Abstract
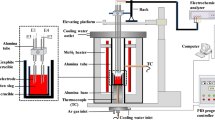
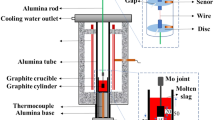
The crystallization and structure of non-conventional lime–silica-based mold fluxes after undergoing slag–steel interaction in casting high-Al transformation induced plasticity (TRIP) steel were studied. The results showed that the crystallization temperatures of the mold fluxes decreased with decreasing the SiO2/Al2O3 ratio, and CaO/MnO2 ratio had an opposite effect on the crystallization temperatures. The crystalline phases precipitated in the mold flux were Ca4Si2O7F2 and NaAlSiO4. Decreasing SiO2/Al2O3 ratio and increasing CaO/MnO2 ratio in the mold fluxes have no influence on the types of crystalline phases. The dominant crystalline phase precipitated in each mold flux was Ca4Si2O7F2 with dendritic morphology, except for part of that with globular morphology in the mold flux without MnO2 addition. NaAlSiO4 crystals are distributed in the space among Ca4Si2O7F2 crystals. The size of Ca4Si2O7F2 crystals in the slag with higher SiO2/Al2O3 ratio is smaller, which is attributed to the polymerization degree of the mold flux with increasing SiO2/Al2O3 ratio. [SiO4]-tetrahedral, [AlO4]-tetrahedral and T–O–T bending (T denotes Si or Al) depolymerized gradually with decreasing SiO2/Al2O3 ratio, and an opposite trend was observed for the case with increasing CaO/MnO2 ratio. The polymerization degree of the mold fluxes decreased, which would result in the decrease in the viscosity of the mold fluxes.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Street, K. James, N. Minor, A. Roelant, J. Tremp, Iron Steel Technol. 5 (2008) 38–49.
K. Blazek, H.B. Yin, G. Skoczylas, M. McClymonds, M. Frazee, Iron Steel Technol. 8 (2011) 231–240.
W.L. Wang, K. Blazek, A. Cramb, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 39 (2008) 66–74.
C.X. Ji, Y. Cui, Z. Zeng, Z.H. Tian, C.L. Zhao, G.S. Zhu, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 22 (2015) Suppl. 1, 53–56.
M.S. Kim, S.W. Lee, J.W. Cho, M.S. Park, H.G. Lee, Y.B. Kang, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 44 (2013) 299–308.
J.W. Cho, K. Blazek, M. Frazee, H.B. Yin, J.H. Park, S.W. Moon, ISIJ Int. 53 (2013) 62–70.
X.J. Fu, G.H. Wen, P. Tang, Q. Liu, Z.Y. Zhou, Ironmak. Steelmak. 41 (2014) 342–349.
D. Xiao, W. Wang, B. Lu, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 46 (2015) 873–881.
B. Lu, K. Chen, W. Wang, B. Jiang, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 45 (2014) 1496–1509.
C.B. Shi, M.D. Seo, J.W. Cho, S.H. Kim, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 45 (2014) 1081–1097.
L. Zhou, H. Li, W. Wang, Z. Wu, J. Yu, S. Xie, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 48 (2017) 2949–2960.
X. Yu, G.H. Wen, P. Tang, B. Yang, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 17 (2010) No. 5, 11–16.
C.B. Shi, J. Li, J. W. Cho, F. Jiang, I. H. Jung, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 46 (2015) 2110–2120.
J.L. Li, Q.F. Shu, X.M. Hou, K.C. Chou, ISIJ Int. 55 (2015) 830–836.
H. Nakada, K. Nagata, ISIJ Int. 46 (2006) 441–449.
M.D. Seo, C.B. Shi, J.W. Cho, S.H. Kim, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 45 (2014) 1874–1886.
M.D. Seo, C.B. Shi, H. Wang, J.W. Cho, S.H. Kim, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 412 (2015) 58–65.
H. Kim, W.H. Kim, I. Sohn, D.J. Min, Steel Res. Int. 81 (2010) 261–264.
J.H. Park, D.J. Min, H.S. Song, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 35 (2004) 269–275.
J.L. Liao, Y.Y. Zhang, S. Sridhar, X.D. Wang, Z.T. Zhang, ISIJ Int. 52 (2012) 753–758.
G.H. Kim, C.S. Kim, I. Sohn, ISIJ Int. 53 (2013) 170–176.
Z.J. Wang, Q.F. Shu, S. Sridhar, M. Zhang, M. Guo, Z.T. Zhang, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 46 (2015) 758–765.
J.R. Kim, Y.S. Lee, D.J. Min, S.M. Jung, S.H. Yi, ISIJ Int. 44 (2004) 1291–1297.
Acknowledgements
The financial support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51874026 and 51774225) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. FRF-TP-18-004A3) is greatly acknowledged. The authors are thankful to the financial support from the State Key Laboratory of Advanced Metallurgy (Grant No. 41618020). This work was also partially financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2016YFB0300604).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Dl., Shi, Cb., Li, Zj. et al. Effect of SiO2 substitution with Al2O3 during high-Al TRIP steel casting on crystallization and structure of low-basicity CaO–SiO2-based mold flux. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 27, 33–41 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-018-0218-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-018-0218-9