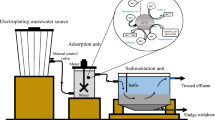
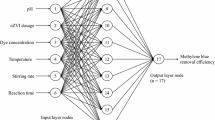
Abstract
Industrial effluents introduce a huge amount of organic load into municipal wastewater. Organic contaminants such as carbohydrates, starch, and fats increase the COD levels to unallowable limits to be discharged into sewage systems. This study successfully prepared Fe/Cu NPs by using the drop by drop method and characterized them using XRD, SEM, and EDAX analysis. The effect of operating experiments was studied at different pH, NP doses, operating times, stirring rates, and initial COD concentrations. The removal efficiencies were between 100 and 69% and between 100 and 800 mg/L for initial COD concentrations at pH 7, NP dose 0.6 g/L, 15 min, and 150 rpm. The adsorption isotherms were studied by applying nonlinear equations of Redlich-Peterson, Hill, Sips, Khan, Toth, Koble-Corrigan, Jovanovic, Freundlich, and Langmuir models. The obtained results indicated that Fe/Cu NPs accept both Koble–Corrigan and Freundlich models with the lowest ∑ = 1.3304. The kinetic analysis was carried by practicing nonlinear equations of pseudo first order (PFO), pseudo second order (PSO), and Elovich, Avrami, and intraparticle kinetic models. The obtained results indicated that Fe/Cu NPs accept the Avrami mechanism with the lowest ∑ = 0.046. The ANNs were trained 28 times and tested 8 times using network structure 6–3-1 indicating that the most significant operating parameter is the effect of concentration 100% followed by the effect of dose 61.1% with a small deviation between the predictive and actual results. RSM relations indicating the positive linear effect of the independent variable “pH,” “dose,” “time,” and “initial concentration” with p-value < 0.05 and insignificant effect for stirring rate with p-value > 0.05.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Arthey, C. Dennis, Vegetable Processing (John Wiley & Sons, 1991)
I.S. Arvanitoyannis, Waste Management for the Food Industries (Academic Press, 2010)
A.N. Bezbaruah, S. Krajangpan, B.J. Chisholm, E. Khan, J.J.E. Bermudez, Entrapment of iron nanoparticles in calcium alginate beads for groundwater remediation applications. J. Hazard. Mater. 166(2), 1339–1343 (2009)
A.N. Bezbaruah, S.S. Shanbhogue, S. Simsek, E. Khan, Encapsulation of iron nanoparticles in alginate biopolymer for trichloroethylene remediation. J. Nanopart. Res. 13(12), 6673–6681 (2011)
M.H. El-Naas, S. Al-Zuhair, M.A. Alhaija, Reduction of COD in refinery wastewater through adsorption on date-pit activated carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 173(1–3), 750–757 (2010)
El-Shafei, M., Mahmoud, A., Mostafa, M. and Peters, R., 2016. Effects of entrapped nZVI in alginate polymer on BTEX removal, AIChE Annual Meeting. San Francisco, CA, pp. 13–18.
E. Eriksson, K. Auffarth, M. Henze, A. Ledin, Characteristics of grey wastewater. Urban water 4(1), 85–104 (2002)
S. Fan, M.S. Mahmoud, B. Wen, Z. Su, Y. Zhang, Bioelectric activity of microbial fuel cell during treatment of old corrugated containerboard discharges. BioResources 13(2), 3545–3553 (2018)
Farag, R., El-Shafei, M.M., Mahmoud, A.S., Mostafa, M.K. and Peters, R., 2018. Green synthesis of nano iron carbide: preparation, characterization and application for removal of phosphate from aqueous solutions, 2018 AIChE Annual Meeting. AIChE.
W.E. Federation, A.P.H. Association, Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater (American Public Health Association (APHA), Washington, DC, USA, 2005)
A. Flores, C. Buckley, R. Fenner, Selecting sanitation systems for sustainability in developing countries. Water Sci. Technol. 60(11), 2973–2982 (2009)
A.T. Fola, A.A. Idowu, A. Adetutu, Removal of Cu2+ from aqueous solution by adsorption onto quail eggshell: Kinetic and isothermal studies. J. Environ. Biotechnol. Res. 5(1), 1–9 (2016)
T.M.A. Ghany et al., Physicochemical characterization of agricultural run-off and groundwater inoculated by trichoderma asperellum and its effect on anti-oxidative enzymes production by irrigated trifolium alexandrinum L. BioResources 16(2), 3272–3284 (2021)
M.I. Gil, M.V. Selma, F. López-Gálvez, A. Allende, Fresh-cut product sanitation and wash water disinfection: problems and solutions. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 134(1–2), 37–45 (2009)
V.K. Gupta, T.A. Saleh, Sorption of pollutants by porous carbon, carbon nanotubes and fullerene-an overview. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 20(5), 2828–2843 (2013)
Harter, T., 2003. Groundwater quality and groundwater pollution. UCANR Publications.
Hynes, N.R.J. et al., 2020. Modern enabling techniques and adsorbents based dye removal with sustainability concerns in textile industrial sector-a comprehensive review. Journal of cleaner production: 122636.
Karam, A. et al., 2019. Small-pilot plant for tertiary treatment of domestic wastewater using algal photo-bioreactor, with artificial intelligence, 2019 AIChE Annual Meeting. AIChE.
A. Karam, K. Zaher, A.S. Mahmoud, Comparative studies of using nano zerovalent iron, activated carbon, and green synthesized nano zerovalent iron for textile wastewater color removal using artificial intelligence, regression analysis, adsorption isotherm, and kinetic studies. Air, Soil and Water Res 13, 1178622120908273 (2020)
Krishnan, S. et al., 2021. Current technologies for recovery of metals from industrial wastes: an overview. Environmental Technology & Innovation: 101525.
G. Langergraber, E. Muellegger, Ecological Sanitation—a way to solve global sanitation problems? Environ. Int. 31(3), 433–444 (2005)
A.S. Mahmoud, M.M. El-Tayieb, N.A.S. Ahmed, A.M. Mostafa, Algorithms and statistics for municipal wastewater treatment using nano zero valent iron (nZVI). J. Environ. Biotechnol. Res. 7(3), 30–44 (2018)
A.S. Mahmoud, R.S. Farag, M.M. Elshfai, Reduction of organic matter from municipal wastewater at low cost using green synthesis nano iron extracted from black tea: Artificial intelligence with regression analysis. Egypt. J. Pet. 29(1), 9–20 (2020)
A.S. Mahmoud, R.S. Farag, M.M. Elshfai, L.A. Mohamed, S.M. Ragheb, Nano zero-valent aluminum (nZVAl) preparation, characterization, and application for the removal of soluble organic matter with artificial intelligence, isotherm study, and kinetic analysis. Air, Soil and Water Res 12, 1178622119878707 (2019)
Mahmoud, A.S. et al., 2019b. Isotherm and kinetic studies for heptachlor removal from aqueous solution using Fe/Cu nanoparticles, artificial intelligence, and regression analysis. Separation Science and Technology: 1–13.
A.S. Mahmoud, M.K. Mostafa, M. Nasr, Regression model, artificial intelligence, and cost estimation for phosphate adsorption using encapsulated nanoscale zero-valent iron. Sep. Sci. Technol. 54(1), 13–26 (2019)
Mahmoud, A.S., Saryel-Deen, R.A., Mostafa, M.K. and Peters, R.W., 2017. Artificial intelligence for organochlorine pesticides removal from aqueous solutions using entrapped nZVI in alginate biopolymer, Annual AIChE Meeting. Minneapolis, MN, October.
S. Manahan, Environmental Chemistry (CRC Press, 2017)
Mostafa, M.K., Mahmoud, A.S., SaryEl-deen, R.A. and Peters, R.W., 2017a. Application of entrapped nano zero valent iron into cellulose acetate membranes for domestic wastewater treatment, 2017 Annual AIChE Meeting; Minneapolis, MN, October 29 - November 3, 2017.
Mostafa, M.K., Mahmoud, A.S., Saryel-Deen, R.A. and Peters, R.W., 2017b. Application of entrapped nano zero valent iron into cellulose acetate membranes for domestic wastewater treatment, Environmental aspects, applications and implications of nanomaterials and nanotechnology 2017–Topical conference at the 2017 AIChE annual meeting, pp. 27–34.
M.K. Mostafa, R.W. Peters, Improve effluent water quality at Abu-Rawash wastewater treatment plant with the application of coagulants. Water Environ. J. 30(1–2), 88–95 (2016)
Okoh, A.I., Odjadjare, E.E., Igbinosa, E.O. and Osode, A.N., 2007. Wastewater treatment plants as a source of microbial pathogens in receiving watersheds. African Journal of Biotechnology, 6(25).
J. Ontiveros, T. Clapp, D. Kosson, Physical properties and chemical species distributions within municipal waste combuster ashes. Environ. Prog. 8(3), 200–206 (1989)
PEDDI, P.K., 2011. Pilot-scale demonstration of hzvi process for treating, Texas A&M University.
Philander, S.G., 2008. Encyclopedia of global warming and climate change. Sage Publications.
Pruss-Ustun, A. and Organization, W.H., 2008. Safer water, better health: costs, benefits and sustainability of interventions to protect and promote health.
F.R. Rijsberman, Water scarcity: fact or fiction? Agric. Water Manag. 80(1–3), 5–22 (2006)
R. Saravanan, V. Gupta, E. Mosquera, F. Gracia, Preparation and characterization of V2O5/ZnO nanocomposite system for photocatalytic application. J. Mol. Liq. 198, 409–412 (2014)
R. Saravanan, V.K. Gupta, V. Narayanan, A. Stephen, Comparative study on photocatalytic activity of ZnO prepared by different methods. J. Mol. Liq. 181, 133–141 (2013)
R. Saravanan et al., Enhanced photocatalytic activity of ZnO/CuO nanocomposite for the degradation of textile dye on visible light illumination. Mater. Sci. Eng., C 33(1), 91–98 (2013)
Saryel-Deen, R.A., Mahmoud, A.S., Mahmoud, M., Mostafa, M.K. and Peters, R.W., 2017a. Adsorption and kinetic studies of using entrapped sewage sludge ash in the removal of chemical oxygen demand from domestic wastewater, with artificial intelligence approach, Annual AIChE meeting.
SaryEl-deen, R.A., Mahmoud, A.S., Mahmoud, M., Mostafa, M.K. and Peters, R.W., 2017b. Adsorption and kinetic studies of using entrapped sewage sludge ash in the removal of chemical oxygen demand from domestic wastewater, with Artificial Intelligence Approach, 2017 Annual AIChE Meeting.
Y.-H. Shih, C.-Y. Hsu, Y.-F. Su, Reduction of hexachlorobenzene by nanoscale zero-valent iron: kinetics, pH effect, and degradation mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 76(3), 268–274 (2011)
P. Simha, M. Ganesapillai, Ecological Sanitation and nutrient recovery from human urine: how far have we come? Rev. Sustain. Environ. Res. 27(3), 107–116 (2017)
A.P. Sincero, G.A. Sincero, Physical-Chemical Treatment of Water and Wastewater (CRC Press, 2002)
Z.-H. Su et al., Industrial scale-up of fiber recovery technology from mixed office waste fine screen rejects. BioResources 15(3), 6420–6430 (2020)
Z.-H. Su, M.S. Mahmoud, S. Fan, Y. Zhang, F. Peng, Combustion properties of mixed black liquor solids from linter and reed pulping. BioResources 14(4), 8278–8288 (2019)
M. Velu et al., Fabrication of nanocomposites mediated from aluminium nanoparticles/Moringa oleifera gum activated carbon for effective photocatalytic removal of nitrate and phosphate in aqueous solution. J. Clean. Prod. 281, 124553 (2021)
G. Walker, J. Hanna, S. Allen, Treatment of hazardous shipyard wastewater using dolomitic sorbents. Water Res. 39(11), 2422–2428 (2005)
Wijesekara, S., Harischandra, I., Kumarathilaka, S. and Vithanage, M., 2014. Fate and transport of selection nutrients and heavy metals in nanoscale zero valent iron amended sand columns.
M.T. Zin, J. Borja, H. Hinode, W. Kurniawan, Synthesis of bimetallic Fe/Cu nanoparticles with different copper loading ratios. Dimensions 13, 19 (2013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahmoud, M.S., Mahmoud, A.S. Wastewater treatment using nano bimetallic iron/copper, adsorption isotherm, kinetic studies, and artificial intelligence neural networks. emergent mater. 4, 1455–1463 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-021-00253-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-021-00253-y