Abstract
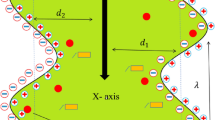
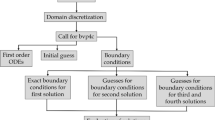
This study uses numerical simulation to model MHD mixed convection nanofluid flow within a permeable trapezoidal chamber with a heated obstacle. Considered are the volume fractions (1–5%) of copper (Cu), alumina (Al2O3), and silver (Ag) nano-sized particles when mixed with water (H2O). With a constant velocity, upper wall moves left to right while bottom wall steps from right to left. A lower temperature is kept on upper wall, while left, right, and bottom walls are kept at warmed. There are two types of obstacles inside the enclosure: a constant square heated obstacle (case-I) and a heat-generating square obstacle (case-II). To investigate how the liquid flow and heat transport properties within the chamber are impacted with the Darcy number (Da) and Richardson number (Ri), the governing PDEs are solved by Galerkin weighted residual based finite element technique. Results are compared to published papers to validate the computational process. The findings are displayed using streamlines, isotherms, temperature, and velocity profiles, and mean Nusselt numbers. The outcomes demonstrate that when Richardson number rises, heat transportation rate increases. It is shown that an effective control parameter for temperature transport is Darcy number. Moreover, it is found that when only 5% nanoparticles are used, heat transport rate augment by 17.12%. Richardson number is an effective control parameter for heat transport via a porous material enclosure. Mass and heat transport rates both rise with an increment in the thermal Darcy number. Furthermore, the flow strength rises as Richardson number rises. Moreover, the average Nu increases by 15.27% for 5% nanoparticles volume at \(Da=1{0}^{-2}\) in case I whereas it increases only 0.3% for same number of nanoparticles in case II.



















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Since no data was generated or investigated for this article, there is no date sharing available.
Abbreviations
- B 0 :
-
Magnetic induction [Wbm−2]
- C p :
-
Specific heat at constant pressure [Jkg−1 K−1]
- q :
-
Heat flux
- ∆T :
-
Dimensional temperature difference [K]
- g :
-
Gravitational acceleration [ms−2]
- h :
-
Convective heat transfer coefficient [Wm−2 K−1]
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity of fluid [W/mK]
- L :
-
Height or base of square cavity [m]
- K :
-
Thermal conductivity ratio fluid
- N :
-
Total number of nodes
- Nu av :
-
Average Nusselt number
- Nu l :
-
Local Nusselt number
- P :
-
Non-dimensional pressure
- p :
-
Pressure
- Gr :
-
Grashof number
- Ha :
-
Hartmann number
- Pr :
-
Prandtl number
- Ra :
-
Rayleigh number
- Re :
-
Reynolds number
- Da :
-
Darcy number
- Ri :
-
Richardson number
- T :
-
Dimensional fluid temperature [K]
- T h :
-
Temperature of hot wall [K]
- T c :
-
Temperature of cold wall [K]
- U :
-
X component of dimensionless velocity
- u :
-
X component of velocity [ms−1]
- V :
-
Y component of dimensionless velocity
- v :
-
Y component of velocity [ms−1]
- U 0 :
-
X component of lid velocity [ms−1]
- V 0 :
-
Y component of lid velocity [ms−1]
- x, y :
-
Cartesian coordinates [m]
- X, Y :
-
Dimensionless coordinates
- ∝:
-
Thermal diffusivity [ms−2]
- β:
-
Coefficient of thermal expansion [K−1]
- ρ:
-
Density of the fluid [kg/m3]
- ∆θ :
-
Dimensionless temperature difference
- θ :
-
Dimensionless fluid temperature
- θ αυ :
-
Average temperature
- μ :
-
Dynamic viscosity of the fluid [m2s−1]
- Ψ :
-
Stream function
- ν :
-
Kinematic viscosity of the fluid [m2s−1]
- σ :
-
Fluid electrical conductivity [Ω−1 m−1]
- ϕ:
-
Nanoparticle volume fraction
- b :
-
Bottom wall
- l :
-
Left wall
- r :
-
Right wall
- c :
-
Cold
- h :
-
Hot
- f :
-
Base fluid
- s :
-
Nanoparticle
- nf :
-
Nanofluid
References
S.P. Jang, S.U.S. Choi, Role of Brownian motion in the enhanced thermal conductivity of nanofluids. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84(21), 4316–4318 (2004)
J.K. Hwang, Y.M. Lee, S.I. Jeong, Y.C.A. Cheong, Production and dispersion stability of nanoparticles in nanofluids. Powder Technol. 186(2), 145–153 (2008)
S.M.S. Murshed, K.C. Leong, C. Yang, Thermophysical and electronics properties of nanofluids-a critical review. Appl. Therm. Eng. 28(17–18), 2109–2125 (2008)
C. Pang, J.W. Lee, Y.T. Kang, Review on combined heat and mass transfer characteristics in nanofluids. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 87, 49–67 (2015)
T. Islam, M. Yavuz, N. Parveen, M.F. Al-Asad, Impact of non-uniform periodic magnetic field on unsteady natural convection flow of nanofluids in square enclosure. Fractal and Fractional 6(2), 101 (2022)
T. Islam, M.N. Alam, M.I. Asjad, N. Parveen, Y.M. Chu, Heatline visualization of MHD natural convection heat transfer of nanofluid in a prismatic enclosure. Sci. Rep. 11, 10972 (2021)
Y. Xuan, Q. Li, Heat transfer enhancement of nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 21, 58–64 (2000)
R. Jou, S. Tzdng, Numerical research of nature convective heat transfer enhancement filled with nanofluids in rectangular enclosure. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Trans. 33, 727–736 (2006)
K. Khanafer, K. Vafai, M. Lightstone, Buoyancy-driven heat transfer enhancement in a two dimensional enclosure utilizing nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Trans. 46, 3639–3653 (2003)
G.A. Sheikhzadeh, M. Dastmalchi, H. Khoarasanizadeh, Effects of walls temperature variation on double diffusive natural convection of A12O3-water nanofluid in an enclosure. Heat Mass Transfer 49, 1689–1700 (2013)
A. Abu-Nada, Z. Masoud, A. Hijazi, Natural convection heat transfer enhancement in horizontal concentric annuli using nanofluids. Int. Commn. Heat Mass Trans. 35, 657–665 (2008)
T. Islam, M.N. Alam, S. Niazai, I. Khan, M. Fayz-Al-Asad, S. Alqahtani, Heat generation/absorption effect on natural convective heat transfer in a wavy triangular cavity filled with nanofluid. Sci. Rep. 13(1), 21171 (2023)
T. Islam, R. Nasrin, Thermal operation by nanofluids with various aspects: a comprehensive numerical appraisal, Waves in Random and Complex Media. (2022).
M. Chandrasekar, S. Suresh, A. Chandra Bose, Experimental investigations and theoretical determination of thermal conductivity and viscosity of Al2O3/water nanofluid. Exper Thermal Fluid Sci 34(2), 210–216 (2010)
J.A. Eastman, S.U.S. Choi, S. Li, W. Yu, L.J. Thompson, Aromalously increased effective thermal conductivities of ethylene glycol-based nanofluids containing copper nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 78(6), 718–720 (2001)
S.M. Aminossadati, B. Ghasemi, Enhanced natural convection in an isosceles triangular enclosure filled with a nanofluid. Comput. Math. Appli. 61, 1739–1753 (2011)
M.A. Ismael, T. Armaghani, A.J. Chamkha, Conjugate heat transfer and entropy generation in a cavity filled with a nanofluid-saturated porous media and heated by a triangular solid. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 59, 138–151 (2016)
M.M. Rahman, H.F. Oztop, A. Ahsan, J. Orfi, Natural convection effects on heat and mass transfer in a curvilinear triangular cavity. Int. J. Heat Mass Trans. 55, 6250–6259 (2012)
J.A. Esfahani, V. Bordbar, Double diffusive natural convection heat transferenhancement in a square enclosure using nanofluids. J. Nanotec. Eng. Medicine 2, 021002–021019 (2011)
P. Keblinski, J.A. Eastman, D.G. Chaill, Nanofluids for thermal transport. Mater. Today 8(6), 36–44 (2005)
F. Selimefendigil, H.F. Oztop, Natural convection and entropy generation of nanofluid filled cavity having different shaped obstacles under the influence of magnetic field and internal heat generation. J. Tai. Ins. Chem. Eng. 56, 42–56 (2015)
M.A. Mansour, M.M. Abd-Elaziz, R.A. Mohamed, S.E. Ahmed, Unsteady natural convection, heat and mass transfer in inclined triangular porous enclosures in the presence of heat source or sink: effect of sinusoidal variation of boundary conditions. Transp. Porous Med. 87, 7–23 (2011)
Y. Varol, H.F. Oztop, A. Varol, Free convection in porous media filled right-angle triangular enclosures. Int. Comm. Heat Mass Transfer 33, 1190–1197 (2006)
T. Basak, C. Thirumalesha, S. Roy, Finite element simulations of natural convection in a right-angle triangular enclosure filled with a porous medium: effects of various thermal boundary conditions. J. Porous Media 11, 159–178 (2008)
A.J. Chamkha, H.A. Naser, Double-diffusive convection in an inclined porous enclosure with opposing temperature and concentration gradients. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 40, 227–244 (2001)
I. Waini, A. Ishak, T. Groşan, I. Pop, Mixed convection of a hybrid nanofluid flow along a vertical surface embedded in a porous medium. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 114, 104565 (2020)
K. Al-Farhany, A.D. Abdulsahib, Study of mixed convection in two layers of saturated porous medium and nanofluid with rotating circular cylinder. Prog. Nucl. Energy 135, 103723 (2021)
M.A. Teamah, Numerical Simulation of double diffusive natural convection in rectangular enclosure in the presences of magnetic field and heat source. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 47, 237–248 (2008)
A.H. Mahmoudi, I. Pop, M. Shahl, Effect of magnetic field on natural convection in a triangular enclosure filled with nanofluid”. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 59, 126–140 (2012)
M.A. Teamah, W.M. El-Maghlany, Augmentation of natural convective heat transfer in square cavity by utilizing nanofluids in the presence of magnetic field and uniform heat generation/absorption. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 58, 130–142 (2012)
E.B. Buyuk Ogut, Natural convection of water-based nanofluids-in an inclined enclosure with a heat source. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 48, 2063–2073 (2009)
T. Basak, S. Roy, S.K. Singh, I. Pop, Analysis of mixed convection in a lid-driven porous square cavity with linearly heated side wall(s). Int J Heat Mass Transfer 53, 1819–1840 (2010)
A.A. Al-Rashed, G.A. Sheikhzadeh, A. Aghaei, F. Monfared, A. Shahsavar, M. Afrand, Effect of a porous medium on flow and mixed convection heat transfer of nanofluids with variable properties in a trapezoidal enclosure. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 139, 741–754 (2020)
E. Colak, Ö. Ekici, H.F. Öztop, Mixed convection in a lid-driven cavity with partially heated porous block. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 126, 105450 (2021)
M. Tahmasbi, M. Siavashi, H.R. Abbasi, M. Akhlaghi, Mixed convection enhancement by using optimized porous media and nanofluid in a cavity with two rotating cylinders. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 141, 1829–1846 (2020)
H.F. Oztop, K. Al-Salem, I. Pop, MHD mixed convection in a lid-driven cavity with corner heater”. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 54, 3494–3504 (2011)
T. Mahalakshmi, N. Nithyadevi, H.F. Oztop, Numerical study of magnetohydrodynamic mixed convective flow in a lid-driven enclosure filled with nanofluid saturated porous medium with center heater. Therm. Sci. 23, 1861–1873 (2019)
M.A. Mansour, R.A. Mohamed, M.M. Abd-Elaziz, S.M. Ahmed, Numerical simulation of mixed convection flows in a square lid-driven cavity partially heated from below using nanofluid. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 37, 1504–1512 (2010)
S. Nazari, R. Ellahi, M.M. Sarafraz, M.R. Safaei, A. Asgari, O.A. Akbari, Numerical study on mixed convection of a non-Newtonian nanofluid with porous media in a two lid-driven square cavity. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 140, 1121–1145 (2020)
H.C. Brinkman, The viscocity of concentrated suspensions and solution. J. Chem. Phys. 20, 571–581 (1952)
R.L. Hamilton, O.K. Grosser, Thermal conductivity of heterogeneous two component system. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundamen. 1, 187–191 (1962)
T. Islam, N. Parveen, R. Nasrin, Mathematical modeling of unsteady flow with uniform/non-uniform temperature and magnetic intensity in a half-moon shaped domain. Heliyon 8(3), e09015 (2022)
A.M. Rashad, H. Togun, M.A. Mansour, T. Salah, T. Armaghani, Unsteady MHD hybrid nanofluid mixed convection heat transfer in a wavy porous cavity with thermal radiation. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 149, 2425–2442 (2024)
F.A. Soomro, R.U. Haq, E.A. Algehyne, I. Tlili, Thermal performance due to magnetohydrodynamics mixed convection flow in a triangular cavity with circular obstacle. J Energy Storage 31, 101702 (2020)
S.S. Shah, R.U. Haq, W. Al-Kouz, Mixed convection analysis in a split lid-driven trapezoidal cavity having elliptic shaped obstacle. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 126, 105448 (2021)
L. Wang, J. Fan, Nanofluids research: key issues. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 5, 1241–1252 (2010)
R. Löhner, Applied computational fluid dynamics techniques: an introduction based on finite element methods (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 2008)
H.F. Oztop, K. Al-Salem, I. Pop, MHD mixed convection in a lid-driven cavity with corner heater. Int J Heat Mass Transfer 54, 3494–3504 (2011)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the editors and reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions.
Funding
There was no external funding for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest related to this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Akter, H., Parveen, N., Munshi, M.J.H. et al. MHD Mixed Convection of Nanofluid in a Lid-Driven Porous Trapezoidal Cavity with a Heated Obstacle. Multiscale Sci. Eng. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42493-024-00113-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42493-024-00113-x