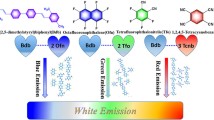
Abstract
Circularly polarized luminescence (CPL)-active nanomaterials have attracted tremendous attention. However, it is still a big challenge to conveniently fabricate multi-color and white CPL-active nanomaterials on a large scale. Herein, a simple and scalable approach to achieve the above goals is presented. Multicolor CPL-active nanofibers are fabricated from chiral helical substituted polyacetylene, achiral fluorescent dyes and polyacrylonitrile via uniaxial electrospinning; the highest luminescence dissymmetry factor (glum) of the resulting nanofibers can reach 10− 2. Furthermore, white CPL-active nanofibers are obtained by coaxial electrospinning, in which the resulting core-shell structure has excellent adjustability and can be utilized to physically isolate different fluorescent dyes to reduce energy transfer efficiency; therefore, stable white CPL emissions can be achieved with high glum values up to 10− 3. Notably, the prepared white-emission CPL nanofibrous films show bright white circularly polarized light when coated on UV chips, demonstrating their future application in constructing low-cost and flexible light-emitting devices such as circularly polarized light-emitting diodes.
Graphical Abstract
Multi-color tunable and white circularly polarized luminescence (CPL)-active nanofibers are prepared from chiral helical polymers and commercial fluorescence dyes via electrospinning process. The obtained composite nanofibers exhibit considerable luminescence dissymmetry factor (glum), with the highest glum up to 10−2. White circularly polarized light-emitting diodes are further fabricated by packaging the white CPL nanofiber film on UV chip.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang S, Hu DP, Guan XY, Cai SL, Shi G, Shuai ZG, Zhang J, Peng Q, Wan XH. Brightening up circularly polarized luminescence of monosubstituted polyacetylene by conformation control: mechanism, switching, and sensing. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2021;60:21918.
Maeda K, Nozaki M, Hashimoto K, Shimomura K, Hirose D, Nishimura T, Watanabe G, Yashima E. Helix-sense-selective synthesis of right- and left-handed helical luminescent poly(diphenylacetylene)s with memory of the macromolecular helicity and their helical structures. J Am Chem Soc. 2020;142:7668.
Wu ZG, Han HB, Yan ZP, Luo XF, Wang Y, Zheng YX, Zuo JL, Pan Y. Chiral octahydro-binaphthol compound-based thermally activated delayed fluorescence materials for circularly polarized electroluminescence with superior EQE of 32.6% and extremely low efficiency roll-off. Adv Mater. 2019;31:1900524.
Jiang HJ, Jiang YQ, Han JL, Zhang L, Liu MH. Helical nanostructures: chirality transfer and a photodriven transformation from superhelix to nanokebab. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2019;58:785.
Han ZS, Wang KY, Guo YF, Chen WJ, Zhang JL, Zhang XR, Siligardi G, Yang SH, Zhou Z, Sun PC, Shi W, Cheng P. Cation-induced chirality in a bifunctional metal-organic framework for quantitative enantioselective recognition. Nat Commun. 2019;10:5117.
Gong ZL, Zhu XF, Zhou ZH, Zhang SW, Yang D, Zhao B, Zhang YP, Deng JP, Cheng YX, Zheng YX, Zang SQ, Kuang H, Duan PF, Yuan MJ, Chen CF, Zhao YS, Zhong YW, Tang BZ, Liu MH. Frontiers in circularly polarized luminescence: molecular design, self-assembly, nanomaterials, and applications. Sci China Chem. 2021;64:2060.
Qu D, Zheng HZ, Jiang HJ, Xu Y, Tang ZY. Chiral photonic cellulose films enabling mechano/chemo responsive selective reflection of circularly polarized light. Adv Opt Mater. 2019;7:1801395.
Gao R, Cao D, Guan Y, Yan DP. Flexible self-supporting nanofibers thin films showing reversible photochromic fluorescence. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7:9904.
Gao R, Cao D, Guan Y, Yan DP. Fast and reversible humidity-responsive luminescent thin films. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2016;55:125.
Yan DP, Williams GR, Zhao M, Li CM, Fan GL, Yang HJ. Flexible free-standing luminescent two-component fiber films with tunable hierarchical structures based on hydrogen-bonding architecture. Langmuir. 2013;29:15673.
Zhou B, Yan DP. Color-tunable persistent luminescence in 1D zinc–organic halide microcrystals for single-component white light and temperature-gating optical waveguides. Chem Sci. 2022;13:7429.
Gao R, Kodaimati MS, Yan DP. Recent advances in persistent luminescence based on molecular hybrid materials. Chem Soc Rev. 2021;50:5564.
Li SZ, Lu B, Fang XY, Yan DP. Manipulating light-induced dynamic macro-movement and static photonic properties within 1D isostructural hydrogen-bonded molecular cocrystals. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2020;59:22623.
Rahmani M, Faridi-Majidi R, Khani MM, Mashaghi A, Noorizadeh F, Ghanbari H. Cross-linked PMS/PLA nanofibers with tunable mechanical properties and degradation rate for biomedical applications. Eur Polym J. 2020;130:109633.
Zhang L, Wang TY, Shen ZC, Liu MH. Chiral nanoarchitectonics: towards the design, self-assembly, and function of nanoscale chiral twists and helices. Adv Mater. 2016;28:1044.
Huo SW, Duan PF, Jiao TF, Peng QM, Liu MH. Self-assembled luminescent quantum dots to generate full-color and white circularly polarized light. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2017;56:12174.
Han JL, You J, Li XG, Duan PF, Liu MH. Full-color tunable circularly polarized luminescent nanoassemblies of achiral AIEgens in confined chiral nanotubes. Adv Mater. 2017;29:1606503.
Goto T, Okazaki Y, Ueki M, Kuwahara Y, Takafuji M, Oda R, Ihara H. Induction of strong and tunable circularly polarized luminescence of nonchiral, nonmetal, low-molecular-weight fluorophores using chiral nanotemplates. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2017;56:2989.
Xu L, Wang C, Li YX, Xu XH, Zhou L, Liu N, Wu ZQ. Crystallization-driven asymmetric helical assembly of conjugated block copolymers and the aggregation induced white-light emission and circularly polarized luminescence. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2020;59:16675.
Würthner F, Saha-Möller CR, Fimmel B, Ogi S, Leowanawat P, Schmidt D. Perylene bisimide dye assemblies as archetype functional supramolecular materials. Chem Rev. 2016;116:962.
Babu SS, Praveen VK, Ajayaghosh A. Functional π-gelators and their applications. Chem Rev. 2014;114:1973.
Kumar J, Tsumatori H, Yuasa J, Kawai T, Nakashima T. Self-discriminating termination of chiral supramolecular polymerization: tuning the length of nanofibers. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2015;54:5943.
Shen ZC, Wang TY, Shi L, Tang ZY, Liu MH. Strong circularly polarized luminescence from the supramolecular gels of an achiral gelator: tunable intensity and handedness. Chem Sci. 2015;6:4267.
Zhao B, Gao XB, Pan K, Deng JP. Chiral helical polymer/perovskite hybrid nanofibers with intense circularly polarized luminescence. ACS Nano. 2021;15:7463.
Li PP, Feng J, Pan K, Deng JP. Preparation and chirality investigation of electrospun nanofibers from optically active helical substituted polyacetylenes. Macromolecules. 2020;53:602.
Zhao B, Pan K, Deng JP. Combining chiral helical polymer with achiral luminophores for generating full-color, on–off, and switchable circularly polarized luminescence. Macromolecules. 2019;52:376.
Zhao B, Pan K, Deng JP. Intense circularly polarized luminescence contributed by helical chirality of monosubstituted polyacetylenes. Macromolecules. 2018;51:7104.
Xue JJ, Wu T, Dai YQ, Xia YN. Electrospinning and electrospun nanofibers: methods, materials, and applications. Chem Rev. 2019;119:5298.
Lee JKY, Chen N, Peng SJ, Li LL, Tian LL, Thakor N, Ramakrishna S. Polymer-based composites by electrospinning: preparation & functionalization with nanocarbons. Prog Polym Sci. 2018;86:40.
Zhang ZG, Deng JP, Zhao WG, Wang JM, Yang WT. Synthesis of optically active poly(N-propargylsulfamides) with helical conformation. J Polym Sci A Polym Chem. 2007;45:500.
Schrock RR, Osborn JA. π-Bonded complexes of the tetraphenylborate ion with rhodium (I) and iridium (I). Inorg Chem. 1970;9:2339.
Wang Z, Zhu CY, Mo JT, Fu PY, Zhao YW, Yin SY, Jiang JJ, Pan M, Su CY. White-light emission from dual-way photon energy conversion in a dye-encapsulated metal–organic framework. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2019;58:9752.
Wen YH, Sheng TL, Zhu XQ, Zhuo C, Su SD, Li HR, Hu SM, Zhu QL, Wu XT. Introduction of red-green-blue fluorescent dyes into a metal–organic framework for tunable white light emission. Adv Mater. 2017;29:1700778.
Qin Z, Wang QT, Wang CZ, Xu DF, Ma GP, Pan K. Electrospun janus nanofibers for white-light emission through efficient spatial isolation to control two-step energy transfer. J Mater Chem C. 2019;7:1065.
Shimomura K, Ikai T, Kanoh S, Yashima E, Maeda K. Switchable enantioseparation based on macromolecular memory of a helical polyacetylene in the solid state. Nat Chem. 2014;6:429.
Yashima E, Maeda K, Okamoto Y. Memory of macromolecular helicity assisted by interaction with achiral small molecules. Nature. 1999;399:449.
Li ZQ, Gong ZL, Shao JY, Yao JN, Zhong YW. Full-color and white circularly polarized luminescence of hydrogen-bonded ionic organic microcrystals. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2021;60:14595.
Cai SL, Chen JX, Wang S, Zhang J, Wan XH. Allostery-mimicking self-assembly of helical poly(phenylacetylene) block copolymers and the chirality transfer. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2021;60:9686.
Shi G, Dai X, Xu Q, Shen J, Wan XH. Enantioseparation by high-performance liquid chromatography on proline-derived helical polyacetylenes. Polym Chem. 2021;12:242.
Zhang DY, Song C, Deng JP, Yang WT. Chiral microspheres consisting purely of optically active helical substituted polyacetylene: the first preparation via precipitation polymerization and application in enantioselective crystallization. Macromolecules. 2012;45:7329.
Chen B, Deng JP, Cui X, Yang WT. Optically active helical substituted polyacetylenes as chiral seeding for inducing enantioselective crystallization of racemic N-(tert-butoxycarbonyl)alanine. Macromolecules. 2011;44:7109.
Zheng D, Zheng L, Yu CY, Zhan YL, Wang Y, Jiang H. Significant enhancement of circularly polarized luminescence dissymmetry factors in quinoline oligoamide foldamers with absolute helicity. Org Lett. 2019;21:2555.
Zinna F, Di Bari L. Lanthanide circularly polarized luminescence: bases and applications.Chirality. 2015;27:1.
Li PP, Deng JP. Switchable chiroptical flexible films based on chiral helical superstructure: handedness inversion and dissymmetric adjustability by stretching. Adv Funct Mater. 2021;31:2105315.
Ikai T, Okubo M, Wada Y. Helical assemblies of one-dimensional supramolecular polymers composed of helical macromolecules: generation of circularly polarized light using an infinitesimal chiral source. J Am Chem Soc. 2020;142:3254.
Yang L, Wang F, Auphedeous DIY, Feng CL. Achiral isomers controlled circularly polarized luminescence in supramolecular hydrogels. Nanoscale. 2019;11:14210.
Kundu S, Sk B, Pallavi P, Giri A, Patra A. Molecular engineering approaches towards all-organic white light emitting materials. Chem Eur J. 2020;26:5557.
Zhang C, Yan ZP, Dong XY, Han Z, Li S, Fu T, Zhu YY, Zheng YX, Niu YY, Zang SQ. Enantiomeric MOF crystals using helical channels as palettes with bright white circularly polarized luminescence. Adv Mater. 2020;32:2002914.
Ding R, Dong FX, An MH, Wang XP, Wang MR, Li XB, Feng J, Sun HB. High-color-rendering and high-efficiency white organic light-emitting devices based on double-doped organic single crystals. Adv Funct Mater. 2019;29:1807606.
Hong YJ, Lee CH, Yoon A, Kim M, Seong HK, Chung HJ, Sone C, Park YJ, Yi GC. Visible-color-tunable light-emitting diodes. Adv Mater. 2011;23:3284.
Chen PK, Li QC, Grindy S, Holten-Andersen N. White-light-emitting lanthanide metallogels with tunable luminescence and reversible stimuli-responsive properties. J Am Chem Soc. 2015;137:11590.
Bu J, Watanabe K, Hayasaka H, Akagi K. Photochemically colour-tuneable white fluorescence illuminants consisting of conjugated polymer nanospheres. Nat Commun. 2014;5:3799.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51973011, 52003022).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, P., Gao, X., Zhao, B. et al. Multi-color Tunable and White Circularly Polarized Luminescent Composite Nanofibers Electrospun from Chiral Helical Polymer. Adv. Fiber Mater. 4, 1632–1644 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-022-00196-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-022-00196-x