Abstract
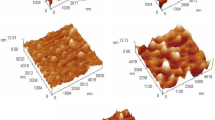
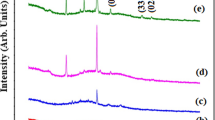
In This work, they made Bismuth oxide (Bi2O3-based) and zinc oxide (ZnO)–doped thin films using thermal evaporation. XRD confirms the phase geometries of monoclinic and (Bi2O3/ZnO) thin films. When ZnO is added, the average crystal size decreases from 17.35 to 8.67 nm. Structures have been examined using Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) and scanning electron microscopy. The Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) investigation found no chemical reactions in the (Bi2O3/ZnO) thin films. A scanning electron microscopy (SEM) examination of the (Bi2O3/ZnO) thin films showed uniform results. Increased ZnO doping reduces the diameter by 67.6%, from 34.20 to 11.06 nm. The optical properties of the (Bi2O3/ZnO) thin film material are examined in this work. It has been shown that (Bi2O3/ZnO) concentration increases absorbance and absorption coefficients. The transmittance and energy band gaps decreased as ZnO concentrations with significant UV light absorption increased. The direct current (D.C) electrical conductivity of (Bi2O3/ZnO) thin films is positively correlated with (ZnO) nanoparticle concentration and temperature, according to experiments. At the same time, the activation energy falls with (ZnO) nanoparticle concentration, given a fixed quantity. The gas sensor showed 96.4% sensitivity to H2S gas at 200 °C. The experiment employed 50 ppm H2S. Finally, the (Bi2O3/ZnO) thin film examination reveals their structural characteristics and conductivity. These results may be helpful in UV sensors and gas sensors. The utilisation of (Bi2O3/ZnO) thin film gas sensor has demonstrated significant potential as a viable option for gas sensing systems, primarily attributed to the enhanced surface area achieved by the application of metal oxide catalysts. The present study also discusses the mechanisms implicated in the augmentation of gas response and the broadened range of applications.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Yes, the data and material are available.
References
S.M. Hosseinpour-Mashkani, M. Maddahfar, A. Sobhani-Nasab, Novel silver-doped NiTiO3: auto-combustion synthesis, characterization and photovoltaic measurements. South Afr. J. Chem. 70, 44–48 (2017). https://doi.org/10.17159/0379-4350/2017/v70a7
R.W. Kelsall, I.W. Hamley, M. Geoghegan, Nanoscale Sci. Technol. (2005). https://doi.org/10.1002/0470020873
J. Teizer, M. Venugopal, W. Teizer, J. Felkl, Nanotechnology and its impact on construction: bridging the gap between researchers and industry professionals. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 138, 594–604 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)co.1943-7862.0000467
M.C. Roco, R.S. Williams, P. Alivisatos, Nanotechnology research directions: IWGN workshop report. Vision for nanotechnology R&D in the next decade. National Science and Technology Councilarlington VA, (1999)
K.P. Chong, Nanoscience and engineering in mechanics and materials. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 65, 1501–1506 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2003.09.032
H.S. Nalwa, Handbook of nanostructured materials and nanotechnology, five-volume set (Academic Press, Cambridge, 1999)
N.A. Ibrahim, Nanomaterials for antibacterial textiles (Elsevier Inc., Amsterdam, 2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-801317-5.00012-8
Z. Yang, H. Peng, W. Wang, T. Liu, Crystallization behavior of poly(ε-caprolactone)/layered double hydroxide nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 116, 2658–2667 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1002/app
S. Murthy, P. Effiong, C.C. Fei, Metal oxide nanoparticles in biomedical applications. Inc (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-817505-7.00011-7
G.A. Kontos, A.L. Soulintzis, P.K. Karahaliou, G.C. Psarras, S.N. Georga, C.A. Krontiras, M.N. Pisanias, Electrical relaxation dynamics in TiO2-polymer matrix composites. Express Polym Lett 1, 781–789 (2007)
S. Laurent, S. Boutry, R.N. Muller, Metal oxide particles and their prospects for applications (Elsevier Ltd., Amsterdam, 2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-08-101925-2.00001-2
M. Abudayyak, E. Öztaş, M. Arici, G. Özhan, Investigation of the toxicity of bismuth oxide nanoparticles in various cell lines. Chemosphere 169, 117–123 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.11.018
M. Schuisky, A. Harsta, Communications epitaxial growth of Bi2O2.33 by halide CVD. Chem. Vap. Depos. 2, 235–238 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1002/cvde.19960020604
L. Leontie, M. Caraman, M. Delibaş, G.I. Rusu, Optical properties of bismuth trioxide thin films. Mater. Res. Bull. 36, 1629–1637 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-5408(01)00641-9
L. Zhang, Y. Hashimoto, T. Taishi, I. Nakamura, Q.Q. Ni, Fabrication of flower-shaped Bi2O3 superstructure by a facile template-free process. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 6577–6582 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2011.02.081
A. Moezzi, A.M. McDonagh, M.B. Cortie, Zinc oxide particles: synthesis, properties and applications. Chem. Eng. J. 185–186, 1–22 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.01.076
S.A. Vanalakar, M.G. Gang, V.L. Patil, T.D. Dongale, P.S. Patil, J.H. Kim, Enhanced gas-sensing response of zinc oxide nanorods synthesized via hydrothermal route for nitrogen dioxide gas. J. Electron. Mater. 48, 589–595 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-018-6752-1
U. Leipzig, E. Physik, Donor-like defects in ZnO substrate materials and ZnO thin films. Appl. Phys. A 139, 135–139 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-007-3966-0
S. Das, S. Mojumder, D. Saha, M. Pal, Influence of major parameters on the sensing mechanism of semiconductor metal oxide based chemiresistive gas sensors: a review focused on personalized healthcare. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 352, 131066 (2022)
N.A. Hassan, I.H. Khudayer, Study of the structural and optical properties of CuAlxIn1-xTe2 thin film, AIP conference proceedings. vol. 2190 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5138536
A. Razzaq, A. Ridha, N.A. Al-isawi, Studying the effect of annealing temperatures on the optical properties of CdS: 1 % Cu nanoparticles thin films prepared by thermal evaporation technique Studying the effect of annealing temperatures on the optical properties of CdS: 1 % Cu nanoparticle, (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1234/1/012029
B.H. Rabee, The optical properties of copper oxide nanoparticles with (polyvinyl alcohol-polyethylene glycol) Blend. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 9(5), 310–314 (2017)
M.H. Meteab, A. Hashim, B.H. Rabee, Synthesis and tailoring the morphological, optical, electronic and photodegradation characteristics of PS–PC/MnO2–SiC quaternary nanostructures. Opt. Quant. Electron. 55, 187 (2023)
H.S. Suhail, A.R. Abdulridha, Investigation of the morphological, optical, and D.C electrical characteristics of synthesized (Bi2O3/ZnO) nanocomposites, as well as their potential use in hydrogen sulfide gas sensor. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. 24, 205–216 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42341-023-00436-w
H.S. Suhail, B.H. Rabee, New nanocomposites (PMMA-SPO-SiC) fabrication and of their structural and electrical properties for pressure sensors. AIP conference proceeding, vol. 2213 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0000093
B.H. Rabee, B. Al-Kareem, B. Al Shafaay, Effect addition Al2O3 on the (AC, DC) electrical properties of ethylene-alpha olefin copolymer. Int J Sci Res 6, 2319–7064 (2017)
S.B. Jagadale, V.L. Patil, S.S. Mali, S.A. Vanalakar, C.K. Hong, P.S. Patil, H.P. Deshmukh, Nanorods to nanosheets structural evolution of NixZn1-xO for NO2 gas sensing application. J. Alloys Compd. 766, 941–951 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.07.040
S.S. Al-abbas, R.A. Ghazi, A.K. Al-shammari, N.R. Aldulaimi, A.R. Abdulridha, S.H. Al-nesrawy, E. Al-bermany, Influence of the polymer molecular weights on the electrical properties of poly (vinyl alcohol)–poly (ethylene glycols)/graphene oxide nanocomposites. Mater. Today Proc. 42, 2469–2474 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.12.565
M.K. Halimah, A. Azuraida, M. Ishak, L. Hasnimulyati, Influence of bismuth oxide on gamma radiation shielding properties of boro-tellurite glass. J. Non Cryst. Solids 512, 140–147 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2019.03.004
S.M. Lam, J.C. Sin, A.Z. Abdullah, A.R. Mohamed, Efficient photodegradation of endocrine-disrupting chemicals with Bi2O3-ZnO nanorods under a compact fluorescent lamp. Water Air Soil Pollut. 224, 1–11 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1565-6
P.D. File, Joint committee on powder diffraction standards, ASTM, Philadelphia, Pa. (1967) pp. 9–185
C. Indium, Crystallographic parameters subfiles and quality comments references peak list, (2010) pp. 1–2
A.K. Sahoo, M.R. Panigrahi, A study on strain and density in graphene-induced Bi2O3 thin film. Bull. Mater. Sci. 44, 1–9 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-021-02515-1
V.K. Landge, S.H. Sonawane, M. Sivakumar, S.S. Sonawane, G. Uday Bhaskar Babu, G. Boczkaj, S-scheme heterojunction Bi2O3-ZnO/Bentonite clay composite with enhanced photocatalytic performance. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 45, 101194 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2021.101194
K.H. Abass, M.K. Mohammed, Fabrication of ZnO:Al/Si solar cell and enhancement its efficiency via Al-doping. Nano Biomed. Eng. 11, 170–177 (2019). https://doi.org/10.5101/nbe.v11i2.p170-177
M. Yasin, M. Saeed, M. Muneer, M. Usman, A. Ul Haq, M. Sadia, M. Altaf, Development of Bi2O3-ZnO heterostructure for enhanced photodegradation of rhodamine B and reactive yellow dyes. Surf. Interfaces 30, 101846 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2022.101846
L. Meng, W. Xu, Q. Zhang, T. Yang, S. Shi, Study of nanostructural bismuth oxide films prepared by radio frequency reactive magnetron sputtering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 472, 165–171 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.02.017
I. Dhahri, M. Ellouze, S. Labidi, Q.M. Al-Bataineh, J. Etzkorn, H. Guermazi, A. Telfah, C.J. Tavares, R. Hergenröder, T. Appel, Optical and structural properties of ZnO NPs and ZnO–Bi2O3 nanocomposites. Ceram. Int. 48, 266–277 (2022)
S. Kumari, D. Mohan, S. Yadav, Effect of Bi2O3 content on non linear optical properties of TeO2.Bi2O3.B2O3.ZnO glass system. AIP conference proceeding. vol. 2093, pp. 2–5, (2019). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5097118
D.K. Eric, Engines of creation. The coming Era of nanotechnology, anchor B. (1986)
A.D. Ghaleb Abdul Wahab, N.N. Hussein, B. Ahmed, T. Rafia, The effect of bismuth oxide Bi2O3 on some optical properties of poly-vinyl alcohol. Br. J. Sci. 4, 117–124 (2012)
H.S. Suhail, A.R. Abdulridha, Synthesis, optical and A.C electrical characteristics of nanocomposites (Bi2O3/ZnO) films prepared by thermal evaporation technique. (2022)
Y. Al-Hadeethi, M.I. Sayyed, Y.S. Rammah, Investigations of the physical, structural, optical and gamma-rays shielding features of B2O3–Bi2O3–ZnO–CaO glasses. Ceram. Int. 45, 20724–20732 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.07.056
S. Indris, P. Heitjans, M. Ulrich, A. Bunde, AC and DC conductivity in nano-and microcrystalline Li2O: B2O3 composites: experimental results and theoretical models, Zeitschrift Fur phys. Chemie 219, 89–103 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1524/zpch.219.1.89.55015
A. Sawalha, A.Ã. Sedky, Electrical conductivity study in pure and doped ZnO ceramic system. Phys. B Condens. Matter 404, 1316–1320 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2008.12.017
M.S. Patil, V.L. Patil, N.L. Tarwal, D.D. More, V.V. Alman, L.D. Kadam, P.S. Patil, J.H. Kim, Gas sensing properties of hydrothermally synthesized button rose-like WO3 thin films. J. Electron. Mater. 48, 526–535 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-018-6756-x
M.H. Sarfi, M. Ghadimi, A. Babaee, H2S gas sensor based on SnO2 and CuO nanoparticles. STEM Fellowsh. J. 1, 21–26 (2016). https://doi.org/10.17975/sfj-2015-012
U.M. Nayef, R.I. Kamel, Bi2O3 nanoparticles ablated on porous silicon for sensing NO2 gas. Optik (Stuttg) 208, 164146 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2019.164146
N.H. Harb, F.A.H. Mutlak, Gas sensing characteristics of WO3NPs sensors fabricated by pulsed laser deposition on PS n-type. J. Opt. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-022-00877-1
S.P. Subin David, S. Veeralakshmi, J. Sandhya, S. Nehru, S. Kalaiselvam, Room temperature operatable high sensitive toluene gas sensor using chemiresistive Ag/Bi2O3 nanocomposite. Sens. Actuators B Chem 320, 128410 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.128410
S.A. Vanalakar, V.L. Patil, N.S. Harale, S.A. Vhanalakar, M.G. Gang, J.Y. Kim, P.S. Patil, J.H. Kim, Controlled growth of ZnO nanorod arrays via wet chemical route for NO2 gas sensor applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem 221, 1195–1201 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.07.084
Q. Zhou, W. Zeng, W. Chen, L. Xu, R. Kumar, A. Umar, High sensitive and low-concentration sulfur dioxide (SO2) gas sensor application of heterostructure NiO-ZnO nanodisks. Sens. Actuators B Chem 298, 126870 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.126870
Acknowledgements
We express our gratitude to the University of Babylon and the Department of Physics for their invaluable assistance in facilitating the successful completion of this work.
Funding
No funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HSS and ARA, the manuscript received feedback from all authors. The final manuscript was read and approved by all of the authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights
The authors assert that the present study does not encompass any human participants, obviating the need for permission. The authors additionally affirm that this paper is an authentic piece of work that has not been previously presented in any form or language.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Suhail, H.S., Abdulridha, A.R. Preparation and Characterization of Thin Films Bismuth(III) Oxide/Zinc Oxide Nanostructures Prepared by Thermal Evaporation Technique as Gas Sensor Applications. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. 25, 1–14 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42341-023-00490-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42341-023-00490-4