Abstract
Membrane distillation (MD) utilizing low-grade thermal energy can be used to effectively desalinate hypersaline brines with a high freshwater recovery for water reuse. Membrane flux and durability are the two main indices used to evaluate MD membrane performance. In the past decade, electrospun nanofibrous distillation membranes (EFDMs) with a low mass transfer resistance have garnered increasing attention in MD research, owing to their high porosity and interconnected-pore structure. However, on the one hand, the pores of EFDMs compared to those of phase-inversion membranes are easily deformed and impacted by water flow, reducing membrane flux; on the other hand, the general hydrophobic interface is susceptible to being wetted, fouled and scaled during the desalination/concentration process, resulting in MD failure. This review will present a comprehensive discussion of the recent progress in electrospun nanofibers for the MD of hypersaline wastewaters with a focus on designing specially wettable membrane interfaces and welding-pore structured membranes to enhance MD distillation efficiency and durability simultaneously. Besides, the challenges and perspectives of MD in treating hypersaline wastewaters are also provided as a guide for future research on sustainable and clean freshwater recovery.
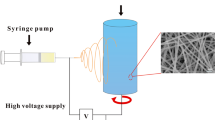
Graphical abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deshmukh A, Boo C, Karanikola V, Lin S, Straub AP, Tong T, Warsinger DM, Elimelech M. Membrane distillation at the water-energy nexus: limits, opportunities, and challenges. Energy Environ Sci 2018;11:1177.
Hoekstra AY. Water scarcity challenges to business. Nat Clim Change 2014;4:318.
Zhu Z, Xu Y, Luo Y, Wang W, Chen X. Porous evaporators with special wettability for low-grade heat-driven water desalination. J Mater Chem A 2021;9:702.
Elimelech M, Phillip WA. The future of seawater desalination: energy, technology, and the environment. Science 2011;333:712.
Shannon MA, Bohn PW, Elimelech M, Georgiadis JG, Mariñas BJ, Mayes AM. Science and technology for water purification in the coming decades. Nature 2008;452:301.
Ali A, Quist-Jensen CA, Jørgensen MK, Siekierka A, Christensen ML, Bryjak M, Hélix-Nielsen C, Drioli E. A review of membrane crystallization, forward osmosis and membrane capacitive deionization for liquid mining. Resour Conserv Recy 2021;168:105273.
Fujiwara M, Imura T. Photo induced membrane separation forwater purification and desalination using azobenzene modified anodized alumina membranes. ACS Nano 2015;9:5705.
Zhu L, Gao M, Peh CKN, Wang X, Ho GW. Self-contained monolithic carbon sponges for solar-driven interfacial water evaporation distillation and electricity generation. Adv Energy Mater 2018;8:1702149.
Dudchenko AV, Chen C, Cardenas A, Rolf J, Jassby D. Frequency-dependent stability of CNT Joule heaters in ionizable media and desalination processes. Nat Nanotechnol 2017;12:557.
Choi Y, Naidu G, Jeong S, Lee S, Vigneswaran S. Effect of chemical and physical factors on the crystallization of calcium sulfate in seawater reverse osmosis brine. Desalination 2018;426:78.
Qasim M, Badrelzaman M, Darwish NN, Darwish NA, Hilal N. Reverse osmosis desalination: a state-of-the-art review. Desalination 2019;459:59.
Anderson WV, Cheng C-M, Butalia TS, Weavers LK. Forward osmosis–membrane distillation process for zero liquid discharge of flue gas desulfurization wastewater. Energy Fuels 2021;35:5130.
Zhang R, Tian J, Gao S, Van der Bruggen B. How to coordinate the trade-off between water permeability and salt rejection in nanofiltration? J Mater Chem A 2020;8:8831.
Chew NGP, Zhang Y, Goh K, Ho JS, Xu R, Wang R. Hierarchically structured Janus membrane surfaces for enhanced membrane distillation performance. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2019;11:25524.
Du Y, Wang D, Wang W, Fu J, Chen X, Wang L, Yang W, Zhang X. Electrospun nanofibrous polyphenylene oxide membranes for high-salinity water desalination by direct contact membrane distillation. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 2019;7:20060.
Chang H, Liu B, Zhang Z, Pawar R, Yan Z, Crittenden JC, Vidic RD. A critical review of membrane wettability in membrane distillation from the perspective of interfacial interactions. Environ Sci Technol 2021;55:1395.
Yin Y, Jeong N, Tong T. The effects of membrane surface wettability on pore wetting and scaling reversibility associated with mineral scaling in membrane distillation. J Membr Sci 2020;614:118503.
Xiao Z, Zheng R, Liu Y, He H, Yuan X, Ji Y, Li D, Yin H, Zhang Y, Li XM, He T. Slippery for scaling resistance in membrane distillation: a novel porous micropillared superhydrophobic surface. Water Res 2019;155:152.
Xiao Z, Li Z, Guo H, Liu Y, Wang Y, Yin H, Li X, Song J, Nghiem LD, He T. Scaling mitigation in membrane distillation: from superhydrophobic to slippery. Desalination 2019;466:36.
Zhu Z, Wang W, Zhang Q, Chen X. Insight into the feed/permeate flow velocity on the trade-off of water flux and scaling resistance of superhydrophobic and welding-pore fibrous membrane in membrane distillation. J Membr Sci 2021;620:118883.
Zhu Z, Zhong L, Horseman T, Liu Z, Zeng G, Li Z, Lin S, Wang W. Superhydrophobic-omniphobic membrane with anti-deformable pores for membrane distillation with excellent wetting resistance. J Membr Sci 2021;620:118768.
Liu Y, Li Z, Xiao Z, Yin H, Li X, He T. Synergy of slippery surface and pulse flow: an anti-scaling solution for direct contact membrane distillation. J Membr Sci 2020;603:118035.
Li C, Li X, Du X, Tong T, Cath TY, Lee J. Antiwetting and antifouling janus membrane for desalination of saline oily wastewater by membrane distillation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2019;11:18456.
Horseman T, Yin Y, Christie KSS, Wang Z, Tong T, Lin S. Wetting, scaling, and fouling in membrane distillation: state-of-the-art insights on fundamental mechanisms and mitigation strategies. ACS ES&T Eng 2020;1:117.
Tan G, Xue X, Zhu Z, Li J. Ultrahigh and stable water recovery of reverse osmosis-concentrated seawater with membrane distillation by synchronously optimizing membrane interfaces and seawater ingredients. ACS ES&T Water 2021;1:1577.
Jiang X, Shao Y, Li J, Wu M, Niu Y, Ruan X, Yan X, Li X, He G. Bioinspired hybrid micro/nanostructure composited membrane with intensified mass transfer and antifouling for high saline water membrane distillation. ACS Nano 2020;14:17376.
Ashoor BB, Mansour S, Giwa A, Dufour V, Hasan SW. Principles and applications of direct contact membrane distillation (DCMD): a comprehensive review. Desalination 2016;398:222.
Anvari A, Kekre KM, Ronen A. Scaling mitigation in radio-frequency induction heated membrane distillation. J Membr Sci 2020;600:117859.
Lawson KW, Lloyd DR. Membrane distillation. J Membr Sci 1997;124:1.
Abdelrazeq H, Khraisheh M, Al Momani F, McLeskey JT, Hassan MK, Gad-el-Hak M, Tafreshi HV. Performance of electrospun polystyrene membranes in synthetic produced industrial water using direct-contact membrane distillation. Desalination 2020;493:114663.
Harandi HB, Asadi A, Fathi H, Sui P-C. Combined macroscopic and pore scale modeling of direct contact membrane distillation with micro-porous hydrophobic membranes. Desalination 2021;514:115171.
Grasso G, Galiano F, Yoo MJ, Mancuso R, Park HB, Gabriele B, Figoli A, Drioli E. Development of graphene-PVDF composite membranes for membrane distillation. J Membr Sci 2020;604:118017.
Li B, Yun Y, Wang M, Li C, Yang W, Li J, Liu G. Superhydrophobic polymer membrane coated by mineralized β-FeOOH nanorods for direct contact membrane distillation. Desalination 2021;500:114889.
Chen Y, Lu KJ, Japip S, Chung TS. Can composite Janus membranes with an ultrathin dense hydrophilic layer resist wetting in membrane distillation? Environ Sci Technol 2020;54:12713.
An AK, Guo J, Lee E-J, Jeong S, Zhao Y, Wang Z, Leiknes T. PDMS/PVDF hybrid electrospun membrane with superhydrophobic property and drop impact dynamics for dyeing wastewater treatment using membrane distillation. J Membr Sci 2017;525:57.
Deka BJ, Guo J, Khanzada NK, An AK. Omniphobic re-entrant PVDF membrane with ZnO nanoparticles composite for desalination of low surface tension oily seawater. Water Res 2019;165:114982.
Boo C, Lee J, Elimelech M. Engineering surface energy and nanostructure of microporous films for expanded membrane distillation applications. Environ Sci Technol 2016;50:8112.
Chen L, Huang A, Chen Y, Chen C, Hsu C, Tsai F, Tung K. Omniphobic membranes for direct contact membrane distillation: effective deposition of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Desalination 2018;428:255.
Kang S, Zhao K, Yu D-G, Zheng X, Huang C. Advances in biosensing and environmental monitoring based on electrospun nanofibers. Adv Fiber Mater 2022;4:404.
Liu H, Wang H, Lu X, Murugadoss V, Huang M, Yang H, Wan F, Yu D-G, Guo Z. Electrospun structural nanohybrids combining three composites for fast helicide delivery. Adv Compos Hybrid Ma 2022;5:1017.
Liu H, Jiang W, Yang Z, Chen X, Yu DG, Shao J. Hybrid films prepared from a combination of electrospinning and casting for offering a dual-phase drug release. Polymers 2022;14:2132.
Wang M, Tan Y, Li D, Xu G, Yin D, Xiao Y, Xu T, Chen X, Zhu X, Shi X. Negative isolation of circulating tumor cells using a microfluidic platform integrated with streptavidin-functionalized PLGA nanofibers. Adv Fiber Mater 2021;3:192.
Zhu Z, Wu P, Liu G, He X, Qi B, Zeng G, Wang W, Sun Y, Cui F. Ultrahigh adsorption capacity of anionic dyes with sharp selectivity through the cationic charged hybrid nanofibrous membranes. Chem Eng J 2017;313:957.
Zhu Z, Wang W, Qi D, Luo Y, Liu Y, Xu Y, Cui F, Wang C, Chen X. Calcinable polymer membrane with revivability for efficient oily-water remediation. Adv Mater 2018;30:e1801870.
Zhu Z, Zhong L, Wang Y, Zeng G, Wang W. Mechanically durable biomimetic fibrous membrane with superhydrophobicity and superoleophilicity for aqueous oil separation. Chin Chem Lett 2020;31:2619.
Wang W, Du X, Vahabi H, Zhao S, Yin Y, Kota AK, Tong T. Trade-off in membrane distillation with monolithic omniphobic membranes. Nat Commun 2019;10:3220.
Zhao S, Jiang C, Fan J, Hong S, Mei P, Yao R, Liu Y, Zhang S, Li H, Zhang H, Sun C, Guo Z, Shao P, Zhu Y, Zhang J, Guo L, Ma Y, Zhang J, Feng X, Wang F, Wu H, Wang B. Hydrophilicity gradient in covalent organic frameworks for membrane distillation. Nat Mater 2021;20:1551.
Huang YX, Wang Z, Jin J, Lin S. Novel Janus membrane for membrane distillation with simultaneous fouling and wetting resistance. Environ Sci Technol 2017;51:13304.
Zhu Z, Zhong L, Chen X, Zheng W, Zuo J, Zeng G, Wang W. Monolithic and self-roughened Janus fibrous membrane with superhydrophilic/omniphobic surface for robust antifouling and antiwetting membrane distillation. J Membr Sci 2020;615:118499.
Li K, Hou D, Fu C, Wang K, Wang J. Fabrication of PVDF nanofibrous hydrophobic composite membranes reinforced with fabric substrates via electrospinning for membrane distillation desalination. J Environ Sci 2019;75:277.
Zhu Z, Liu Z, Zhong L, Song C, Shi W, Cui F, Wang W. Breathable and asymmetrically superwettable Janus membrane with robust oil-fouling resistance for durable membrane distillation. J Membr Sci 2018;563:602.
Li X, Yu X, Cheng C, Deng L, Wang M, Wang X. Electrospun superhydrophobic organic/inorganic composite nanofibrous membranes for membrane distillation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2015;7:21919.
Li Z, Cheng B, Ju J, Kang W, Liu Y. Development of a novel multi-scale structured superhydrophobic nanofiber membrane with enhanced thermal efficiency and high flux for membrane distillation. Desalination 2021;501:114834.
Deng L, Li P, Liu K, Wang X, Hsiao BS. Robust superhydrophobic dual layer nanofibrous composite membranes with a hierarchically structured amorphous polypropylene skin for membrane distillation. J Mater Chem A 2019;7:11282.
Deng L, Liu K, Li P, Sun D, Ding S, Wang X, Hsiao BS. Engineering construction of robust superhydrophobic two-tier composite membrane with interlocked structure for membrane distillation. J Membr Sci 2020;598:117813.
Li Z, Liu Y, Yan J, Wang K, Xie B, Hu Y, Kang W, Cheng B. Electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride/fluorinated acrylate copolymer tree-like nanofiber membrane with high flux and salt rejection ratio for direct contact membrane distillation. Desalination 2019;466:68.
Li Y, Zhu Z, Yu J, Ding B. Carbon nanotubes enhanced fluorinated polyurethane macroporous membranes for waterproof and breathable application. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2015;7:13538.
Francis L, Ahmed FE, Hilal N. Electrospun membranes for membrane distillation: the state of play and recent advances. Desalination 2022;526:115511.
Madalosso HB, Machado R, Hotza D, Marangoni C. Membrane surface modification by electrospinning, coating, and plasma for membrane distillation applications: a state-of-the-art review. Adv Eng Mater 2021;23:2001456.
Sheng J, Xu Y, Yu J, Ding B. Robust fluorine-free superhydrophobic amino-silicone oil/SiO2 modification of electrospun polyacrylonitrile membranes for waterproof-breathable application. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2017;9:15139.
Ji C, Zhu Z, Zhong L, Zhang W, Wang W. Design of firm-pore superhydrophobic fibrous membrane for advancing the durability of membrane distillation. Desalination 2021;519:115185.
Xue X, Tan G, Zhu Z. All-polymer and self-roughened superhydrophobic PVDF fibrous membranes for stably concentrating seawater by membrane distillation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2021;13:45977.
Vitale A, Massaglia G, Chiodoni A, Bongiovanni R, Pirri CF, Quaglio M. Tuning porosity and functionality of electrospun rubber nanofiber mats by photo-crosslinking. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2019;11:24544.
Raza A, Ding B, Zainab G, El-Newehy M, Al-Deyab SS, Yu J. In situ cross-linked superwetting nanofibrous membranes for ultrafast oil–water separation. J Mater Chem A 2014;2:10137.
Su C, Horseman T, Cao H, Christie K, Li Y, Lin S. Robust superhydrophobic membrane for membrane distillation with excellent scaling resistance. Environ Sci Technol 2019;53:11801.
Wang N, Zhai Y, Yang Y, Yang X, Zhu Z. Electrostatic assembly of superwetting porous nanofibrous membrane toward oil-in-water microemulsion separation. Chem Eng J 2018;354:463.
Wan H, Wang N, Yang J, Si Y, Chen K, Ding B, Sun G, El-Newehy M, Al-Deyab SS, Yu J. Hierarchically structured polysulfone/titania fibrous membranes with enhanced air filtration performance. J Colloid Interface Sci 2014;417:18.
Li Y, Yang F, Yu J, Ding B. Hydrophobic fibrous membranes with tunable porous structure for equilibrium of breathable and waterproof performance. Adv Mater Interfaces 2016;3:1600516.
Wang N, Zhu Z, Sheng J, Al-Deyab SS, Yu J, Ding B. Superamphiphobic nanofibrous membranes for effective filtration of fine particles. J Colloid Interface Sci 2014;428:41.
Zhong L, An L, Han Y, Zhu Z, Liu D, Liu D, Zuo D, Wang W, Ma J. In situ three-dimensional welded nanofibrous membranes for robust membrane distillation of concentrated seawater. Environ Sci Technol 2021;55:11308.
Li C, Li X, Du X, Zhang Y, Wang W, Tong T, Kota AK, Lee J. Elucidating the trade-off between membrane wetting resistance and water vapor flux in membrane distillation. Environ Sci Technol 2020;54:10333.
Cassie ABD, Baxter S. Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans Faraday Soc 1944;40:546.
Rezaei M, Warsinger DM, Lienhard VJ, Duke MC, Matsuura T, Samhaber WM. Wetting phenomena in membrane distillation: mechanisms, reversal, and prevention. Water Res 2018;139:329.
Lu KJ, Chen Y, Chung TS. Design of omniphobic interfaces for membrane distillation—a review. Water Res 2019;162:64.
Hong SK, Kim H, Lee H, Lim G, Cho SJ. A pore-size tunable superhydrophobic membrane for high-flux membrane distillation. J Membr Sci 2022;641:119862.
Jiang L, Chen L, Zhu L. Fouling process of membrane distillation for seawater desalination: an especial focus on the thermal-effect and concentrating-effect during biofouling. Desalination 2020;485:114457.
Kim HW, Yun T, Hong S, Lee S, Jeong S. Retardation of wetting for membrane distillation by adjusting major components of seawater. Water Res 2020;175:115677.
Chen Q-B, Li P-F, Wang J, Xu Y, Wang J, Dong L, Zhao J. Transport of salts and monoethylene glycol (MEG) during electrodialysis desalination of industrial hypersaline MEG wastewater. Desalination 2022;530:115683.
Lin S, Zhao H, Zhu L, He T, Chen S, Gao C, Zhang L. Seawater desalination technology and engineering in China: a review. Desalination 2021;498:114728.
Panagopoulos A. Energetic, economic and environmental assessment of zero liquid discharge (ZLD) brackish water and seawater desalination systems. Energy Convers Manage 2021;235:113957.
Wang K, Hou D, Wang J, Wang Z, Tian B, Liang P. Hydrophilic surface coating on hydrophobic PTFE membrane for robust anti-oil-fouling membrane distillation. Appl Surf Sci 2018;450:57.
Hou D, Ding C, Li K, Lin D, Wang D, Wang J. A novel dual-layer composite membrane with underwater-superoleophobic/hydrophobic asymmetric wettability for robust oil-fouling resistance in membrane distillation desalination. Desalination 2018;428:240.
Wang Z, Hou D, Lin S. Composite membrane with underwater-oleophobic surface for anti-oil-fouling membrane distillation. Environ Sci Technol 2016;50:3866.
Zuo G, Wang R. Novel membrane surface modification to enhance anti-oil fouling property for membrane distillation application. J Membr Sci 2013;447:26.
Tijing LD, Woo YC, Choi J-S, Lee S, Kim S-H, Shon HK. Fouling and its control in membrane distillation—a review. J Membr Sci 2015;475:215.
Wu Y, Kong Y, Liu J, Zhang J, Xu J. An experimental study on membrane distillation-crystallization for treating waste water in taurine production. Desalination 1991;80:235.
García-Payo MdC, Essalhi M, Khayet M. Effects of PVDF-HFP concentration on membrane distillation performance and structural morphology of hollow fiber membranes. J Membr Sci 2010;347:209.
Liu G, Zhu C, Cheung CS, Leung CW. Theoretical and experimental studies on air gap membrane distillation. Heat Mass Tansfer 1998;34:329.
Deka BJ, Lee EJ, Guo J, Kharraz J, An AK. Electrospun nanofiber membranes incorporating pdms-aerogel superhydrophobic coating with enhanced flux and improved antiwettability in membrane distillation. Environ Sci Technol 2019;53:4948.
Liao Y, Wang R, Fane AG. Fabrication of bioinspired composite nanofiber membranes with robust superhydrophobicity for direct contact membrane distillation. Environ Sci Technol 2014;48:6335.
Lee J, Boo C, Ryu WH, Taylor AD, Elimelech M. Development of omniphobic desalination membranes using a charged electrospun nanofiber scaffold. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2016;8:11154.
Ni T, Lin J, Kong L, Zhao S. Omniphobic membranes for distillation: opportunities and challenges. Chin Chem Lett 2021;32:3298.
Yan Z, Lu Z, Chen X, Fan G, Qu F, Pang H, Liang H. Integration of seeding- and heating-induced crystallization with membrane distillation for membrane gypsum scaling and wetting control. Desalination 2021;511:115115.
Liu L, He H, Wang Y, Tong T, Li X, Zhang Y, He T. Mitigation of gypsum and silica scaling in membrane distillation by pulse flow operation. J Membr Sci 2021;624:119107.
Christie KSS, Yin Y, Lin S, Tong T. Distinct behaviors between gypsum and silica scaling in membrane distillation. Environ Sci Technol 2020;54:568.
Karanikola V, Boo C, Rolf J, Elimelech M. Engineered slippery surface to mitigate gypsum scaling in membrane distillation for treatment of hypersaline industrial wastewaters. Environ Sci Technol 2018;52:14362.
Chen Y, Lu KJ, Chung T-S. An omniphobic slippery membrane with simultaneous anti-wetting and anti-scaling properties for robust membrane distillation. J Membr Sci 2020;595:117572.
Razmjou A, Arifin E, Dong G, Mansouri J, Chen V. Superhydrophobic modification of TiO2 nanocomposite PVDF membranes for applications in membrane distillation. J Membr Sci 2012;415–416:850.
Lee EJ, Deka BJ, Guo J, Woo YC, Shon HK, An AK. Engineering the re-entrant hierarchy and surface energy of PDMS-PVDF membrane for membrane distillation using a facile and benign microsphere coating. Environ Sci Technol 2017;51:10117.
Zhu Z, Liu Y, Hou H, Shi W, Qu F, Cui F, Wang W. Dual-bioinspired design for constructing membranes with superhydrophobicity for direct contact membrane distillation. Environ Sci Technol 2018;52:3027.
Tan G, Xu D, Zhu Z, Zhang X, Li J. Tailoring pore size and interface of superhydrophobic nanofibrous membrane for robust scaling resistance and flux enhancement in membrane distillation. J Membr Sci 2022;658:120751.
Zhu Z, Tan G, Lei D, Yang Q, Tan X, Liang N, Ma D. Omniphobic membrane with process optimization for advancing flux and durability toward concentrating reverse-osmosis concentrated seawater with membrane distillation. J Membr Sci 2021;639:119763.
Ye Y, Yu S, Hou L, Liu B, Xia Q, Liu G, Li P. Microbubble aeration enhances performance of vacuum membrane distillation desalination by alleviating membrane scaling. Water Res 2019;149:588.
Zhong L, Zhang X, Ma J, Liu D, Liu D, Wang Y, Cui F, Wang W. Synergy of feed-side aeration and super slippery interface in membrane distillation for enhanced water flux and scaling mitigation. Water Res 2022;215:118246.
Horseman T, Su C, Christie KSS, Lin S. Highly effective scaling mitigation in membrane distillation using a superhydrophobic membrane with gas purging. Environ Sci Technol Lett 2019;6:423.
Liu Y, Horseman T, Wang Z, Arafat HA, Yin H, Lin S, He T. Negative pressure membrane distillation for excellent gypsum scaling resistance and flux enhancement. Environ Sci Technol 2022;56:1405.
Yin Y, Jeong N, Minjarez R, Robbins CA, Carlson KH, Tong T. Contrasting behaviors between gypsum and silica scaling in the presence of antiscalants during membrane distillation. Environ Sci Technol 2021;55:5335.
Qu F, Yan Z, Yu H, Fan G, Pang H, Rong H, He J. Effect of residual commercial antiscalants on gypsum scaling and membrane wetting during direct contact membrane distillation. Desalination 2020;486:114493.
Yu W, Song D, Chen W, Yang H. Antiscalants in RO membrane scaling control. Water Res 2020;183:115985.
Elcik H, Fortunato L, Alpatova A, Soukane S, Orfi J, Ali E, AlAnsary H, Leiknes T, Ghaffour N. Multi-effect distillation brine treatment by membrane distillation: effect of antiscalant and antifoaming agents on membrane performance and scaling control. Desalination 2020;493:114653.
He F, Sirkar KK, Gilron J. Effects of antiscalants to mitigate membrane scaling by direct contact membrane distillation. J Membr Sci 2009;345:53.
Ben Ahmed S, Tlili M, Ben AM. Influence of a polyacrylate antiscalant on gypsum nucleation and growth. Cryst Res Technol 2008;43:935.
Wang P, Cheng W, Zhang X, Liu Q, Li J, Ma J, Zhang T. Membrane scaling and wetting in membrane distillation: mitigation roles played by humic substances. Environ Sci Technol 2022;56:3258.
Yan Z, Qu F, Liang H, Yu H, Pang H, Rong H, Fan G, Van der Bruggen B. Effect of biopolymers and humic substances on gypsum scaling and membrane wetting during membrane distillation. J Membr Sci 2021;617:118638.
Xu D, Zhu Z, Tan G, Xue X, Li J. Mechanism insight into gypsum scaling of differently wettable membrane surfaces with antiscalants in membrane distillation. J Membr Sci 2022;652:120499.
Lin P, Yang M, Li Y, Chen J. Prevention of surfactant wetting with agarose hydrogel layer for direct contact membrane distillation used in dyeing wastewater treatment. J Membr Sci 2015;475:511.
Huang Y, Wang Z, Hou D, Lin S. Coaxially electrospun super-amphiphobic silica-based membrane for anti-surfactant-wetting membrane distillation. J Membr Sci 2017;531:122.
Lu C, Su C, Cao H, Horseman T, Duan F, Li Y. Nanoparticle-free and self-healing amphiphobic membrane for anti-surfactant-wetting membrane distillation. J Environ Sci 2021;100:298.
Chen Y, Wang Z, Jennings GK, Lin S. Probing pore wetting in membrane distillation using impedance: early detection and mechanism of surfactant-induced wetting. Environ Sci Technol Lett 2017;4:505.
Li K, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Liu L, Liu H, Wang J. Electrothermally driven membrane distillation for low-energy consumption and wetting mitigation. Environ Sci Technol 2019;53:13506.
Lin S, Nejati S, Boo C, Hu Y, Osuji CO, Elimelech M. Omniphobic membrane for robust membrane distillation. Environ Sci Technol Lett 2014;1:443.
Deng L, Ye H, Li X, Li P, Zhang J, Wang X, Zhu M, Hsiao BS. Self-roughened omniphobic coatings on nanofibrous membrane for membrane distillation. Sep Purif Technol 2018;206:14.
Anish T, Wonjae C, Joseph MM, Gareth HM, Robert EC. Robust omniphobic surfaces. PANS 2008;105:18200.
Woo YC, Kim Y, Yao M, Tijing LD, Choi J-S, Lee S, Kim S-H, Shon HK. Hierarchical composite membranes with robust omniphobic surface using layer-by-layer assembly technique. Environ Sci Technol 2018;52:2186.
Hou D, Ding C, Fu C, Wang D, Zhao C, Wang J. Electrospun nanofibrous omniphobic membrane for anti-surfactant-wetting membrane distillation desalination. Desalination 2019;468:114068.
Xu Y, Yang Y, Fan X, Liu Z, Song Y, Wang Y, Tao P, Song C, Shao M. In-situ silica nanoparticle assembly technique to develop an omniphobic membrane for durable membrane distillation. Desalination 2021;499:114832.
Tuteja A, Choi W, Ma M, Mabry JM, Mazzella SA, Rutledge GC, McKinley GH, Cohen RE. Designing superoleophobic surfaces. Science 2007;318:1618.
Pan S, Kota AK, Mabry JM, Tuteja A. Superomniphobic surfaces for effective chemical shielding. J Am Chem Soc 2013;135:578.
Chhatre SS, Choi W, Tuteja A, Park KC, Mabry JM, McKinley GH, Cohen RE. Scale dependence of omniphobic mesh surfaces. Langmuir 2010;26:4027.
Jin M, Wang J, Yao X, Liao M, Zhao Y, Jiang L. Underwater oil capture by a three-dimensional network architectured organosilane surface. Adv Mater 2011;23:2861.
Zhang J, Seeger S. Superoleophobic coatings with ultralow sliding angles based on silicone nanofilaments. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 2011;50:6652.
Zhang M, Zhang T, Cui T. Wettability conversion from superoleophobic to superhydrophilic on titania/single-walled carbon nanotube composite coatings. Langmuir 2011;27:9295.
Zhou H, Wang H, Niu H, Lin T. Superphobicity/philicity Janus fabrics with switchable, spontaneous, directional transport ability to water and oil fluids. Sci Rep 2013;3:2964.
Yuan L, Wu T, Zhang W, Ling S, Xiang R, Gui X, Zhua Y, Tang Z. Engineering superlyophobic surfaces on curable materials based on facile and inexpensive microfabrication. J Mater Chem A 2014;2:6952.
Zhao H, Law KY. Directional self-cleaning superoleophobic surface. Langmuir 2012;28:11812.
Wong WS, Liu G, Tricoli A. Superamphiphobic bionic proboscis for contamination-free manipulation of nano and core-shell droplets. Small 2017;13:1603688.
Wong WS, Liu G, Nasiri N, Hao C, Wang Z, Tricoli A. Omnidirectional self-assembly of transparent superoleophobic nanotextures. ACS Nano 2017;11:587.
Li B, Zhang J. Durable and self-healing superamphiphobic coatings repellent even to hot liquids. Chem Commun 2016;52:2744.
Wang H, Zhou H, Gestos A, Fang J, Lin T. Robust, superamphiphobic fabric with multiple self-healing ability against both physical and chemical damages. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2013;5:10221.
Chen Y, Lu KJ, Gai W, Chung TS. Nanofiltration-inspired Janus membranes with simultaneous wetting and fouling resistance for membrane distillation. Environ Sci Technol 2021;55:7654.
Jiang L, Chen L, Zhu L. Minimize the trade-off between wetting resistance and water permeance in membrane distillation with ion-sieving coating layer. Chem Eng J 2022;430:133165.
Zhao S, Tao Z, Chen L, Han M, Meng F. An antifouling catechol/chitosan-modified polyvinylidene fluoride membrane for sustainable oil-in-water emulsions separation. Front Environ Sci Eng 2021;15:1.
Matin A, Laoui T, Falath W, Farooque M. Fouling control in reverse osmosis for water desalination & reuse: current practices & emerging environment-friendly technologies. Sci Total Environ 2021;765:142721.
Su Q, Zhang J, Zhang L-Z. Fouling resistance improvement with a new superhydrophobic electrospun PVDF membrane for seawater desalination. Desalination 2020;476:114246.
Zhang J, Seeger S. Polyester materials with superwetting silicone nanofilaments for oil/water separation and selective oil absorption. Adv Funct Mater 2011;21:4699.
Zhang F, Zhang WB, Shi Z, Wang D, Jin J, Jiang L. Nanowire-haired inorganic membranes with superhydrophilicity and underwater ultralow adhesive superoleophobicity for high-efficiency oil/water separation. Adv Mater 2013;25:4192.
Wang B, Liang W, Guo Z, Liu W. Biomimetic super-lyophobic and super-lyophilic materials applied for oil/water separation: a new strategy beyond nature. Chem Soc Rev 2015;44:336.
Zhang S, Jiang G, Gao S, Jin H, Zhu Y, Zhang F, Jin J. Cupric phosphate nanosheets-wrapped inorganic membranes with superhydrophilic and outstanding anticrude oil-fouling property for oil/water separation. ACS Nano 2018;12:795.
Zhang W, Zhu Y, Liu X, Wang D, Li J, Jiang L, Jin J. Salt-induced fabrication of superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic PAA-g-PVDF membranes for effective separation of oil-in-water emulsions. Angew Chem Int Ed 2014;53:856.
Ge J, Zhang J, Wang F, Li Z, Yu J, Ding B. Superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic nanofibrous membrane with hierarchical structured skin for effective oil-in-water emulsion separation. J Mater Chem A 2017;5:497.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52000105), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK20200478) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No.30922010806).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
There are no interests that are directly or indirectly related to the work submitted for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, D., Zhu, Z. & Li, J. Recent Progress in Electrospun Nanofibers for the Membrane Distillation of Hypersaline Wastewaters. Adv. Fiber Mater. 4, 1357–1374 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-022-00193-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-022-00193-0