Abstract
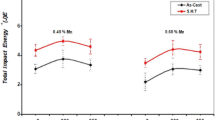
A study was carried out to investigate the effects of iron content, porosity and solidification rate on the impact properties and fracture behavior of A356.2-type alloys. The results show that impact properties improve with increase in solidification rate and decrease in Fe content. Unmodified A356.2 alloys show linear correlations, while modified A356.2 alloys show logarithmic correlations at all solidification rates (R 2 > 0.95 in all cases). Impact properties obtained at the highest solidification rate are far superior to those obtained at other solidification rates. The β-Al5FeSi intermetallic deteriorates impact properties significantly, the effect being most apparent within 10–50 μm β-platelet sizes in A356.2 alloy. Fairly good correlations between porosity and impact properties are obtained. Strontium is effective in improving impact energy, even at high Fe levels. A good inverse relation is obtained between average crack speed and impact energy, highest crack speeds being observed in unmodified samples obtained at highest Fe contents and lowest solidification rates. Impact testing is sensitive to variations in microstructure or casting defects. Impact energy–strength plots show exponential relationships, whereas impact energy–ductility plots display linear relationships for all alloys, modified or not, regardless of the alloy composition. In A356.2 alloys, cracks initiate mainly through the fracture of Si particles or their debonding from the Al matrix, while crack propagation occurs through the coalescence of fractured Si particles, except when β-Al5FeSi platelets are present, in which case the latter take precedence.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. Ma, A.M. Samuel, F.H. Samuel, H.W. Doty, S. Valtierra, Effect of iron and cooling rate on tensile properties of B319.2 alloys in non-modified and Sr-modified conditions. AFS Trans. 112, 131–140 (2004)
B. Golbahar, A.M. Samuel, F.H. Samuel, H.W. Doty, S. Valtierra, Effect of grain refiner–modifier interaction on the microstructure and mechanical properties of A356.2 alloys. AFS Trans. 115, 1–13 (2007)
J.A. Taylor, Iron-containing intermetallic phases in Al–Si based casting alloys. Proc. Mater. Sci. 1, 19–33 (2012)
L.A. Narayanan, F.H. Samuel, J.E. Gruzleski, Dissolution of iron intermetallics in Al–Si alloys through nonequilibrium heat treatment. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 26, 2161–2174 (1995)
Z. Ma, A.M. Samuel, F.H. Samuel, H.W. Doty, Effect of Fe content and cooling rate on the impact toughness of cast 319 and 356 aluminum alloys, in Transactions of the American Foundry Society: volume 111; 107th casting congress April 26–29, 2003 (American Foundry Society, 2003), pp. 255–265
S. Ji, W. Yang, F. Gao, D. Watson, Z. Fan, Effect of iron on the microstructure and mechanical property of Al–Mg–Si–Mn and Al–Mg–Si diecast alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 564, 130–139 (2013)
Y. Komiyama, K. Uchida, M. Gunshi, Effect of Fe, Mn, Zn and Ti on mechanical properties and microstructures of Al–Si–Cu–Mg casting alloy. J. Jpn. Inst. Light Met. 26, 311–319 (1976). (in Japanese)
Z. Ma, E. Samuel, A.M.A. Mohamed, A.M. Samuel, F.H. Samuel, H.W. Doty, Parameters controlling the microstructure of Al–11Si–2.5Cu–Mg alloys. Mater. Des. 31, 902–912 (2010)
S. Nishi, T. Kobayashi, A study on the toughness of aluminum alloy castings. J. Jpn. Foundrymen’s Soc. 46, 905–912 (1974). (in Japanese)
M.A. Moustafa, F.H. Samuel, H.W. Doty, Effect of solution heat treatment and additives on the hardness, tensile properties and fracture behaviour of Al–Si (A413.1) automotive alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 38, 4523–4534 (2003)
M.F. Hafiz, T. Kobayashi, N. Fat-Halla, Tensile properties influencing variables in eutectic Al–Si casting alloys. Scr. Metall. Mater. 31, 701–705 (1994)
M.D. Dighe, A.M. Gokhale, Relationship between microstructural extremum and fracture path in a cast Al–Si–Mg alloy. Scr. Mater. 37, 1435–1440 (1997)
M.F. Ibrahim, A.M. Samuel, H.W. Doty, F.H. Samuel, Effect of aging conditions on precipitation hardening in Al–Si–Mg and Al–Si–Cu–Mg alloys. Int. J. Metalcasting (2016). doi:10.1007/s40962-016-0057-z
M.F. Ibrahim, E. Samuel, A.M. Samuel, A.M.A. Al-Ahmari, F.H. Samuel, Impact toughness and fractography of Al–Si–Cu–Mg base alloys. Mater. Des. 32, 3900–3910 (2011)
H.W. Doty, S.A. Alkahtani, O. Elsebaie, F.H. Samuel, Influence of metallurgical parameters on the impact toughness of near eutectic Al–Si alloys, in 119th Metalcasting Congress, AFS 2015, Columbus, OH, April 21–23, 2015 (American Foundry Society, Columbus, 2015)
K.A. Abuhasel, M.F. Ibrahim, E.M. Elgallad, F.H. Samuel, On the impact toughness of Al–Si cast alloys. Mater. Des. 91, 388–397 (2016)
F.T. Lee, J.F. Major, F.H. Samuel, Effect of silicon particles on the fatigue crack growth characteristics of Al–12 wt% Si–0.35 wt% Mg–(0 to 0.02) Wt% Sr casting alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 26, 1553–1570 (1995)
L. Liu, Metallurgical parameters controlling the microstructural evolution of Al-Si-Mg and Al-Si-Cu alloys, PhD Thesis, Université du Québec à Chicoutimi, Québec, Canada, 2004
R.C. Voigt, D.R. Bye, Microstructural aspects of fracture in A356. AFS Trans. 99, 33–50 (1991)
A.M. Samuel, H.W. Doty, S. Valtierra, F.H. Samuel, Influence of oxides on porosity formation in Sr-treated alloys. Int. J. Metal Casting (2016). doi:10.1007/s40962-016-0118-3
O. Vorren, J.E. Evensen, T.B. Pedersen, Microstructure and mechanical properties of AlSi(Mg) casting alloys. AFS Trans. 92, 459–466 (1984)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like also to thank Dr. Ehab Samuel of the National Research Council Canada (NRC-ATC) for editing the present article. Thanks are also due to Hicham Farid for improving the quality of the drawings used in the present article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samuel, A.M., Doty, H.W., Valtierra, S. et al. On the Impact Properties and Fracture Mechanisms of A356.2-Type Cast Alloys. Inter Metalcast 11, 766–777 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-016-0122-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-016-0122-7