Abstract
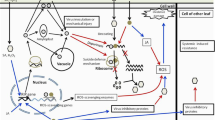
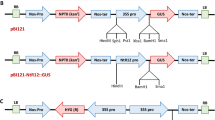
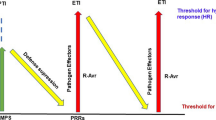
Genetic engineering has emerged as an attractive strategy for incorporating resistance in plants against diverse pathogens and has been largely achieved through transgenic expression of ribosome-inactivating proteins (RIPs), pathogenesis-related (PR) proteins, pathogen-derived genes, or strategies involving RNA interference and clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats/CRISPR-associated protein 9 (CRISPR/Cas9) gene editing tool. RIPs are rRNA N-glycosylases that commonly exert their protective effects through suppression of translation by enzymatically inactivating ribosomes, thereby arresting protein synthesis. Additionally, a few RIPs may possess other enzymatic activities viz. superoxide dismutase, chitinase, DNase and phosphatase, contributing towards pathogen resistance in plants. RIPs are mostly produced by plants and conventionally classified into three types. Type I RIPs are monomeric, with catalytic A chains, exhibiting rRNA N-glycosylase activity. Type II RIPs are dimeric, comprising the enzymatically active A chain associated with the lectin B chain enabling an access inside the cells, hence these are often highly toxic. Less common Type III RIPs include the jasmonic acid inducible protein such as JIP-60, with the catalytic domain becoming functional upon removal of an internal peptide segment and following cleavage of a C-terminal domain which resembles the eukaryotic initiation factor 4e. Unusual RIPs and RIP-related proteins, that cannot be grouped into the classical three types of RIPs, because of their difference in size, structure, or function, also exist. Several RIPs have been recombinantly expressed and demonstrated to possess catalytic activity. Plants carrying RIP transgenes exhibit resistance against viruses, fungi and insects. More often, such studies have been carried out using model systems comprising tobacco, potato or tomato, transformed via Agrobacterium tumefaciens, and employing the most widely used promoter such as CaMV 35S, to enable a high-level expression of the RIP gene. This review focuses on the recent developments in the recombinant DNA approach for the modification of crops with RIP genes to reduce the impact of pathogens and pests.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajji PK, Walder K, Puri M (2016) Functional analysis of a type-I ribosome inactivating protein balsamin from Momordica balsamina with anti-microbial and DNase activity. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 71:265–271
Balasaraswathi R, Sadasivam S, Ward M, Walker JM (1998) An antiviral protein from Bougainvillea spectabilis roots; purification and characterisation. Phytochemistry 47:1561–1565
Balasubrahmanyam A, Baranwal VK, Lodha ML, Varma A, Kapoor HC (2000) Purification and properties of growth stage-dependent antiviral proteins from the leaves of Celosia cristata. Plant Sci 154:13–21
Balconi C, Lanzanova C, Conti E, Triulzi T, Forlani F, Cattaneo M, Lupotto E (2007) Fusarium head blight evaluation in wheat transgenic plants expressing the maize b-32 antifungal gene. Eur J Plant Pathol 117:129–140
Baranwal VK, Tumer NE, Kapoor HC (2002) Depurination of ribosomal RNA and inhibition of viral RNA translation by an antiviral protein of Celosia cristata. Indian J Exp Biol 40:1195–1197
Barbieri L, Gorini P, Valbonesi P, Castiglioni P, Stirpe F (1994) Unexpected activity of saporins. Nature 372:624
Barbieri L, Valbonesi P, Bonora E, Gorini P, Bolognesi A, Stirpe F (1997) Polynucleotide:adenosine glycosidase activity of ribosome-inactivating proteins: effect on DNA, RNA and poly(A). Nucleic Acids Res 25:518–522
Barbieri L, Polito L, Bolognesi A, Ciani M, Pelosi E, Farini V, Jha AK, Sharma N, Vivanco JM, Chambery A, Parente A, Stirpe F (2006) Ribosome-inactivating proteins in edible plants and purification and characterization of a new ribosome-inactivating protein from Cucurbita moschata. Biochim Biophys Acta 1760:783–792
Begam M, Narwal S, Roy S, Kumar S, Lodha ML, Kapoor HC (2006) An antiviral protein having deoxyribonuclease and ribonuclease activity from leaves of the post-flowering stage of Celosia cristata. Biochem (Moscow) 71:S44–S48
Bertholdo-Vargas LR, Martins JN, Bordin D, Salvador M, Schafer AE, Barros NM, Barbieri L, Stirpe F, Carlini CR (2009) Type 1 ribosome-inactivating proteins - entomotoxic, oxidative and genotoxic action on Anticarsia gemmatalis (Hübner) and Spodoptera frugiperda (J.E. Smith) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J Insect Physiol 55:51–58
Bhatia S, Lodha ML (2005) RNase and DNase activities of antiviral proteins from leaves of Bougainvillea xbuttiana. Ind J Biochem Biophys 42:152–155
Bhatia S, Kapoor HC, Lodha ML (2004) Modification of antioxidant status of host cell in response to Bougainvillea antiviral proteins. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol 18:113–119
Bieri S, Potrykus I, Fütterer J (2000) Expression of active barley seed ribosome-inactivating protein in transgenic wheat. Theor Appl Genet 100:755–763
Bolognesi A, Polito L, Olivieri F, Valbonesi P, Barbieri L, Battelli MG, Carusi MV, Benvenuto E, Del Vecchio BF, Di Maro A, Parente A, Di Loreto M, Stirpe F (1997) New ribosome-inactivating proteins with polynucleotide:adenosine glycosidase and antiviral activities from Basella rubra L. and Bougainvillea spectabilis Willd. Planta 203:422–429
Bolognesi A, Polito L, Lubelli C, Barbieri L, Parente A, Stirpe F (2002) Ribosome-inactivating and adenine polynucleotide glycosylase activities in Mirabilis jalapa L. tissues. J Biol Chem 277:13709–13716
Broekaert WF, Nsimba-Lubaki M, Peeters B, Peumans WJ (1984) A lectin from elder (Sambucus nigra L.) bark. Biochem J 221:163–169
Bulgari D, Landi N, Ragucci S, Faoro F, Di Maro A (2020) Antiviral activity of PD-L1 and PD-L4, type 1 ribosome inactivating proteins from leaves of Phytolacca dioica L. in the pathosystem Phaseolus vulgaris–tobacco necrosis virus (TNV). Toxins 12:524
Cao B, Lei J, Chen G, Cao P, Liu X, Chen Q, Wei X (2011) Testing of disease-resistance of pokeweed antiviral protein gene (PacPAP) in transgenic cucumber (Cucumis sativus). Afr J Biotechnol 10:6883–6890
Carzaniga R, Sinclair L, Fordham-Skelton AP, Harris N, Croy RRD (1994) Cellular and subcellular distribution of saporins, type-1 ribosome-inactivating proteins, in soapwort (Saponaria officinalis L.). Planta 194:461–470
Cavalieri A, Czapla T, Howard J, Rao G (1995) Larvicidal lectins and plant insect resistance based thereon. U.S. Patent 5407454
Chaudhry B, Müller-Uri F, Cameron-Mills V, Gough S, Simpson D, Skriver K, Mundy J (1994) The barley 60 kDa jasmonate-induced protein (JIP60) is a novel ribosome-inactivating protein. Plant J 6:815–824
Chen Z, White RF, Antoniw JF, Lin Q (1991) Effect of pokeweed antiviral protein (PAP) on the infection of plant viruses. Plant Pathol 40:612–620
Chen Z, Antoniw JF, White RF (1993) A possible mechanism for the antiviral activity of pokeweed antiviral protein. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 42:249–258
Chen H, Wang Y, Yan M, Yu M, Yao Q (1996) 5’-AMP phosphatase activity on trichosanthin and other single chain ribosome inactivating proteins. Chin Biochem J 12:125–130
Chen Y, Peumans WJ, Van Damme EJM (2002) The Sambucus nigra type-2 ribosome-inactivating protein SNA-I’ exhibits in planta antiviral activity in transgenic tobacco. FEBS Lett 516:27–30
Chen GJ, Shi L, Lei JJ, Cao BH, Zeng GP (2008) Cloning of pokeweed antiviral protein gene from Phytolacca acinosa and its transfer to pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Acta Hortic Sin 35:847–852
Chhikara S, Chaudhury D, Dhankher OP, Jaiwal PK (2012) Combined expression of a barley class II chitinase and type I ribosome inactivating protein in transgenic Brassica juncea provides protection against Alternaria brassicae. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 108:83–89
Cho KJ, Lee SM, Kim YT, Hwang YS (2000) Purification and characterization of an antiviral ribosome-inactivating protein from Chenopodium album L. J Appl Biol Chem 43:125–130
Chopra R, Saini R (2014) Transformation of blackgram (Vigna mungo (L.) Hepper) by barley chitinase and ribosome-inactivating protein genes towards improving resistance to Corynespora leaf spot fungal disease. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 174:2791–2800
Choudhary N, Kapoor HC, Lodha ML (2008a) Cloning and expression of antiviral/ribosome-inactivating protein from Bougainvillea xbuttiana. J Biosci 33:91–101
Choudhary N, Yadav OP, Lodha ML (2008b) Ribonuclease, deoxyribonuclease and antiviral activity of Escherichia coli-expressed Bougainvillea xbuttiana antiviral protein 1. Biochem Mosc 73:273–277
Choudhary N, Lodha ML, Baranwal VK (2020) The role of enzymatic activities of antiviral proteins from plants for action against plant pathogens. 3 Biotech 10:505
Citores L, Iglesias R, Gay C, Ferreras JM (2016) Antifungal activity of the ribosome-inactivating protein BE27 from sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) against the green mould Penicillium digitatum. Mol Plant Pathol 17:261–271
Citores L, Iglesias R, Ferreras JM (2021) Antiviral activity of ribosome-inactivating proteins. Toxins 13:80
Corrado G, Bovi PD, Ciliento R, Gaudio L, Di Maro A, Aceto S, Lorito M, Rao R (2005) Inducible expression of a Phytolacca heterotepala ribosome-inactivating protein leads to enhanced resistance against major fungal pathogens in tobacco. Phytopathology 95:206–215
Corrado G, Scarpetta M, Alioto D, Di Maro A, Polito L, Parente A, Rao R (2008) Inducible antiviral activity and rapid production of the ribosome-inactivating protein I from Phytolacca heterotepala in tobacco. Plant Sci 174:467–474
Dai W, Bonos S, Guo Z, Meyer W, Day P, Belanger F (2003) Expression of pokeweed antiviral proteins in creeping bentgrass. Plant Cell Rep 21:497–502
De Zaeytijd J, Rouge P, Smagghe G, Van Damme EJM (2019) Structure and activity of a cytosolic ribosome-inactivating protein from rice. Toxins 11:325
De Zaeytijd J, Chen P, Scheys F, Subramanyam K, Dubiel M, De Schutter K, Smagghe G, Van Damme EJM (2020) Involvement of OsRIP1, a ribosome-inactivating protein from rice, in plant defense against Nilaparvata lugens. Phytochemistry 170:112190
Desmyter S, Vandenbussche F, Hao Q, Proost P, Peumans WJ, Van Damme EJM (2003) Type-1 ribosome-inactivating protein from iris bulbs: a useful agronomic tool to engineer virus resistance? Plant Mol Biol 51:567–576
Di Maro A, Citores L, Russo R, Iglesias R, Ferreras JM (2014) Sequence comparison and phylogenetic analysis by the maximum likelihood method of ribosome-inactivating proteins from angiosperms. Plant Mol Biol 85:575–588
Di R, Tumer NE (2005) Expression of a truncated form of ribosomal protein L3 confers resistance to pokeweed antiviral protein and the Fusarium mycotoxin deoxynivalenol. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 18:762–770
Domashevskiy AV, Cheng SY (2015) Thermodynamic analysis of binding and enzymatic properties of pokeweed antiviral protein (PAP) toward tobacco etch virus (TEV) RNA. J Nat Sci 1:e82
Dong OX, Ronald PC (2019) Genetic engineering for disease resistance in plants: recent progress and future perspectives. Plant Physiol 180:26–38
Dowd PF, Zuo WN, Gillikin JW, Johnson ET, Boston RS (2003) Enhanced resistance to Helicoverpa zea in tobacco expressing an activated form of maize ribosome-inactivating protein. J Agric Food Chem 51:3568–3574
Dowd PF, Holmes RA, Pinkerton TS, Johnson ET, Lagrimini LM, Boston RS (2006) Relative activity of a tobacco hybrid expressing high levels of a tobacco anionic peroxidase and maize ribosome-inactivating protein against Helicoverpa zea and Lasioderma serricorne. J Agric Food Chem 54:2629–2634
Dowd PF, Johnson ET, Price NP (2012) Enhanced pest resistance of maize leaves expressing monocot crop plant-derived ribosome-inactivating protein and agglutinin. J Agric Food Chem 60:10768–10775
Dutt S, BalasubrahmanyamLodha AM (2000) Purification and partial characterization of antiviral proteins from Chenopodium album L. leaves. J Plant Physiol 156:808–810
Dutt S, Narwal S, Kapoor HC, Lodha ML (2003) Isolation and characterization of two protein isoforms with antiviral activity from Chenopodium album L. leaves. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol 12:117–122
Dutt S, Yadav OP, Kapoor HC, Lodha ML (2004) Possible mechanism of action of antiviral proteins from the leaves of Chenopodium album L. Indian J Biochem Biophys 41:29–33
Endo Y, Tsurugi K (1987) RNA N-glycosidase activity of ricin A-chain. Mechanism of action of the toxic lectin ricin on eukaryotic ribosomes. J Biol Chem 262:8128–8130
Fong WP, Mock WY, Ng TB (2000) Intrinsic ribonuclease activities in ribonuclease and ribosome-inactivating proteins from the seeds of bitter gourd. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 32:571–577
Fu DL, Wang LL, Zhang HY, Chen ZH (2000) Introduction of PAP cDNA into potato by the laser microbeam puncture techniques. Acta Photonica Sin 29:970–974
Gandhi R, Manzoor M, Hudak KA (2008) Depurination of brome mosaic virus RNA3 in vivo results in translation-dependent accelerated degradation of the viral RNA. J Biol Chem 283:32218–32228
Gatehouse AMR, Barbieri L, Stirpe F, Croy RRD (1990) Effects of ribosome inactivating proteins on insect development differences between Lepidoptera and Coleoptera. Entomol Exp Appl 54:43–51
Gholizadeh A (2019) Purification of a ribosome-inactivating protein with antioxidation and root developer potencies from Celosia plumosa. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 25:243–251
Gholizadeh A, Kumar M, Balasubrahmanyam A, Sharma S, Narwal S, Lodha ML, Kapoor HC (2004) Antioxidant activity of antiviral proteins from Celosia cristata. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol 13:13–18
Girbés T, Ferreras JM, Arias FJ, Stirpe F (2004) Description, distribution, activity and phylogenetic relationship of ribosome-inactivating proteins in plants, fungi and bacteria. Mini Rev Med Chem 4:461–476
Gonzales-Salazar R, Cecere B, Ruocco M, Rao R, Corrado G (2017) A comparison between constitutive and inducible transgenic expression of the PhRIP I gene for broad-spectrum resistance against phytopathogens in potato. Biotechnol Lett 39:1049–1058
Guller A, Sipahioğlu HM, Usta M, Durak ED (2018) Antiviral and antifungal activity of biologically active recombinant bouganin protein from Bougainvillea spectabilis willd. J Agric Sci 24:227–237
Hamshou M, Shang C, Smagghe G, Van Damme EJM (2016) Ribosome-inactivating proteins from apple have strong aphicidal activity in artificial diet and in planta. Crop Prot 87:19–24
Hamshou M, Shang C, De Zaeytijd J, Van Damme EJ, Smagghe G (2017) Expression of ribosome-inactivating proteins from apple in tobacco plants results in enhanced resistance to Spodoptera exigua. J Asia-Pac Entomol 20:1–5
Hartley MR, Chaddock JA, Bonness MS (1996) The structure and function of ribosome inactivating proteins. Trends Plant Sci 1:254–260
Hiramatsu A, Kobayashi N, Osawa N (1987) Properties of two inhibitors of plant virus infection from fruiting bodies of Lentinus edodes and from leaves of Yucca recurvifolia salisb. Agric Biol Chem 51:897–904
Hong Y, Saunders K, Hartley MR, Stanley J (1996) Resistance to geminivirus infection by virus-induced expression of dianthin in transgenic plants. Virology 220:119–127
Horsch RB, Fry JE, Hoffmann NL, Eichholtz D, Rogers SG, Fraley RT (1985) A simple and general method for transferring genes into plants. Science 227:1229–1231
Huang M, Hou P, Wei Q, Xu Y, Chen F (2008) A ribosome-inactivating protein (curcin 2) induced from Jatropha curcas can reduce viral and fungal infection in transgenic tobacco. Plant Growth Regul 54:115–123
Hudak KA, Wang P, Tumer NE (2000) A novel mechanism for inhibition of translation by pokeweed antiviral protein: depurination of the capped RNA template. RNA 6:369–380
Iglesias R, Pérez Y, de Torre C, Ferreras JM, Antolín P, Jiménez P, Rojo MA, Méndez E, Girbés T (2005) Molecular characterization and systemic induction of single-chain ribosome-inactivating proteins (RIPs) in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris) leaves. J Exp Bot 56:1675–1684
Iglesias R, Citores L, Di Maro A, Ferreras JM (2015) Biological activities of the antiviral protein BE27 from sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.). Planta 241:421–433
Iglesias R, Citores L, Ragucci S, Russo R, Di Maro A, Ferreras JM (2016) Biological and antipathogenic activities of ribosome-inactivating proteins from Phytolacca dioica L. Biochim Biophys Acta 1860:1256–1264
Irvin JD, Kelly T, Robertus JD (1980) Purification and properties of a second antiviral protein from Phytolacca americana which inactivates eukaryotic ribosomes. Arch Biochem Biophys 200:418–425
ISAAA (2019) Global status of commercialized biotech/GM crops in 2019: biotech crops drive socio-economic development and sustainable environment in the new frontier. ISAAA Brief No. 55. ISAAA: Ithaca, NY
Jach G, Görnhardt B, Mundy J, Logemann J, Pinsdorf E, Leah R, Schell J, Maas C (1995) Enhanced quantitative resistance against fungal disease by combinatorial expression of different barley antifungal proteins in transgenic tobacco. Plant J 8:97–109
Jiang GY, Weng ML, Jin DM, Wang B (1998) Characteristics of TCS transgenic tomato. Acta Hortic Sin 25:395–396
Jiang GY, Jin DM, Weng ML, Guo BT, Wang B (1999) Transformation and expression of trichosanthin gene in tomato. Acta Bot Sin 41:334–336
Karran RA, Hudak KA (2008) Depurination within the intergenic region of brome mosaic virus RNA3 inhibits viral replication in vitro and in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res 36:7230–7239
Karran RA, Hudak KA (2011) Depurination of brome mosaic virus RNA3 inhibits its packaging into virus particles. Nucleic Acids Res 39:7209–7222
Kaur S, Samota MK, Choudhary M, Choudhary M, Pandey AK, Sharma A, Thakur J (2022) How do plants defend themselves against pathogens—Biochemical mechanisms and genetic interventions. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 28:485–504
Kim JK, Jang IC, Wu R, Zuo WN, Boston RS, Lee YH, Ahn IP, Nahm BH (2003) Co-expression of a modified maize ribosome-inactivating protein a rice basic chitinase gene in transgenic rice plants confers enhanced resistance to sheath blight. Transgenic Res 12:475–484
Kim YS, Park SC, Oh SK, Lee H, Cho JW, Chung CH (1999a) Antiviral proteins, amarandin 1 and 2, from Amaranthus viridis, DNAs encoding therefrom. United States Patent No. 6001986-A
Kim YS, Park SC, Oh SK, Lee H, Cho JW, Chung CH (1999b) DNA encoding amarandin-S ribosome inactivating protein of Amaranthus viridis. United States Patent No. 5977335-A
Krishnan R, McDonald KA, Dandekar AM, Jackman AP, Falk B (2002) Expression of recombinant trichosanthin, a ribosome-inactivating protein, in transgenic tobacco. J Biotechnol 97:69–88
Kubo S, Ikeda T, Imaizumi S, Takanami Y, Mikami Y (1990) A potent plant virus inhibitor found in Mirabilis jalapa L. Ann Phytopath Soc Japan 56:481–487
Kumar MA, Timm DE, Neet KE, Owen WG, Peumans WJ, Rao AG (1993) Characterization of the lectin from the bulbs of Eranthis hyemalis (winter aconite) as an inhibitor of protein synthesis. J Biol Chem 268:25176–25183
Kumar R, Bhattacharjee A, Tiwari S (2022) Plant-derived ribosome-inactivating proteins involved in defense against plant viruses. Eur J Plant Pathol 162:515–537
Kushwaha GS, Pandey N, Sinha M, Singh SB, Kaur P, Sharma S, Singh TP (2012) Crystal structures of a type-1 ribosome inactivating protein from Momordica balsamina in the bound and unbound states. Biochim Biophys Acta 1824:679–691
Kwon SY, An CS, Liu JR, Paek KH (1997) A ribosome-inactivating protein from Amaranthus viridis. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 61:1613–1614
Kwon SY, An CS, Liu JR, Kwak SS, Lee HS, Kim JK, Paek KH (2000) Molecular cloning of a cDNA encoding ribosome inactivating protein from Amaranthus viridis and its expression in E. coli. Mol Cells 10:8–12
Lam YH, Wong YS, Wang B, Wong RNS, Yeung HW, Shaw PC (1996) Use of trichosanthin to reduce infection by turnip mosaic virus. Plant Sci 114:111–117
Landi N, Ragucci S, Citores L, Clemente A, Hussain HZF, Iglesias R, Ferreras JM, Di Maro A (2022) Isolation, characterization and biological action of type-1 ribosome-inactivating proteins from tissues of Salsola soda L. Toxins (basel) 14:566
Lanzanova C, Giuffrida MG, Motto M, Baro C, Donn G, Hartings H, Lupotto E, Careri M, Elviri L, Balconi C (2009) The Zea mays b-32 ribosome-inactivating protein efficiently inhibits growth of Fusarium verticillioides on leaf pieces in vitro. Eur J Plant Pathol 124:471–482
Leah R, Tommerup H, Svendsen I, Mundy J (1991) Biochemical and molecular characterization of three barley seed proteins with antifungal properties. J Biol Chem 266:1564–1573
Lee S, Cho K, Kim Y, Park H, Kim S, Hwang Y, Kim D (1999) Antiviral activity of a type 1 ribosome-inactivating protein from Chenopodium album L. J Appl Biol Chem 42:161–165
Li XD, Chen WF, Liu WY, Wang GH (1997) Large-scale preparation of two new ribosome-inactivating proteins–cinnamomin and camphorin from the seeds of Cinnamomum camphora. Protein Expr Purif 10:27–31
Li Y, Jia Y, Zhang Z, Chen X, He H, Fang R, Hao X (2007) Purification and characterization of a new ribosome inactivating protein from cinchonaglycoside c-treated tobacco leaves. J Integr Plant Biol 49:1327–1333
Li L, Li Y, Chen D, Feng H, Wang X (2013) Improved resistance to cucumber mosaic virus in Petunia transformed with non-cytotoxic pokeweed antiviral protein gene. J Phytopathol 161:239–245
Lin JY, Kao WY, Tserng KY, Chen CC, Tung TC (1970) Effect of crystalline abrin on the biosynthesis of protein, RNA, and DNA in experimental tumors. Cancer Res 30:2431–2433
Lodge JK, Kaniewski WK, Tumer NE (1993) Broad-spectrum virus resistance in transgenic plants expressing pokeweed antiviral protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:7089–7093
Lodha ML, Agarwal S, Biswas K, Vasudev S, Dubey SC (2010) Antimicrobial activity of native and recombinant antiviral proteins from Bougainvillea xbuttiana leaves against plant pathogenic fungi and viruses. Indian J Agric Biochem 23:83–90
Logemann J, Jach G, Tommerup H, Mundy J, Schell J (1992) Expression of a barley ribosome-inactivating protein leads to increased fungal protection in transgenic tobacco plants. Nat Biotechnol 10:305–308
Lombard S, Helmy ME, Piéroni G (2001) Lipolytic activity of ricin from Ricinus sanguineus and Ricinus communis on neutral lipids. Biochem J 358:773–781
Maddaloni M, Forlani F, Balmas V, Donini G, Stasse L, Corazza L, Motto M (1997) Tolerance to the fungal pathogen Rhizoctonia solani AG4 of transgenic tobacco expressing the maize ribosome-inactivating protein b-32. Transgenic Res 6:393–402
M’hamdi M, Rouhou HC, Boughalleb N, deGalarretaGómez JIR (2012) Enhanced resistance to Rhizoctonia solani by combined expression of chitinase and ribosome inactivating protein in transgenic potatoes (Solanum tuberosum L.). Span J Agric Res 10:778–785
Moon YH, Jeon HS, Choi KW, Lee JS (1994) Development of virus-resistant potato by expression of Phytolacca antiviral protein. Mol Cells 4:183–188
Moon YH, Song SK, Choi KW, Lee JS (1997) Expression of a cDNA encoding Phytolacca insularis antiviral protein confers virus resistance on transgenic potato plants. Mol Cells 7:807–815
Narwal S, Balasubrahmanyam A, Lodha ML, Kapoor HC (2001a) Purification and properties of antiviral proteins from the leaves of Bougainvillea xbuttiana. Indian J Biochem Biophys 38:342–347
Narwal S, Balasubrahmanyam A, Sadhna P, Kapoor HC, Lodha ML (2001b) A systemic resistance inducing antiviral protein with N-glycosidase activity from Bougainvillea xbuttiana leaves. Indian J Exp Biol 39:600–603
Ng TB, Parkash A (2002) Hispin, a novel ribosome inactivating protein with antifungal activity from hairy melon seeds. Protein Expr Purif 26:211–217
Ng TB, Parkash A, Tso WW (2003) Purification and characterization of alpha- and beta-benincasins, arginine/glutamate-rich peptides with translation-inhibiting activity from wax gourd seeds. Peptides 24:11–16
Noman A, Aqeel M, Islam W, Khalid N, Akhtar N, Qasim M, Yasin G et al (2021) Insects–plants-pathogens: toxicity, dependence and defense dynamics. Toxicon 197:87–98
Oerke EC (2006) Crop losses to pests. J Agric Sci 144:31–43
Olivieri F, Prasad V, Valbonesi P, Srivastava S, Ghosal-Chowdhury P, Barbieri L, Bolognesi A, Stirpe F (1996) A systemic antiviral resistance-inducing protein isolated from Clerodendrum inerme Gaertn. is a polynucleotide: adenosine glycosidase (ribosome-inactivating protein). FEBS Lett 396:132–134
Olsnes S, Pihl A (1972) Ricin—a potent inhibitor of protein synthesis. FEBS Lett 20:327–329
Osawa N, Hiramatsu A (1987) Purification and chemical properties of an inhibitor of plant virus infection from leaves of Yucca recurvifolia salisb. Agric Biol Chem 51:891–896
Parkash A, Ng TB, Tso WW (2002) Isolation and characterization of luffacylin, a ribosome inactivating peptide with anti-fungal activity from sponge gourd (Luffa cylindrica) seeds. Peptides 23:1019–1024
Picard D, Kao CC, Hudak KA (2005) Pokeweed antiviral protein inhibits brome mosaic virus replication in plant cells. J Biol Chem 280:20069–20075
Prasad V, Srivastava S, Varsha, Verma HN (1995) Two basic proteins isolated from Clerodendrum inerme Gaertn. are inducers of systemic antiviral resistance in susceptible plants. Plant Sci 110:73–82
Prasad V, Mishra SK, Srivastava S, Srivastava A (2014) A virus inhibitory protein isolated from Cyamopsis tetragonoloba (L.) Taub. upon induction of systemic antiviral resistance shares partial amino acid sequence homology with a lectin. Plant Cell Rep 33:1467–1478
Qian Q, Huang L, Yi R, Wang S, Ding Y (2014) Enhanced resistance to blast fungus in rice (Oryza sativa L.) by expressing the ribosome-inactivating protein alpha-momorcharin. Plant Sci 217:1–7
Ragucci S, Bulgari D, Landi N, Russo R, Clemente A, Valletta M, Chambery A, Gobbi E, Faoro F, Di Maro A (2021) The structural characterization and antipathogenic activities of quinoin, a type 1 ribosome-inactivating protein from quinoa seeds. Int J Mol Sci 22:8964
Ready MP, Brown DT, Robertus JD (1986) Extracellular localization of pokeweed antiviral protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 83:5053–5056
Rezaei-Moshaei M, Dehestani A, Bandehagh A, Pakdin-Parizi A, Golkar M, Heidari-Japelaghi R (2021) Recombinant pebulin protein, a type 2 ribosome-inactivating protein isolated from dwarf elder (Sambucus ebulus L.) shows anticancer and antifungal activities in vitro. Int J Biol Macromol 174:352–361
Roy S, Sadhana P, Begum M, Kumar S, Lodha ML, Kapoor HC (2006) Purification, characterization and cloning of antiviral/ribosome inactivating protein from Amaranthus tricolor leaves. Phytochemistry 67:1865–1873
Ruan XL, Liu LF, Li H (2007) Transgenic tobacco plants with ribosome inactivating protein gene cassin from Cassia occidentalis and their resistance to tobacco mosaic virus. Zhi Wu Sheng Li Yu Fen Zi Sheng Wu XueXue Bao J Plant Physiol Molecul Biol 33:517–523
Ruggiero A, Chambery A, Di Maro A, Mastroianni A, Parente A, Berisio R (2007) Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of PD-L1, a highly glycosylated ribosome inactivating protein with DNase activity. Protein Pept Lett 14:407–409
Sargolzaei M, Ho CL, Wong MY (2016) Characterization of novel type I ribosome-inactivating proteins isolated from oil palm (Elaeis guineensis) inoculated with Ganoderma boninense the causal agent of basal stem rot. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 94:53–61
Savary S, Willocquet L, Pethybridge SJ, Esker P, McRoberts N, Nelson A (2019) The global burden of pathogens and pests on major food crops. Nat Ecol Evol 3:430–439
Schrot J, Weng A, Melzig MF (2015) Ribosome-Inactivating and Related Proteins. Toxins 7:1556–1615
Shahidi-Noghabi S, Van Damme EJM, Smagghe G (2008) Carbohydrate-binding activity of the type-2 ribosomes-inactivating protein SNA-I from elderberry (Sambucus nigra) is a determining factor for its insecticidal activity. Phytochemistry 69:2972–2978
Shahidi-Noghabi S, Van Damme EJM, Smagghe G (2009) Expression of Sambucus nigra agglutinin (SNA-I′) from elderberry bark in transgenic tobacco plants results in enhanced resistance to different insect species. Transgenic Res 18:249–259
Shahidi-Noghabi S, van Damme EJM, Iga M, Smagghe G (2010) Exposure of insect midgut cells to Sambucus nigra L. agglutinins I and II causes cell death via caspase-dependent apoptosis. J Insect Physiol 56:1101–1107
Sharma N, Park SW, Vepachedu R, Barbieri L, Ciani M, Stirpe F, Savary BJ, Vivanco JM (2004) Isolation and characterization of an rip (ribosome-inactivating protein)-like protein from tobacco with dual enzymatic activity. Plant Physiol 134:171–181
Shih NR, McDonald KA, Jackman AP, Girbés T, Iglesias R (1997) Bifunctional plant defence enzymes with chitinase and ribosome inactivating activities from Trichosanthes kirilowii cell cultures. Plant Sci 130:145–150
Sipahioglu HM, Kaya I, Usta M, Ünal M, Ozcan D, Özer M, Güller A, Pallás V (2017) Pokeweed (Phytolacca americana L.) antiviral protein inhibits zucchini yellow mosaic virus infection in a dose-dependent manner in squash plants. Turk J Agric for 41:256–262
Smirnov S, Shulaev V, Tumer NE (1997) Expression of pokeweed antiviral protein in transgenic plants induced virus resistance in grafted wild-type plants independently of salicylic acid accumulation and pathogenesis-related protein synthesis. Plant Physiol 114:1113–1121
Song SK, Choi Y, Moon YH, Kim SG, Choi YD, Lee JS (2000) Systemic induction of a Phytolacca insularis antiviral protein gene by mechanical wounding, jasmonic acid, and abscisic acid. Plant Mol Biol 43:439–450
Srivastava A, Trivedi S, Krishna SK, Verma HN, Prasad V (2009) Suppression of papaya ringspot virus infection in Carica papaya with CAP-34, a systemic antiviral resistance inducing protein from Clerodendrum aculeatum. Eur J Plant Pathol 123:241–246
Srivastava S, Verma HN, Srivastava A, Prasad V (2015) BDP-30, a systemic resistance inducer from Boerhaavia diffusa L., suppresses TMV infection, and displays homology with ribosome-inactivating proteins. J Biosci 40:125–135
Stirpe F, Battelli MG (2006) Ribosome-inactivating proteins: progress and problems. Cell Mol Life Sci 63:1850–1866
Stirpe F, Williams DG, Onyon LJ, Legg RF, Stevens WA (1981) Dianthins, ribosome-damaging proteins with anti-viral properties from Dianthus caryophyllus L. (carnation). Biochem J 195:399–405
Straub P, Adam G, Mundry KW (1986) Isolation and characterization of a virus inhibitor from spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.). J Phytopathol 115:357–367
Takanami Y, Kuwata S, Ikeda T, Kubo S (1990) Purification and characterization of the anti-plant viral protein from Mirabilis jalapa L. Ann Phytopathol Soc Japan 56:488–494
Taylor S, Massiah A, Lomonossoff G, Roberts LM, Lord JM, Hartley M (1994) Correlation between the activities of five ribosome-inactivating proteins in depurination of tobacco ribosomes and inhibition of tobacco mosaic virus infection. Plant J 5:827–835
Torky ZA (2012) Isolation and characterization of antiviral protein from Salsola longifolia leaves expressing polynucleotide adenosine glycoside activity. Online J Sci Technol 2:52–58
Tumer NE, Hwang DJ, Bonness M (1997) C-terminal deletion mutant of pokeweed antiviral protein inhibits viral infection but does not depurinate host ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:3866–3871
Van Damme EJ, Barre A, Rougé P, Van Leuven F, Peumans WJ (1996) The NeuAc(alpha-2,6)-Gal/GalNAc-binding lectin from elderberry (Sambucus nigra) bark, a type-2 ribosome-inactivating protein with an unusual specificity and structure. Eur J Biochem 235:128–137
Van Damme EJ, Roy S, Barre A, Citores L, Mostafapous K, Rougé P, Van Leuven F, Girbés T, Goldstein IJ, Peumans WJ (1997) Elderberry (Sambucus nigra) bark contains two structurally different Neu5Ac(alpha2,6)Gal/GalNAc-binding type 2 ribosome-inactivating proteins. Eur J Biochem 245:648–655
Vandenbussche F, Desmyter S, Ciani M, Proost P, Peumans WJ, Van Damme EJ (2004a) Analysis of the in planta antiviral activity of elderberry ribosome-inactivating proteins. Eur J Biochem 271:1508–1515
Vandenbussche F, Peumans WJ, Desmyter S, Proost P, Ciani M, Van Damme EJM (2004b) The type-1 and type-2 ribosome-inactivating proteins from Iris confer transgenic tobacco plants local but not systemic protection against viruses. Planta 220:211–221
Vargas LRB, Carlini CR (2014) Insecticidal and antifungal activities of ribosome-inactivating proteins. In: Stirpe F, Lappi DA (eds) Ribosome-inactivating proteins: Ricin and related proteins. Wiley Blackwell Press, NJ, USA, pp 212–222
Vepachedu R, Bais HP, Vivanco JM (2003) Molecular characterization and post-transcriptional regulation of ME1, a type-I ribosome-inactivating protein from Mirabilis expansa. Planta 217:498–506
Verma HN, Srivastava S, Varsha, Kumar D (1996) Induction of systemic resistance in plants against viruses by a basic protein from Clerodendrum aculeatum leaves. Phytopathology 86:485–492
Vivanco JM, Tumer NE (2003) Translation inhibition of capped and uncapped viral RNAs mediated by ribosome-inactivating proteins. Phytopathology 93:588–595
Vivanco JM, Querci M, Salazar LF (1999a) Antiviral and antiviroid activity of MAP-containing extracts from Mirabilis jalapa roots. Plant Dis 83:1116–1121
Vivanco JM, Savary BJ, Flores HE (1999b) Characterization of two novel type I ribosome-inactivating proteins from the storage roots of the andean crop Mirabilis expansa. Plant Physiol 119:1447–1456
Walsh TA, Morgan AE, Hey TD (1991) Characterization and molecular cloning of a proenzyme form of a ribosome-inactivating protein from maize. Novel mechanism of proenzyme activation by proteolytic removal of a 2.8-kilodalton internal peptide segment. J Biol Chem 266:23422–23427
Wang HX, Ng TB (2000) Lagenin, a novel ribosome-inactivating protein with ribonucleolytic activity from bottle gourd (Lagenaria siceraria) seeds. Life Sci 67:2631–2638
Wang P, Zoubenko O, Tumer NE (1998) Reduced toxicity and broad spectrum resistance to viral and fungal infection in transgenic plants expressing pokeweed antiviral protein II. Plant Mol Biol 38:957–964
Wang S, Zhang Y, Liu H, He Y, Yan J, Wu Z, Ding Y (2012) Molecular cloning and functional analysis of a recombinant ribosome-inactivating protein (alpha-momorcharin) from Momordica charantia. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 96:939–950
Wang S, Zheng Y, Yan J, Zhu Z, Wu Z, Ding Y (2013) Alpha-momorcharin: a ribosome-inactivating protein from Momordica charantia, possessing DNA cleavage properties. Protein Pept Lett 20:1257–1263
Wei GQ, Liu RS, Wang Q, Liu WY (2004) Toxicity of two type II ribosome-inactivating proteins (cinnamomin and ricin) to domestic silkworm larvae. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 57:160–165
Wong JH, Bao H, Ng TB, Chan HHL, Ng CCW, Man GCW, Wang H, Guan S, Zhao S, Fang EF, Rolka K, Liu Q, Li C, Sha O, Xia L (2020) New ribosome-inactivating proteins and other proteins with protein synthesis-inhibiting activities. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104:4211–4226
Wytynck P, Lambin J, Chen S, Demirel Asci S, Verbeke I, De Zaeytijd J, Subramanyam K, Van Damme EJM (2021) Effect of RIP overexpression on abiotic stress tolerance and development of rice. Int J Mol Sci 22:1434
Yang T, Meng Y, Chen LJ, Lin HH, Xi DH (2016) The roles of alpha-momorcharin and jasmonic acid in modulating the response of Momordica charantia to cucumber mosaic virus. Front Microbiol 7:1796
Yang T, Zhu LS, Meng Y, Lv R, Zhou Z, Zhu L, Lin HH, Xi DH (2018) Alpha-momorcharin enhances tobacco mosaic virus resistance in tobaccoNN by manipulating jasmonic acid-salicylic acid crosstalk. J Plant Physiol 223:116–126
Yuan H, Ming X, Wang L, Hu P, An C, Chen Z (2002) Expression of a gene encoding trichosanthin in transgenic rice plants enhances resistance to fungus blast disease. Plant Cell Rep 20:992–998
Zhang H, Tian Y, Zhou Y, Dang B, Lan H, Song G, Wang L, Liu G, Zhang L, Chen Z (1999) Introduction of pokeweed antiviral protein cDNA into Brassica napus and acquisition of transgenic plants resistant to viruses. Chin Sci Bull 44:701–704
Zhao S, Lei JJ, Chen GJ, Cao BH (2008) Obtainment of transgenic mustard (Brassica juncea Coss.) with pokeweed antiviral protein gene and its resistance to TuMV. J Agric Biotechnol 16:971–976
Zhou X, Li XD, Yuan JZ, Tang ZH, Liu WY (2000) Toxicity of cinnamomin–a new type II ribosome-inactivating protein to bollworm and mosquito. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 30:259–264
Zhu F, Zhang P, Meng YF, Xu F, Zhang DW, Cheng J, Lin HH, Xi DH (2013) Alpha momorcharin a RIP produced by bitter melon enhances defense response in tobacco plants against diverse plant viruses and shows antifungal activity in vitro. Planta 237:77–88
Zhu F, Yuan S, Zhang ZW, Qian K, Feng JG, Yang YZ (2016) Pokeweed antiviral protein (PAP) increases plant systemic resistance to tobacco mosaic virus infection in Nicotiana benthamiana. Eur J Plant Pathol 146:541–549
Zhu F, Zhou YK, Ji ZL, Chen XR (2018) The plant ribosome-inactivating proteins play important roles in defense against pathogens and insect pest attacks. Front Plant Sci 9:146
Zhu F, Zhu PX, Xu F, Che YP, Ma YM, Ji ZL (2020) Alpha-momorcharin enhances Nicotiana benthamiana resistance to tobacco mosaic virus infection through modulation of reactive oxygen species. Mol Plant Pathol 21:1212–1226
Zoubenko O, Uckun F, Hur Y, Chet I, Tumer N (1997) Plant resistance to fungal infection induced by nontoxic pokeweed antiviral protein mutants. Nat Biotechnol 15:992–996
Zoubenko O, Hudak K, Tumer NE (2000) A non-toxic pokeweed antiviral protein mutant inhibits pathogen infection via a novel salicylic acid-independent pathway. Plant Mol Biol 44:219–229
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, R., Srivastava, S. & Prasad, V. Genetic modification of crop plants with ribosome-inactivating protein genes for enhanced resistance to pathogens and pests. J Plant Dis Prot 130, 669–687 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41348-023-00713-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41348-023-00713-z