Abstract
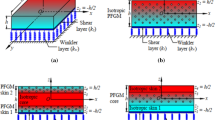
In the present work, the bending analysis of a multi-directional porous functionally graded plate (MDPFG) resting on an elastic foundation involves determining the deflection and stress distribution of the plate under I, T and L loads. The material properties of MDPFG plates are to be graded in the thickness and length directions according to modified power-law distribution considering uniformly and nonuniformly types of porosity distributions. The energy principle produces the plate’s governing differential equations (GDEs). The strong form formulation is discretized using Wendland radial basis function (WRBF) is used to solve GDEs and determine the deflection and stress distribution of the plate under applied loading. To generate the numerical results, a code has been computed in MATLAB (2019). The normalized deflection and stresses of MDPFG plates are investigated with respect to the grading index, span-to-thickness ratio, aspect ratio, transverse loading type, porosity fraction, and porosity distribution. Future investigations of MDPFG plates may use new numerical results as standards.



















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No data was used for the research described in the article.
References
Ameur M, Tounsi A, Mechab I, El Bedia AA (2011) A new trigonometric shear deformation theory for bending analysis of functionally graded plates resting on elastic foundations. KSCE J Civ Eng 15:1405–1414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-011-1361-z
Arshid E, Khorasani M, Soleimani-Javid Z, Amir S, Tounsi A (2022) Porosity-dependent vibration analysis of FG microplates embedded by polymeric nanocomposite patches considering hygrothermal effect via an innovative plate theory. Eng Comput 38:4051–4072. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-021-01382-y
Babaei M, Asemi K, Safarpour P (2019) Buckling and static analyses of functionally graded saturated porous thick beam resting on elastic foundation based on higher order beam theory. Iran J Mech Eng Trans ISME 20:94–112
Babaei M, Hajmohammad MH, Asemi K (2020) Natural frequency and dynamic analyses of functionally graded saturated porous annular sector plate and cylindrical panel based on 3D elasticity. Aerosp Sci Technol 96:105524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ast.2019.105524
Babaei M, Asemi K, Kiarasi F (2021) Dynamic analysis of functionally graded rotating thick truncated cone made of saturated porous materials. Thin-Walled Struct 164:107852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2021.107852
Behravan RA (2018) Static analysis of non-uniform 2D functionally graded auxetic-porous circular plates interacting with the gradient elastic foundations involving friction force. Aerosp Sci Technol 76:315–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ast.2018.01.036
Bekkaye THL, Fahsi B, Bousahla AA, Bourada F, Tounsi A, Benrahou KH et al (2020) Porosity-dependent mechanical behaviors of FG plate using refined trigonometric shear deformation theory. Comput Concrete, Int J 26:439–450
Bellifa H, Selim MM, Chikh A, Bousahla AA, Bourada F, Tounsi A et al (2021) Influence of porosity on thermal buckling behavior of functionally graded beams. Smart Struct Syst 27:719–728. https://doi.org/10.12989/sss.2021.27.4.719
Benferhat R, Hassaine Daouadji T, Hadji L, Said Mansour M (2016) Static analysis of the FGM plate with porosities. Steel Compos Struct 21:123–136. https://doi.org/10.12989/scs.2016.21.1.123
Bever MB, Duwez PE (1972) Gradients in composite materials. Mater Sci Eng 10:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/0025-5416(72)90059-6
Carrera E, Brischetto S, Robaldo A (2008) Variable kinematic model for the analysis of functionally graded material plates. AIAA J 46:194–203. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.32490
Cuong-Le T, Nguyen KD, Le-Minh H, Phan-Vu P, Nguyen-Trong P, Tounsi A (2022) Nonlinear bending analysis of porous sigmoid FGM nanoplate via IGA and nonlocal strain gradient theory. Adv Nano Res 12:441–455. https://doi.org/10.12989/anr.2022.12.5.441
Farahani BV, Berardo J, Belinha J, Ferreira AJ, Tavares PJ, Moreira PM (2017) On the optimal shape parameters of distinct versions of RBF meshless methods for the bending analysis of plates. Eng Anal Bound Elements 84:77–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enganabound.2017.08.010
Ferreira AJM, Batra RC, Roque CMC, Qian LF, Martins PALS (2005) Static analysis of functionally graded plates using third-order shear deformation theory and a meshless method. Compos Struct 69:449–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2004.08.003
Ferreira AJM, Roque CMC, Jorge RMN, Fasshauer GE, Batra RC (2007) Analysis of functionally graded plates by a robust meshless method. Mech Adv Mater Struct 14:577–587. https://doi.org/10.1080/15376490701672732
Guellil M, Saidi H, Bourada F, Bousahla AA, Tounsi A, Al-Zahrani MM et al (2021) Influences of porosity distributions and boundary conditions on mechanical bending response of functionally graded plates resting on Pasternak foundation. Steel and Compos Struct 38:1–15. https://doi.org/10.12989/scs.2021.38.1.001
Gupta A, Talha M (2018) Influence of porosity on the flexural and vibration response of gradient plate using nonpolynomial higher-order shear and normal deformation theory. Int J Mech Mater Des 14:277–296. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10999-017-9369-2
Hadji M, Bouhadra A, Mamen B, Menasria A, Bousahla AA, Bourada F et al (2023) Combined influence of porosity and elastic foundation parameters on the bending behavior of advanced sandwich structures. Steel Compos Struct 46(1):1–13
Kansa EJ (1990) Multiquadrics—A scattered data approximation scheme with applications to computational fluid-dynamics—II solutions to parabolic, hyperbolic and elliptic partial differential equations. Comput Math Appl 19:147–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/0898-1221(90)90271-K
Kiarasi F, Babaei M, Asemi K, Dimitri R, Tornabene F (2021) Three-dimensional buckling analysis of functionally graded saturated porous rectangular plates under combined loading conditions. Appl Sci 11:10434. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112110434
Kumar R, Khare S (2022) Effect of uniform and nonuniform porosity on free vibration of functionally graded circular plate. Int J Comp Mat Sci Eng 11:2250001. https://doi.org/10.1142/S2047684122500014
Kumar R, Singh J (2018) Assessment of higher order transverse shear deformation theories for modeling and buckling analysis of FGM plates using RBF based meshless approach. Multi Modelg Mat Struct. https://doi.org/10.1108/MMMS-07-2017-0069
Kumar R, Lal A, Singh BN, Singh J (2019a) New transverse shear deformation theory for bending analysis of FGM plate under patch load. Compos Struct 208:91–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2018.10.014
Kumar R, Lal A, Singh BN, Singh J (2019b) Meshfree approach on buckling and free vibration analysis of porous FGM plate with proposed IHHSDT resting on the foundation. Curved Layer Struct 6:192–211. https://doi.org/10.1515/cls-2019-0017
Kumar R, Lal A, Singh BN, Singh J (2020) Non-linear analysis of porous elastically supported FGM plate under various loading. Compos Struct 233:111721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.111721
Kumar Y, Gupta A, Tounsi A (2021) Size-dependent vibration response of porous graded nanostructure with FEM and nonlocal continuum model. Adv Nano Res 11:1–17. https://doi.org/10.12989/anr.2021.11.1.001
Kumar R, Lal A, Singh BN, Singh J (2022a) Numerical simulation of the thermomechanical buckling analysis of bidirectional porous functionally graded plate using collocation meshfree method. Proc Inst Mech Eng, Part l: J Mater: Design Appl 236:787–807. https://doi.org/10.1177/14644207211058573
Kumar R, Bajaj M, Singh J, Shukla KK (2022b) New HSDT for free vibration analysis of elastically supported porous bidirectional functionally graded sandwich plate using collocation method. Proc Inst Mech Eng C J Mech Eng Sci 236:9109–9123. https://doi.org/10.1177/09544062221090075
Kumar R, Singh BN, Singh J, Singh J (2022c) Meshfree approach for flexure analysis of bidirectional porous FG plate subjected to I, L, and T types of transverse loading. Aerosp Sci Technol 129:107824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ast.2022.107824
Kumar R, Gupta KK, Singh J, Singh J (2022d) Radial basis collocation method for free vibration analysis of elastically supported porous bi-directional FGM plate under various types of porosity distribution. Adv Mater Process Technol. https://doi.org/10.1080/2374068X.2022.2093003
Li S, Zheng S, Chen D (2020) Porosity-dependent isogeometric analysis of bi-directional functionally graded plates. Thin-Walled Struct 156:106999. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2020.106999
Liew KM, Zhao X, Ferreira AJM (2011) A review of meshless methods for laminated and functionally graded plates and shells. Compos Struct 93:2031–2041. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2011.02.018
Liu G, Wu S, Shahsavari D, Karami B, Tounsi A (2022) Dynamics of imperfect inhomogeneous nanoplate with exponentially-varying properties resting on viscoelastic foundation. Eur J Mech – A/Solids 95:104649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euromechsol.2022.104649
Lucy LB (1977) A numerical approach to the testing of the fission hypothesis. Astron J 82:1013–1024. https://doi.org/10.1086/112164
Malekzadeh P, Karami G (2008) A mixed differential quadrature and finite element free vibration and buckling analysis of thick beams on two-parameter elastic foundations. Appl Math Model 32:1381–1394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2007.04.019
Mantari JL, Oktem AS, Guedes SC (2012) Bending response of functionally graded plates by using a new higher order shear deformation theory. Compos Struct 94:714–723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2011.09.007
Mechab I, Atmane HA, Tounsi A, Belhadj HA, Bedia EAA (2010) A two variable refined plate theory for the bending analysis of functionally graded plates. Acta Mech Sin 26:941–949. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-010-0372-1
Meksi A, Benyoucef S, Houari MSA, Tounsi A (2015) A simple shear deformation theory based on neutral surface position for functionally graded plates resting on Pasternak elastic foundations. Struct Eng Mech: Int J 53(6):1215–1240
Neves AMA, Ferreira AJM, Carrera E, Roque CMC, Cinefra M, Jorge RMN et al (2011) Bending of FGM plates by a sinusoidal plate formulation and collocation with radial basis functions. Mech Res Commun 38:368–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechrescom.2011.04.011
Neves AMA, Ferreira AJM, Carrera E, Roque CMC, Cinefra M, Jorge RMN et al (2012) A quasi-3D sinusoidal shear deformation theory for the static and free vibration analysis of functionally graded plates. Compos B Eng 43:711–725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2011.08.009
Sayyad AS, Ghugal YM (2018) Analytical solutions for bending, buckling, and vibration analyses of exponential functionally graded higher order beams. Asian J Civ Eng 19:607–623. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42107-018-0046-z
Singh J, Shukla KK (2012) Nonlinear flexural analysis of functionally graded plates under different loadings using RBF based meshless method. Eng Anal Bound Elem 36:1819–1827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enganabound.2012.07.001
Singh S, Singh J, Shukla KK (2013) Buckling of laminated composite plates subjected to mechanical and thermal loads using meshless collocations. J Mech Sci Technol 27:327–336. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-012-1249-y
Singh J, Singh S, Shukla KK (2014) Meshless analysis of laminated composite and sandwich plates subjected to various types of loads. Int J Comput Methods Eng Sci Mech 15:158–171. https://doi.org/10.1080/15502287.2013.874060
Sobhy M (2013) Buckling and free vibration of exponentially graded sandwich plates resting on elastic foundations under various boundary conditions. Compos Struct 99:76–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2012.11.018
Tahir SI, Chikh A, Tounsi A, Al-Osta MA, Al-Dulaijan SU, Al-Zahrani MM (2021) Wave propagation analysis of a ceramic-metal functionally graded sandwich plate with different porosity distributions in a hygro-thermal environment. Compos Struct 269:114030. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2021.114030
Talha M, Singh BN (2010) Static response and free vibration analysis of FGM plates using higher order shear deformation theory. Appl Math Model 34:3991–4011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2010.03.034
Thai H-T, Kim S-E (2013) A simple quasi-3D sinusoidal shear deformation theory for functionally graded plates. Compos Struct 99:172–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2012.11.030
Thai H-T, Park M, Choi D-H (2013) A simple refined theory for bending, buckling, and vibration of thick plates resting on elastic foundation. Int J Mech Sci 73:40–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2013.03.017
Tran LV, Ferreira AJM, Nguyen-Xuan H (2013) Isogeometric analysis of functionally graded plates using higher-order shear deformation theory. Compos B Eng 51:368–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2013.02.045
Tran V-K, Pham Q-H, Nguyen-Thoi T (2022) A finite element formulation using four-unknown incorporating nonlocal theory for bending and free vibration analysis of functionally graded nanoplates resting on elastic medium foundations. Eng Comput 38:1465–1490. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-020-01107-7
Van Vinh P, Van Chinh N, Tounsi A (2022) Static bending and buckling analysis of bi-directional functionally graded porous plates using an improved first-order shear deformation theory and FEM. Eur J Mech – A/Solids 96:104743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euromechsol.2022.104743
Winkler E (1867) Die Lehre von der Elastizitat and Festigkeit
Wu C-P, Chiu K-H, Wang Y-M (2011) RMVT-based meshless collocation and element-free Galerkin methods for the quasi-3D analysis of multilayered composite and FGM plates. Compos Struct 93:923–943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2010.07.001
Xiang S, Kang G (2013a) Static analysis of functionally graded plates by the various shear deformation theory. Compos Struct 99:224–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2012.11.021
Xiang S, Kang G (2013b) A nth-order shear deformation theory for the bending analysis on the functionally graded plates. Eur J Mech A Solids 37:336–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euromechsol.2012.08.005
Yaghoobi H, Fereidoon A (2014) Mechanical and thermal buckling analysis of functionally graded plates resting on elastic foundations: an assessment of a simple refined nth-order shear deformation theory. Compos B Eng 62:54–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2014.02.014
Yahia SA, Atmane HA, Houari MSA, Tounsi A (2015) Wave propagation in functionally graded plates with porosities using various higher-order shear deformation plate theories. Struct Eng Mech 53:1143–1165. https://doi.org/10.12989/sem.2015.53.6.1143
Zenkour AM (2006) Generalized shear deformation theory for bending analysis of functionally graded plates. Appl Math Model 30:67–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2005.03.009
Zhong Z, Shang E (2008) Closed-form solutions of three-dimensional functionally graded plates. Mech Adv Mater Struct 15:355–363. https://doi.org/10.1080/15376490801977528
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MCS developed the theory, wrote the computer code, and drafted the manuscript. JS participated as a research mentor, checked the codes, data analysis, and scrutinized the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix-I
Appendix-I
The first part of GDEs (13) \(\delta u_{0}:\frac{{\partial N_{xx} }}{\partial x} + \frac{{\partial N_{xy} }}{\partial y} = 0\) are discretized using WRBF and are expressed as
Similarly, other parts of GDEs are discretized.
The boundary conditions can be discretized in similar fashion. For, e.g., simply supported boundary condition at the edge x = 0 (Eq. 22) is discretized and finally expressed as
nbx0 = number of nodes on the boundary x = 0.
Similarly, other boundary conditions at the edges x = a, y = 0 and y = b are discretized. The resulting equation is written as matrix form as
where
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Srivastava, M.C., Singh, J. Influences of elastic foundation on bending analysis of multidirectional porous functionally graded plate under industrial used loading: a meshfree approach. Multiscale and Multidiscip. Model. Exp. and Des. 6, 519–535 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41939-023-00156-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41939-023-00156-x