Abstract
Objective
Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is the leading cause of end-stage renal disease around the world. This study investigated the role of microRNA (miR)-29b-3p in DN and the mechanism of the miR-29b-3p/EZH2 axis in DN.
Methods
Peripheral blood samples of DN patients were collected and miR-29b-3p and EZH2 expression levels were evaluated using RT-qPCR. DN mouse models were successfully established, and then treated with miR-29b-3p overexpression or EZH2 silence. IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α levels were assessed by ELISA. Blood glucose, serum creatinine (Scr), 24-h urine volume, 24-h urine protein, and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) levels were examined by automatic biochemical analyzer detection. HE staining was performed to observe the renal histopathology, and TUNEL staining was implemented to test apoptosis in renal tissues. The binding relationship between miR-29b-3p and EZH2 was validated by using a bioinformatics website and dual luciferase reporter gene assay.
Results
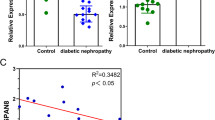
miR-29b-3p was lowly expressed, and EZH2 was highly expressed in patients with DN. Overexpressing miR-29b-3p or silencing EZH2 attenuated renal dysfunction, suppressed inflammation and apoptosis, and relieved renal injuries in mice with DN. miR-29b-3p inhibited EZH2, and miR-29b-3p overexpression mitigated renal injuries in DN mice by repressing EZH2.
Conclusion
miR-29b-3p suppresses EZH2 expression thereby inhibiting the progression of DN in mice.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu D, Zheng W, Pan S, Liu Z (2020) Concise review: current trends on applications of stem cells in diabetic nephropathy. Cell Death Dis 11(11):1000. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-03206-1
Bonner R, Albajrami O, Hudspeth J, Upadhyay A (2020) Diabetic kidney disease. Prim Care 47(4):645–659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pop.2020.08.004
Selby NM, Taal MW (2020) An updated overview of diabetic nephropathy: diagnosis, prognosis, treatment goals and latest guidelines. Diabetes Obes Metab 22(Suppl 1):3–15. https://doi.org/10.1111/dom.14007
Leoncini G, Viazzi F, De Cosmo S, Russo G, Fioretto P, Pontremoli R (2020) Blood pressure reduction and RAAS inhibition in diabetic kidney disease: therapeutic potentials and limitations. J Nephrol 33(5):949–963. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-020-00803-3
Yarahmadi A, Shahrokhi SZ, Mostafavi-Pour Z, Azarpira N (2021) MicroRNAs in diabetic nephropathy: From molecular mechanisms to new therapeutic targets of treatment. Biochem Pharmacol 189:114301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114301
Sankrityayan H, Kulkarni YA, Gaikwad AB (2019) Diabetic nephropathy: the regulatory interplay between epigenetics and microRNAs. Pharmacol Res 141:574–585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2019.01.043
Peters LJF, Floege J, Biessen EAL, Jankowski J, van der Vorst EPC (2020) MicroRNAs in chronic kidney disease: four candidates for clinical application. Int J Mol Sci 21(18). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186547
Gondaliya P, DasareJash APK, Tekade RK, Srivastava A, Kalia K (2020) miR-29b attenuates histone deacetylase-4 mediated podocyte dysfunction and renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy. J Diabetes Metab Disord 19(1):13–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-019-00469-0
Xing LN, Wang H, Yin PH, Liu YJ, Chi YF, Wang YM, Peng W (2014) Reduced mir-29b-3p expression up-regulate CDK6 and contributes to IgA nephropathy. Int J Clin Exp Med 7(12):5275–5281
Zhang X, Zhao X, Fiskus W, Lin J, Lwin T, Rao R, Zhang Y, Chan JC, Fu K, Marquez VE, Chen-Kiang S, Moscinski LC, Seto E, Dalton WS, Wright KL, Sotomayor E, Bhalla K, Tao J (2012) Coordinated silencing of MYC-mediated miR-29 by HDAC3 and EZH2 as a therapeutic target of histone modification in aggressive B-Cell lymphomas. Cancer Cell 22(4):506–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2012.09.003
Li Z, Yu Z, Meng X, Yu P (2018) LncRNA LINC00968 accelerates the proliferation and fibrosis of diabetic nephropathy by epigenetically repressing p21 via recruiting EZH2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 504(2):499–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.08.048
Komers R, Mar D, Denisenko O, Xu B, Oyama TT, Bomsztyk K (2013) Epigenetic changes in renal genes dysregulated in mouse and rat models of type 1 diabetes. Lab Invest 93(5):543–552. https://doi.org/10.1038/labinvest.2013.47
Wan J, Hou X, Zhou Z, Geng J, Tian J, Bai X, Nie J (2017) WT1 ameliorates podocyte injury via repression of EZH2/beta-catenin pathway in diabetic nephropathy. Free Radic Biol Med 108:280–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.03.012
Zhou X, Zang X, Guan Y, Tolbert T, Zhao TC, Bayliss G, Zhuang S (2018) Targeting enhancer of zeste homolog 2 protects against acute kidney injury. Cell Death Dis 9(11):1067. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-1012-0
Li T, Yu C, Zhuang S (2021) Histone methyltransferase EZH2: a potential therapeutic target for kidney diseases. Front Physiol 12:640700. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2021.640700
Li Y, Yu W, Xiong H, Yuan F (2022) Circ_0000181 regulates miR-667-5p/NLRC4 axis to promote pyroptosis progression in diabetic nephropathy. Sci Rep 12(1):11994. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-15607-7
Zhang L, Zhao S, Zhu Y (2020) Long noncoding RNA growth arrest-specific transcript 5 alleviates renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy by downregulating matrix metalloproteinase 9 through recruitment of enhancer of zeste homolog 2. FASEB J 34(2):2703–2714. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201901380RR
Li HY, Oh YS, Choi JW, Jung JY, Jun HS (2017) Blocking lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 signaling inhibits diabetic nephropathy in db/db mice. Kidney Int 91(6):1362–1373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2016.11.010
Chen H, Jin G (2021) Downregulation of Salusin-beta protects renal tubular epithelial cells against high glucose-induced inflammation, oxidative stress, apoptosis and lipid accumulation via suppressing miR-155-5p. Bioengineered 12(1):6155–6165. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2021.1972900
Zhang S, Wang H, Liu Y, Yang W, Liu J, Han Y, Liu Y, Liu F, Sun L, Xiao L (2020) Tacrolimus ameliorates tubulointerstitial inflammation in diabetic nephropathy via inhibiting the NFATc1/TRPC6 pathway. J Cell Mol Med 24(17):9810–9824. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.15562
Luo W, Chen X, Ye L, Chen X, Jia W, Zhao Y, Samorodov AV, Zhang Y, Hu X, Zhuang F, Qian J, Zheng C, Liang G, Wang Y (2021) Kaempferol attenuates streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy by downregulating TRAF6 expression: the role of TRAF6 in diabetic nephropathy. J Ethnopharmacol 268:113553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2020.113553
Wang L, Li H (2020) MiR-770-5p facilitates podocyte apoptosis and inflammation in diabetic nephropathy by targeting TIMP3. Biosci Rep 40(4). 10.1042/BSR20193653
Ji TT, Qi YH, Li XY, Tang B, Wang YK, Zheng PX, Li W, Qu X, Feng L, Bai SJ (2020) Loss of lncRNA MIAT ameliorates proliferation and fibrosis of diabetic nephropathy through reducing E2F3 expression. J Cell Mol Med 24(22):13314–13323. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.15949
Yang Q, Wu F, Mi Y, Wang F, Cai K, Yang X, Zhang R, Liu L, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Wang X, Xu M, Gui Y, Li Q (2020) Aberrant expression of miR-29b-3p influences heart development and cardiomyocyte proliferation by targeting NOTCH2. Cell Prolif 53(3):e12764. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.12764
Zheng T, Wang HY, Chen Y, Chen X, Wu ZL, Hu QY, Sun H (2022) Src activation aggravates podocyte injury in diabetic nephropathy via suppression of FUNDC1-mediated mitophagy. Front Pharmacol 13:897046. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.897046
Zeng Y, Cui Z, Liu J, Chen J, Tang S (2019) MicroRNA-29b-3p promotes human retinal microvascular endothelial cell apoptosis via Blocking SIRT1 in diabetic retinopathy. Front Physiol 10:1621. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2019.01621
Wang B, Komers R, Carew R, Winbanks CE, Xu B, Herman-Edelstein M, Koh P, Thomas M, Jandeleit-Dahm K, Gregorevic P, Cooper ME, Kantharidis P (2012) Suppression of microRNA-29 expression by TGF-beta1 promotes collagen expression and renal fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 23(2):252–265. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2011010055
Al Dhaybi O, Bakris GL (2020) Non-steroidal mineralocorticoid antagonists: prospects for renoprotection in diabetic kidney disease. Diabetes Obes Metab 22(Suppl 1):69–76. https://doi.org/10.1111/dom.13983
Rudnicki M, Beckers A, Neuwirt H, Vandesompele J (2015) RNA expression signatures and posttranscriptional regulation in diabetic nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 30 Suppl 4: iv35–42. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfv079.
Li YY, Xu QW, Xu PY, Li WM (2020) MSC-derived exosomal miR-34a/c-5p and miR-29b-3p improve intestinal barrier function by targeting the Snail/Claudins signaling pathway. Life Sci 257:118017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118017
Drummond CA, Fan X, Haller ST, Kennedy DJ, Liu J, Tian J (2018) Na/K-ATPase signaling mediates miR-29b-3p regulation and cardiac fibrosis formation in mice with chronic kidney disease. PLoS One 13(5):e0197688. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0197688
Patel V, Noureddine L (2012) MicroRNAs and fibrosis. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 21(4):410–416. https://doi.org/10.1097/MNH.0b013e328354e559
Shi S, Song L, Yu H, Feng S, He J, Liu Y, He Y (2020) Knockdown of LncRNA-H19 ameliorates kidney fibrosis in diabetic mice by suppressing miR-29a-mediated EndMT. Front Pharmacol 11:586895. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.586895
Ebadi Z, Moradi N, Kazemi Fard T, Balochnejadmojarrad T, Chamani E, Fadaei R, Fallah S (2019) Captopril and Spironolactone can attenuate diabetic nephropathy in Wistar rats by targeting microRNA-192 and microRNA-29a/b/c. DNA Cell Biol 38(10):1134–1142. https://doi.org/10.1089/dna.2019.4732
Sun SF, Tang PMK, Feng M, Xiao J, Huang XR, Li P, Ma RCW, Lan HY (2018) Novel lncRNA Erbb4-IR promotes diabetic kidney injury in db/db mice by targeting miR-29b. Diabetes 67(4):731–744. https://doi.org/10.2337/db17-0816
Chen HY, Zhong X, Huang XR, Meng XM, You Y, Chung AC, Lan HY (2014) MicroRNA-29b inhibits diabetic nephropathy in db/db mice. Mol Ther 22(4):842–853. https://doi.org/10.1038/mt.2013.235
Stamato MA, Juli G, Romeo E, Ronchetti D, Arbitrio M, Caracciolo D, Neri A, Tagliaferri P, Tassone P, Amodio N (2017) Inhibition of EZH2 triggers the tumor suppressive miR-29b network in multiple myeloma. Oncotarget 8(63):106527–106537. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.22507
Yin H, Wang Y, Wu Y, Zhang X, Zhang X, Liu J, Wang T, Fan J, Sun J, Yang A, Zhang R (2020) EZH2-mediated epigenetic silencing of miR-29/miR-30 targets LOXL4 and contributes to tumorigenesis, metastasis, and immune microenvironment remodeling in breast cancer. Theranostics 10(19):8494–8512. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.44849
Liu DW, Zhang JH, Liu FX, Wang XT, Pan SK, Jiang DK, Zhao ZH, Liu ZS (2019) Silencing of long noncoding RNA PVT1 inhibits podocyte damage and apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy by upregulating FOXA1. Exp Mol Med 51(8):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-019-0259-6
Wang C, Liu G, Yang H, Guo S, Wang H, Dong Z, Li X, Bai Y, Cheng Y (2021) MALAT1-mediated recruitment of the histone methyltransferase EZH2 to the microRNA-22 promoter leads to cardiomyocyte apoptosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Sci Total Environ 766:142191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142191
Liang H, Huang Q, Liao MJ, Xu F, Zhang T, He J, Zhang L, Liu HZ (2019) EZH2 plays a crucial role in ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury by regulating p38 signaling. Inflamm Res 68(4):325–336. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-019-01221-3
Liu H, Chen Z, Weng X, Chen H, Du Y, Diao C, Liu X, Wang L (2020) Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 modulates oxidative stress-mediated pyroptosis in vitro and in a mouse kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury model. FASEB J 34(1):835–852. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201901816R
Zhou X, Xiong C, Tolbert E, Zhao T C, Bayliss G, Zhuang S (2018) Targeting histone methyltransferase enhancer of zeste homolog-2 inhibits renal epithelial-mesenchymal transition and attenuates renal fibrosis. FASEB J fj201800237R. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201800237R
Das F, Bera A, Ghosh-Choudhury N, Sataranatarajan K, Kamat A, Kasinath BS, Choudhury GG (2021) High glucose-stimulated enhancer of zeste homolog-2 (EZH2) forces suppression of deptor to cause glomerular mesangial cell pathology. Cell Signal 86:110072. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2021.110072
Zhou X, Chen H, Li J, Shi Y, Zhuang S, Liu N (2022) The role and mechanism of lysine methyltransferase and arginine methyltransferase in kidney diseases. Front Pharmacol 13:885527. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.885527
Varambally S, Cao Q, Mani RS, Shankar S, Wang X, Ateeq B, Laxman B, Cao X, Jing X, Ramnarayanan K, Brenner JC, Yu J, Kim JH, Han B, Tan P, Kumar-Sinha C, Lonigro RJ, Palanisamy N, Maher CA, Chinnaiyan AM (2008) Genomic loss of microRNA-101 leads to overexpression of histone methyltransferase EZH2 in cancer. Science 322(5908):1695–1699. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1165395
Chen G, Subedi K, Chakraborty S, Sharov A, Lu J, Kim J, Mi X, Wersto R, Sung MH, Weng NP (2018) Ezh2 regulates activation-induced CD8(+) T cell cycle progression via repressing Cdkn2a and Cdkn1c expression. Front Immunol 9:549. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.00549
Dai X, Liao R, Liu C, Liu S, Huang H, Liu J, Jin T, Guo H, Zheng Z, Xia M, Ling W, Xiao Y (2021) Epigenetic regulation of TXNIP-mediated oxidative stress and NLRP3 inflammasome activation contributes to SAHH inhibition-aggravated diabetic nephropathy. Redox Biol 45:102033. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2021.102033
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This study of clinical samples and experimental animals obtained approval from the experimental animal ethics committee of the Fourth People's Hospital of Shenyang, Liaoning, China.
Informed consent
Informed consent of the patients and their families was obtained.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Li, D., Zhou, P. et al. microRNA-29b-3p attenuates diabetic nephropathy in mice by modifying EZH2. Hormones 22, 223–233 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42000-022-00426-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42000-022-00426-2