abundance of zooplankton in the limnetic zone of seven reservoirs of the Paranapanema River, Brazil. Brazilian Journal of Biology, 62, 525–545. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1519-69842002000300018
Sartori, M., Martins, B. A., & Perbiche-Neves, G. (2021). A variação da diversidade de microcrustáceos (Cladocera e Copepoda) a jusante de pequenos reservatórios é influenciada por táxons litorâneos. Iheringia, Série Zoológica. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-4766e2021004
Segovia, B. T., Dias, J. D., Cabral, A. F., Meira, B. R., Lansac-Tôha, F. M., Lansac-Tôha, F. A., Bini, L. M., & Velho, L. F. M. (2017). Common and rare taxa of planktonic ciliates: Influence of flood events and biogeographic patterns in Neotropical floodplains. Microbial Ecology, 74, 522–533. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-017-0974-2
Silva, N. J., Lansac-Tôha, F. M., Lansac-Tôha, F. A., Sales, P. C. L., & Rocha, J. R. S. (2021). Beta diversity patterns in zooplankton assemblages from a semiarid river ecosystem. International Review of Hydrobiology, 106, 29–40. https://doi.org/10.1002/iroh.201902018
Shannon, C. E., & Weaver, W. (1949). The mathematical theory of communication. University of Illinois Press.
Siemensma, F. J. (2021). Microworld, world of amoeboid organisms. World-wide electronic publication, Kortenhoef, the Netherlands. https://arcella.nl. Accessed March 04, 2022.
Soininen, J., Heino, J., & Wang, J. (2018). A met-analysis of nestedness and turnover components of beta diversity across organisms and ecosystems. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 27, 96–109. https://doi.org/10.1111/geb.12660
Souza, M. B. G. (2008). Guias das Tecamebas, Bacia do Rio Peruaçu – Minas Gerais. Subsídio para conservação e monitoramento da bacia do Rio São Francisco. UFMG, Belo Horizonte.
Statzner, B., & Higler, B. (1985). Questions and comments on the river continuum concept. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 42, 1038–1044. https://doi.org/10.1139/f85-129
Strahler, A. N. (1957). Quantitative analysis of watershed geomorphology. Eos, Transactions American Geophysical Union, 38, 913–920. https://doi.org/10.1029/TR038i006p00913
Thorp, J. H., Thoms, M. C., & Delong, M. D. (2006). The riverine ecosystem synthesis: Biocomplexity in river networks across space and time. River Research and Applications, 22, 123–147. https://doi.org/10.1002/rra.901
Vanotte, R. L., Minshall, G. W., Cummins, K. W., Sedell, J. R., & Cushing, C. E. (1980). The river continuum concept. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 37, 130–137. https://doi.org/10.1139/f80-017
Velho, L. F. M., Alves, G. M., Lansac-Tôha, F. A., Bonecker, C. C., & Pereira, D. G. (2004). Testate amoebae Abundance in plankton samples from Paraná state reservoirs. Acta Scientiarum, 26, 415–419. https://doi.org/10.4025/actascibiolsci.v26i4.1522
Wetzel, R. G., & Likens, G. E. (2001). Limnological analyses (2nd ed.). New York: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4757-3250-4
Willianson, C. E., Reid, C. J. (2001). Copepoda. In: Thorp, J. H., & Covich, A. P. (Eds.) Ecology and classification of North American Freshwater Invertebrates. San Diego. Academic Press. pp 915–924. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-690647-9.50028-4
Wohl, E. (2017). Connectivity in rivers. Progress in Physical Geography, 41, 345–362. https://doi.org/10.1177/0309133317714972
Acknowledgements
We thank the Araucária Foundation for funding and granting the scholarship; Nupélia/PEA/UEM and UENP for the logistical support for the execution of this work; the CI trainees of GERCOL/LaMoCEQ for the help during the collections. We also thank to Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) for research scholarships for Lansac-Tôha, F. M, and Bianca Ramos de Meira and support the research developed by Velho, L. F. M., and the Cesumar Institute of Science, Technology, and Innovation (ICETI) for granted the researcher Velho, L. F. M. On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aggio, C.E.G., Oliveira, F.R., Progênio, M. et al. The zooplankton of tropical streams: is it determinism or stochasticity that drives the spatial and temporal patterns in community structure?. COMMUNITY ECOLOGY 23, 219–229 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42974-022-00099-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42974-022-00099-2