Abstract
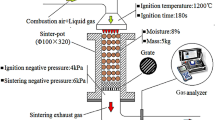
Hot air sintering technology is used to improve the quality and production efficiency of sintered ore. However, the current thick layer condition highlights the disadvantage of the low oxygen potential of the hot air sintering layer. Therefore, it is considered to use oxygen enrichment sintering to improve the environment of hot air sintering. Traditional sintering, hot air sintering, and oxygen-rich hot air sintering were compared through sintering cup experiments, and the influence of hot air and oxygen-rich hot air on sintering indexes was clarified. Hot air reduced the vertical sintering velocity, while improved the yield and tumbler index. Oxygen-rich hot air sintering contributed to improving the vertical sintering velocity while ensuring the quality of sintered ore, thus comprehensively improving production efficiency. Under the action of hot air, the highest temperature of the sintering layer increased and the high-temperature holding time was prolonged. After oxygen enrichment, the combustion efficiency of fuels in the upper layer of materials was promoted, which optimized heat distribution in the middle and lower layers of materials and increased the content of calcium ferrite in the sintered ore, thus strengthening the sintering process.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y.Z. Wang, J.L. Zhang, Z.J. Liu, C.B. Du, JOM 69 (2017) 2404–2411.
Q. Zhong, H.B. Liu, L.P. Xu, X. Zhang, M.J. Rao, Z.W. Peng, G.H. Li, T. Jiang, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 28 (2021) 1366–1374.
C.F. Sun, P.S. Ma, J.Y. Deng, L.X. Bai, Z.H. Liao, Y.D. Peng, Q.Y. Zhang, J. Xu, Fuel 322 (2023) 125955.
M. Gan, X.H. Fan, X.L. Chen, Z.Y. Ji, W. Lv, Y. Wang, Z.Y. Yu, T. Jiang, ISIJ Int 52 (2012) 1574–1578.
L. Kieush, M. Yaholnyk, M. Boyko, A. Koveria, V. Ihnatenko, Acta Metall. Slovaca 25 (2019) 55–64.
N. Oyama, Y. Iwami, T. Yamamoto, S. Machida, T. Higuchi, H. Sato, M. Sato, K. Takeda, Y. Watanabe, M. Shimizu, K. Nishioka, ISIJ Int 51 (2011) 913–921.
Y.F. Wu, X.H. Fan, Z.Y. Ji, M. Gan, Y. Tu, G.G. Zhao, H.Y. Zhou, Z.Q. Sun, X.L. Chen, X.X. Huang, F.Q. Zou, J. Clean. Prod. 374 (2022) 133907.
X.L. Chen, X.H. Fan, M. Gan, Y.S. Huang, Z.Y. Yu, Ironmak. Steelmak. 45 (2018) 434–440.
X.H. Fan, G.J. Wong, M. Gan, X.L. Chen, Z.Y. Yu, Z.Y. Ji, J. Clean. Prod. 235 (2019) 1549–1558.
X.H. Fan, Z.Y. Yu, M. Gan, W.Q. Li, Z.Y. Ji, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 20 (2013) No. 6, 1–6.
X.L. Chen, Y.S. Huang, M. Gan, X.H. Fan, Z.Y. Yu, L.S. Yuan, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 22 (2015) 1107–1112.
X.H. Fan, Z.Y. Yu, M. Gan, X.L. Chen, Q. Chen, S. Liu, Y.S. Huang, ISIJ Int. 55 (2015) 2074–2081.
Z.Y. Yu, X.H. Fan, M. Gan, X.L. Chen, Q. Chen, Y.S. Huang, J. Air Waste Manage. Assoc. 66 (2016) 687–697.
H. Kang, S. Choi, W. Yang, B. Cho, ISIJ Int. 51 (2011) 1065–1071.
Z.Y. Ji, Y.F. Wang, X.H. Fan, G.G. Zhao, M. Gan, L.Y. Tang, Y. Tu, X.L. Wang, H.X. Zheng, X.L. Chen, X.X. Huang, Z.Q. Sun, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. (2023) https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-023-00915-7.
L.H. Hsieh, J.A. Whiteman, ISIJ Int. 29 (1989) 625–634.
Y. Iwami, T. Yamamoto, T. Higuchi, K. Nushiro, M. Sato, N. Oyama, ISIJ Int. 53 (2013) 1633–1641.
Y. Iwami, T. Yamamoto, T. Higuchi, N. Oyama, M. Sato, Y. Sodani, ISIJ Int. 55 (2015) 2350–2357.
D.K. Rajak, N.B. Ballal, N.N. Viswanathan, M. Singhai, ISIJ Int. 61 (2021) 79–85.
D.W. Yang, W. Wang, J.X. Li, X.H. Chen, P.F. Chen, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 30 (2023) 1921–1928.
W. Wang, X.H. Chen, R.S. Xu, J. Li, W.J. Shen, S.P. Wang, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 27 (2020) 367–379.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51974371 and 52274344), the Science and Technology Innovation Program of Hunan Province (No. 2023RC3042), Provincial Natural Science Foundation of Hunan (Nos. 2023JJ20068 and 2022JJ30723), and China Baowu Low Carbon Metallurgy Innovation Foundation (BWLCF202118).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Zhi-yun Ji is a youth editorial board member for Journal of Iron and Steel Research International and was not involved in the editorial review or the decision to publish this article. The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gan, M., Zheng, Hx., Fan, Xh. et al. Influence of oxygen-rich hot air composite gas medium on sintering performance and function mechanism. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 31, 1071–1081 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-023-01127-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-023-01127-9