Abstract
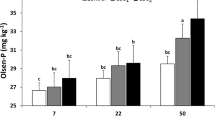
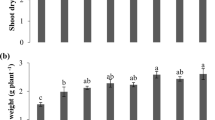
Higher pH of calcareous soils and mineral fertilizers lowers the bioavailability of plant nutrients. Hence, it requires amending the nature of nutrients input through suitable bioactive materials, like sulfur (S), organic, microbial, and nano-materials. This study assessed the effects of S-enriched composites of organo-phosphate (OP) and bio-organic phosphate (BOP) on soil and plant attributes. Elemental sulfur (ES) and nano-sulfur (NS) were admixed separately in compost and rock phosphate (RP) with/without sulfur-oxidizing bacteria (SOB), viz., Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans. Sulfur-based amalgams were incubated at 25–35 °C for 60 days to develop S-enriched organo-phosphate (ES-OP) and bio-organic phosphate (ES-BOP and NS-BOP) composites. Greenhouse and micro-plot experiments were conducted to evaluate the impact of these composites on nutrients bioavailability and vegetative growth of maize. Treatments included control (no sulfur), ES (12.5 kg ha−1), ES-OP (50 kg ha−1), ES-BOP (50 kg ha−1), and NS-BOP (50 kg ha−1) application in soil. Inoculation with SOB in both ES-BOP and NS-BOP reduced the pH and increased macronutrients as compared to ES-OP. Thus, ES-BOP and NS-BOP improved maize growth and soil nutrients status. Composite NS-BOP rendered the highest N, P, K, and S concentrations in both soil and plants due to lower soil pH. Application of S-BOP containing Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans, and use of nano-S are beneficial for improving nutrients bioavailability and plant growth in calcareous soils via pH reduction. These composites are low-cost, nutrients-rich, and have greater efficiency than fertilizers in calcareous soil.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amin AEAZ, Mihoub A (2021) Effect of sulfur-enriched biochar in combination with sulfur-oxidizing bacterium (Thiobacillus spp.) on release and distribution of phosphorus in high calcareous p-fixing soils. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 21:2041–2047. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-021-00500-5
Anisuzzaman M, Rafii MY, Jaafar NM, Izan RS, Ikbal MF, Haque MA (2021) Effect of organic and inorganic fertilizer on the growth and yield components of traditional and improved rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes in Malaysia. Agron 11:1830. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11091830
Aziz EE, Taalab ASM (2004) Dragonhead plants (Dracocephalum moldavica) responses to salt stress and different sources of sulphur. Egypt J Appl Sci 19:239–257
Babar S, Jilani G, Mihoub A, Jamal A, Ahmad I, Chaudhary AN, Saeed MF, Alam T (2022) Bacterial redox cycling of manganese in calcareous soil enhances the nutrients bioavailability to wheat. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 22:1215–1223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-021-00725-4
Bardsley CE, Lancaster JD (1960) Determination of reserve sulfur and soluble sulfates in soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 24:265–268. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1960.03615995002400040015x
Beijerinck MW (1904) Phenomenes de reduction proguits parles microbes Arch. Sci Exactes Nat Haarlem Ser 2:9131–9157. https://doi.org/10.12691/jaem-2-1-1
Besharati H, Astashnama K, Hatami S (2007) Biosuper as a phosphate fertilizer in a calcareous soil with low available phosphorus. Afr J Biotechnol 6:1325–1329. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB2007.000-2184
Bhardwaj D, Ansari MW, Sahoo RK, Tuteja N (2014) Biofertilizers function as key player in sustainable agriculture by improving soil fertility, plant tolerance and crop productivity. Microbiol 13:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-13-66
Brahim S, Niess A, Pflipen M, Neuhoff D, Scherer H (2017) Effect of combined fertilization with rock phosphate elemental sulfur on yield and nutrient uptake of soybean. Plant Soil Eviron 63:89–95. https://doi.org/10.17221/22/2017-PSE
Brenner DJ, Krieg NR, Staley JT, Garrity GM (2005) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, 2nd Ed, Vol 2 (The Proteobacteria), part C (The Alpha-, Beta-, Delta-, and Epsilonproteobacteria) Springer New York
Cha JM, Cha WS, Heon JL (1999) Removal of organosulphur odour compounds by Thiobacillus novellus SRM, sulphur-oxidizing bacteria. Process Biochem 34:659–665. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(98)00139-3
Daliran T, Halajnia A, Lakzian A (2022) Thiobacillus bacteria-enhanced iron biofortification of soybean in a calcareous soil enriched with ferrous sulfate, mill scale, and pyrite. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 22:2221–2234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-022-00804-0
Das A, Biswas PK (2020) Effect of Sulphur and biofertilizer in nutrient uptake by sesame and microbial population in red and lateritic soil of West Bengal. Agri Sci Dig-A Res J 40:226–233. https://doi.org/10.18805/ag.D-4916
Dhlamini B, Paumo HK, Katata-Seru L, Kutu FR (2020) Sulphate-supplemented NPK nanofertilizer and its effect on maize growth. Mater Res Express 7:095011. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/abb69d
Edi-Premono M, Moawad AM, Vlek PLG (1996) Effect of phosphate solubilizing Pseudomonas putida on the growth of maize and its survival in the rhizosphere. Ind J Crop Sci 11:13–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.11.013
El-Assiouty FMM, Abo-Sedera SA (2005) Effect of bio and chemical fertilizers on seed production and quality of spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.). Int J Agric Biol 6:947–952
Esmaeil MA, AbdElghany SH, Fatta AA, Arafat AA (2020) Assessment of the effect of nano sulfur on some soil properties and maize productivity in saline soil. Curr Sci Int 19:656–665. https://doi.org/10.36632/csi/2020.9.4.59
Etesami H, Jeong BR, Glick BR (2021) Contribution of Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, phosphate–solubilizing bacteria, and silicon to P uptake by plant. Front Plant Sci 12:699618. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.699618
Fang JZ, Tausz M, Kok LJ (2008) Role of sulfur for plant production in agricultural and natural ecosystems. Sulfur Metabol Phototrop Org 27:417–435. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11070626
Fuentes-Lara LO, Medrano-Macías J, Pérez-Labrada F, Rivas-Martínez EN, García-Enciso EL, González-Morales S, Juárez-Maldonado A, Rincón-Sánchez F, Benavides-Mendoza A (2019) From elemental sulfur to hydrogen sulfide in agricultural soils and plants. Molecules 24:2282. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24122282
Guimaraes GG, Klaic R, Giroto AS, Majaron VF, Avansi W, Farinas CS, Ribeiro C (2018) Smart fertilization based on sulfur–phosphate composites: synergy among materials in a structure with multiple fertilization roles. ACS Sust Chem Eng 6:12187–12196. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b02511
Haider MIS, Ahmad R, Hyder S, Mahmood A, Khalid A, Fatima N, Jilani G (2020) Role of bacterial consortia in promoting plant growth and nutrient bioavailability. Pak J Agric Sci 57:1211–1220. https://doi.org/10.21162/PAKJAS/20.8444
Helmke PA, Sparks DL (1996) Methods of soil analysis part 3. Soil Sci Soc Amer. No. 5. Madison, Wisconsin, USA 551–601
Heydarnezhad F, Shahinroshsar P, Besharati SHV, H, (2012) Influence of elemental sulfur and sulfur oxidizing bacteria on some nutrient deficiency in calcareous soils. Int J Agr Crop Sci 4:735–739
Huluka G, Miller R (2014) Particle size determination by hydrometer method. Sout Coop Series Bull 419:180–184
Imtiaz M, Rashid A, Khan P, Memon MY, Aslam M (2010) The role of micronutrients in crop production and human health. Pak J Bot 42:2565–2578. https://doi.org/10.31579/2637-8914/063
Jazaeri M, Akhgar A, Sarcheshmehpour M, Hossein M (2016) Bioresources efficacy of phosphate rock, sulfur and Thiobacillus inoculum in improving soil phosphorus availability. Comm Soil Sci Plant Anal 47:1441–1450. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2016.1179750
Johnson SE, Lauren JG, Welch RM, Duxbury JM (2005) A comparison of the effects of micronutrient seed priming and soil fertilization on the mineral nutrition of chickpea (Cicerarietinum), lentil (Lens culinaris), rice (Oryza sativa) and wheat (Triticum aestivum) in Nepal. Exp Agric 41:427–448. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0014479705002851
Khalid AK (2012) Biological fertilization and its effect on medicinal and aromatic plants. Biosci 4:124–133. https://doi.org/10.13057/nusbiosci/n040307
Khan A, Jilani G, Zhang D, Akbar S, Malik KM, Rukh S, Mujtaba G (2020) Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans IW16 and sulfur synergistically with struvite aggrandize the phosphorus bioavailability to wheat in alkaline soil. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 20:95–104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-019-00104-0
Khattak RA, Hussain Z (2007) Evaluation of soil fertility status and nutrition of orchards. Soil, Plant Environ 26:22–32
Kjeldahl J (1883) Neue Methods zur Bestimmung des Stickstoffs in organischenkorpern (New method for the determination of nitrogen in organic substances). Zeits Für Analytis Chemie 22:366–383. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01338151
Knudsen D, Peterson GA, Pratt PF (1982) Potassium. Methods of soil analysis. Chemical and microbiological properties. America Soc Agron Soil Sci America, Inc. Madison, Wisconsin, USA 67:229–230. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronmonogr9.2.2ed
Kolmert A, Wikström HKB (2000) A Fast and simple turbidimetric method for the determination of sulfate in sulfate-reducing bacterial cultures. J Microbiol Meth 41:179–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-7012(00)00154-8
Lacalle RG, Garbisu C, Becerril JM (2020) Effects of the application of an organic amendment and nanoscale zero-valent iron particles on soil Cr (VI) remediation. Environ 27:31726–31736. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09449-x
McLean EO (1983) Soil pH and lime requirement. Methods of soil analysis: Part 2 Chem Microbiol Prop 9:199–224. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronmonogr9.2.2ed.c12
Miransari M, Smith DL (2007) Overcoming the stressful effects of salinity and acidity on soybean nodulation and yields using signal molecule genistein under field conditions. J Plant Nutr 30:1967–1992. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904160701700384
Olsen SR, Sommers LE (1982) Phosphorus Methods of Soil Anal 45:403–430. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.201400327
Patra P, Kumar PB, Ghosh GK, Mura S (2013) Effect of bio fertilizer and sulfur on growth yield and oil content of hybrid sunflower (Helianthus annuus. L) in typical lateritic soil Sci Rep 21–5. https://doi.org/10.4172/scientificreports.603
Patrick A, Ndakidemi S, Bambara Joachim H, Makoi JR (2012) Micronutrient uptake in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) as affected by Rhizobium inoculation, and the supply of molybdenum and lime. Plant Omics 4:40–52
Prasad MNV, Strzalka K (2013) Physiology and biochemistry of metal toxicity and tolerance in plants. Springer Netherlands, Heidelberg, pp 325–355
Rhoades JD (1982) Soluble salts (electrical conductivity). In: Page, A. L., R.H. Miller and D.R. Keey. Eds. Methods of soil analysis part 2 American SocAgron No.9. Wisconsin USA 172–173. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.19851480319
Ryan J, Estefan G, Rashid A (2001) Soil Plant Anal Lab Man ICARDA
Salem N, Mansour A, Ciuffo M, Falk BW, Turina M (2016) A new tobamo virus infecting tomato crops in Jordan. Arch Virol 161:503–506. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-015-2677-7
Sarangi AD, Athukorala NP (2021) Solubilization of micronutrients using indigenous microorganisms. In: Bhatt P, Gangola S, Udayanga D, Kumar G (ed) Micro Technol for Sust Environ 365–417. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-3840-4_21
Sheoran V, Sheoran AS, Poonia P (2010) Soil reclamation of abandoned mine land by revegetation: a review. Intern J Soil, Sed Water 3:13
Smibert RM, Kreig NR (1994) Phenotypic characterization In: Methods for general and molecular bacteriology. Amer Soc Microbiol 12:607–654. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11123393
Soliman SS, Abo-Sedera SA, El-Sonbaty MR (2006) Improvement the growth, productivity and fruit quality of Maghrabi banana by biofertilizer application. Egypt J Soil Sci 46:237
Stamford NP, Santos P, Moura AM, Santos CE, Freitas AD (2003) Biofertilizers with natural phosphate, sulphur and Acidithiobacillus in a soil with low available-P. Sci Agric 60:767–773. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-90162003000400024
Steel RGD, Torrie JH, Dicky DA (1997) Principles and procedures of statistics. A biometrical approach, 3rd edn. McGraw-Hill Co Inc, New York
Sun L, Song K, Shi L, Duan D, Zhang H, Sun Y, Xue Y (2021) Influence of elemental sulfur on cadmium bioavailability, microbial community in paddy soil and Cd accumulation in rice plants. Sci Rep 11:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-91003-x
Ullah I, Jilani G, Khan KS, Akhtar MS, Rasheed M (2014) Sulfur oxidizing bacteria from sulfur rich ecologies exhibit high capability of phosphorous solubilization. Int J Agric Biol 16:550–556
White PJ, Brown PH (2010) Plant nutrition for sustainable development and global health. Ann Bot 105:1073–1080. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcq085
Acknowledgements
This article is based on the MS thesis research of Ayesha Shakoor. We are thankful to the Institute of Soil & Environmental Sciences, PMAS Arid Agriculture University, Rawalpindi, Pakistan, for assistance in executing the laboratory analyses, and providing staff for greenhouse and field work. We gratefully acknowledge the Engro Fertilizers Limited, Pakistan for providing meshed rock phosphate and sulfur materials, especially nano-sulfur used in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shakoor, A., Jilani, G., Iqbal, T. et al. Synthesis of Elemental- and Nano-sulfur-enriched Bio-organic Phosphate Composites, and Their Impact on Nutrients Bioavailability and Maize Growth. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 23, 3281–3289 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-023-01244-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-023-01244-0