Abstract
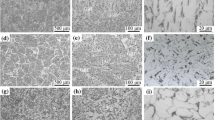
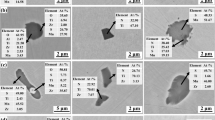
In accordance with the minimum degree of disregistry mechanism in oxide metallurgy, the intragranular acicular ferrite (IAF) generated by microalloying elements in austenite was studied. Herein, the effect of Mg treatment on the microstructure and toughness of the heat-affected zone (HAZ) in shipbuilding steel was investigated. Mg treatment produced inclusions that influenced the formation of acicular ferrite in the microstructure. This refined the HAZ microstructure and improved its toughness. Electron backscatter diffraction was used to determine the oxides of titanium and the MgO·Al2O3 or MgAl2O4 complex inclusions that induced the formation of IAF. MnS precipitated on MgAl2O4 on a specific habit plane and in a specific direction. MnS had a specific orientation relationship with MgAl2O4, i.e., \({\{100\}}_{{\mathrm{MgAl}}_{2}{\mathrm{O}}_{4}}\)//{100}MnS. The 35-mm-thick plate obtained in the industrial test after welding at a welding heat input of 120 kJ/cm had an average impact absorbed energy of 282.7 J at − 40 °C and 2 mm from the weld joint in the HAZ. The two-dimensional disregistry index between inclusions can be used as the basis for controlling their distribution and adsorption force. Microalloy addition in the order of Al–Mg–Ti is key to obtaining abundant dispersion and fine nucleation in austenite.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Wang, R.D.K. Misra, M.H. Shi, P.Y. Zhang, Z.D. Wang, F.X. Zhu, G.D. Wang, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 594 (2014) 218–228.
H. Suito, A.V. Karasev, M. Hamada, R. Inoue, K. Nakajima, ISIJ Int. 51 (2011) 1151–1162.
Y. Tomita, N. Saito, T. Tsuzuki, Y. Tokunaga, K. Okamoto, ISIJ Int. 34 (1994) 829–835.
J. Hu, L.X. Du, M. Zang, S.J. Yin, Y.G. Wang, X.Y. Qi, X.H. Gao, R.D.K. Misra, Mater. Charact. 118 (2016) 446–453.
M. Hasegawa, K. Takeshita, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 3 (1978) 383–388.
H. Ohta, H. Suito, ISIJ Int. 46 (2006) 480–489.
Y. Hou, W. Zheng, Z. Wu, G. Li, N. Moelans, M. Guo, B.S. Khan, Acta Mater. 118 (2016) 8–16.
X.B. Li, T.S. Zhang, M. Yin, C.J. Liu, M.F. Jiang, Ironmak. Steelmak. 46 (2017) 292–300.
L.Y. Xu, J. Yang, R.Z. Wang, Y.N. Wang, W.L. Wang, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 47 (2016) 3354–3364.
F. Chai, C.F. Yang, H. Su, Y.Q. Zhang, Z. Xu, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 16 (2009) No. 1, 69–74.
C.H. Chang, I.H. Jung, S.C. Park, H.S. Kim, H.G. Lee, Ironmak. Steelmak. 32 (2005) 251–257.
S.H. Wang, C.C. Chiang, S.H. Chan, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 344 (2003) 288–295.
H.S. Kim, C.H. Chang, H.G. Lee, Scripta Mater. 53 (2005) 1253–1258.
S. Kimura, K. Nakajima, S. Mizoguchi, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 32 (2001) 79–85.
Z.H. Wu, W. Zheng, G.Q. Li, H. Matsuura, F. Tsukihashi, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 46 (2015) 1226–1241.
Y. Kang, K. Han, J.H. Park, C.H. Lee, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 45 (2014) 4753–4757.
D. Zhang, H. Terasaki, Y.I. Komizo, Acta Mater. 58 (2010) 1369–1378.
Y. Li, X.L. Wan, L. Cheng, K.M. Wu, Mater. Sci. Technol. 32 (2016) 88–93.
Z.H. Xiong, S.L. Liu, X.M. Wang, C.J. Shang, X. Li, R.D.K. Misra, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 636 (2015) 117–123.
X.D. Zou, D.P. Zhao, J.C. Sun, C. Wang, H. Matsuura, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 49 (2018) 481–489.
X.K. Cui, B. Song, Z.B. Yang, Z. Liu, L.F. Li, L. Wang, Steel Res. Int. 91 (2020) 1900563.
Y. Min, X.B. Li, Z. Yu, C.J. Liu, M.F. Jiang, Steel Res. Int. 87 (2016) 1503–1510.
F. Zhao, N.B. Zhou, M.B. Jiang, J.X. Xie, Y.Z. Liu, Steel Res. Int. 88 (2017) 133–143.
F. Ishikawa, T. Takahashi, ISIJ Int. 35 (1995) 1128–1133.
Z.H. Xiong, S.L. Liu, X.M. Wang, C.J. Shang, R.D.K. Misra, Mater. Charact. 106 (2015) 232–239.
Y. Murakami, Y. Takeuchi, K. Hase, S. Endo, T. Sakimoto, T. Handa, Int. J. Offshore Polar Eng. 24 (2014) 286–291.
A. Kojima, A. Kiyose, R. Uemori, M. Minagawa, Nippon Steel Tech. Rep. 380 (2004) 1–6.
J.G. Huang, China Metallurgy Reports 2015–03–10 (001).
B.X. Wang, F.X. Zhu, C. Wang, H.N. Lou, Z.D. Wang, G.D. Wang, Iron and Steel 54 (2019) No. 9, 12–21.
C.H. Gu, K. Zhan, World Metals Reports 2018–08–12 (001).
L.G. Zhu, Y. Wang, S.M. Wang, Q.J. Zhang, C.J. Zhang, Ironmak. Steelmak. 46 (2019) 499–507.
D.S. Sarma, A.V. Karasev, P.G. Jönsson, ISIJ Int. 49 (2009) 1063–1074.
A.J. Derado, Int. Mater. Rev. 48 (2003) 371–402.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 52004094 and 51874137) and the Hebei Province Natural Science Fund Project (E2021209037, E2020209044, and E2020209036) and Fundamental Innovation Team of High Quality Clean Steel in Tangshan from Tangshan Science and Technology Bureau (21130209D).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Zhu, Lg., Huo, Jx. et al. Relationship between crystallographic structure of complex inclusions MgAl2O4/Ti2O3/MnS and improved toughness of heat-affected zone in shipbuilding steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 29, 1277–1290 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-021-00725-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-021-00725-9