Abstract
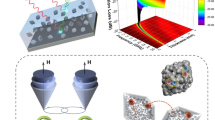
Refining the electromagnetic wave absorption characteristics of traditional metal–organic framework (MOF)-derived carbon composites remains a challenge because of their discontinuous conductive path. To overcome this limitation, in this work, MOF-derived hierarchical Cu9S5/C nanocomposite fibers are fabricated by electrospinning and subsequent carbonization-sulfurization process. Morphological analyses show that MOF-derived octahedral Cu9S5/C particles are evenly monodispersed inside carbonaceous fibers. This configuration creates a unique hierarchical structure, ranging from Cu9S5 particle embedding, MOF-derived skeleton, to a three-dimensional network. The optimized composite fibers (Cu9S5/C-40) exhibit extraordinary electromagnetic wave absorption performance at a low mass fraction (20 wt%): the minimum reflection loss value reaches − 69.6 dB, and the maximum effective absorption bandwidth achieves 5.81 GHz with an extremely thin thickness of only 1.83 mm. Systematic investigations demonstrate that constructing the three-dimensional conductive network to connect MOF derivatives is crucial for activating performance enhancement. The unique nano-micro hierarchical structure synergized with elaborate-configured components endows the materials with optimal impedance matching and amplifies the loss capacity of each part. This work provides a reliable example and theoretical guidance for fabricating new-generation high-efficiency MOF-derived fibrous electromagnetic wave absorbers.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data substantiating the findings of this study can be accessed from the corresponding author upon a reasonable request.
References
Lv HL, Yang ZH, Pan HG, Wu RB. Electromagnetic absorption materials: current progress and new frontiers. Prog Mater Sci. 2022;127: 100946.
Wu Y, Tan SJ, Zhao Y, Liang LL, Zhou M, Ji GB. Broadband multispectral compatible absorbers for radar, infrared and visible stealth application. Prog Mater Sci. 2023;135: 101088.
Qin M, Zhang LM, Wu HJ. Dielectric loss mechanism in electromagnetic wave absorbing materials. Adv Sci. 2022;9:2105553.
Pan YL, Zhu QQ, Zhu JH, Cheng YH, Yu BY, Jia ZR, Wu GL. Macroscopic electromagnetic synergy network-enhanced N-doped Ni/C gigahertz microwave absorber with regulable microtopography. Nano Res. 2023;16(7):10666–77.
Jia ZR, Lan D, Chang M, Han Y, Wu GL. Heterogeneous interfaces and 3D foam structures synergize to build superior electromagnetic wave absorbers. Mater Today Phys. 2023;37: 101215.
Zhang X, Qiao J, Jiang YY, Wang FL, Tian XL, Wang Z, Wu LL, Liu W, Liu JR. Carbon-based MOF derivatives: emerging efficient electromagnetic wave absorption agents. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021;13:135.
Wu YL, Lan D, Ren JW, Zhang SJ. A mini review of MOFs derived multifunctional absorbents: from perspective of components regulation. Mater Today Phys. 2023;36: 101178.
Li JJ, Zhu QQ, Zhu JH, Cheng YH, Jia ZR, Lu F, Wang C, Wu GL. Inimitable 3D pyrolytic branched hollow architecture with multi-scale conductive network for microwave absorption. J Mater Sci Technol. 2024;173:170–80.
Yang YF, Xu DM, Lyu LF, Wang FL, Wang Z, Wu LL, Liu W, Liu JR. Synthesis of MOF-derived Fe7S8/C rod-like composites by controlled proportion of carbon for highly efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf. 2021;142: 106246.
Xu DM, Yang YF, Le K, Wang GW, Ouyang AC, Li B, Liu W, Wu LL, Wang Z, Liu JR, Wang FL. Bifunctional Cu9S5/C octahedral composites for electromagnetic wave absorption and supercapacitor applications. Chem Eng J. 2021;417: 129350.
Ren SN, Yu HJ, Wang L, Huang ZK, Lin TF, Huang YD, Yang J, Hong YC, Liu JY. State of the art and prospects in metal-organic framework-derived microwave absorption materials. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022;14:68.
Gao ZG, Iqbal A, Hassan T, Zhang LM, Wu HJ, Koo CM. Texture regulation of metal–organic frameworks, microwave absorption mechanism-oriented structural optimization and design perspectives. Adv Sci. 2022;9:2204151.
Zhang X, Qiao J, Liu C, Wang FL, Jiang YY, Cui P, Wang Q, Wang Z, Wu LL, Liu JR. A MOF-derived ZrO2/C nanocomposite for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. Inorg Chem Front. 2020;7:385–93.
Zhang X, Tian XL, Liu C, Qiao J, Liu W, Liu JR, Zeng ZH. MnCo-MOF-74 derived porous MnO/Co/C heterogeneous nanocomposites for high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon. 2022;149:257–66.
Liu Y, Zeng ZH, Zheng SN, Qiao J, Liu W, Wu LL, Liu JR. Facile manufacturing of Ni/MnO nanoparticle embedded carbon nanocomposite fibers for electromagnetic wave absorption. Compos B Eng. 2022;235: 109800.
Zhang F, Jia ZR, Zhou JX, Liu JK, Wu GL, Yin PF. Metal-organic framework-derived carbon nanotubes for broadband electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem Eng J. 2022;450: 138205.
Shu RW, Li XH, Ge CQ, Wang LY. Synthesis of FeCoNi/C decorated graphene composites derived from trimetallic metal-organic framework as ultrathin and high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbers. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2023;630:754–62.
Jia ZR, Kong MY, Yu BW, Ma YZ, Pan JY, Wu GL. Tunable Co/ZnO/C@MWCNTs based on carbon nanotube-coated MOF with excellent microwave absorption properties. J mater sci technol. 2022;127:153–63.
Yang BT, Fang JF, Xu CY, Cao H, Zhang RX, Zhao B, Huang MQ, Wang XY, Lv HL, Che RC. One-dimensional magnetic FeCoNi alloy toward low-frequency electromagnetic wave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022;14:170.
Qiao J, Zhang X, Xu DM, Kong LX, Lv LF, Yang F, Wang FL, Liu W, Liu JR. Design and synthesis of TiO2/Co/carbon nanofibers with tunable and efficient electromagnetic absorption. Chem Eng J. 2020;380: 122591.
Ma ML, Liao ZJ, Su XW, Zheng QX, Liu YY, Wang Y, Ma Y, Wan F. Magnetic CoNi alloy particles embedded N-doped carbonaceous fibers with polypyrrole for excellent electromagnetic wave absorption. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2022;608:2203–12.
Wang CX, Liu Y, Jia ZR, Zhao WR, Wu GL. Multicomponent nanoparticles synergistic one-dimensional nanofibers as heterostructure absorbers for tunable and efficient microwave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 2023;15:13.
Zhang S, Liu XH, Jia CY, Sun ZS, Jiang HW, Jia ZR, Wu GL. Integration of multiple heterointerfaces in a hierarchical 0D@2D@1D structure for lightweight, flexible, and hydrophobic multifunctional electromagnetic protective fabrics. Nano-Micro Lett. 2023;15:204.
Wu SM, Qiao J, Tang YX, Zhang X, Meng XW, Hao SY, Tian HY, Li BD, Zuo XY, Liu JR, Wu LL, Wang Z, Wang FL. Heterogeneous Cu9S5/C nanocomposite fibers with adjustable electromagnetic parameters for efficient electromagnetic absorption. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2023;630:47–56.
Guo RD, Su D, Chen F, Cheng YZ, Wang X, Gong RZ, Luo H. Hollow beaded Fe3C/N-doped carbon fibers toward broadband microwave absorption. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022;14:3084–94.
Chen JB, Zheng J, Wang F, Huang QQ, Ji GB. Carbon fibers embedded with FeIII-MOF-5-derived composites for enhanced microwave absorption. Carbon. 2021;174:509–17.
Sun RL, Yan GL, Zhang XL, Li ZY, Chen JY, Wang L, Wu YP, Wang YQ, Li H. Fe-ZIF-derived hollow porous carbon nanofibers for electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem Eng J. 2023;455: 140608.
Yu WJ, Shao GF. Morphology engineering of defective graphene for microwave absorption. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2023;640:680–7.
Lai QX, Zhao YX, Liang YY, He JP, Chen JH. In situ confinement pyrolysis transformation of ZIF-8 to nitrogen-enriched meso-microporous carbon frameworks for oxygen reduction. Adv Funct Mater. 2016;26:8334–44.
Rao LJ, Wang L, Yang CD, Zhang RX, Zhang JC, Liang CY, Che RC. Confined diffusion strategy for customizing magnetic coupling spaces to enhance low-frequency electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv Funct Mater. 2023;33:2213258.
Xu HY, Li B, Jiang XY, Shi YN, Zhang X, Zhu CL, Zhang XT, Chen YJ. Fabrication of N−doped carbon nanotube/carbon fiber dendritic composites with abundant interfaces for electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon. 2023;201:234–43.
Wang L, Li X, Li QQ, Yu XF, Zhao YH, Zhang J, Wang M, Che RC. Oriented polarization tuning broadband absorption from flexible hierarchical ZnO arrays vertically supported on carbon cloth. Small. 2019;15:1900900.
Liang HS, Chen G, Liu D, Li ZJ, Hui SC, Yun JJ, Zhang LM, Wu HJ. Exploring the Ni 3d orbital unpaired electrons induced polarization loss based on Ni single-atoms model absorber. Adv Funct Mater. 2023;33:2212604.
Liu JL, Zhang LM, Zang DY, Wu HJ. A competitive reaction strategy toward binary metal sulfides for tailoring electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv Funct Mater. 2021;31:2105018.
Chen G, Liang HS, Yun JJ, Zhang LM, Wu HJ, Wang JY. Ultrasonic field induces better crystallinity and abundant defects at grain boundaries to develop CuS electromagnetic wave absorber. Adv Mater. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202305586.
Liang HS, Zhang LM, Wu HJ. Exploration of twin-modified grain boundary engineering in metallic copper predominated electromagnetic wave absorber. Small. 2022;18:2203620.
Tuinstra F, Koenig JL. Raman spectrum of graphite. J Chem Phys. 1970;53:1126–30.
Nemanich RJ, Solin SA. First- and second-order Raman scattering from finite-size crystals of graphite. Phys Rev B. 1979;20:392–401.
Liu PB, Gao S, Wang Y, Huang Y, He WJ, Huang WH, Luo JH. Carbon nanocages with N-doped carbon inner shell and Co/N-doped carbon outer shell as electromagnetic wave absorption materials. Chem Eng J. 2020;381: 122653.
Zhang Y, Huang YY, Srot V, Aken PAV, Maier J, Yu Y. Enhanced pseudo-capacitive contributions to high-performance sodium storage in TiO2/C nanofibers via double effects of sulfur modification. Nano-Micro Lett. 2020;12:165.
Shi YN, Li B, Jiang XY, Zhang X, Zhang XT, Chen YJ, Zhu CL. The enhanced dielectric property of the graphene composite anchored with non-planar iron single-atoms. Appl Phys Lett. 2022;121: 073102.
Li B, Xu J, Xu HY, Yan F, Zhang X, Zhu CL, Zhang XT, Chen YJ. Grafting thin N-doped carbon nanotubes on hollow N-doped carbon nanoplates encapsulated with ultrasmall cobalt particles for microwave absorption. Chem Eng J. 2022;435: 134846.
Zhang XC, Shi YN, Xu J, Ouyang QY, Zhang X, Zhu CL, Zhang XL, Chen YJ. Identification of the intrinsic dielectric properties of metal single atoms for electromagnetic wave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022;14:27.
Xu J, Liu LN, Zhang XC, Li B, Zhu CL, Chou SL, Chen YJ. Tailoring electronic properties and polarization relaxation behavior of MoS2 monolayers for electromagnetic energy dissipation and wireless pressure micro-sensor. Chem Eng J. 2021;425: 131700.
Xing XL, Liu RJ, Anjass M, Cao KC, Kaiser U, Zhang GJ, Streb C. Bimetallic manganese-vanadium functionalized N, S-doped carbon nanotubes as efficient oxygen evolution and oxygen reduction electrocatalysts. Appl Catal B. 2020;277: 119195.
Zhi DD, Li T, Qi ZH, Li JZ, Tian YR, Deng WT, Meng FB. Core-shell heterogeneous graphene-based aerogel microspheres for high-performance broadband microwave absorption via resonance loss and sequential attenuation. Chem Eng J. 2022;433: 134496.
Yusuf M, Hira SA, Park KH. Light-harvesting novel hierarchical porous Cu9S5–MnWO4 hybrid structures in photocatalytic oxidative homocoupling of alkynes and amines. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022;14:15529–40.
Liu Y, Fang YJ, Zhao ZW, Yuan CZ, Lou XW. A ternary Fe1−xS@porous carbon nanowires/reduced graphene oxide hybrid film electrode with superior volumetric and gravimetric capacities for flexible sodium ion batteries. Adv Energy Mater. 2019;9:1803052.
Yang SS, Wang YW, Zhang HJ, Zhang Y, Liu L, Fang L, Yang XH, Gu X, Wang Y. Unique three-dimensional Mo2C@MoS2 heterojunction nanostructure with S vacancies as outstanding all-pH range electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution. J Catal. 2019;371:20–6.
Feng XT, Jiao QZ, Li Q, Shi Q, Dai Z, Zhao Y, Li HS, Feng CH, Zhou W, Feng TY. NiCo2S4 spheres grown on N, S co-doped rGO with high sulfur vacancies as superior oxygen bifunctional electrocatalysts. Electrochim Acta. 2020;331: 135356.
Qiao J, Zhang X, Liu C, Zeng ZH, Yang YF, Wu LL, Wang FL, Wang Z, Liu W, Liu JR. Facile synthesis of MnS nanoparticle embedded porous carbon nanocomposite fibers for broadband electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon. 2022;191:525–34.
Chen WX, Xing HL, Gao ST, Yang P, Ji XL. Bi-semiconductor heterojunction Cu9S5@VO2 microspheres with morphology regulation as broadband high-performance electromagnetic wave absorber. Appl Surf Sci. 2023;610: 155539.
Tao FJ, Green M, Tran ATV, Zhang YL, Yin YS, Chen XB. Plasmonic Cu9S5 nanonets for microwave absorption. ACS Appl Nano Mater. 2019;2:3836–47.
Liao J, Ye MQ, Han AJ, Guo JM, Chen CL. Nanosheet architecture of Cu9S5 loaded with Fe3O4 microspheres for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. Ceram Int. 2021;47:8803–11.
Liao J, Ye MQ, Han AJ, Guo JM, Liu QZ, Yu GQ. Boosted electromagnetic wave absorption performance from multiple loss mechanisms in flower-like Cu9S5/RGO composites. Carbon. 2021;177:115–27.
Guo YL, Chang Q, Shi ZXH, Xie JY, Yun JJ, Zhang LM, Wu HJ. Regulating conduction and polarization losses by adjusting bonded N in N-doped Cu/CuO/C composites. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2023;639:444–53.
Yan J, Huang Y, Han XP, Gao XG, Liu PB. Metal organic framework (ZIF-67)-derived hollow CoS2/N-doped carbon nanotube composites for extraordinary electromagnetic wave absorption. Compos Part B Eng. 2019;163:67–76.
Yang HL, Shen ZJ, Peng HL, Xiong ZQ, Liu CB, Xie Y. 1D–3D mixed-dimensional MnO2@nanoporous carbon composites derived from Mn-metal organic framework with full-band ultra-strong microwave absorption response. Chem Eng J. 2021;417: 128087.
Zhu HH, Liang J, Jiao XG, Fu RR, Jiao QZ, Feng CH, Li HS, Zhang YY, Zhao Y. MOF-derived core-shell structured Cu9S5/NC@Co3S4/NC composite as a high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorber. Ceram Int. 2023;49:9534–42.
Wang P, Cheng LF, Zhang LT. One-dimensional carbon/SiC nanocomposites with tunable dielectric and broadband electromagnetic wave absorption properties. Carbon. 2017;125:207–20.
Cui C, Geng L, Jiang S, Bai WH, Dai LL, Jiang SX, Hu J, Ren EH, Guo RH. Construction of hierarchical carbon fiber aerogel@hollow Co9S8 polyhedron for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption at low-frequency. Chem Eng J. 2023;466: 143122.
Chen XT, Wang ZD, Zhou M, Zhao Y, Tang SL, Ji GB. Multilevel structure carbon aerogels with 99.999% electromagnetic wave absorptivity at 1.8 mm and efficient thermal stealth. Chem Eng J. 2023;452: 139110.
Dou YY, Liu N, Zhang XY, Jiang WT, Jiang XH, Yu LM. Synthesis of polymer-derived N, O-doped bowl-like hollow carbon microspheres for improved electromagnetic wave absorption using controlled template pyrolysis. Chem Eng J. 2023;463: 142398.
Liu JL, Zhang LM, Wu HJ. Anion-doping-induced vacancy engineering of cobalt sulfoselenide for boosting electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv Funct Mater. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202200544.
Liang LY, Li QM, Yan X, Feng YZ, Wang YM, Zhang HB, Zhou XP, Liu CT, Shen CY, Xie XL. Multifunctional magnetic Ti3C2Tx MXene/graphene aerogel with superior electromagnetic wave absorption performance. ACS Nano. 2021;15:6622–32.
Zhang X, Tian XL, Qiao J, Fang XR, Liu KY, Liu C, Lin JP, Li LT, Liu W, Liu JR, Zeng ZH. In-situ fabrication of sustainable-N-doped-carbon-nanotube-encapsulated CoNi heterogenous nanocomposites for high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption. Small. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202302686.
Cheng HR, Pan YM, Wang X, Liu CT, Shen CY, Schubert DW, Guo ZH, Liu XH. Ni flower/MXene-melamine foam derived 3D magnetic/conductive networks for ultra-efficient microwave absorption and infrared stealth. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022;14:63.
Li MH, Zhu WJ, Li X, Xu HL, Fan XM, Wu HJ, Ye F, Xue JM, Li XQ, Cheng LF, Zhang LT. Ti3C2Tx/MoS2 self-rolling rod-based foam boosts interfacial polarization for electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv Sci. 2022;9:2201118.
Jiang HJ, Cai L, Pan F, Shi YY, Cheng J, Yang Y, Shi Z, Chai XL, Wu HJ, Lu W. Ordered heterostructured aerogel with broadband electromagnetic wave absorption based on mesoscopic magnetic superposition enhancement. Adv Sci. 2023;10:2301599.
Xu J, Liu MJ, Zhang XC, Li B, Zhang X, Zhang XL, Zhu CL, Chen YJ. Atomically dispersed cobalt anchored on N-doped graphene aerogels for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption with an ultralow filler ratio. Appl Phys Rev. 2022;9: 011402.
Lan D, Wang Y, Wang YY, Zhu XF, Li HF, Guo XM, Ren JN, Guo ZH, Wu GL. Impact mechanisms of aggregation state regulation strategies on the microwave absorption properties of flexible polyaniline. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2023;651:494–503.
Xu J, Zhang X, Zhao ZB, Hu H, Li B, Zhu CL, Zhang XT, Chen YJ. Lightweight, fire-retardant, and anti-compressed honeycombed-like carbon aerogels for thermal management and high-efficiency electromagnetic absorbing properties. Small. 2021;17:2102032.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2021ME194, 2022TSGC2448, 2023TSGC0545), and the key research and development program of Shandong Province(2021ZLGX01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, S., Wang, C., Tang, Y. et al. Metal–Organic Framework-Derived Hierarchical Cu9S5/C Nanocomposite Fibers for Enhanced Electromagnetic Wave Absorption. Adv. Fiber Mater. 6, 430–443 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-023-00362-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-023-00362-9