Abstract
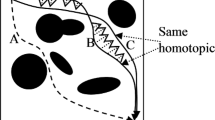
Two robot paths are said to be in the same homotopic group if one can be obtained from the other by multiple small deformations. Knowledge of robot homotopic groups gives information regarding the obstacle structure and enables timely computation of optimal path. Making a roadmap which misses out on a single homotopic group in such approaches may lead to sub-optimal decisions. E.g. one may prefer to go through a very narrow corridor if that reduces the path length significantly, but not if the resulting path has too many such narrow segments. Similarly knowledge of homotopic groups may enable distribution and scheduling of robots across homotopic groups for decentralized planning of multiple robots. For an unstructured robot environment, sampling based approaches give an insight into homotopic groups. The aim of the work is to make a homotopy conscious Probabilistic Roadmap such that the roadmap is capable of generating paths corresponding to as many homotopic groups as possible. Experimental results confirm that the proposed approach gives the best results as compared to the other sampling techniques subject to the test scenarios run.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kala, R.: Rapidly-exploring Random Graphs: Motion Planning of Multiple Mobile Robots. Adv. Rob 27(14), 1113–1122 (2013)
Kala, R.: Coordination in Navigation of Multiple Mobile Robots. Cybern. Syst 45(1), 1–24 (2014)
Kala, R., Warwick, K.: Multi-Level Planning for Semi-Autonomous Vehicles in Traffic Scenarios based on Separation Maximization. J. Intell. Rob. Syst 72(3-4), 559–590 (2013)
Kala, R., Warwick, K.: Planning Autonomous Vehicles in the Absence of Speed Lanes using an Elastic Strip. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst 14(4), 1743–1752 (2013)
Kavraki, L.E., Svestka, P., Latombe, J.-C., Overmars, M.H.: Probabilistic roadmaps for path planning in high-dimensional configuration spaces. IEEE Trans. Rob. Automat 12(4), 566–580 (1996)
Bohlin, R., Kavraki, L.E.: Path planning using lazy prm. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 521–528. IEEE (2000)
Nieuwenhuisen, D., Overmars, M.H.: Useful cycles in probabilistic roadmap graphs. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 446–452. IEEE (2004)
Marble, J.D., Bekris, K.E.: Computing spanners of asymptotically optimal probabilistic roadmaps. In: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 4292–4298. IEEE (2011)
Marble, J.D., Bekris, K.E.: Asymptotically Near-Optimal Planning With Probabilistic Roadmap Spanners. IEEE Trans. Rob 29(2), 432–444 (2013)
Gayle, R., Sud, A., Andersen, E., Guy, S.J., Lin, M.C., Manocha, D.: Interactive Navigation of Heterogeneous Agents Using Adaptive Roadmaps. IEEE Trans. Visual. Comput. Graph 15(1), 34–48 (2009)
Gayle, R., Sud, A., Lin, M.C., Manocha, D.: Reactive Deformation Roadmaps: Motion Planning of Multiple Robots in Dynamic Environments. In: Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 3777–3783. IEEE, San Diego (2007)
Hilgert, J., Hirsch, K., Bertram, T., Hiller, M.: Emergency path planning for autonomous vehicles using elastic band theory. In: Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, vol. 2, pp. 1390–1395. IEEE (2003)
Quinlan, S., Khatib, O.: Elastic bands: connecting path planning and control. In: Proceedings of the 1993 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 802–807. IEEE (1993)
LaValle, S.M., Kuffner, J.J.: Randomized kinodynamic planning. Int. J. Robot. Res. 20(5), 378–400 (2001)
Kuffner, J.J., LaValle, S.M.: RRT-connect: An efficient approach to single-query path planning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 995–1001. IEEE (2000)
Lie, T.Y., Shie, Y.C.: An incremental approach to motion planning with roadmap management. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, vol. 4, pp. 3411–3416. IEEE (2002)
Morales, M., Rodriguez, S., Amato, N.: Improving the connectivity of PRM roadmaps. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 4427–4432. IEEE (2003)
Plaku, E., Bekris, K.E., Chen, B.Y., Ladd, A.M., Kavraki, E.E.: Sampling-Based Roadmap of Trees for Parallel Motion Planning. IEEE Trans. Rob 21(4), 597–608 (2005)
Raveh, B., Enosh, A., Halperin, D.: A little more, a lot better: improving path quality by a path-merging algorithm. IEEE Trans. Rob 27, 365–371 (2011)
Amato, N.M., Bayazit, O.B., Dale, L.K., Jones, C., Vallejo, D.: Obprm: An obstacle-based prm for 3d workspaces. In: Agarwal, P., Kavraki, L.E., Mason, M. (eds.) Robotics: The Algorithmic Perspective, pp. 155–168. A.K. Peters (1998)
Yeh, H.Y., Thomas, S., Eppstein, D., Amato, N.M.: UOBPRM: A uniformly distributed obstacle-based PRM. In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 2655–2662. IEEE (2012)
Hsu, D., Jiang, T., Reif, J., Sun, Z.: The bridge test for sampling narrow passages with probabilistic roadmap planners. In: Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, vol. 3, pp. 4420–4426. IEEE (2003)
Boor, V., Overmars, M.H., van der Stappen, A.F.: The Gaussian sampling strategy for probabilistic roadmap planners. In: Proceedings of the 1999 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, vol. 2, pp. 1018–1023. IEEE (1999)
Sun, Z., Hsu, D., Jiang, T., Kurniawati, H., Reif, J.H.: Narrow passage sampling for probabilistic roadmap planning. IEEE Trans. Rob 21(6), 1105–1115 (2005)
Denny, J., Amato, N.M.: Toggle PRM: A Coordinated Mapping of C-free and C-obstacle in Arbitrary Dimension. In: Proceedings of the International Workshop on Algorithmic Foundations of Robotics, pp. 297–312. Springer, Boston (2012)
Wilmarth, S.A., Amato, N.M., Stiller, P.F.: MAPRM: A Probabilistic Roadmap Planner with Sampling on the Medial Axis of the Free Space. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 1024–1031. Detroit (1999)
Holleman, C., Kavraki, L.E.: A framework for using the workspace medial axis in prm planners. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 1408–1413. IEEE (2000)
Schmitzberger, E., Bouchet, J.L., Dufaut, M., Wolf, D., Husson, R.: Capture of homotopy classes with probabilistic road map. In: Proceedings of the 2002. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, vol. 3, pp. 2317–2322. IEEE (2002)
Bhattacharya, S., Likhachev, M., Kumar, V.: Topological constraints in search-based robot path planning. Auton Rob 33(3), 273–290 (2012)
Demyen, D., Buro, M.: Effιcient triangulation-based pathfιnding. In: 21st National conference on Artifιcial Intelligence, pp. 942–947. IEEE (2006)
Grigoriev, D., Slissenko, A.: Polytime algorithm for the shortest path in a homotopy class amidst semi-algebraic obstacles in the plane. In: Proceedings of the 1998 international symposium on Symbolic and algebraic computation, pp. 17–24. IEEE (1998)
Hsu, D., Sanchez-Ante, G., Sun, Z.: Hybrid PRM Sampling with a Cost-Sensitive Adaptive Strategy. In: Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 3874–3880. IEEE (2005)
Shi, K., Denny, J., Amato, N.M.: Spark PRM: Using RRTs within PRMs to efficiently explore narrow passages. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 4659–4666. IEEE (2014)
Siméon, T., Laumond, J.P., Nissoux, C.: Visibility-based probabilistic roadmaps for motion planning. Adv. Rob 14(6), 477–493 (2000)
Jaillet, L., Cortes, J., Simeon, T.: Transition-based RRT for path planning in continuous cost spaces. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 2145–2150. IEEE, France (2008)
Dobson, A., Bekris, K.E.: Sparse roadmap spanners for asymptotically near-optimal motion planning. Int. J. Rob. Res 33, 18–47 (2014)
Littlefield, Z., Li, Y., Bekris, K.E.: Efficient sampling-based motion planning with asymptotic near-optimality guarantees for systems with dynamics. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 1779–1785. IEEE (2013)
Dobson, A., Krontiris, A., Bekris, K.E.: Sparse Roadmap Spanners. In: Algorithmic Foundations of Robotics X, Springer Tracts in Advanced Robotics, vol. 86, pp. 279–296. Springer (2013)
Ferguson, D., Stentz, A.: Anytime RRTs. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 5369–5375. IEEE, Beijing (2006)
Kalisiak, M., van de Panne, M.: RRT-blossom: RRT with a local flood-fill behavior, pp. 1237–1242. IEEE, Orlando (2006)
Strandberg, M.: Augmenting RRT-planners with local trees. In: Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, vol. 4, pp. 3258–3262. IEEE (2004)
Urmson, C., Simmons, R.: Approaches for heuristically biasing RRT growth. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, vol. 2, pp. 1178–1183. IEEE, Las Vegas (2003)
Kala, R., Shukla, A., Tiwari, R.: Robotic Path Planning using Evolutionary Momentum based Exploration. J. Exp. Theor. Artif. Intell 23(4), 469–495 (2011)
Bennewitz, M., Burgard, W., Thrun, S.: Optimizing schedules for prioritized path planning of multi -robot systems. In: Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, pp. 271–276. IEEE (2001)
Bennewitz, M., Burgard, W., Thrun, S.: Finding and optimizing solvable priority schemes for decoupled path planning techniques for teams of mobile robots. Rob. Auton. Syst. 41(2-3), 89–99 (2002)
Clark, C.M., Bretl, T., Rock, S.: Applying kinodynamic randomized motion planning with a dynamic priority system to multi-robot space systems. In: Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE Aerospace Conference Proceedings, vol. 7, pp. 3621–3631. IEEE (2002)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kala, R. Homotopic Roadmap Generation for Robot Motion Planning. J Intell Robot Syst 82, 555–575 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-015-0278-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-015-0278-z