Abstract
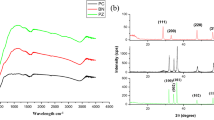
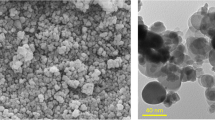
Nanoscaled Bi2O3 particles coated on ZnO nanorods (ZNRs) have been fabricated by combining hydrothermal technique with a chemical precipitation method. X-ray diffraction, field emission-scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and UV–vis absorption and photoluminescence studies were adapted to characterize the structure, morphologies, and optical properties of the nanocomposites. The results indicated that small Bi2O3 nanoparticles were well distributed on the surfaces of ZNRs. And the Bi2O3–ZNR nanocomposites showed high charge separation efficiency and •OH generation ability as evidenced by photoluminescence spectra. Under irradiation of a 55-W compact fluorescent lamp, the Bi2O3–ZNR nanocomposites demonstrated photocatalytic activities higher than pure ZNRs in the degradation of two endocrine-disrupting chemicals, phenol and methylparaben, which might be attributed to the high separation efficiency of photogenerated electron–hole pairs based on the cooperative role of Bi2O3 loading on ZNRs. Moreover, the Bi2O3–ZNR nanocomposite could be easily recovered and reused due to their one-dimensional nanostructural property. All these characteristics brought enormous benefits of Bi2O3–ZNR nanocomposites to the practical application in indoor environmental remediation.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benotti, M. J., Trenholm, R. A., Vanderford, B. J., Holady, J. C., Stanford, B. D., & Snyder, S. A. (2009). Pharmaceuticals and endocrine disrupting compounds in U.S. drinking water. Environmental Science and Technology, 43, 597–603.
Brouwers, M. M., Besselink, H., Bretveld, R. W., Anzion, R., Scheepers, P. T. J., Brouwer, A., et al. (2011). Estrogenic and androgenic activities in total plasma measured with reporter-gene bioassays: relevant exposure measures for endocrine disruptors in epidemiologic studies? Environment International, 37, 557–564.
Flores, N. M., Pal, U., & Mora, E. S. (2011). Photocatalytic behavior of ZnO and Pt-incorporated ZnO nanoparticles in phenol degradation. Applied Catalysis A: General, 394, 269–275.
Gultekin, I., & Ince, N. H. (2007). Synthetic endocrine disruptors in the environment and water remediation by advanced oxidation processes. Journal of Environmental Management, 85, 816–832.
Hameed, A., Gombac, V., Montini, T., Felisari, L., & Fornasiero, P. (2009). Photocatalytic activity of zinc modified Bi2O3. Chemical Physics Letters, 483, 254–261.
Harvey, P. W., & Everett, D. J. (2004). Significance of the detection of esters of p-hydroxyybenzoic acid (parabens) in human breast tumours. Journal of Applied Toxicology, 24, 1–4.
He, J., Luo, Q., Cai, Q. Z., Li, X. W., & Zhang, D. Q. (2011). Microstructure and photocatalytic properties of WO3/TiO2 composite films by plasma electrolytic oxidation. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 129, 242–248.
Huang, W. B., & Chen, C. Y. (2010). Photocatalytic degradation of diethyl phthalate (DEP) in water using TiO2. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 207, 349–355.
Ishibashi, K. I., Fujishima, A., Watanabe, T., & Hashimoto, K. (2000). Quantum yields of active oxidative species formed on TiO2 photocatalyst. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 134, 139–142.
Jia, T. K., Wang, W. M., Long, F., Fu, Z. Y., Wang, H., & Zhang, Q. J. (2009). Fabrication, characterization and photocatalytic activity of La-doped ZnO nanowires. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 484, 410–415.
Kaneko, M., & Okura, I. (2002). Photocatalysis science and technology (pp. 261–276). New York: Springer.
Kundu, V., Himan, R. L., Maan, A. S., & Goyal, D. R. (2009). Optical and spectroscopic studies of ZnO–Bi2O3–B2O3 glasses. Journal Optoelectronics and Advanced Materials, 11, 1595–1600.
Lam, S. M., Sin, J. C., & Mohamed, A. R. (2010). Parameter effect on photocatalytic degradation of phenol using TiO2-P25/activated carbon (AC). Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 27, 1109–1116.
Lam, S. M., Sin, J. C., Abdullah, A. Z., & Mohamed, A. R. (2012). Degradation of wastewaters containing organic dyes photocatalysed by zinc oxide: a review. Desalination and Water Treatment, 41, 131–169.
Lam, S. M., Sin, J. C., Abdullah, A. Z., & Mohamed, A. R. (2013a). ZnO nanorod surface-decorated by WO3 nanoparticles for photocatalytic degradation of endocrine disruptors under a compact fluorescent lamp. Ceramics International, 39, 2343–2352.
Lam, S. M., Sin, J. C., Abdullah, A. Z., & Mohamed, A. R. (2013b). Green hydrothermal synthesis of ZnO nanotubes for photocatalytic degradation of methylparaben. Materials Letters, 93, 423–426.
Lau, G. K., Zhang, T. S., & Goh, G. K. L. (2010). Photochemical properties of CeO2-coated ZnO nanorods. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 10, 4733–4737.
Liu, J. P., Huang, X. T., Li, Y. Y., Ji, X. X., Li, Z. K., He, X., et al. (2007). Vertically aligned 1D ZnO nanostructures on bulk alloy substrates: direct solution synthesis, photoluminescence and field emission. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 111, 4990–4997.
Liu, Z. Y., Bai, H. B., Xu, S. P., & Sun, D. D. L. (2011). Hierarchical CuO/ZnO “corn-like” architecture for photocatalytic hydrogen generation. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 36, 13473–13480.
Liu, S. Z., Zhang, Y. C., Wang, T. X., & Yang, F. X. (2012). Green synthesis of hollow-nanostructured ZnO2 and ZnO. Materials Letters, 71, 154–156.
Mohajerani, M. S., Lak, A., & Simchi, A. (2009). Effect of morphology on the solar photocatalytic behavior of ZnO nanostructures. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 485, 616–620.
Nayak, J., Sahu, S. N., Kasuya, J., & Nozaki, S. (2008). CdS–ZnO composite nanorods: synthesis, characterization and application for photocatalytic degradation of 3,4-dihydroxy benzoic acid. Applied Surface Science, 254, 7215–7218.
Pant, H. R., Park, C. H., Pant, B., Jing, L. D. T., Kim, H. Y., & Kim, C. S. (2011). Synthesis, characterization, and photocatalytic properties of ZnO nano-flower containing TiO2 NPs. Ceramics International, 38, 2943–2950.
Pardeshi, S. K., & Patil, A. B. (2008). A simple route for photocatalytic degradation of phenol in aqueous zinc oxide suspension using solar energy. Solar Energy, 82, 700–705.
Park, W. I., Kim, D. W., Jung, S. W., & Yi, G. C. (2006). Catalyst-free growth of ZnO nanorods and their nanodevice applications. International Journal of Nanotechnology, 3, 373–395.
Pugazhendhi, D., Pope, G. S., & Darbre, P. D. (2005). Oestrogenic activity of p-hydroxybenzoic acid (common metabolite of paraben esters) and methylparaben in human breast cancer cell lines. Journal of Applied Toxicology, 25, 301–309.
Qiu, R. L., Zhang, D. D., Mo, Y. Q., Song, L., Brewer, E., Huang, X. F., et al. (2008). Photocatalytic activity of polymer-modified ZnO under visible light irradiation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 156, 80–85.
Qiu, Y. F., Yang, M. L., Fan, H. B., Zuo, Y. Z., Shao, Y. Y., Xu, Y. J., et al. (2011). Nanowires of α- and β-Bi2O3: phase-selective synthesis and application in photocatalysis. Crystal Engineering Communications, 13, 1843–1850.
Sin, J. C., Lam, S. M., Mohamed, A. R., & Lee, K. T. (2012). Degrading endocrine disrupting chemicals from wastewater by TiO2 photocatalysis: a review. International Journal of Photoenergy. doi:10.1155/2012/185159.
Sin, J. C., Lam, S. M., Lee, K. T., & Mohamed, A. R. (2013). Preparation and photocatalytic properties of visible light-driven samarium-doped ZnO nanorods. Ceramics International. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.01.004.
Sobczynski, A., Duczmal, L., & Zmudzinski, W. (2004). Phenol destruction by photocatalysis on TiO2: an attempt to solve the reaction mechanism. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical, 213, 225–230.
Walker, C. H. (2009). Organic pollutant: An ecotoxicological perspective (pp. 265–292). Boca Raton: Taylor and Francis.
Wang, Y. X., Li, X. Y., Lu, G., Chen, G. H., & Chen, Y. Y. (2008). Synthesis and photo-catalytic degradation property of nanostructured-ZnO with different morphology. Materials Letters, 62, 2359–2362.
Wang, C. H., Shao, C. L., Wang, L. J., Zhang, L. N., Li, X. H., & Liu, Y. C. (2009a). Electrospinning preparation, characterization and photocatalytic properties of Bi2O3 nanofibers. Journal of Colloid and Interface Sciences, 333, 242–248.
Wang, L. S., Xiao, M. W., Huang, X. J., & Wu, Y. D. (2009b). Synthesis, characterization, and photocatalytic activities of titanate nanotubes surface-decorated by zinc oxide nanoparticles. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 161, 49–54.
Wang, X., Liu, G., Lu, G. Q., & Cheng, H. M. (2010). Stable photocatalytic hydrogen evolution from water over ZnO–CdS core-shell nanorods. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 35, 8199–8205.
Wang, W., Lu, C. H., Ni, Y. R., Song, J. B., Su, M. X., & Xu, Z. Z. (2012). Enhanced visible-light photoactivity of 001 facets dominated TiO2 nanosheets with even distributed bulk oxygen vacancy and Ti3+. Catalysis Communications, 22, 19–23.
Yang, J. Y., Lin, Y., Meng, Y. M., & Liu, Y. H. (2012). A two-step route to synthesize highly oriented ZnO nanotube arrays. Ceramics International, 38, 4555–4559.
Zhang, J., Sun, L. D., Liao, C. S., & Yan, C. H. (2002). A simple route towards tubular ZnO. Chemical Communications, 2002, 262–263.
Zhang, X. Y., Dai, J. Y., Ong, H. C., Wang, N., Chan, H. L. W., & Choy, C. L. (2004). Hydrothermal synthesis of oriented ZnO nanobelts and their temperature dependent photoluminescence. Chemical Physics Letters, 393, 17–21.
Zhang, L. S., Wang, W. Z., Yang, J., Chen, Z. G., Zhang, W. Q., Zhou, L., et al. (2006). Sonochemical synthesis of nanocrystallite Bi2O3 as a visible-light-driven photocatalyst. Applied Catalysis A: General, 308, 105–110.
Zhang, J. H., Liu, H. Y., Wang, Z. L., & Ming, N. B. (2008). Low-temperature growth of ZnO with controllable shapes and band gaps. Journal of Crystal Growth, 310, 2848–2853.
Zhang, D. D., Qiu, R. L., Song, L., Brewer, E., Mo, Y. Q., & Huang, X. F. (2009). Role of oxygen active species in the photocatalytic degradation of phenol using polymer sensitized TiO2 under visible light irradiation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 163, 843–847.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a Research Universiti grant (no. 814176) and a Post Graduate Research Grant Scheme (no. 8045030) from Universiti Sains Malaysia as well as a My PhD scholarship through the Malaysian Government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lam, SM., Sin, JC., Abdullah, A.Z. et al. Efficient Photodegradation of Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals with Bi2O3–ZnO Nanorods Under a Compact Fluorescent Lamp. Water Air Soil Pollut 224, 1565 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1565-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1565-6