Abstract
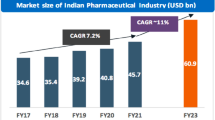
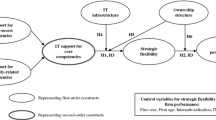
Progressive firms strive to incorporate flexibility into their processes to survive and achieve competitiveness in a complex uncertain business environment. The complexity faced by organizations dealing with rapid change prompted us to investigate the inter-relationship between flexibility and competitiveness. The domain of pharmaceutical industry is undoubtedly the most demanding one owing to rapid change and intense R&D requirements. This study deals with projecting the significance of enterprise flexibility on firm competitiveness at macro and micro levels using the statistical tool—Multiple Regression—on data collected in the form of a structured questionnaire from 324 higher-level managers from pharmaceutical firms in India. Seven hypotheses were proposed and tested against one dependent variable. According to regression analysis, enterprise flexibility was found to be a strong predictor of competitiveness. The study also demonstrates that 'enterprise flexibility' significantly impacts firm competitiveness not only at the macro level but also at the micro level. The findings are expected to fill a knowledge gap among top executives as only a few researchers have investigated the relationship between enterprise flexibility and competitiveness, thus allowing a more effective strategy formulation.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data sharing does not apply to this article due to privacy and ethical concerns, neither the data of industry experts nor its source can be made available to the public.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Aldrighetti, R., Zennaro, I., Finco, S., & Battini, D. (2019). Healthcare supply chain simulation with disruption considerations: a case study from Northern Italy. Global Journal of Flexible Systems Management, 20(1), 81–102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40171-019-00223-8
Anning-Dorson, T. (2021). Organizational culture and leadership as antecedents to organizational flexibility: Implications for SME competitiveness. Journal of Entrepreneurship in Emerging Economies., 13(5), 1309–1325. https://doi.org/10.1108/JEEE-08-2020-0288
Bhat, S., & Momaya, K. S. (2019). Learning from the giants: Critical success factors for pharmaceutical EMNEs from India. Journal of International Business and Economy, 20(2), 29–53. https://doi.org/10.51240/jibe.2019.2.2
Bhawsar, P., & Chattopadhyay, U. (2015). Competitiveness: Review, reflections and directions. Global Business Review, 16(4), 665–679. https://doi.org/10.1177/0972150915581115
Brozovic, D. (2018). Strategic flexibility: A review of the literature. International Journal of Management Reviews, 20(1), 3–31. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijmr.12111
Contador, J. C., Satyro, W. C., Contador, J. L., & Spinola, M. D. M. (2020). Flexibility in the Brazilian industry 4.0: Challenges and opportunities. Global Journal of Flexible Systems Management, 21(1), 15–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40171-020-00240-y.
Gartner, C., & Schon, O. (2016). Modularizing business models: Between strategic flexibility and path dependence. Journal of Strategy and Management, 9(1), 39–57. https://doi.org/10.1108/JSMA-12-2014-0096
Goncalves, J. M., Ferreira, F. A., Ferreira, J. J., & Farinha, L. M. (2018). A multiple criteria group decision-making approach for the assessment of small and medium-sized enterprise competitiveness. Management Decision, 57, 480–500. https://doi.org/10.1108/MD-02-2018-0203
Gopakumar, K., & Suresh, M. (2020, October). Applications of marketing flexibility in manufacturing and service sectors. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering (Vol. 954, No. 1, p. 012003). IOP Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/954/1/012003.
Haldar, A., Rao, S. N., & Momaya, K. S. (2016). Can flexibility in corporate governance enhance international competitiveness? Evidence from knowledge-based industries in India. Global Journal of Flexible Systems Management, 17, 389–402. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40171-016-0135-3
Islam, M. R., Hossain, M. A., Uddin, M. S., & Bahta, D. T. (2020). Does Financial Flexibility foster Investment Efficiency? Evidence from an Emerging Market. Asian Business Review, 10(2), 121–136. https://doi.org/10.18034/abr.v10i2.476.
Koev, S. R., Pavliuk, S., Derhaliuk, M., Sokolova, L., & Portna, O. (2020). Resource strategy for enterprise management as a tool to ensure its competitiveness. Academy of Strategic Management Journal, 19(4), 1–8.
Lim, B. T., Ling, F. Y., Ibbs, C. W., Raphael, B., & Ofori, G. (2011). An Empirical Analysis of the Determinants of Organizational Flexibility in Construction business. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management, 137(3), 225–237. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)CO.1943-7862.0000272
Mahajan, V., Nauriyal, D. K., & Singh, S. P. (2020). Domestic market competitiveness of Indian drug and pharmaceutical industry. Review of Managerial Science, 14(3), 519–559. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11846-018-0299-7
Nadkarni, S., & Narayanan, V. K. (2007). Strategic schemas, strategic flexibility, and firm performance: the moderating role of industry clockspeed. Strategic Management Journal, 28, 243–270. https://doi.org/10.1002/smj.576
Nelson, K. M., & Ghods, M. (1998). Measuring technology flexibility. European Journal of Information Systems, 7(4), 232–240. https://doi.org/10.1057/palgrave.ejis.3000310
Ni, G., Xu, H., Cui, Q., Qiao, Y., Zhang, Z., Li, H., & Hickey, P. J. (2021). Influence mechanism of organizational flexibility on enterprise competitiveness: The mediating role of organizational innovation. Sustainability, 13(1), 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13010176
Pharmaceuticals Industry Report (2022, June). Indian Brand Equity Foundation (IBEF). Retrieved Nov. 26, 2022, from https://www.ibef.org/industry/indian-pharmaceuticals-industry-analysis-presentation.
Rugman, A. M., & Verbeke, A. (2001). Location, competitiveness, and the multinational enterprise. The Oxford handbook of international business, 150177. https://doi.org/10.1093/0199241821.003.0006.
Saeed, M. A., Tabassum, H., Zahid, M. M., Jiao, Y., & Nauman, S. (2022). Organizational flexibility and project portfolio performance: The roles of environmental uncertainty and innovation capability. Engineering Management Journal, 34(2), 249–264. https://doi.org/10.1080/10429247.2021.1884450
Samiei, E., & Habibi, J. (2020). The mutual relation between Enterprise resource planning and knowledge management: A review. Global Journal of Flexible Systems Management, 21(1), 53–66. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40171-019-00229-2
Shi, D., & Daniels, R. L. (2003). A survey of manufacturing flexibility: Implications for e-business flexibility. IBM Systems Journal, 42(3), 414–427. https://doi.org/10.1147/sj.423.0414.
Singh, R.K., Kumar, R. & Kumar, K.P. (2016). Strategic issues in pharmaceutical supply chains: a review. International Journal of Pharmaceutical and Healthcare Marketing, Vol 10, Issue 3. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJPHM-10-2015-0050.
Stoyanova, T., & Angelova, M. (2018, June). Impact of the internal factors on the competitiveness of business organizations. In 2018 International Conference on High Technology for Sustainable Development (HiTech) (pp. 1–3). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/hitech.2018.8566386.
Sushil. (2017). Small steps for a giant leap: Flexible organization. Global Journal of Flexible Systems Management, 18(4), 273–274. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40171-017-0163-7
Volberda, H. W. (1998). Building the flexible firm: How to remain competitive. Corporate Reputation Review, 2(1), 94–96. https://doi.org/10.1093/acprof:oso/9780198295952.001.0001
Yi, J. (2020). Financial flexibility, dynamic capabilities, and the performance of manufacturing enterprises. Journal of Research in Emerging Markets, 2(2), 19–33. https://doi.org/10.30585/jrems.v2i2.465.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the reviewers and the Editor-in-Chief for their comments which have helped in improving the quality of the paper.
Funding
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors. All the authors declare that there are neither any financial nor non-financial interests associated with this research. No funding from any source has been received for this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MA: literature, research instrument development; data analysis and interpretation; drafted the paper. SN: concept development, guidance and revision. ZN: data collection; material preparation; revisions and suggestions. All authors have read and approved on the revised version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that they do not have any conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
The paper is original and not published elsewhere. The respondent’s detail is confidential and is used for research purpose only.
Informed consent
The authors have given the consent to the publisher for publication.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Asim, M., Nasim, S. & Naz, Z. Impact of Enterprise Flexibility on Firm’s Competitiveness: An Empirical Study of Select Pharmaceutical Firms in India. JGBC 18, 35–42 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42943-023-00079-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42943-023-00079-x