Abstract
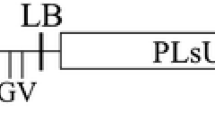
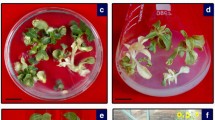
The feasibility of controlling peanut stem necrosis disease caused by Tobacco streak virus (TSV) in groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.) was explored by expressing double-stranded RNA of the replicase (Rep) gene of TSV in groundnut through genetic engineering. A hairpin (hp) RNAi construct containing 535-bp sense and antisense TSV-Rep sequences flanking a 742-bp spacer sequence (Pdk intron) under the control of the constitutive Cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter was made in the binary vector pART27. This chimeric gene construct was then mobilized into Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain LBA4404 via triparental mating using pRK2013 as a helper. Cotyledon explants of groundnut cultivar TMV-7 were transformed with A. tumefaciens harboring the hpRNA cassette. The presence of the transgene in the transgenic plants was confirmed up to T3 generation by PCR amplification of the 535-bp fragment of TSV-Rep gene. The bioassay results indicated that necrotic lesions were observed on the leaves of the wild-type plants 7–9 days after inoculation with TSV and stem necrosis appeared 16–20 days after inoculation, whereas the transgenic plants did not develop symptoms until harvest. ELISA results indicated that the wild-type plants inoculated with TSV recorded the highest virus concentration as compared to the transgenic lines.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abhary MK, Anfoka GH, Nakhla MK, Maxwell DP (2006) Post-transcriptional gene silencing in controlling viruses of the Tomato yellow leaf curl virus complex. Arch Virol 151:2349–2363
Ammara UE, Mansoor S, Saeed M, Amin I, Briddon RW, Al-Sadi AM (2015) RNA interference-based resistance in transgenic tomato plants against Tomato yellow leaf curl virus-Oman (TYLCV-OM) and its associated betasatellite. Virol J 12:38
An G (1987) Binary Ti vectors for plant transformation and promoter analysis. Methods Enzymol 153:292–305
Andika IB, Kondo H, Tamada T (2005) Evidence that RNA silencing-mediated resistance to Beet necrotic yellow vein virus is less effective in roots than in leaves. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 18:194–204
Azadi P, Otang NV, Supaporn H, Khan RS, Chin DP, Nakamura I, Mii M (2011) Increased resistance to cucumber mosaic virus (CMV) in Lilium transformed with a defective CMV replicase gene. Biotechnol Lett 33:1249–1255
Bag S, Singh RS, Jain RK (2007) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of groundnut with coat protein gene of Tobacco streak virus. Indian J Virol 18:65–69
Baulcomb DC (1996) Mechanisms of pathogen-derived resistance to viruses in transgenic plants. Plant Cell 8:1833–1844
Baulcombe DC (1994) Replicase-mediated resistance: a novel type of virus resistance in transgenic plants. Trends Microbiol 2:60–63
Baulcombe DC (2002) RNA silencing. Curr Biol 12:2–84
Bonfim K, Faria JC, Nogueira EO, Mendes EA, Aragao FJ (2007) RNAi-mediated resistance to Bean golden mosaic virus in genetically engineered common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). Mol Plant Microbe Interact 20:717–726
Brederode FT, Taschner PE, Posthumus E, Bol JF (1995) Replicase-mediated resistance to alfalfa mosaic virus. Virology 207:467–474
Brunetti A, Tavazza M, Noris E, Tavazza R, Caciagli P, Ancor G, Crespi S, Accotto GP (1997) High expression of truncated viral rep protein confers resistance to tomato yellow leaf curl virus in transgenic tomato plants. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 10:571–579
Canto T, Palukaitis P (1999) Replicase-mediated resistance to cucumber mosaic virus does not inhibit localization and/or trafficking of the viral movement protein. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 12:743–747
Carr JP, Gal-on A, Palukaitis P, Zaitlin M (1994) Replicase-mediated resistance to cucumber mosaic virus in transgenic plants involves suppression of both virus replication in the inoculated leaves and long-distance movement. Virology 199:439–447
Cillo F, Palukaitis P (2014) Transgenic resistance. Adv Virus Res 90:35–146
Dietzgen RG, Callaghan B, Higgins CM, Birch RG, Chen K, Xu Z (2001) Differentiation of peanut seedborne potyviruses and curcumoviruses by RT-PCR. Plant Dis 859:989–992
Ehrenfeld N, Roman E, Serrano C, Arce-Johnson P (2004) Replicase mediated resistance against Potato Leaf roll Virus in potato Desiree plants. Biol Res 37:71–82
Elayabalan S, Kalaiponmani K, Subramaniam S, Selvarajan R, Panchanathan R, Muthuvelayoutham R, Kumar KK, Balasubramanian P (2013) Development of Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of highly valued hill banana cultivar Virupakshi (AAB) for resistance to BBTV disease. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 29:589–596
Faria JC, Albino MMC, Dias BBA, Cancado LJ, da Cunha NB, Silva LM, Vianna GR, Aragao FJL (2006) Partial resistance to Bean golden mosaic virus in a transgenic common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) line expressing a mutated rep gene. Plant Sci 171:565–571
Gal-On A, Wolf D, Pilowski M, Zelcer A (2000) Transgenic F1 hybrids harboring a defective viral replicase exhibit high resistance to CMV in the field. Acta Physiol Plant 22:311–312
Golemboski DB, Lomonossoff GP, Zaitlin M (1990) Plants transformed with a tobacco mosaic virus nonstructural gene sequence are resistant to the virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:6311–6315
Goodwin J, Chapman K, Swaney S, Parks TD, Wernsman EA, Dougherty WG (1996) Genetic and biochemical dissection of transgenic RNA-mediated virus resisitance. Plant Cell 8:95–105
Hellwald KH, Palukaitis P (1995) Viral RNA as a potential target for two independent mechanisms of replicase-mediated resistance against Cucumber mosaic virus. Cell 83:937–946
Ibrahim AB, Aragao FJ (2015) RNAi-mediated resistance to viruses in genetically engineered plants. Methods Mol Biol 1287:81–92
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW (1987) GUS fusions: beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6:3901–3907
Kalantidis K, Psaradakis S, Tabler M, Sagris M (2002) The occurrence of CMV-specific short RNAs in transgenic tobacco expressing virus-derived double-stranded RNA is indicative of resistance to the virus. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 15:826–833
Kalyani G, Reddy AS, Kumar PL, Rao RDVJP, Aruna R, Waliyar F, Nigam SN (2007) Sources of resistance to Tobacco streak virus in wild Arachis (Fabaceae: Papilionoidae) germplasm. Plant Dis 91:1585–1590
Kamo K, Jordan R, Guaragna MA, Hsu HT, Ueng P (2010) Resistance to Cucumber mosaic virus in Gladiolus plants transformed with either a defective replicase or coat protein subgroup II gene from Cucumber mosaic virus. Plant Cell 29:695–704
Le DT, Chu HD, Sasaya T (2015) Creation of transgenic rice plants producing small interfering RNA of Rice tungro spherical virus. GM Crops Food 6:47–53
Longstaff M, Brigneti G, Boccard F, Chapman S, Baulcombe D (1993) Extreme resistance to potato virus X infection in plants expressing a modified component of the putative viral replicase. EMBO J 12:379–386
Matzke AJM, Matzke MA (1998) Position effects and epigenetic silencing of plant transgenes. Curr Opin Plant Biol 1:142–148
Mehta R, Radhakrishnan T, Kumar A, Yadav R, Dobaria JR, Thirumalaisamy PP, Jain RK, Chigurupati P (2013) Coat protein-mediated transgenic resistance of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) to peanut stem necrosis disease through Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation. Indian J Virol 24:205–213
Missiou A, Kalantidis K, Boutla A, Tzortzakaki S, Tabler M, Tsagris M (2004) Generation of transgenic potato plants highly resistant to potato virus Y (PVY) through RNA silencing. Mol Breeding 14:185–197
Mitter N, Dietzgen RG (2012) Use of hairpin RNA constructs for engineering plant virus resistance. Methods Mol Biol 894:191–208
Murashige T, Skoog FA (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Nomura K, Ohshima K, Anai T, Uekusa H, Kita N (2004) RNA silencing of the introduced coat protein gene of Turnip mosaic virus confers broad-spectrum resistance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Phytopathology 94:730–736
Noris E, Accotto GP, Tavazza R, Brunetti A, Crespi S, Tavazza M (1996) Resistance to tomato yellow leaf curl geminivirus in Nicotiana benthamiana plants transformed with a truncated viral C1 gene. Virology 224:130–138
Ntui VO, Kynet K, Khan RS, Ohara M, Goto Y, Watanabe M, Fukami M, Nakamura I, Mii M (2014) Transgenic tobacco lines expressing defective CMV replicase-derived dsRNA are resistant to CMV-O and CMV-Y. Mol Biotechnol 56:50–63
Ogwok E, Odipio J, Halsey M, Gaitan-Solis E, Bua A, Taylor NJ, Fauquet CM, Alicai T (2012) Transgenic RNA interference (RNAi)-derived field resistance to cassava brown streak disease. Molecular Plant Pathology 13:1019–1031
Palukaitis P, Zaitlin M (1997) Replicase-mediated resistance to plant virus disease. Adv Virus Res 48:349–377
Pooggin M, Shivaprasad PV, Veluthambi K, Hohn T (2003) RNAi targeting of DNA virus in plants. Nat Biotechnol 21:131–132
Pradeep K, Satya VK, Selvapriya M, Vijayasamundeeswari A, Ladhalakshmi D, Paranidharan V, Rabindran R, Samiyappan R, Balasubramanian P, Velazhahan R (2012) Engineering resistance against Tobacco streak virus (TSV) in sunflower and tobacco using RNA interference. Biol Plant 56:735–741
Prasada Rao RDVJ, Reddy AS, Reddy SV, Thirumala Devi K, Chander Rao S, Manoj Kumar V, Subramanyam K, Yellamanda Reddy T, Nigam SN, Reddy DVR (2003) The host range of Tobacco streak virus in India and transmission by thrips. Ann Appl Biol 142:365–368
Prins M, Goldbach R (1996) RNA-mediated virus resistance in transgenic plants. Arch Virol 141:2259–2276
Ramiah M, Bhat AI, Jain RK, Pant RP, Ahlawat YS, Prabhakar K, Varma A (2001) Isolation of an isometric virus causing sunflower necrosis disease in India. Plant Dis 85:443
Reddy AS, Prasada Rao RDVJ, Thirumala Devi K, Reddy SV, Mayo MA, Roberts I, Satyanarayana T, Subramaniam K, Reddy DVR (2002) Occurrence of Tobacco streak virus on peanut (Arachis hypogaea) in India. Plant Dis 86:173–178
Sanford JC, Johnston SA (1985) The concept of parasite-derived resistance-deriving resistance genes from the parasite’s own genome. J Theor Biol 113:395–405
Sharma KK, Anjaiah V (2000) An efficient method for the production of transgenic plants of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) through Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated genetic transformation. Plant Sci 159:7–19
Sharma VK, Basu S, Chakraborty S (2015) RNAi mediated broad-spectrum transgenic resistance in Nicotiana benthamiana to chilli-infecting begomoviruses. Plant Cell Rep 34:1389–1399
Shekhawat UK, Ganapathi TR, Hadapad AB (2012) Transgenic banana plants expressing small interfering RNAs targeted against viral replication initiation gene display high-level resistance to banana bunchy top virus infection. J Gen Virol 93:1804–1813
Shimizu T, Nakazono-Nagaoka E, Akita F, Uehara-Ichiki T, Omura T, Sasaya T (2011) Immunity to Rice black streaked dwarf virus, a plant reovirus, can be achieved in rice plants by RNA silencing against the gene for the viroplasm component protein. Virus Res 160:400–403
Shimizu T, Ugamino T, Hiraguri A, Nakazono-Nagaoka F, Uehara-Ichiki T, Nakajima M, Akutsu K, Omura T, Sasaya T (2013) Strong resistance against Rice grassy stunt virus is induced in transgenic rice plants expressing double-stranded RNA of the viral genes for nucleocapsid or movement proteins as targets for RNA interference. Phytopathology 103:513–519
Shukla S, Kalyani G, Kulkarni N, Waliyar F, Nigam SN (2005) Mechanism of transmission of Tobacco streak virus by Scirtothrips dorsalis, Frankliniella schultzei and Megalurothrips usitatus in groundnut, Arachis hypogaea L. J Oilseeds Res 22:215–217
Sijen T, Wellink J, Hiriart JP, van Kammen A (1996) RNA-mediated virus resistance: role of repeated transgenes and delineation of targeted regions. Plant Cell 8:2277–2294
Smith NA, Singh SP, Wang MB, Stoutjesdijk P, Green A, Waterhouse PM (2000) Total silencing by intron-spliced hairpin RNA. Nature 407:319–320
Thomas PE, Lawson EC, Zalewski JC, Reed GL, Kaniewski WK (2000) Extreme resistance to Potato leaf roll virus in potato cv. Russet Burbank mediated by the viral replicase gene. Virus Res 71:49–62
Tyagi H, Rajasubramaniam S, Rajam MV, Dasgupta I (2008) RNA-interference in rice against Rice tungro bacilliform virus results in its decreased accumulation in inoculated rice plants. Transgenic Res 17:897–904
Vanitharani R, Chellappan P, Fauquet CM (2003) Short interfering RNA-mediated interference of gene expression and viral DNA accumulation in cultured plant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:9632–9636
Vazquez RC, Asurmendi S, Hopp HE (2001) Transgenic resistance in potato plants expressing potato leaf roll virus (PLRV) replicase gene sequences is RNA-mediated and suggests the involvement of post-transcriptional gene silencing. Arch Virol 146:1337–1353
Vemana K, Jain RK (2010) New experimental hosts of Tobacco streak virus and absence of true seed transmission in leguminous hosts. Indian J Virol 21:117–127
Wang F, Li W, Zhu J, Fan F, Wang J, Zhong W, Wang MB, Liu Q, Zhu QH, Zhou T, Lan Y, Zhou Y, Yang J (2016) Hairpin RNA targeting multiple viral genes confers strong resistance to Rice black streaked dwarf virus. Int J Mol Sci 17:705
Wang MB, Abbott D, Waterhouse PM (2000) A single copy of a virus derived transgene encoding hairpin RNA gives immunity to barley yellow dwarf virus. Mol Plant Pathol 1:401–410
Waterhouse PM, Graham MW, Wang MB (1998) Virus resistance and gene silencing in plants can be induced by simultaneous expression of sense and antisense RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:13959–13964
Wesley SV, Helliwell CA, Smith NA, Wang M, Rouse DT, Liu Q, Gooding PS, Singh SP, Abbott D, Stoutjesdijk PA, Robinson SP, Gleave AP, Green AG, Waterhouse PM (2001) Construct design for efficient, effective and high-throughput gene silencing in plants. Plant J 27:581–590
Yang Y, Sherwood TA, Patte CP, Hiebert E, Polston JE (2004) Use of Tomato yellow leaf curl virus (TYLCV) Rep gene sequences to engineer TYLCV resistance in tomato. Phytopathology 94:490–496
Zhou Y, Yuan Y, Yuan F, Wang M, Zhong H, Gu M, Liang G (2012) RNAi-directed down-regulation of RSV results in increased resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Biotechnol Lett 34:965–972
Acknowledgments
We thank the CSIRO Plant Industry, Australia, for providing the vectors pHANNIBAL and pART27. We are grateful to Dr. S. Muthukrishnan, Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biophysics, Kansas State University, Manhattan, Kansas, USA, for critical reading of the manuscript. This study was funded by the University Grants Commission, New Delhi, India (Grant No. 42-200/2013-SR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article is original and not published elsewhere. Corresponding author confirms that all authors have approved the manuscript and there are no ethical issues in publication of the manuscript. The study has been approved by the Institutional Bio-safety Committee (IBSC) of Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore, India.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reddy, M.G., Senthilraja, C., Adhithya, R. et al. Integration of a hairpin RNA-encoding gene derived from Tobacco streak virus confers resistance in groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.) against peanut stem necrosis disease. J Plant Dis Prot 123, 205–214 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41348-016-0039-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41348-016-0039-7