Abstract
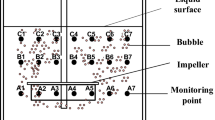
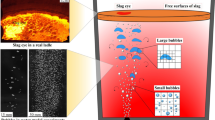
In order to increase the contact area and promote the mass transfer process of gas and liquid, the process of the bubble refinement in a metallurgical reactor with mechanical agitation was studied by physical simulation. Based on the capillary number, a prediction equation for the bubble refinement was established. The effects of the gas flow rate, the stirring speed and the stirring depth on the bubble refinement in the reactor were discussed in detail. The distribution of the bubble diameter in the reactor was obtained under different conditions. The results show that when the stirring speed reaches 300 r/min, the bubble diameter mainly distributes in the range of 1–2 mm. A higher gas flow rate may increase the number of bubbles in the melt and promote the bubble refinement process. The mechanism of bubble refinement under mechanical agitation was analyzed, and the results indicated that the stirring speed, the blade area and the blade inclination are the main influencing factors.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.P. Sun, Y.C. Liu, M.J. Lu, ISIJ Int. 49 (2009) 771–776.
D. Lindström, D. Sichen, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 46 (2015) 83–92.
W.J. Ma, H.B. Li, Y. Cui, B. Chen, G.L. Liu, J.L. Ji, ISIJ Int. 57 (2017) 214–219.
G.A. Irons, R.I.L. Guthrie, Metall. Trans. B 12 (1981) 755–767.
J. Yang, K. Okumura, M. Kuwabara, M. Sano, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 34 (2003) 619–629.
J. Yang, S. Ozaki, R. Kakimoto, K. Okumura, M. Kuwabara, M. Sano, ISIJ Int. 41 (2001) 945–954.
J. Yang, K. Okumura, M. Kuwabara, M. Sano, ISIJ Int. 41 (2001) 965–973.
J. Yang, K. Okumura, M. Kuwabara, M. Sano, ISIJ Int. 42 (2002) 595–607.
G.A. Irons, R.I.L. Guthrie, Can. Metall. Quart. 19 (1980) 381–387.
N.J. Themelis, P. Goyal, Can. Metall. Quart. 22 (1983) 313–320.
S. Mukawa, Y. Ueshima, M. Sano, J. Yang, M. Kuwabara, ISIJ Int. 46 (2006) 1778–1782.
W. Zheng, H. Tu, G.Q. Li, X. Shen, Y.L. Xu, C.Y. Zhu, K. Lu, J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing 36 (2014) No. S1, 53–59.
S.G. Zheng, M.Y. Zhu, Acta Metall. Sin. 42 (2006) 1143–1148.
J.H. Ji, R.Q. Liang, J.C. He, ISIJ Int. 57 (2017) 453–462.
G. Irons, A. Senguttuvan, K. Krishnapisharody, ISIJ Int. 55 (2015) 1–6.
Y. Liu, Z.M. Zhang, S. Masamichi, J. Zhang, P. Shao, T.A. Zhang, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 21 (2014) 135–143.
Y. Liu, M. Sano, T.A. Zhang, Q. Wang, J.C. He, ISIJ Int. 49 (2009) 17–23.
X.F. Xu, J. Zhang, F.X. Liu, X.J. Wang, W. Wei, Z.J. Liu, Int. J. Multiphase Flow 95 (2017) 84–90.
T. Haiyan, G. Xiaochen, W. Guanghui, W. Yong, ISIJ Int. 56 (2016) 2161–2170.
R. Hagemann, R. Schwarze, H.P. Heller, P.R. Scheller, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 44 (2013) 80–90.
F.M. Meng, Fundamentals of metallurgical macro-kinetics, Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, China, 2014.
P.J. Pritchard, J.W. Mitchell, Introduction to fluid Me980-chanics, John Wiley & Sons, USA, 2011.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U1508217, U1702253 and 51774078) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (N172506009 and N170908001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, Jm., Dou, Zh., Zhang, Ta. et al. Physical simulation of bubble refinement in bottom blowing process with mechanical agitation. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 27, 1137–1144 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-020-00368-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-020-00368-2