Abstract
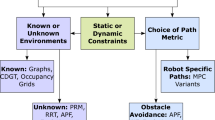
Path planning is an intrinsic component of autonomous robotics, be it industrial, research or consumer robotics. Such avenues experience constraints around which paths must be planned. While the choice of an appropriate algorithm is application-dependent, the starting point of an ideal path planning algorithm is the review of past work. Historically, algorithms were classified based on the three tenets of autonomous robotics which are the ability to avoid different constraints (static/dynamic), knowledge of the environment (known/unknown) and knowledge of the robot (general/model specific). This division in literature however, is not comprehensive, especially with respect to dynamics constraints. Therefore, to remedy this issue, we propose a new taxonomy, based on the fundamental tenet of characterizing space, i.e., as a set of distinct, unrelated points or as a set of points that share a relationship. We show that this taxonomy is effective in addressing important parameters of path planning such as connectivity and partitioning of spaces. Therefore, path planning spaces may now be viewed either as a set of points or, as a space with structure. The former relies heavily on robot models, since the mathematical structure of the environment is not considered. Thus, the approaches used are variants of optimization algorithms and specific variants of model-based methods that are tailored to counteract effects of dynamic constraints. The latter depicts spaces as points with inter-connecting relationships, such as surfaces or manifolds. These structures allow for unique characterizations of paths using homotopy-based methods. The goals of this work, viewed specifically in light with dynamic constraints, are therefore as follows: First, we propose an all-encompassing taxonomy for robotic path planning literature that considers an underlying structure of the space. Second, we provide a detailed accumulation of works that do focus on the characterization of paths in spaces formulated to show underlying structure. This work accomplishes the goals by doing the following: It highlights existing classifications of path planning literature, identifies gaps in common classifications, proposes a new taxonomy based on the mathematical nature of the path planning space (topological properties), and provides an extensive conglomeration of literature that is encompassed by this new proposed taxonomy.
























Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
There is no data or materials to share.
Abbreviations
- APF :
-
Artificial potential field
- CDGT :
-
Cell decomposition and graph traversal
- DC :
-
Dynamic constraint
- EA :
-
Evolutionary algorithm
- \(HA^{*}\) :
-
Homotopic A*
- HB :
-
Homotopic bug
- HBM :
-
Homotopy based method
- HCM :
-
Homotopy continuation methods
- HRRT :
-
Homotopic RRT
- LAG :
-
L-augmented graph
- MBM :
-
Model based methods
- MPC :
-
Model predictive control
- NAES :
-
Non-linear algebraic equation system
- NF :
-
Navigation functions
- OA :
-
Optimization algorithm
- PPM :
-
Path planning manifold
- PPP :
-
Path planning problem
- PPS :
-
Path planning space
- PRM :
-
Probabilistic road map
- RRT :
-
Rapidly exploring random tree
- SA :
-
Sampling algorithm
- SC :
-
Static constraint
- SHIO :
-
Single homotopy inducing obstacle
- VOS :
-
Velocity obstacle sets
- \(H-signature\) :
-
Unique measure associated to a homotopic class
- \({{\textbf {p}}^{\text {start}}}{\in \mathcal {P}}\) :
-
Starting point in \({\mathcal {P}}\)
- \({{\textbf {p}}^{\text {goal}}}{\in \mathcal {P}}\) :
-
Destination point in \({\mathcal {P}}\)
References
Agirrebeitia, J., Avilés, R., de Bustos, I.F., Ajuria, G.: A new APF strategy for path planning in environments with obstacles. Mech. Mach. Theory 40(6), 645–658 (2005)
Akbaripour, H., Akbaripour, H., Masehian, E., Masehian, E.: Semi-lazy probabilistic roadmap: a parameter-tuned, resilient and robust path planning method for manipulator robots. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 89(5), 1401–1430 (2017)
Ataka, A., Lam, H.-K., Althoefer, K.: Reactive magnetic-field-inspired navigation method for robots in unknown convex 3-D environments. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 3(4), 3583–3590 (2018)
Atramentov, A., LaValle, S.M.: Efficient nearest neighbor searching for motion planning. In: Proceedings 2002 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (Cat. No.02CH37292), vol. 1, pp. 632–6371 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1109/ROBOT.2002.1013429
Barraquand, J., Latombe, J.-C.: Robot motion planning: a distributed representation approach. Int. J. Robot. Res. 10(6), 628–649 (2016)
Belkhouche, F.: Reactive path planning in a dynamic environment. IEEE Trans. Robot. 25(4), 902–911 (2009)
Belkhouche, F., Bendjilali, B.: Reactive path planning for 3-D autonomous vehicles. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 20(1), 249–256 (2012)
Bevilacqua, P., Frego, M., Fontanelli, D., Palopoli, L.: Reactive planning for assistive robots. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 3(2), 1276–1283 (2018)
Bhattacharya, S., Kumar, V., Likhachev, M.: Search-based path planning with homotopy class constraints. In: Proceedings of the Twenty-Fourth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. AAAI’10, pp. 1230–1237. AAAI Press, Atlanta (2010)
Bhattacharya, S., Likhachev, M., Kumar, V.: Identification and representation of homotopy classes of trajectories for search-based path planning in 3D. In: Robotics. MIT Press, Cambridge (2012a)
Bhattacharya, S., Likhachev, M., Kumar, V.: Search-based path planning with homotopy class constraints in 3D. In: Invited Paper for Sub-area Spotlights Track on ’Best-paper Talks’, Proceedings of Twenty-Sixth Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI-12) (2012b)
Bloch, A., Camarinha, M., Colombo, L.J.: Dynamic interpolation for obstacle avoidance on Riemannian manifolds. Int. J. Control 94(3), 588–600 (2021)
Bohlin, R., Kavraki, L.E.: Path planning using lazy PRM. In: Proceedings 2000 ICRA. Millennium Conference. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Symposia Proceedings (Cat. No.00CH37065), vol. 1, pp. 521–5281 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1109/ROBOT.2000.844107
Cabello, S., Liu, Y., Mantler, A., Snoeyink, J.: Testing homotopy for paths in the plane. Discrete Comput. Geom. 31(1), 61–81 (2004)
Cockayne, E.J., Hall, G.W.C.: Plane motion of a particle subject to curvature constraints. SIAM J. Control 13(1), 197–220 (1975)
Cui, P., Yan, W., Wang, Y.: Reactive path planning approach for docking robots in unknown environment. J. Adv. Transport. 2017, 1–11 (2017)
Dale, L.K., Amato, N.M.: Probabilistic roadmaps-putting it all together. In: Proceedings 2001 ICRA. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (Cat. No.01CH37164), vol. 2, pp. 1940–19472 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1109/ROBOT.2001.932892
De Filippis, L., Guglieri, G., Quagliotti, F.: Path planning strategies for UAVs in 3D environments. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 65(1), 247–264 (2012)
Diankov, R., Kuffner, J.: Randomized statistical path planning. In: 2007 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 1–6 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS.2007.4399557
Diaz-Arango, G., Sarmiento-Reyes, A., Hernandez-Martinez, L., Vazquez-Leal, H., Lopez-Hernandez, D.D., Marin-Hernandez, A.: Path optimization for terrestrial robots using homotopy path planning method. In: 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), pp. 2824–2827. IEEE, Lisbon (2015)
Diaz-Arango, G., Vazquez-Leal, H., Hernandez-Martinez, L., Manuel Jimenez-Fernandez, V., Heredia-Jimenez, A., Ambrosio, R.C., Huerta-Chua, J., De Cos-Cholula, H., Hernandez-Mendez, S.: Multiple-target homotopic quasi-complete path planning method for mobile robot using a piecewise linear approach. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland) 20(11), 3265 (2020)
Diéguez, A.R., Sanz, R., López, J.: Deliberative on-line local path planning for autonomous mobile robots. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 37(1), 1–19 (2003)
Duchoň, F., Babinec, A., Kajan, M., Beňo, P., Florek, M., Fico, T., Jurišica, L.: Path planning with modified a star algorithm for a mobile robot. Proc. Eng. 96, 59–69 (2014)
Eduardo De Cos-Cholula, H., Ulises Diaz-Arango, G., Hernandez-Martinez, L., Vazquez-Leal, H., Sarmiento-Reyes, A., Teresa Sanz-Pascual, M., Leobardo Herrera-May, A., Castaneda-Sheissa, R.: FPGA implementation of homotopic path planning method with automatic assignment of repulsion parameter. Energies (Basel) 13(10), 2623 (2020)
Elbanhawi, M., Simic, M.: Sampling-based robot motion planning: a review. IEEE Access 2, 56–77 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2014.2302442
Faverjon, B., Tournassoud, P.: A local based approach for path planning of manipulators with a high number of degrees of freedom. In: Proceedings. 1987 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, vol. 4, pp. 1152–1159 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1109/ROBOT.1987.1087982
Ferguson, D., Stentz, A.: Anytime RRTs. In: 2006 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 5369–5375 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS.2006.282100
Fiorini, P., Shiller, Z.: Motion planning in dynamic environments using velocity obstacles. Int. J. Robot. Res. 17(7), 760–772 (1998)
Ginesi, M., Meli, D., Roberti, A., Sansonetto, N., Fiorini, P.: Dynamic movement primitives: volumetric obstacle avoidance using dynamic potential functions. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 101(4), 1–20 (2021)
Gregoire, J., Čáp, M., Frazzoli, E.: Locally-optimal multi-robot navigation under delaying disturbances using homotopy constraints. Auton. Robots 42(4), 895–907 (2018)
Hernandez, E., Carreras, M., Ridao, P., Antich, J., Ortiz, A.: A search-based path planning algorithm with topological constraints. application to an AUV. IFAC Proc. Vol. 44(1), 13654–13659 (2011)
Hernández, E., Carreras, M., Ridao, P.: A bug-based path planner guided with homotopy classes. In: ICINCO 2012—Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics, vol. 2, pp. 123–131 (2012)
Hernández, E., Carreras, M., Ridao, P.: A path planning algorithm for an AUV guided with homotopy classes. In: Proceedings of the Twenty-First International Conference on Automated Planning and Scheduling, vol. 21 (2011)
Hernandez, E., Carreras, M., Ridao, P.: A comparison of homotopic path planning algorithms for robotic applications. Robot. Auton. Syst. 64, 44–58 (2015)
Hildebrandt, A.-C., Klischat, M., Wahrmann, D., Wittmann, R., Sygulla, F., Seiwald, P., Rixen, D., Buschmann, T.: Real-time path planning in unknown environments for bipedal robots. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2(4), 1856–1863 (2017)
Hossain, M.A., Ferdous, I.: Autonomous robot path planning in dynamic environment using a new optimization technique inspired by bacterial foraging technique. Robot. Auton. Syst. 64, 137–141 (2015)
Hsu, D., Zheng, S.: Adaptively combining multiple sampling strategies for probabilistic roadmap planning. In: IEEE Conference on Robotics, Automation and Mechatronics, 2004, vol. 2, pp. 774–7792 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1109/RAMECH.2004.1438016
Hughes, K., Tokuta, A., Ranganathan, N.: Trulla: an algorithm for path planning among weighted regions by localized propagations. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, vol. 1, pp. 469–476 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS.1992.587377
Jaillet, L., Cortés, J., Siméon, T.: Sampling-based path planning on configuration-space costmaps. IEEE Trans. Robot. 26(4), 635–646 (2010)
Jenkins, K.D.: The shortest path problem in the plane with obstacles: a graph modeling approach to producing finite search lists of homotopy classes. Master’s thesis, Naval Postgraduate School Monterey California (1991)
Kala, R.: Homotopy conscious roadmap construction by fast sampling of narrow corridors. Appl. Intell. (Dordrecht, Netherlands) 45(4), 1089–1102 (2016)
Kala, R.: Homotopic roadmap generation for robot motion planning. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 82(3), 555–575 (2016)
Karaman, S., Frazzoli, E.: Sampling-based algorithms for optimal motion planning. Int. J. Robot. Res. 30(7), 846–894 (2011)
Kavraki, L.E., Svestka, P., Latombe, J.-C., Overmars, M.H.: Probabilistic roadmaps for path planning in high-dimensional configuration spaces. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 12(4), 566–580 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1109/70.508439
Khatib, O.: Real-time obstacle avoidance for manipulators and mobile robots. Int. J. Robot. Res. 5(1), 90–98 (1986)
Khosla, P., Volpe, R.: Superquadric artificial potentials for obstacle avoidance and approach. In: Proceedings. 1988 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 1778–17843 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1109/ROBOT.1988.12323
Kim, D., Kang, M., Yoon, S.-E.: Volumetric tree: adaptive sparse graph for effective exploration of homotopy classes. In: 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 1496–1503. IEEE, Macau (2019)
Kim, S., Sreenath, K., Bhattacharya, S., Kumar, V.: Trajectory planning for systems with homotopy class constraints. In: Latest Advances in Robot Kinematics (ARK), Innsbruck, pp. 83–90 (2012)
Koditschek, D.: Exact robot navigation by means of potential functions: Some topological considerations. In: Proceedings. 1987 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, vol. 4, pp. 1–6 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1109/ROBOT.1987.1088038
Koditschek, D.E., Rimon, E.: Robot navigation functions on manifolds with boundary. Adv. Appl. Math. 11(4), 412–442 (1990)
Kolur, K., Chintalapudi, S., Boots, B., Mukadam, M.: Online motion planning over multiple homotopy classes with gaussian process inference. In: 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 2358–2364. IEEE, Macau (2019)
Kowalczyk, W.: Rapid navigation function control for two-wheeled mobile robots. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 93(3–4), 687–697 (2018)
Kowalczyk, W., Kowalczyk, W., Przybyla, M., Przybyla, M., Kozlowski, K., Kozlowski, K.: Set-point control of mobile robot with obstacle detection and avoidance using navigation function—experimental verification. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 85(3), 539–552 (2017)
Kuffner, J.J., LaValle, S.M.: RRT-connect: an efficient approach to single-query path planning. In: Proceedings 2000 ICRA. Millennium Conference. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Symposia Proceedings (Cat. No.00CH37065), vol. 2, pp. 995–10012 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1109/ROBOT.2000.844730
Kuwata, Y., Teo, J., Karaman, S., Fiore, G., Frazzoli, E., How, J.: Motion planning in complex environments using closed-loop prediction. In: AIAA Guidance, Navigation and Control Conference and Exhibit (2008). https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2008-7166. AIAA
Lamiraux, F., Bonnafous, D., Lefebvre, O.: Reactive path deformation for nonholonomic mobile robots. IEEE Trans. Robot. 20(6), 967–977 (2004)
M.LaValle, S.: Rapidly-exploring random trees: a new tool for path planning. Technical report, Iowa State University, Ames (1998)
LaValle, S.M., Kuffner, J.J.: Randomized kinodynamic planning. Int. J. Robot. Res. 20(5), 378–400 (2001)
LaValle, S.M., Branicky, M.S., Lindemann, S.R.: On the relationship between classical grid search and probabilistic roadmaps. Int. J. Robot. Res. 23(7–8), 673–692 (2004)
Lee, J., Pippin, C., Balch, T.: Cost based planning with RRT in outdoor environments. In: 2008 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 684–689 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS.2008.4651052
Lengyel, J., Reichert, M., Donald, B.R., Greenberg, D.P.: Real-time robot motion planning using rasterizing computer graphics hardware. Comput. Graph. (New York, N. Y.) 24(4), 327–335 (1990)
Li, X., Zhao, G., Li, B.: Generating optimal path by level set approach for a mobile robot moving in static/dynamic environments. Appl. Math. Model. 85, 210–230 (2020)
Lin, Y., Saripalli, S.: Sampling-based path planning for uav collision avoidance. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transport. Syst. 18(11), 3179–3192 (2017)
Liu, Y., Qi, N., Yao, W., Zhao, J., Xu, S.: Cooperative path planning for aerial recovery of a UAV swarm using genetic algorithm and homotopic approach. Appl. Sci. 10(12), 4154 (2020)
Liu, Y., Zheng, Z., Qin, F.: Homotopy based optimal configuration space reduction for anytime robotic motion planning. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 34(1), 364–379 (2021)
Lumelsky, V.J., Stepanov, A.A.: Path-planning strategies for a point mobile automaton moving amidst unknown obstacles of arbitrary shape. Algorithmica 2(1–4), 403–430 (1987)
Masehian, E., Amin-Naseri, M.R.: A Voronoi diagram-visibility graph-potential field compound algorithm for robot path planning. J. Robot. Syst. 21(6), 275–300 (2004)
McFetridge, L., Ibrahim, M.Y.: A new methodology of mobile robot navigation: the agoraphilic algorithm. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 25(3), 545–551 (2009)
Mediavilla, M., González, J.L., Fraile, J.C., Ramón Perán, J.: Reactive approach to on-line path planning for robot manipulators in dynamic environments. Robotica 20(4), 375–384 (2002)
Molina, C.P., Ortego, R.G., Pérez, F.M.: Perspectives on Technological Developments Applied to Robotics, pp. 59–86. Springer, London (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4471-5358-0_5
Montiel, O., Orozco-Rosas, U., Sepúlveda, R.: Path planning for mobile robots using bacterial potential field for avoiding static and dynamic obstacles. Expert Syst. Appl. 42(12), 5177–5191 (2015)
Murphy, R.R., Hughes, K., Marzilli, A., Noll, E.: Integrating explicit path planning with reactive control of mobile robots using trulla. Robot. Auton. Syst. 27(4), 225–245 (1999)
Noreen, I., Khan, A., Ryu, H., Doh, N.L., Habib, Z.: Optimal path planning in cluttered environment using RRT-AB. Intell. Serv. Robot. 11(1), 41–52 (2017)
Park, J., Karumanchi, S., Iagnemma, K.: Homotopy-based divide-and-conquer strategy for optimal trajectory planning via mixed-integer programming. IEEE Trans. Robot. 31(5), 1101–1115 (2015)
Qin, L., Yin, Q., Zha, Y., Peng, Y.: Dynamic detection of topological information from grid-based generalized Voronoi diagrams. Math. Probl. Eng. 2013, 1–11 (2013)
Quillen, P., Muñoz, J., Subbarao, K.: Path planning to a reachable state using minimum control effort based navigation functions. J. Astronaut. Sci. 66(4), 554–581 (2019)
Radhakrishnan, S., Gueaieb, W.: A state-of-the-art review on topology and differential geometry-based robotic path planning—part I: planning under static constraints. Int. J. Intell. Robot. Appl. (2023)
Radhakrishnan, S.: Observable 2D SLAM and Evidential Occupancy Grids. Master’s thesis, Carleton University (2014)
Savkin, A.V., Hoy, M.: Reactive and the shortest path navigation of a wheeled mobile robot in cluttered environments. Robotica 31(2), 323–330 (2013)
Stentz, A.: Optimal and efficient path planning for partially-known environments. In: Proceedings of the 1994 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 3310–33174 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1109/ROBOT.1994.351061
Stopp, A., Riethmuller, T.: Fast reactive path planning by 2d and 3d multi-layer spatial grids for mobile robot navigation. In: Proceedings of Tenth International Symposium on Intelligent Control, pp. 545–550. IEEE, Monterey (1995)
Suh, J., Gong, J., Oh, S.: Fast sampling-based cost-aware path planning with nonmyopic extensions using cross entropy. IEEE Trans. Robot. 33(6), 1313–1326 (2017)
Tao, S., Tan, J.: Path planning with obstacle avoidance based on normalized r-functions. J. Robot. 2018, 1–10 (2018)
van den Berg, J., Overmars, M.: Planning time-minimal safe paths amidst unpredictably moving obstacles. Int. J. Robot. Res. 27(11–12), 1274–1294 (2008)
Vazquez-Leal, H., Marin-Hernandez, A., Khan, Y., Yıldırım, A., Filobello-Nino, U., Castaneda-Sheissa, R., Jimenez-Fernandez, V.M.: Exploring collision-free path planning by using homotopy continuation methods. Appl. Math. Comput. 219(14), 7514–7532 (2013)
Volpe, R., Khosla, P.: Artificial potentials with elliptical isopotential contours for obstacle avoidance. In: 26th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, vol. 26, pp. 180–185 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1109/CDC.1987.272738
Volpe, R., Khosla, P.: Manipulator control with superquadric artificial potential functions: theory and experiments. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 20(6), 1423–1436 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1109/21.61211
Wada, H., Kinugawa, J., Kosuge, K.: Reactive motion planning using time-layered c-spaces for a collaborative robot pady. Adv. Robot. 35(8), 490–503 (2021)
Wang, W., Zuo, L., Xu, X.: A learning-based multi-rrt approach for robot path planning in narrow passages. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 90(1–2), 81–100 (2017)
Wang, B., Liu, Z., Li, Q., Prorok, A.: Mobile robot path planning in dynamic environments through globally guided reinforcement learning. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 5(4), 6932–6939 (2020)
Wu, A., How, J.P.: Guaranteed infinite horizon avoidance of unpredictable, dynamically constrained obstacles. Auton. Robots 32(3), 227–242 (2012)
Yao, W., Qi, N., Zhao, J., Wan, N.: Bounded curvature path planning with expected length for Dubins vehicle entering target manifold. Robot. Auton. Syst. 97, 217–229 (2017)
Yi, D., Goodrich, M., Seppi, K.: Homotopy-aware RRT: Toward human-robot topological path-planning. In: The Eleventh ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human Robot Interaction. HRI ’16, pp. 279–286. IEEE Press, Christchurch (2016)
Funding
This work was partially supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC). Grant RGPIN-2014-06512.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Sindhu Radhakrishnan. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Sindhu Radhakrishnan and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Radhakrishnan, S., Gueaieb, W. A state-of-the-art review on topology and differential geometry-based robotic path planning—part II: planning under dynamic constraints. Int J Intell Robot Appl (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41315-024-00331-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41315-024-00331-4