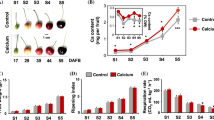
Abstract
The objective of this research was to explore the candidate genes involved in calcium absorption of R. roxburghii plants, as well as their relationship with the bioactive substance accumulation in the fruit. RNA-seq and qRT-PCR were used to analyze the transcriptomic profiles of the roots and leaves of plants during calcium absorption. Based on the correlation between gene expression and calcium absorption rate, ion channels and carrier proteins were selected to further verify their response to exogenous calcium supplement and functions on the accumulation of ascorbate (AsA), flavonoid, and triterpenoid in the fruit. Transcriptome and qRT-PCR analysis revealed that a total of 25 candidate genes from seven families have been found to be closely associated with Ca2+ absorption, namely, cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel (CNGC), zinc transporter (ZTP), metal tolerance protein (MTP), ER-type Ca2+ ATPase (ECA), auto-inhibited Ca2+ ATPase (ACA), glutamate receptor (GLR), and natural resistance-associated macrophage protein (NRAMP). Among these, RrCNGC1/7/10/12 and RrMTP2 play a vital role in responding to changes in external calcium levels. Moreover, exogenous Ca2+ promoted the accumulation of bioactive compounds such as AsA, total flavonoid, and total triterpenoid in fruits. RrCNGC2/3/12, RrZTP1, and RrGLR1 significantly responded to exogenous Ca2+ supplement, of which RrCNGC12 positively correlating with the levels of the above three types of bioactive substances. Seven families of ion channels and carrier proteins were jointly involved in calcium absorption and homeostasis in R. roxburghii plants, and RrCNGC12 play a critical role in the calcium-mediated regulation of fruit quality formation.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All sequencing data are available through the NCBI Sequence Read Archive under the accession number PRJNA993289.
References
Ahmad P, Latef AAA, Abd Allah EF, Hashem A, Sarwat M, Anjum NA, Gucel S (2016) Calcium and potassium supplementation enhanced growth, osmolyte secondary metabolite production, and enzymatic antioxidant machinery in cadmium-exposed chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Front Plant Sci 7:513. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00513
Alcock TD, Thomas CL, Ó Lochlainn S, Pongrac P, Wilson M, Moore C, Reyt G, Vogel-Mikuš K, Kelemen M, Hayden R, Wilson L, Stephenson P, Østergaard L, Irwin JA, Hammond JP, King GJ, Salt DE, Graham NS, White PJ, Broadley MR (2021) Magnesium and calcium overaccumulate in the leaves of a schengen3 mutant of Brassica rapa. Plant Physiol 186:1616–1631. https://doi.org/10.1093/plphys/kiab150
Apweiler R, Bairoch A, Wu CH, Barker WC, Boeckmann B, Ferro S, Gasteiger E, Huang H, Lopez R, Magrane M, Martin MJ, Natale DA, O’Donovan C, Redaschi N, Yeh LS (2004) UniProt: the Universal Protein knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res 32:D115-119. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkh131
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT, Harris MA, Hill DP, Issel-Tarver L, Kasarskis A, Lewis S, Matese JC, Richardson JE, Ringwald M, Rubin GM, Sherlock G (2000) Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Gene Ontol Consortium Nat Genet 25:25–29. https://doi.org/10.1038/75556
Baltaci AK, Yuce K (2018) Zinc transporter proteins. Neurochem Res 43:517–530. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2454-y
Bi GZ, Su M, Li N, Liang Y, Dang S, Xu JC, Hu MJ, Wang JZ, Zou MX, Deng YA, Li QY, Huang SJ, Li JJ, Chai JJ, He KM, Chen YH, Zhou JM (2021) The ZAR1 resistosome is a calcium-permeable channel triggering plant immune signaling. Cell 184:3528–3541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2021.05.003
Bonza MC, De Michelis MI (2011) The plant Ca2+-ATPase repertoire: biochemical features and physiological functions. Plant Biol 13:421–430. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1438-8677.2010.00405.x
Boursiac Y, Lee SM, Romanowsky S, Blank R, Sladek C, Chung WS, Harper JF (2010) Disruption of the vacuolar calcium-ATPases in Arabidopsis results in the activation of a salicylic acid-dependent programmed cell death pathway. Plant Physiol 154:1158–1171. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.110.159038
Bräutigam A, Gowik U (2010) What can next generation sequencing do for you? Next generation sequencing as a valuable tool in plant research. Plant Biol 12:831–841. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1438-8677.2010.00373.x
Buchfink B, Xie C, Huson DH (2015) Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat Methods 12:59–60. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth
Chen S, Zhou Y, Chen Y, Gu J (2018) fastp: an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 34:i884–i890. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty560
Cheval C, Aldon D, Galaud JP, Ranty B (2013) Calcium/calmodulin-mediated regulation of plant immunity. Bba-Mol Cell Res 1833:1766–1771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.01.031
Cho KM, Nguyen HT, Kim SY, Shin JS, Cho DH, Hong SB, Shin JS, Ok SH (2016) CML10, a variant of calmodulin, modulates ascorbic acid synthesis. New Phytol 209:664–678. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13612
Costa A, Luoni L, Marrano CA, Hashimoto K, Koster P, Giacometti S, De Michelis MI, Kudla J, Bonza MC (2017) Ca2+-dependent phosphor regulation of the plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase ACA8 modulates stimulus-induced calcium signatures. J Exp Bot 68:3215–3230. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erx162
Demidchik V, Shabala S, Isayenkov S, Cuin TA, Pottosin I (2018) Calcium transport across plant membranes: mechanisms and functions. New Phytol 220:49–69. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.15266
Deng YY, Li JQ, Wu SF, Zhu YP, Zhu YP, Chen YW, He FC (2006) Integrated nr database in protein annotation system and its localization. Comput Eng 32:71–74. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-3428.2006.05.026
Dodd AN, Kudla J, Sanders D (2010) The language of calcium signaling. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:593–620. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-070109-104628
Ehrnstorfer IA, Geertsma ER, Pardon E, Steyaert J, Dutzler R (2014) Crystal structure of a SLC11 (NRAMP) transporter reveals the basis for transition-metal ion transport. Nat Struct Mol Biol 21:990–996. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2904
Fan WG, Yang HQ (2014) Response of root architecture, nutrients uptake and shoot growth of Malus hupehensis seedling to the shape of root zone. Chinese Agricultural Science 47:3907–3913. https://doi.org/10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2014.19.020
Farthing EC, Menguer PK, Fett JP, Williams LE (2017) OsMTP11 is localised at the Golgi and contributes to Mn tolerance. Sci Rep 7:15258. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-15324-6
Finn RD, Bateman A, Clements J, Coggill P, Eberhardt RY, Eddy SR, Heger A, Hetherington K, Holm L, Mistry J, Sonnhammer EL, Tate J, Punta M (2014) Pfam: the protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D222-230. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1223
Gao QF, Gu LL, Wang HQ, Fei CF, Fang X, Hussain J, Sun SJ, Dong JY, Liu HT, Wang YF (2016) Cyclic nucleotide-gated channel 18 is an essential Ca2+ channel in pollen tube tips for pollen tube guidance to ovules in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:3096–3101. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1524629113
Gao H, Xie W, Yang C, Xu J, Li J, Wang H, Chen X, Huang CF (2018) NRAMP2, a trans-Golgi network-localized manganese transporter, is required for Arabidopsis root growth under manganese deficiency. New Phytol 217:179–193. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14783
Ge H, Shao Q, Chen J, Chen J, Li X, Tan Y, Lan W, Yang L, Wang Y (2022a) A metal tolerance protein, MTP10, is required for the calcium and magnesium homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Plant Signal Behav 17:2025322. https://doi.org/10.1080/15592324.2021.2025322
Ge H, Wang Y, Chen J, Zhang B, Chen R, Lan W, Luan S, Yang L (2022b) An Arabidopsis vasculature distributed metal tolerance protein facilitates xylem magnesium diffusion to shoots under high-magnesium environments. J Integr Plant Biol 64:166–182. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.13187
Gobert A, Park G, Amtmann A, Sanders D, Maathuis FJM (2006) Arabidopsis thaliana cyclic nucleotide gated channel 3 forms a non-selective ion transporter involved in germination and cation transport. J Exp Bot 57:791–800. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erj064
Gong Z, Xiong L, Shi H, Yang S, Herrera-Estrella LR, Xu G, Chao DY, Li J, Wang PY, Qin F, Li J, Ding Y, Shi Y, Wang Y, Yang Y, Guo Y, Zhu JK (2020) Plant abiotic stress response and nutrient use efficiency. Sci China Life Sci 63:635–674. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-020-1683-x
Görlach BM, Sagervanshi A, Henningsen JN, Pitann B, Mühling KH (2021) Uptake, subcellular distribution, and translocation of foliar-applied phosphorus: short-term effects on ion relations in deficient young maize plants. Plant Physiol Bioch 166:677–688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.06.028
Gu D, Zhou X, Ma Y, Xu E, Yu Y, Liu Y, Chen X, Zhang W (2021) Expression of a Brassica napus metal transport protein (BnMTP3) in Arabidopsis thaliana confers tolerance to Zn and Mn. Plant Sci 304:110754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2020.110754
He KM, Chen YH, Zhou JM (2021) The ZAR1 resistosome is a calcium-permeable channel triggering plant immune signaling. Cell 184:3528–3541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2021.05.003
Hirschi KD (2004) The calcium conundrum. Both versatile nutrient and specific signal. Plant Physiol 136:2438–2442. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.104.046490
Huda KM, Banu MS, Tuteja R, Tuteja N (2013) Global calcium transducer P-type Ca2+-ATPases open new avenues for agriculture by regulating stress signalling. J Exp Bot 64:3099–3109. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ert182
Jacob P, Kim NH, Wu FH, El Kasmr F, Chi Y, Walton WG, Furzer OJ, Lietzan AD, Sunil S, Kempthorn K, Redinbo MR, Pei ZM, Wan L, Dangl JL (2021) Plant “helper” immune receptors are Ca2+-permeable nonselective cation channels. Science 373:420–425. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abg7917
James ZM, Zagotta WN (2018) Structural insights into the mechanisms of CNBD channel function. J Gen Physiol 150:225–244. https://doi.org/10.1085/jgp.201711898
Juric S, Stracenski KS, Krol-Kilinska Z, Zutic I, Uher SF, Dermic E, Topolovec-Pintaric S, Vincekovic M (2020) The enhancement of plant secondary metabolites content in Lactuca sativa L. by encapsulated bioactive agents. Sci Rep 10:3737. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-60690-3
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Kawashima S, Okuno Y, Hattori M (2004) The KEGG resource for deciphering the genome. Nucleic Acids Res 32:D277–D280. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkh063
Kanehisa M, Araki M, Goto S, Hattori M, Hirakawa M, Itoh M, Katayama T, Kawashima S, Okuda S, Tokimatsu T, Yamanishi Y (2008) KEGG for linking genomes to life and the environment. Nucleic Acids Res 36:D480-484. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkm882
Kim D, Langmead B, Salzberg SL (2015) HISAT: a fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat Methods 12:357–360. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3317
Kim NH, Jacob P, Dangl JL (2022) Con-Ca2+-tenating plant immune responses via calcium-permeable cation channels. New Phytol 234:813–818. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.18044
Koonin EV, Fedorova ND, Jackson JD, Jacobs AR, Krylov DM, Makarova KS, Mazumder R, Mekhedov SL, Nikolskaya AN, Rao BS, Rogozin IB, Smirnov S, Sorokin AV, Sverdlov AV, Vasudevan S, Wolf YI, Yin JJ, Natale DA (2004) A comprehensive evolutionary classification of proteins encoded in complete eukaryotic genomes. Genome Biol 5:R7. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2004-5-2-r7
Lecourieux D, Ranjeva R, Pugin A (2006) Calcium in plant defence-signalling pathways. New Phytol 171:249–269. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2006.01777.x
Li L, Zhu Z, Liao Y, Yang C, Fan N, Zhang J, Yamaji N, Dirick L, Ma JF, Curie C, Huang CF (2022) NRAMP6 and NRAMP1 cooperatively regulate root growth and manganese translocation under manganese deficiency in Arabidopsis. Plant J 110:1564–1577. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.15754
Li LL, An HM (2016) Effects of Ca2+ and Cu2+ on the expression of genes related to AsA metabolism in Rosa roxburghii. Fruits. J Hortic 43:1377–1382. https://doi.org/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2016-0013
Liang C, Zhang Y, Ren X (2021) Calcium regulates antioxidative isozyme activity for enhancing rice adaption to acid rain stress. Plant Sci 306:110876. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2021.110876
Liu JY, Niu YF, Zhang JJ, Zhou YQ, Ma Z, Huang X (2018) Ca2+ channels and Ca2+ signals involved in abiotic stress responses in plant cells: recent advances. Plant Cell Tiss Org 132:413–424. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-017-1350-0
Love MI, Huber W, Anders S (2014) Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol 15:550. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8
Luo C, Fan WG, Liu JP, An HM (2004) Effects of different treatments on fruit development of Rosa roxburghii Tratt. J Guizhou Normal Univ (Natl Sci Ed) 4:7–11. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1004-5570.2004.04.002
Makavitskaya M, Svistunenko D, Navaselsky I, Hryvusevich P, Mackievic V, Rabadanova C, Tyutereva E, Samokhina V, Straltsova D, Sokolik A, Voitsekhovskaja O, Demidchik V (2018) Novel roles of ascorbate in plants: induction of cytosolic Ca2+ signals and efflux from cells via anion channels. J Exp Bot 69:3477–3489. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ery056
Mani A, Sankaranarayanan K (2018) In silico analysis of natural resistance-associated macrophage protein (NRAMP) family of transporters in rice. Protein J 37:237–247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10930-018-9773-y
Martins V, Unlubayir M, Teixeira A, Geros H, Lanoue A (2021) Calcium and methyl jasmonate cross-talk in the secondary metabolism of grape cells. Plant Physiol Bioch 165:228–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.05.034
Meng QJ, Fan WG (2022) Calcium-tolerance type and adaptability to high-calcium habitats of Rosa roxburghii. Chin J Plant Ecol 46:1562–1572. https://doi.org/10.17521/cjpe.2022.0172
Meng X, Luo SL, Dawuda MM, Gao XQ, Wang SY, Xie JM, Tang ZQ, Liu ZC, Wu Y, Jin L, Lyu J, Yu JH (2021) Exogenous silicon enhances the systemic defense of cucumber leaves and roots against CA-induced autotoxicity stress by regulating the ascorbate-glutathione cycle and photosystem II. Ecotox Environ Safe 227:112879. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112879
Michailidis M, Karagiannis E, Tanou G, Sarrou E, Stavridou E, Ganopoulos I, Karamanoli K, Madesis P, Martens S, Molassiotis A (2019) An integrated metabolomic and gene expression analysis identifies heat and calcium metabolic networks underlying postharvest sweet cherry fruit senescence. Planta 250:2009–2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-019-03272-6
Migocka M, Papierniak A, Kosieradzka A, Posyniak E, Maciaszczyk-Dziubinska E, Biskup R, Garbiec A, Marchewka T (2015) Cucumber metal tolerance protein CsMTP9 is a plasma membrane H+-coupled antiporter involved in the Mn2+ and Cd2+ efflux from root cells. Plant J 84:1045–1058. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13056
Migocka M, Małas K, Maciaszczyk-Dziubinska E, Posyniak E, Migdal I, Szczech P (2018) Cucumber Golgi protein CsMTP5 forms a Zn-transporting heterodimer with high molecular mass protein CsMTP12. Plant Sci 277:196–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2018.09.011
Moeder W, Phan V, Yoshioka K (2019) Ca2+ to the rescue - Ca2+ channels and signaling in plant immunity. Plant Sci 279:19–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2018.04.012
Nevo Y, Nelson N (2006) The NRAMP family of metal-ion transporters. Bba-Mol Cell Res 1763:609–620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.05.007
Niu JH, Liu C, Huang ML, Liu KZ, Yan DY (2021) Effects of foliar fertilization: a review of current status and future perspectives. J Soil Sci Plant Nut 21:104–118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-020-00346-3
Ojo O, Mphahlele MP, Oladeji OS, Mmutlane EM, Ndinteh DT (2022) From wandering weeds to pharmacy: an insight into traditional uses, phytochemicals and pharmacology of genus Chromolaena (Asteraceae). J Ethnopharmacol 291:115155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2022.115155
Pertea M, Pertea GM, Antonescu CM, Chang TC, Mendell JT, Salzberg SL (2015) StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat Biotechnol 33:290–295. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3122
Price MB, Kong D, Okumoto S (2013) Inter-subunit interactions between glutamate-like receptors in Arabidopsis. Plant Signal Behav 8:e27034. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.27034
Sanders D, Brownlee C, Harper JF (1999) Communicating with calcium. Plant Cell 11:691–706. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.11.4.691
Sanders D, Pelloux J, Brownlee C, Harper JF (2002) Calcium at the crossroads of signalling. Plant Cell. 14:S401–S417. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.002899
Shao HB, Song WY, Chu LY (2008) Advances of calcium signals involved in plant anti-drought. Cr Biol 331:587–596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crvi.2008.03.012
Shi QW, Song QB, Wang HX, Bai CM, Wu D, Dong QP, Cheng X, Han XR, Liu YF (2017) Research progress of plant calcium nutrition and calcium/cold signal interaction. ABSR BBE 2017 4:99–102. https://doi.org/10.2991/bbe-17.2017.16
Suda H, Toyota M (2022) Integration of long-range signals in plants: a model for wound-induced Ca2+, electrical, ROS, and glutamate waves. Curr Opin Plant Biol 69:102270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2022.102270
Tang RJ, Luan S (2017) Regulation of calcium and magnesium homeostasis in plants: from transporters to signaling network. Curr Opin Plant Biol 39:97–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2017.06.009
Tatusov RL, Galperin MY, Natale DA, Koonin EV (2000) The COG database: a tool for genome-scale analysis of protein functions and evolution. Nucleic Acids Res 28:33–36. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/28.1.33
Vafadar F, Amooaghaie R, Ehsanzadeh P, Ghanadian M, Talebi M, Ghanati F (2020) Melatonin and calcium modulate the production of rosmarinic acid, luteolin, and apigenin in Dracocephalum kotschyi under salinity stress. Phytochemistry 177:112422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2020.112422
Véry AA, Davies JM (2000) Hyperpolarization-activated calcium channels at the tip of Arabidopsis root hairs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:9801–9806. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.160250397
Vincill ED, Clarin AE, Molenda JN, Spalding EP (2013) Interacting glutamate receptor-like proteins in phloem regulate lateral root initiation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 25:1304–1313. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.113.110668
Wang M, Xu Q, Yu J, Yuan M (2010) The putative Arabidopsis zinc transporter ZTP29 is involved in the response to salt stress. Plant Mol Biol 73:467–479. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-010-9633-4
Wang XK, Yang RQ, Zhou YL, Gu ZX (2016) A comparative transcriptome and proteomics analysis reveals the positive effect of supplementary Ca2+ on soybean sprout yield and nutritional qualities. J Proteomics 143:161–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2016.04.020
Wang XH, Feng CX, Tian LL, Hou CC, Tian W, Hu B, Zhang Q, Ren ZJ, Niu Q, Song JL, Kong DD, Liu LY, He YK, Ma LG, Chu CC, Luan S, Li LG (2021a) A transceptor-channel complex couples nitrate sensing to calcium signaling in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 14:774–786. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2021.02.005
Wang Y, Gong Q, Wu Y, Huang F, Ismayil A, Zhang D, Li H, Gu H, Ludman M, Fátyol K, Qi Y, Yoshioka K, Hanley-Bowdoin L, Hong Y, Liu Y (2021b) A calmodulin-binding transcription factor links calcium signaling to antiviral RNAi defense in plants. Cell Host Microbe 29:1393–1406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2021.07.003
Wang Z, Wang LH, Li JX, Yang W, Ci JB, Ren XJ, Wang W, Wang YB, Jiang LY, Yang WG (2022) Identification and expression analysis revealed drought stress-responsive Calmodulin and Calmodulin-like genes in maize. J Plant Interact 17:450–461. https://doi.org/10.1080/17429145.2022.2047235
Wang LL, An HM (2013) Optimization of a method for the determination of vitamin C in Rosa roxburghii fruits by HPLC. Modern Food Science and Technology 29: 397–400. https://doi.org/10.13982/j.mfst.1673-9078.2013.02.009
Yang HR, Fan WG (2022) Effects of different calcium supply levels on growth, mineral element absorption and related physiological and biochemical characteristics of Rosa roxburghii seedlings. J Fruit Sci 39:1891–1902. https://doi.org/10.13925/j.cnki.gsxb.20220101
Yang JS, Li WL, Xing C, Xing GN, Guo YX, Yuan HL (2022) Ca2+ participates in the regulation of microalgae triacylglycerol metabolism under heat stress. Environ Res 208:112696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.112696
Young MD, Wakefield MJ, Smyth GK, Oshlack A (2010) Gene ontology analysis for RNA-seq: accounting for selection bias. Genome Biol 11:R14. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2010-11-2-r14
Yu J, Zhu MT, Wang MJ, Xu YS, Chen WT, Yang GS (2020) Transcriptome analysis of calcium-induced accumulation of anthocyanins in grape skin. Sci Hortic-Amsterdam 260:108871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2019.108871
Yuan LY, Du J, Yuan YH, Shu S, Sun J, Guo SR (2013) Effects of 24-epibrassinolide on ascorbate-glutathione cycle and polyamine levels in cucumber roots under Ca(NO3)2 stress. Acta Physiol Plant 35:253–262. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-012-1071-2
Zhang X, Yang M, An HM, Huang W, Liu W (2012) Effects of exogenous divalent cations Ca2+, Mg2+, and Cu2+ and acriflavine on ascorbate biosynthesis in Rosa roxburghii fruits. Chin Agric Sci 45:1144–1149. https://doi.org/10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2012.06.012
Zhang XM, Liu LX, Su ZM, Shen ZJ, Gao GF, Yi Y, Zheng HL (2019) Transcriptome analysis of Medicago lupulina seedlings leaves treated by high calcium provides insights into calcium oxalate formation. Plant Soil 444:299–314. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-019-04283-8
Zhang X, Li Q, Xu W, Zhao H, Guo F, Wang P, Wang Y, Ni D, Wang M, Wei C (2020) Identification of MTP gene family in tea plant (Camellia sinensis L.) and characterization of CsMTP8.2 in manganese toxicity. Ecotox Environ Safe 202:110904. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110904
Zhao J, Davis LC, Verpoorte R (2005) Elicitor signal transduction leading to production of plant secondary metabolites. Biotechnol Adv 23:283–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2005.01.003
Funding
This work was supported by the Joint Fund of the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Karst Science Research Center of Guizhou Province (No. U1812401) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 32260730).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Huaming An: conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, writing — review and editing, visualization, supervision, funding acquisition. Min Lu: resources, validation, investigation. Zhao Wang: software, formal analysis, investigation, visualization, writing — original draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• We conducted experiments using Rosa roxburghii saplings as materials in three stages: Ca2+ starvation, rapid Ca2+ uptake, and Ca2+ saturation.
• We investigated the Ca2+ uptake patterns and molecular mechanisms in Rosa roxburghii plants.
• Some genes associated with Ca2+ uptake have an impact on fruit bioactive substance accumulation.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Lu, M. & An, H. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Candidate Genes Involved in Calcium Absorption of Rosa roxburghii Plants and their Effects on the Bioactive Substance Accumulation in Fruit. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 24, 732–748 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-023-01579-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-023-01579-8