Abstract
Objective
To quantitatively compare the diagnostic and differential diagnostic value of intra-voxel incoherent motion imaging (IVIM) and diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) for prostate cancer (PCa) and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
Methods
68 cases of prostate confirmed by pathology, including 33 cases of PCa and 35 cases of BPH were analyzed retrospectively. All patients were underwent T1WI, T2WI, DWI and IVIM sequences to obtain the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), pure apparent diffusion coefficient (Pure-ADC/D), standard apparent diffusion coefficient (standard-ADC/Ds), fast apparent diffusion coefficient (fast-ADC/D*), fraction of fast apparent diffusion coefficient (f) values. All the multiple parameters were statistically analyzed for the differential diagnosis of BPH and PCa. P < 0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
Results
The differences in D, Ds, f and ADC values between BPH and PCa groups were statistically significant (all P values < 0.001), respectively. Among them, D value in the IVIM model had the highest diagnostic efficiency for PCa, the area under the curve (AUC) was 0.967, and the AUC combined with the ADC value and D value reaches 0.973.
Conclusion
The diagnostic efficacy of multiple parameters in the IVIM model for PCa was higher than the ADC value of the quantitative parameter of DWI. D value had the highest diagnostic efficiency. The combined diagnosis of ADC and D value was more effective, more advantageous in the diagnosis and differential diagnosis of PCa.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
PCa was one of the most common malignant tumors in elderly men. Although the prevalence of prostate cancer in East Asian men was lower than that in Western, autopsy studies and evaluations of prostatectomy specimens prove that its prevalence was similar to that in Western countries [1, 2]. DWI was a conventional MRI imaging sequences currently used for prostate cancer [3]. It could assess the diffusion activity of water molecules in biological tissues, meanwhile, it provided a quantitative parameter ADC value representing the level of diffusion. However, there was a certain degree of overlap between the ADC values of PCa and BPH [4, 5], which leaded to false positives in the diagnosis of PCa [6]. In addition, the diffusion of water molecules was also partly affected by the microcirculation blood perfusion. Bihan et al. [7] firstly proposed the IVIM model with parameters including D, Ds, D* and f. Its advantage was that can effectively separate the diffusion of water molecules from microvascular perfusion without using a contrast agent. In recent years, studies have reported that the quantitative parameters of the IVIM model showed high sensitivity and specificity in the detection and differential diagnosis of tumors in different organs [8, 9]. In this experiment, self-developed professional software was used for image post-processing, which could more accurately quantify the diagnostic and differential diagnosis value of the two models of IVIM and DWI for PCa. In addition, the study compared the diagnostic efficacy of conventional DWI and IVIM sequences for PCa, and intended to find quantitative parameters with higher diagnostic value to further evaluate the invasiveness of PCa lesions noninvasively.
Materials and methods
Clinical data
The study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of our hospital, and all the subjects signed the informed consent. Retrospective analysis of MRI data of 68 prostate cases in our hospital from November 2016 to July 2018. Age ranges 46–85 years. All pathological results were confirmed by rectal ultrasound guided puncture or radical surgery within 2 weeks after MRI examination was completed. The samples inclusion and exclusion criteria were shown in Fig. 1. Among them, 33 patients in the PCa group were (70.2 ± 9.6) years old, 17 cases were confirmed by ultrasound-guided needle biopsy (standard 5 zone 13 needle method) and 16 cases were confirmed by radical surgery; 35 patients in the BPH group were (66.3 ± 9.9) years old. There was no statistical difference in age between the groups (P > 0.05). The level of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) was 1.9–360.9 ng/ml. The Gleason score from 6 to 10, with relatively few cases in the low-risk group.
MR examination method
All the data were acquired by GE 750 superconducting 3.0 T MR (GE, USA) scanning. The 8-channel phased array surface coil of the abdomen was used to complete the acquisition. The patient cleaned the intestines the night before the examination, and drank moderately before the examination to fill the bladder moderately. The imaging plan included conventional axial, coronal and sagittal T2WI, small field of vision (FOV) T2WI, axial T1WI, DWI and IVIM sequences. The coronal T2WI adopted the fast recovery fast spin-echo (FRFSE) fat-reducing sequences. T2WI with small axial FOV adopted FRFSE sequences. DWI used echo planar imaging (EPI) technology, and the b values were 0, and 1000 s/mm2. IVIM adopted single excitation EPI technology, and multi-b values were 0, 10, 20, 40, 80, 150, 200, 400, 800, 1000, 1200, 1500, 1700, 2000, 2500, 3000, and 3500 s/mm2. The relevant parameters of each sequence scan protocol were shown in Table 1.
Image processing
After the MRI examinations were completed, data were analyzed by two radiologists with more than 5 years of experience in the diagnosis of urogenital MRI before the pathological results were turned out. The original images were imported into the AW4.6 post-processing workstation to generate post-processing diagrams of various parameters. The post-processed image was transferred to the self-developed MedFIA V1.0 [9] (National Software Registration Right, 2014SR014913) software, and the ADC, D, Ds, D* and f value of the lesions were measured. We tested and improved the software in detail in the previous study on quantitative evaluation of early efficacy of liver cancer embolization. Principle of ROI placement: it was outlined (three consecutive scan levels) along the margin containing the maximum contour of the solid component of the lesion on the transection map and avoided cystic change, hemorrhage, calcification and normal prostate tissue (Fig. 2). PCa was measured when multiple lesions were in which the largest diameter was measured; ticked the three consecutive scan levels that showed the greatest contour of the hyperplastic nodule at the ROI. Those with multifocal hyperplasia were ticked three consecutive levels containing the maximum contour of the central zone of the prostate as an ROI.
Statistical methods
SPSS V25 statistical software was used for data analysis. The intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) was used to measure the reliability of measurement parameters between two physicians. The normal distribution (KS) test within the group was performed first, and independent sample t test was used to compare the DWI and IVIM model parameters ADC, D, Ds, D* and f values between the two groups. The diagnostic efficacy of each parameter for PCa was analyzed by ROC. P < 0.05 was statistically different.
Results
Inter-observer measurement reliability and consistency test and within-group normal distribution test
After testing the ICC values of ADC, D, DS, D* and f values were all > 0.75 (Table 2), the interobserver reliability of the measured parameters was good and the interobserver agreement of the measured parameters was high for all quantitative parameters in the study. Using K–S non-parametric test method, it was proved that all data obeyed normal distribution.
Comparison of quantitative parameter values of DWI and IVIM in PCa and BPH
The measurement results of each quantitative parameter were shown in Table 3. The original images of T2WI, ADC and pseudo-color images of each parameter were shown in Fig. 3. By independent samples t-test, it was concluded that the PCa group had lower ADC, D, DS as well as f values than the BPH group, with significant statistical significance (P < 0.001).The diagnostic potencies of ADC, D, D*, DS as well as f were shown in Fig. 4.When the diagnostic cut-off values of ADC, D, Ds, and f were 0.371 × 10−3 s/mm2, 0.699 × 10−3 s/mm2, 0.637 × 10−3 s/mm2 and 48.705%, the sensitivity and specificity for discriminating between BPH and PCa were (91.4%, 75.8%), (88.6%, 97.0%), (91.4%, 90.9%) and (91.4%, 87.9%), respectively. The 95% CI were 0.815–0.974, 0.928–1.000, 0.874–1.000 and 0.861–0.992, respectively.
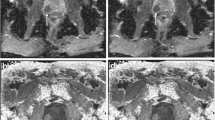
Male, 62 years old, diagnosed with PCa. a DWI sequences, there is a patchy signal reduction area in the right peripheral zone of the prostate, and the boundary is unclear, breaking through the right side of the prostate (arrow); b ADC image, the lesion is located in the peripheral area of the prostate, and a significant signal reduction area is visible (arrow); c–f pseudo-color post-processing images of D, D*, Ds, and f, respectively, and the lesions are shown in the figure (arrow). Pathological results: prostate cancer; Gleason Score: 4 + 3
Analysis of the diagnostic efficacy of IVIM combined with DWI quantitative parameters for PCa
After logistic regression analysis, the probability of each parameter was obtained. The ROC curve showed that the ADC value combined with the D value had the highest diagnostic efficiency (AUC = 0.973, 95% CI 0.941–1.000, Fig. 5). The sensitivity and specificity for distinguishing BPH and PCa were 94.3% and 93.9%, respectively.
Discussion
Multiparameter MRI of the prostate was composed of anatomical sequences and functional sequences. T2WI was mainly used for anatomical evaluation. Although DWI was mainly used for functional evaluation, the conventional DWI was only based on a single index model. Luciani et al. [11] and Liu et al. [12] found that the limited diffusion observed in cirrhotic liver was not only pure molecular diffusion, but also affected by microcirculation perfusion. The curves of DWI in breast malignant tumors, benign lesions and normal tissues showed a double exponential fit. Meanwhile, IVIM sequences based on the double exponential model, can simultaneously capture both diffusion and perfusion information and measure them separately. In the recent years, IVIM has gradually become a new research focus in multiple systems.
In the experiment, the values of D, DS as well as f were lower in the PCa group than in the BPH group. The above results were consistent with the conclusions drawn by the IVIM research using different b-value combinations [13, 14]. Among them, the area under the curve of D value, which characterizes the diffusion level of pure water molecules, was the largest one. The above results were as same as the research conclusions of Lei et al. [15]. Of the two model parameters in the study, D* value had the lowest sensitivity and specificity in distinguishing prostate hyperplasia and prostate cancer, this result was similar to the related studies on renal lesions [16], the reason for analysis may be related to the degree of tumor vascular differentiation among different tumors as well as the existence of differences in types. The experiment of Beyhan et al. [17] showed lower f values in benign prostate tissue than in malignant tumors, and the results of this experiment showed smaller f values in the PCa group than in the BPH group, which contradicts the theory of intratumoral angiogenesis demonstrated in dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI [18], and the reason for this result can be explained by the theory that f not only reflected perfusion but also was more sensitive to the flow of glandular secretions and fluid; another reason may be that part of PCa was secondary to chronic inflammation of the prostate caused by nutritional factors or hormones. Chronic inflammation and the deposition of collagen fibers can change the brownian motion level of water molecules and the blood flow of the prostate capillaries.
The improvement of IVIM relative to DWI mathematical modeling may improve the accuracy of its curve fitting signal attenuation behavior [19]. This experiment found that compared with conventional DWI, IVIM parameters effectively improved the diagnostic performance, and when used in combination with conventional DWI, the specificity was increased from 75.8 to 93.9%, and the sensitivity was increased from 91.4 to 94.3%. Therefore, it provided more accurate microenvironmental information using IVIM bi-exponential model with multiple b-values to analyze prostate lesions, which was particularly important for the diagnosis, prognosis, and evaluation of curative effects in patients with renal insufficiency who were not injected with contrast media. In addition, the difference of parameter values in the different models above may represent the nature of the lesions as well as different grades, which was very helpful for clinical surgery and biopsy targeting.
In the past, many small sample methods [20] were used to measure the average value of the parameters in the selected ROI, so a certain degree of sampling deviation was inevitably produced. In the study, the self-developed MedFIA V1.0 medical functional imaging analysis software used a semi-automatic method to outline tumor tissue as a whole, which could effectively avoid normal prostate tissue, necrosis, and calcification, thereby reducing the subjectivity of ROI setting.
There were some shortcomings in the study. Firstly, the pathologic findings in approximately only half of the cases were obtained by radical prostatectomy. Secondly, it was not possible to completely rule out the possibility of a false negative result because of the small sample size. Sufficient experimental evidence shown that the deviation of the diffusion model from Gaussian diffusion appeared as a double exponential form when the range of b-value increased [21]. When the contribution of non-Gaussian diffusion was ignored, it was not clear in the IVIM model how high the value of b should be to avoid this deviation [22], but studies found that [23] the error of parameter measurement decreases as the number of b-values increases. Therefore, we used 16 b-values in our study to characterize the nature of the lesion more accurately, although the plausibility still needs further investigation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, IVIM model provided more accurate quantitative parameters than DWI sequences, and had the potential to become a routine sequences for prostate scanning. In our experiment, PCa foci occurring in the peripheral zone as well as the transitional zone were not subdivided. Previous studies suggested that the sites of tumorigenesis are different (transitional zone and peripheral zone) [17], and their parameters of blood perfusion and water molecule diffusion might also appear to differ to some extent, which required further refinement of the experimental design in future studies.
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67(1):7–30. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21387.
Monn MF, Tatem AJ, Cheng L. Prevalence and management of prostate cancer among East Asian men: current trends and future perspectives. Urol Oncol Semin Orig Investig. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urolonc.2015.09.003.
Haider MA, Van KTH, Tanguay J, et al. Combined T2-weighted and diffusion-weighted MRI for localization of prostate cancer. Am J Roentgenol. 2007;189(2):323–8. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.07.2211.
Panebianco V, Barchetti F, Sciarra A, et al. Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging vs. standard care in men being evaluated for prostate cancer: a randomized study. Urol Oncol Semin Orig Investig. 2015;33(1):17.e1-17.e7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urolonc.2014.09.013.
Oto A, Kayhan A, Jiang Y, et al. Prostate cancer: differentiation of central gland cancer from benign prostatic hyperplasia by using diffusion-weighted and dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology. 2010;257(3):715–23. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.10100021.
Hakmin L, Il HS, Jong LH, et al. Diagnostic performance of diffusion-weighted imaging for prostate cancer: peripheral zone versus transition zone. PLoS ONE. 2018;13(6):e0199636. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0199636.
Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, et al. Separation of diffusion and perfusion in intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging. Radiology. 1988;168(2):497–505. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.168.2.3393671.
Ma W, Zhang G, Ren J, et al. Quantitative parameters of intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion weighted imaging (IVIM-DWI): potential application in predicting pathological grades of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2018;8(3):301. https://doi.org/10.21037/qims.2018.04.08.
Pesapane F, Patella F, Fumarola EM, et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) in the periferic prostate cancer detection and stratification. Med Oncol. 2017;34(3):35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-017-0892-7.
Fang R, Yingjuan C, Qi P, et al. Design and application of DWI-based quantitative evaluation software for early hepatocarcinoma embolization. China Med Equip. 2018;2:123–5. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1674-1633.2018.02.032.
Luciani A, Vignaud A, Cavet M, et al. Liver cirrhosis: intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging-pilot study. Radiology. 2009;249(3):891–9. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2493080080.
Liu C, Liang C, Liu Z, et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) in evaluation of breast lesions: comparison with conventional DWI. Eur J Radiol. 2013;82(12):e782–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2013.08.006.
Mazaheri Y, Vargas HA, Akin O, et al. Reducing the influence of b-value selection on diffusion-weighted imaging of the prostate: evaluation of a revised monoexponential model within a clinical setting. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012;35(3):660–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.22888.
Valerio M, Zini C, Fierro D, et al. 3T multiparametric MRI of the prostate: does intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion imaging have a role in the detection and stratification of prostate cancer in the peripheral zone? Eur J Radiol. 2016;85(4):790–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2016.01.006.
Zhou L, Peng J, Hu H, et al. Meta-analysis of the value of molecular diffusion coefficient in the diagnosis of prostate cancer in diffusion-weighted imaging of incoherent motion within voxel. Radiol Pract. 2019;34(9):1007–12 ((CNKI:SUN:FSXS.0.2019-09-020)).
Chandarana H, Lee VS, Hecht E, et al. Comparison of biexponential and monoexponential model of diffusion weighted imaging in evaluation of renal lesions. Investig Radiol. 2010;46(5):285–91. https://doi.org/10.1097/rli.0b013e3181ffc485.
Beyhan M, Sade R, Koc E, et al. The evaluation of prostate lesions with IVIM DWI and MR perfusion parameters at 3T MRI. La Radiol Med. 2019;124(2):87–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-018-0930-3.
Franiel T, Hamm B, Hricak H. Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging and pharmacokinetic models in prostate cancer. Eur Radiol. 2011;21(3):616–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-010-2037-7.
Shinmoto H, Tamura C, Soga S, et al. An intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging study of prostate cancer. Am J Roentgenol. 2012;199(4):W496-500. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.11.8347.
Tamura C, Shinmoto H, Soga S, et al. Diffusion kurtosis imaging study of prostate cancer: preliminary findings. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015;40(3):723–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.24379.
Shinmoto H, Oshio K, Tanimoto A, et al. Biexponential apparent diffusion coefficients in prostate cancer. Magn Reson Imaging. 2009;27(3):355–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mri.2008.07.008.
Pang Y, Turkbey B, Bernardo M, et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) MR imaging for prostate cancer: an evaluation of perfusion fraction and diffusion coefficient derived from different b-value combinations. Magn Reson Med. 2013;69(2):553–62. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.24277.
Malagi AV, Das CJ, Khare K, et al. Effect of combination and number of b values in IVIM analysis with post-processing methodology: simulation and clinical study. MAGMA Magn Reson Mater Phys Biol Med. 2019;32(5):519–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-019-00764-0.
Acknowledgements
This manuscript was supported by Health research fund of Shaanxi Province, China, no. 2016D070.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving Human Participants and/or animals
The experiment was approved by the local ethical committee and the institutional review board. All processes involved in the experiment comply with the Helsinki Declaration formulated by the World Medical Association. Retrospective analysis of MRI data of 68 prostate cases in our hospital from November 2016 to July 2018. Age ranges 46–85 years. All the patients underwent MR scanning and gave informed consent. The samples inclusion and exclusion criteria were shown in Fig. 1.
Informed consent
All the subjects signed the informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, R., Liu, W., Ren, F. et al. Comparative study of diagnostic value between IVIM and DWI for prostate cancer at 3.0 T magnetic resonance. Chin J Acad Radiol 4, 186–193 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42058-021-00079-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42058-021-00079-x