Abstract
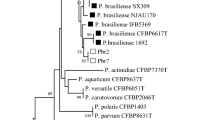
Strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa Duch.) is one of the high-economic soft fruit crops, which plays an important role in farmers’ incomes in Turkey. In a disease survey conducted in 2018 and 2019 growing seasons, typical disease symptoms resembling fire blight caused by Erwinia amylovora were observed in Yozgat and Mersin province of Turkey. The diseased strawberry plants showed intense black to brown necrotic areas in the midribs and veins on the leaf area and the attached stems. Twelve strains of E. amylovora were isolated from naturally infected strawberry plants on the basis of disease symptoms. The strains were initially characterized based on physiological, biochemical characters, and pathogenicity tests and identified using MALDI TOF MS analyses. All strains were identified as E. amylovora based on their protein fingerprint patterns obtained by the MALDI TOF MS system. The identification of representative strains was further confirmed by PCR amplification of a specific region by using taxon-specific primers, sequencing 16S rDNA and 3 housekeeping genes (gapA, mdh and recA). Obtained partial nucleotide sequences of each gene were submitted to BLAST analysis and strains shared 100% (for gapA), 99.45% (for mdh) and 100% (for recA) nucleotide identity with each other and sequence of complete genomes of E. amylovora strains available in GenBank. Constructed phylogenetic trees with concatenated sequences of gapA, mdh and recA genes allowed distinctly to separate strawberry E. amylovora strains from other Erwinia species. Representative bacterial strains were further tested for copper and streptomycin sensitivity. None of the strains grown on the nutrient medium containing 2.56 mM copper sulphate and 5 ppm streptomycin sulphate indicated that strawberry isolates are sensitive to copper and streptomycin for now. This study is the first report of a natural outbreak of bacterial fire blight disease caused by E. amylovora on strawberries in Turkey. Since disease is transmitted by bees, the presence of the pathogen may seriously influence local strawberry production in the future.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aksoy HM, Kaya Y, Ozturk M, Secgin Z, Onder H, Okumus A (2017) Pseudomonas putida–Induced response in phenolic profile of tomato seedlings (Solanum lycopersicum L.) infected by Clavibacter michiganensis subsp. michiganensis. Biol Control 105:6–12
Aktan ZC, Soylu S (2020) Prevalence and characterization of plant growth promoting mechanisms of endophytic and epiphytic bacterial species isolated from almond trees growing in Diyarbakır Province of Turkey. KSU J Agric Nat 23:641–654
Al-Daoude A, Arabi MIE, Ammouneh H (2009) Studying Erwinia amylovora isolates from Syria for copper resistance and streptomycin sensitivity. J Plant Pathol 91:203–205
Amirabad YM, Khodakaramian G (2017) Isolation and characterization of Erwinia piriflorinigrans causal agent flower necrosis of red poppy. Australas Plant Pathol 46(6):611–616
Anonymous (2019) FAOSTAT Agriculture Database, Crops and livestock products. https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL/visualize. Accessed 15 Jan 2018
Atanasova I, Kabadjova P, Bogatzevska N, Moncheva P (2005) New host plants of Erwinia amylovora in Bulgaria. Z Naturforsch C 60(11–12):893–898
Aysan Y, Mirik M, Sahin F, Kotan R, Saygili H (2006) Phenotypic characterization of Erwinia amylovora from pome fruits in Turkey. Acta Hortic 704:459–464
Bajpai S, Shukla PS, Adil M, Asiedu S, Pruski K, Prithiviraj B (2020) First report of bacterial leaf blight of strawberry caused by Pantoea ananatis in Nova Scotia. Canada Plant Dis 104(1):276–276
Barbé S, Bertolini E, Roselló M, Llop P, López MM (2014) Conventional and real-time PCRs for detection of Erwinia piriflorinigrans allow its distinction from the fire blight pathogen. Erwinia Amylovora Appl Environ Microbiol 80(8):2390–2398
Bastas KK (2012) First report of Erwinia amylovora on firethorn (Pyracantha coccinea) and Mountainash (Sorbus sp.) in Turkey. Plant Dis 96(12):1818–1818
Bastas KK, Sahin F (2012) First report of fire blight disease caused by Erwinia amylovora on rockspray (Cotoneaster horizontalis) in Turkey. Plant Dis 96(11):1690–1690
Bastas KK, Sahin F, Atasagun R (2013) First report of fire blight caused by Erwinia amylovora on rosehip (Rosa canina) in Turkey. Plant Dis 97(12):1652
Bastas KK, Ozturk AY (2013) First report of fire blight caused by Erwinia amylovora on crabapple (Malus floribunda) in Turkey. Plant Dis 97(9):1244–1244
Benlioglu K, Ozakman M (1999) Characterization of Turkish isolates of Erwinia amylovora (burr.) Winslow et al. Acta Hortic 489:127–132
Bastas KK, Sahin F (2014) First report of fire blight caused by Erwinia amylovora on meadowsweet (Spirea prunifolia) in Turkey. Plant Dis 98(1):153
Bereswill S, Jock S, Bellemann P, Geider K (1998) Identification of Erwinia amylovora by growth morphology on agar containing copper sulphate and by capsule staining with lectin. Plant Dis 82(2):158–164
Bull CT, Huerta AI, Koike ST (2009) First report of blossom blight of strawberry (Fragaria× ananassa) caused by Pseudomonas marginalis. Plant Dis 93(12):1350
Cha JS, Cooksey DA (1991) Copper resistance in Pseudomonas syringae mediated by periplasmic and outer membrane proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci 88(20):8915–8919
Cigna J, Dewaegeneire P, Beury A, Gobert V, Faure D (2017) A gapA PCR-sequencing assay for identifying the Dickeya and Pectobacterium potato pathogens. Plant Dis 101(7):1278–1282
Dardouri S, Chehimi S, Murillo Martínez J, Hajlaoui MR (2017) Molecular characterization of Tunisian strains of Erwinia amylovora. J Plant Pathol 99:331–337
Demirsoy L, Serçe S (2016) Strawberry culture in Turkey. Acta Hortic 1139:479–486
Demirsoy L, Mısır D, Nafiye ADAK (2017) Topraksız Tarımda Çilek Yetiştiriciliği. Anadolu Ege Tarım Araş Enst Derg 27(1):71–80
Duman K, Soylu S (2019) Characterization of antagonistic and plant growth-promoting traits of endophytic bacteria isolated from bean plants against Pseudomonas syringae pv. phaseolicola. Plant Protect Bull 59(3):59–69
EPPO (2013) PM 7/20 (2)* Erwinia amylovora. EPPO Bull 43(1):21–45
EPPO (2020) Erwinia amylovora. EPPO datasheets on pests recommended for regulation. Available online. https://gd.eppo.int
Geider K, Auling G, Du Z, Jakovljevic V, Jock S, Völksch B (2006) Erwinia tasmaniensis sp. nov., a non-phytopathogenic bacterium from apple and pear trees. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56(12):2937–2943
Goto M, Shıramatsu T, Nozaki K, Kawaguchi K (1978) Studies on bacterial wilt of strawberry caused by Pseudomonas solanacearum (Smith) Smith. Japanese J Phytopathol 44(3):270–276
Hauben L, Moore ER, Vauterin L, Steenackers M, Mergaert J, Verdonck L, Swings J (1998) Phylogenetic position of phytopathogens within the Enterobacteriaceae. Syst Appl Microbiol 21(3):384–397
Hepaksoy S, Ünal A, Can HZ, Saygili H, Türküsay H (1999) Distribution of fire blight (Erwinia amylovora (Burrill) Winslow et al.) disease in Western Anatolia region in Turkey. Acta Hortic 489:193–196
Holeva MC, Morán F, Scuderi G, Gonzalez A, López MM, Llop P (2019) Development of a real-time PCR method for the specific detection of the novel pear pathogen Erwinia uzenensis. PLoS One 14(7):e0219487
Ivanović M, Obadović A, Gašić K, Minsavage GV, Dickstein ER, Jones JB (2012) Exploring diversity of Erwinia amylovora population in Serbia by conventional and automated techniques and detection of new PFGE patterns. Eur J Plant Pathol 133(3):715–727
Janse JD, Rossi MP, Gorkink RFJ, Derks JJ, Swings J, Janssens D, Scortichini M (2001) Bacterial leaf blight of strawberry (Fragaria (x) ananassa) caused by a pathovar of Xanthomonas arboricola, not similar to Xanthomonas fragariae Kennedy & King Description of the causal organism as Xanthomonas arboricola pv. fragariae (pv. nov., comb. nov.). Plant Pathol 50(6):653–665
Jones AL, Geider K (2001) Erwinia amylovora group. In: Schaad NW, Jones JB, Chun W (eds) Laboratory Guide for Identification of Plant Pathogenic Bacteria, pp 40–55. APS Press, St. Paul, MN, USA
Juke TH, Cantor CR (1969) Evolution of protein molecules. Mammalian Protein Metabolism Vol 3 (Munro HN, ed)
Kafkas E (2017) Strawberry growing in Turkey: Current status and future prospects. Acta Hortic 1156:903–908
Kennedy BW, King TH (1962) Angular leaf spot of strawberry caused by Xanthomonas fragariae sp. nov. Phytopathol 52:873–875
Kim WS, Gardan L, Rhim SL, Geider K (1999) Erwinia pyrifoliae sp. nov., a novel pathogen that affects Asian pear trees (Pyrus pyrifolia Nakai). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 49(2):899–906
Kim WS, Hildebrand M, Jock S, Geider K (2001) Molecular comparison of pathogenic bacteria from pear trees in Japan and the fire blight pathogen Erwinia amylovora. Microbiol 147(11):2951–2959
Kıpçak C, Akköprü A (2017) The fire blight problem on apples in Lake Van basin: The status and incidence of the disease. YYU J Agric Sci 27(2):204–211
King EO, Ward MK, Raney DE (1954) Two simple media for the demonstration of pyocyanin and fluorescin. J Lab Clin Med 44(2):301–307
Laala S, Manceau C, Valentini F, Kerkoud M, Kheddam M (2012) Fire blight survey and first characterization of Erwinia amylovora isolates from Algeria. J Plant Pathol 94(3):693–696
Lamichhane JR, Osdaghi E, Behlau F, Köhl J, Jones JB, Aubertot JN (2018) Thirteen decades of antimicrobial copper compounds applied in agriculture. A Review Agron Sustain Dev 38(3):28
Lelliott RA, Stead DE (1987) Methods for the diagnosis of bacterial diseases of plants. Blackwell Scientific Publications
Loper JE, Henkels MD, Roberts RG, Grove GG, Willet MJ (1991) Evaluation of streptomycin, oxytetracycline, and copper resistance of Erwinia amylovora isolated from pear orchards in Washington State. Plant Dis 75(3):287–290
Lopez MM, Rosello M, Llop P, Ferrer S, Christen R, Gardan L (2011) Erwinia piriflorinigrans sp. nov., a novel pathogen that causes necrosis of pear blossoms. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61(3):561–567
Ma B, Hibbing ME, Kim HS, Reedy RM, Yedidia I, Breuer J, Breuer J, Glasner JD, Perna NT, Kelman A, Charlowski AO (2007) Host range and molecular phylogenies of the soft rot Enterobacterial genera Pectobacterium and Dickeya. Phytopathology 97(9):1150–1163
Maas JL (1998) Compendium of Strawberry Diseases, 2nd edn. APS Press, St. Paul, Minnesota, USA
Maas JL (2004) Strawberry disease management. In: Diseases of Fruits and Vegetables: Volume II Springer. Dordrecht pp 441–483
Mergaert J, Hauben L, Cnockaert MC, Swings J (1999) Reclassification of non-pigmented Erwinia herbicola strains from trees as Erwinia billingiae sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 49(2):377–383
Matsuura T, Mizuno A, Tsukamoto T, Shimizu Y, Saito N, Sato S, Sawada H (2012) Erwinia uzenensis sp. nov., a novel pathogen that affects European pear trees (Pyrus communis L.). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62(8):1799–1803
Matsuura T, Shinohara H, Inoue Y, Azegami K, Tsushima S, Tsukamoto T, Mizuno A (2007) Erwinia isolates from the bacterial shoot blight of pear in Japan are closely related to Erwinia pyrifoliae based on phylogenetic analyses of gyrB and rpoD genes. J General Plant Pathol 73(1):53–58
McGhee G, Sundin G (2012) Erwinia amylovora CRISPR elements provide new tools for evaluating strain diversity and for microbial source tracking. PLoS One 7:e41706
Mirmajlessi SM, Destefanis M, Gottsberger RA, Mänd M, Loit E (2015) PCR-based specific techniques used for detecting the most important pathogens on strawberry: a systematic review. Syst Rev 4(1):9
Mizuno A, Tsukamoto T, Shimizu Y, Ooya H, Matsuura T, Saito N, Sato S, Kikuchi S, Uzuki T, Azegami K (2010) Occurrence of bacterial black shoot disease of European pear in Yamagata Prefecture. J Gen Plant Pathol 76(1):43–51
Momol MT, Zeller W (1992) Identification and spread of Erwinia amylovora on pear in Turkey. Plant Dis 76(11):1114–1116
Momol MT, Aldwinckle HS (2000) Genetic diversity and host range of Erwinia amylovora. In: Vanneste JL (ed) Fire blight: the disease and its causative agent, Erwinia amylovora. CAB International, New York, NY, pp 55–72
Naum M, Brown EW, Mason-Gamer RJ (2008) Is 16S rDNA a reliable phylogenetic marker to characterize relationships below the family level in the Enterobacteriaceae?. J Mol Evol 66(6):630–642
Nourrisseau JG, Lansac M, Garnier M (1993) Marginal chlorosis, a new disease of strawberries associated with a bacterium-like organism. Plant Dis 77(10):1055–1059
Öktem YE, Benlioğlu K (1988) Studies on fire blight (Erwinia amylovora (Burr.) Winslow et al.) of pome fruits. J Turk Phytopathol 17(3):106
Panda A, Kurapati S, Samantaray JC, Myneedu VP, Verma A, Srinivasan A, Ahmad H, Behera D, Singh UB (2013) Rapid identification of clinical mycobacterial isolates by protein profiling using matrix assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. Indian J Med Microbiol 31:117–122
Pavlovic M, Konrad R, Iwobi AN, Sing A, Busch U, Huber I (2012) A dual approach employing MALDI-TOF MS and real-time PCR for fast species identification within the Enterobacter cloacae complex. FEMS Microbiol Lett 328:46–53
Powney R, Smits TH, Sawbridge T, Frey B, Blom J, Frey JE, Plummer KM, Beer SV, Luck J, Duffy B, Rodoni B (2011) Genome sequence of an Erwinia amylovora strain with pathogenicity restricted to Rubus plants. J Bacteriol 193(3):785–786
Puławska J, Sobiczewski P (2012) Phenotypic and genetic diversity of Erwinia amylovora: the causal agent of fire blight. Trees 26(1):3–12
Rezzonico F, Smits TH, Born Y, Blom J, Frey JE, Goesmann A, Montesinos E (2016) Erwinia gerundensis sp. nov., a cosmopolitan epiphyte originally isolated from pome fruit trees. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66(3):1583–1592
Rhim SL, Völksch B, Gardan L, Paulin JP, Langlotz C, Kim WS, Geider K (1999) Erwinia pyrifoliae, an Erwinia species different from Erwinia amylovora, causes a necrotic disease of Asian pear trees. Plant Pathol 48(4):514–520
Roselló M, Peñalver J, Llop P, Gorris MT, Cambra M, López MM, Montón C (2006) Identification of an Erwinia sp. different from Erwinia amylovora and responsible for necrosis on pear blossoms. Can J Plant Pathol 28(1):30–41
Sahin M, Mısırlı A, Ozaktan H, Kucuk E, Gokkur S, Aksoy D, Cavdar A (2020) Evaluation of Turkey quince genebank for resistance breeding to fire blight disease. Acta Hortic 1282:59–66
Saleeb PG, Drake SK, Murray PR, Zelazny AM (2011) Identification of mycobacteria in solid-culture media by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. J Clin Microbiol 49:1790–1794
Schaad NW, Jones JB, Chun W (2001) Laboratory guide for the identification of plant pathogenic bacteria (3rd Ed). Am Phytopathol Soc (APS Press)
Singhal N, Kumar M, Kanaujia PK, Virdi JS (2015) MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry: an emerging technology for microbial identification and diagnosis. Front Microbiol 6:791
Smits TH, Rezzonico F, Kamber T, Blom J, Goesmann A, Frey JE, Duffy B (2010) Complete genome sequence of the fire blight pathogen Erwinia amylovora CFBP 1430 and comparison to other Erwinia spp. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 23(4):384–393
Soylu EM, Soylu S, Kara M, Kurt Ş (2020) Determinations of in vitro antagonistic effects of microbiomes isolated from vermicompost against major plant fungal disease agents of vegetables. KSU J Agric Nat 23:7–18
Sundin GW, Bender CL (1993) Ecological and genetic analysis of copper and streptomycin resistance in Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae. Appl Environ Microbiol 59(4):1018–1024
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30(12):2725–2729
Taylor RK, Guilford PJ, Clark RG, Hale CN, Forster RLS (2001) Detection of Erwinia amylovora in plant material using novel polymerase chain reaction (PCR) primers. N Z J Crop Hortic Sci 29(1):35–43
Van der Zwet T (2006) Present worldwide distribution of fire blight and closely related diseases. Acta Hortic 704:35–36
Van der Zwet T, Keil HL (1979) Fire blight, a bacterial disease of rosaceous plants. USDA Agriculture Handbook 510, Science and Education Administration USDA. Washington DC USA 200 pp
Waleron M, Waleron K, Podhajska AJ, Łojkowska E (2002) Genotyping of bacteria belonging to the former Erwinia genus by PCR-RFLP analysis of a recA gene fragment. Microbiol 148(2):583–595
Weisburg WG, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Lane DJ (1991) 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173(2):697–703
Wensing A, Gernold M, Geider K (2012) Detection of Erwinia species from the apple and pear flora by mass spectroscopy of whole cells and with novel PCR primers. J Appl Microbiol 112(1):147–158
Wenneker M, Bergsma-Vlami M (2015) Erwinia pyrifoliae, a new pathogen on strawberry in the Netherlands. J Berry Res 5(1):17–22
Zhang Y, Jock S, Geider K (2000) Genes of Erwinia amylovora involved in yellow color formation and release of a low-molecular-weight compound during growth in the presence of copper ions. Mol Gen Genet 264(3):233–240
Zreik L, Bove JM, Garnier M (1998) Phylogenetic characterization of the bacterium-like organism associated with marginal chlorosis of strawberry and proposition of a Candidatus taxon for the organism ‘Candidatus Phlomobacter fragariae’. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 48(1):257–261
Acknowledgements
This study was supported financially by a grant from the Office of Scientific Research Projects Coordination of Yozgat Bozok University (Project no. 6602c-ZF/18-190). The author would like to sincerely thank A. Demirci diligent proofreading of this manuscript. The authors would like to thank Prof. Dr. Aleksa Obradovic for supplying the refence strains of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Research involving human participants and/or animals
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any authors.
Informed consent
This manuscript is new and not being considered elsewhere. The authors have read and approved the submission of this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest for this submission.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Öztürk, M., Soylu, S. A new disease of strawberry, bacterial blight caused by Erwinia amylovora in Turkey. J Plant Pathol 104, 269–280 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42161-021-00994-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42161-021-00994-z