Abstract
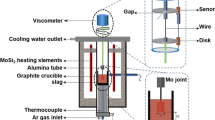
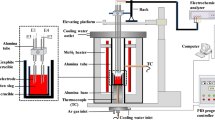
The effect of TiO2 absorption into two different CaO–BaO–SiO2–Al2O3-based mold slags from the steel plant on the viscosity, melting performance and microstructure of slags was investigated through the measurement of the viscosity–temperature relationship, melting temperature and Raman spectroscopy. The parameter of the number of non-bridging oxygen per tetrahedrally-coordinated atom (NBO/T) was also calculated to explain the microstructure variation of molten slags with different TiO2 absorption. The variation of the actual slag consumption and the depth of the liquid slag in mold was explained through the comparison of the viscosity and the melting temperature of two different slags. The viscosity of mold slags (basicity = 0.6) decreased from 1.1 to 0.68 Pa s with the increase in the TiO2 absorption from 0 to 10%, while that of slags (basicity = 0.7) decreased from 0.76 to 0.56 Pa s with the TiO2 absorption from 0 to 6%. The activation energy of both two groups of slags had the tendency to decrease with the increasing TiO2 absorption. The network structure of both two groups of slags measured by the Raman spectra showed that the fraction of complex structure units (Q1, Q2, Q3 and Al–O–Al) decreased and simple structure units (Al–O− and Q0) increased with the increase in TiO2 absorption. NBO/T also increased with the increase in the TiO2 absorption, indicating that the absorption of TiO2 into slags resulted in the destruction of silicate/aluminate structure. Hence, the absorption of TiO2 into the current CaO–BaO–SiO2–Al2O3 mold slags decreased the degree of polymerization of these slags and then led to the decrease of viscosity.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
X.J. Wang, S. Qu, R. Liu, L.G. Zhu, Z.L. Piao, T.C. Di, Y. Wang, Mater. Rep. 35 (2021) No. Z1, 467–472.
Z. Hao, W. Chen, C. Lippold, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 41 (2010) 805–812.
Z. Wang, Q.F. Shu, X.M. Hou, K.C. Chou, Ironmak. Steelmak. 39 (2012) 210–215.
L. Zhou, Z. Pan, W. Wang, J. Chen, L. Xue, T. Zhang, L. Zhang, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 51 (2020) 85–94.
Z. Wang, Q. Shu, K. Chou, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 44 (2013) 606–613.
T. Mukongo, P.C. Pistorius, A.M. Garbers-Craig, Ironmak. Steelmak. 31 (2004) 135–143.
J.L. Liao, J. Li, X.D. Wang, Z.T. Zhang, Ironmak. Steelmak. 39 (2012) 133–139.
H. Park, J.Y. Park, G.H. Kim, I. Sohn, Steel Res. Int. 83 (2012) 150–156.
Z. Piao, L. Zhu, X. Wang, Z. Liu, B. Wang, P. Xiao, Z. Yuan, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 51 (2020) 2119–2130.
Z. Piao, Research on exploitation and metallurgical properties of CaO-Al2O3-TiO2-based mold flux for high titanium steel, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing, China, 2021.
Z. Wang, Q. Shu, K. Chou, High Temp. Mater. Process. 32 (2013) 265–273.
J.L. Li, Q.F. Shu, K.C. Chou, Can. Metall. Quart. 54 (2015) 85–91.
J.T. Ju, G.H. Ji, J.L. An, C.M. Tang, Ironmak. Steelmak. 48 (2021) 109–115.
Z. Li, Research on reactivity control and basic structure properties of mold flux for high-Mn high-Al steel, Chongqing University, Chongqing, China, 2019.
L. Zhu, Q. Wang, Q. Wang, S. Zhang, S. He, Ironmak. Steelmak. 46 (2019) 865–871.
L.L. Zhu, Q. Wang, Q.Q. Wang, S.D. Zhang, Ironmak. Steelmak. 46 (2019) 865–871.
G. Urbain, Y. Bottinga, P. Richet, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 46 (1982) 1061–1072.
P. McMillan, B. Piriou, A. Navrotsky, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 46 (1982) 2021–2037.
E. Gao, W. Wang, L. Zhang, J. Non Cryst. Solids 473 (2017) 79–86.
Y. Sun, H. Wang, Z. Zhang, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 49 (2018) 677–687.
I. Daniel, P. Gillet, B.T. Poe, P.F. McMillan, Phys. Chem. Miner. 22 (1995) 74–86.
B.O. Mysen, D. Virgo, C.M. Scarfe, Am. Mineralogist 65(1980) 690–710.
D.L. Zheng, C.B. Shi, Z.J. Li, J. Li, J.W. Cho, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 27 (2020) 33–41.
B. Mysen, D. Neuville, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 59 (1995) 325–342.
B. Mysen, F. Ryerson, D. Virgo. Am. Mineralogist 65 (1980) 1150–1165.
Z. Yan, X. Lv, Z. Pang, X. Lv, C. Bai, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 49 (2018) 1322–1330.
L. Zhou, H. Li, W. Wang, D. Xiao, L. Zhang, J. Yu, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 49 (2018) 2232–2240.
D. Liang, Z. Yan, X. Lv, J. Zhang, C. Bai, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 48 (2017) 573–581.
J. Ji, Y. Cui, S. Wang, S. He, Q. Wang, X. Zhang, Ceram. Int. 48 (2022) 256–265.
Z.J. Wang, Q.F. Shu, S. Sridhar, M. Zhang, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 46 (2015) 758–765.
B. Mysen, L. Finger, V. David, F. Seifert. Am. Mineralogist 67(1982) 686–695.
B.O. Mysen, D. Virgo, F.A. Seifert, Rev. Geophys. 20 (1982) 353–383.
L.G. Hwa, S.L. Hwang, L.C. Liu, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 238 (1998) 193–197.
J. Li, Y. Sun, Z. Li, Z. Zhang, ISIJ Int. 56 (2016) 752–758.
R. Akagi, N. Ohtori, N. Umesaki, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 293–295 (2001) 471–476.
J. Tan, S. Zhao, W. Wang, G. Davies, X. Mo, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 106 (2004) 295–299.
B. Mysen, J. Frantz, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 117 (1994) 1–14.
Z. Wang, Q. Shu, K. Chou, ISIJ Int. 51 (2011) 1021–1027.
K.C. Mills, ISIJ Int. 33 (1993) 148–155.
X. Yan, W. Pan, X. Wang, X. Zhang, S. He, Q. Wang, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 52 (2021) 2526–2535.
Y. Sasaki, M. Iguchi, M. Hino, ISIJ Int. 47 (2007) 638–642.
D.L. Zheng, G.J. Ma, X. Zhang, M.K. Liu, J. Xu, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 30 (2023) 717–725.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for support from the National Natural Science Foundation China (Grant Nos. 52274317, 52074054, and 52004045), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. 2023CDJXY-020), and College of Materials Science and Engineering at Chongqing University, China, and the Henan Tongyu Metallurgy Materials Group Co. Ltd., Xixia, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, Yt., Wang, Xy., Zhang, Xb. et al. Viscosity and structure of CaO–BaO–SiO2–Al2O3-based mold slags for continuous casting of high titanium steel with different TiO2 absorption. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-024-01176-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-024-01176-8